Class 5 Science - Air and Water - Question Answers
Q1: What is the atmosphere?
Ans: Air is a layer around the earth. This layer is called the Earth’s atmosphere. An atmosphere is a blanket of gases that surrounds Earth.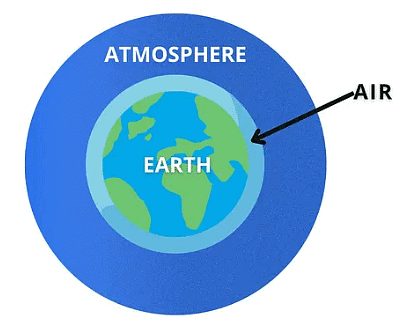 AtmosphereQ2: Name the various layers of the atmosphere.
AtmosphereQ2: Name the various layers of the atmosphere.
Ans: The various layers of the atmosphere are:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
- Exosphere
Q3: How does the atmosphere protect us from meteoroid hits?
Ans: The atmosphere protects us from meteoroid hits by burning them up in the mesosphere before they can hit the surface of the earth.
Q4: What is air pressure?
Ans: The weight of air pushing everything around in all directions is called air pressure. In other words, the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth's surface is known as air pressure.
Q5: Name any three impurities that make water unfit for use.
Ans: The three impurities that make water unfit for use are:
- Sand
- Mud
- Dirt
Q6: The two types of impurities in water? Give examples.
Ans: The two types of impurities in water are:
- Impurities that dissolve in water are called soluble impurities.
Eg: salt, sugar. - Impurities that do not dissolve in water are called insoluble impurities.
Eg: sand, mud.
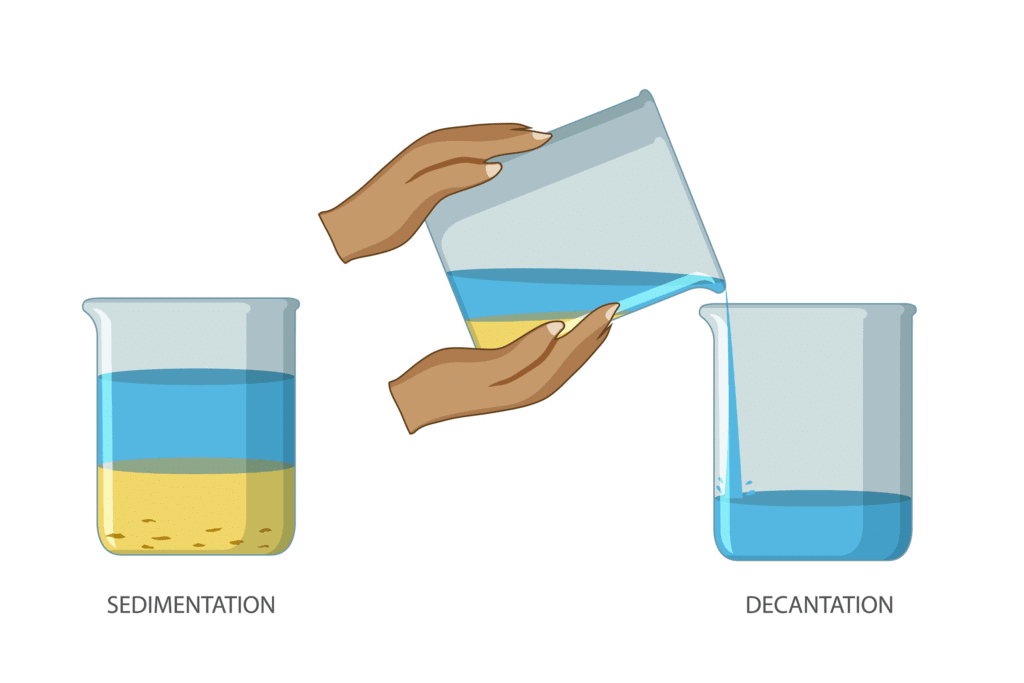
Q7: Differentiate between sedimentation and decantation.
Ans:
- Sedimentation is the process of heavier particles of an insoluble solid settling down in a liquid is known as sedimentation. It is a technique for separating mixtures of chemicals.
- Decantation is the process of removing liquid from a container without disturbing the sediment.
Q8: What is loading?
Ans: The rate of sedimentation can be increased by adding special chemicals like alum. This process is called loading.
Q9: Differentiate between boiling and distillation.
Ans:
1. Both boiling and distilling water are methods that are used for making water safe.
2. Boiling is the simple way of purifying water, and it is also the quickest way of purifying water.
3. When compared to boiling, distillation is an elaborate process. The process starts with boiling. Once water gets boiled, the steam is condensed and then cooled.
4. When comparing boiled water and distilled water, distilled water is considered to be the purest form.
5. Unlike boiled water, distilled water will be completely free of any impurities. Distillation kills not only germs, parasites, and viruses but also gets rid of impurities that are not visible such as minerals, metals, and chemicals.
6. Distillation is a complex mechanism, and it cannot be performed in homes.
7. Distilled water is used in conducting various experiments and is also used as a coolant in the auto industry. Boiled water is mainly used for drinking and also for preparing dishes.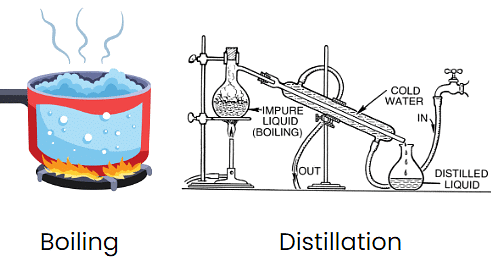
Q10: Describe with examples how air pressure helps in our everyday life.
Ans: Air pressure helps us in our everyday life. We would not be able to do many things if there is no air pressure. Some examples are:-
- Filling up fountain pens.
- Filling up a syringe.
- Drinking through a straw.
- Using droppers.
For example, if we try to open a juice can and we make a small slit on one side, the juice will flow out slowly. But if we make another slit the juice will flow out rapidly. This happens because air enters the juice can from the second slit and air pressure pushes the juice out of the can.
Q11: Describe the different ways by which insoluble impurities can be removed from water.
Ans: the different ways by which insoluble impurities can be removed from water are the following:
- Filtration
- Sedimentation and Decantation
Filtration: In this process, insoluble impurities are removed from water by passing the impure water through a filter paper. A circular piece of filter paper is taken and folded twice to make a cone and this is kept inside a funnel. A flask is kept below the funnel and the mixture is poured into the flask through the funnel. Sand is retained on the filter paper and clean water is obtained in the flask.
Sedimentation and Decantation:
- The mixture of insoluble impurities for example, (mud ) and water is allowed to stand undisturbed in a beaker.
- After some time the mud settles down at the bottom of the container as sediments. This process is called sedimentation.
- Clean water can then be poured out into a separate container without disturbing the sediments. This process is called decantation.
Q12: Describe the different ways by which soluble impurities can be removed from water.
Ans: The different ways by which soluble impurities can be removed from water are:
- Evaporation: In this process, a solution containing soluble impurities like common salt or sugar is heated. After some time water will change into steam and the soluble impurity will be left behind in the container.
- Distillation: This process involves the following steps:
(i) Impure water is taken in a round-bottomed flask and heated.
(ii) On heating, water changes into steam and the impurities are left behind. When the steam is through the condenser, it cools and turns into water (liquid).
(iii) Pure water is collected in a flask.
Q13: Describe the different ways by which water can be purified.
Ans: The different ways by which water can be purified are:
- Boiling: Boiling is a very simple method of water disinfection. Heating water to a high temperature, 100°C, kills most of the pathogenic organisms, particularly viruses and bacteria causing waterborne diseases.
- Sedimentation and decantation: Sedimentation is the process of heavier particles of an insoluble solid settling down in a liquid is known as sedimentation. It is a technique for separating mixtures of chemicals. Decantation is the process of removing liquid from a container without disturbing the sediment.
- Distillation: It relies on evaporation to purify water. Contaminated water is heated to form steam. Inorganic compounds and large non-volatile organic molecules do not evaporate with the water and are left behind. The steam then cools and condenses to form purified water.
- Filtration: A method for separating an insoluble substance from a liquid is filtration. When a sand and water mixture is filtered using filter paper. The sand remains in the filter paper (it becomes the residue), while the water passes through (it becomes the filtrate).
- Chlorination: In this method chlorine is added to kill the germs in water. Chlorine tablets are also available in the market which can be used for this process.
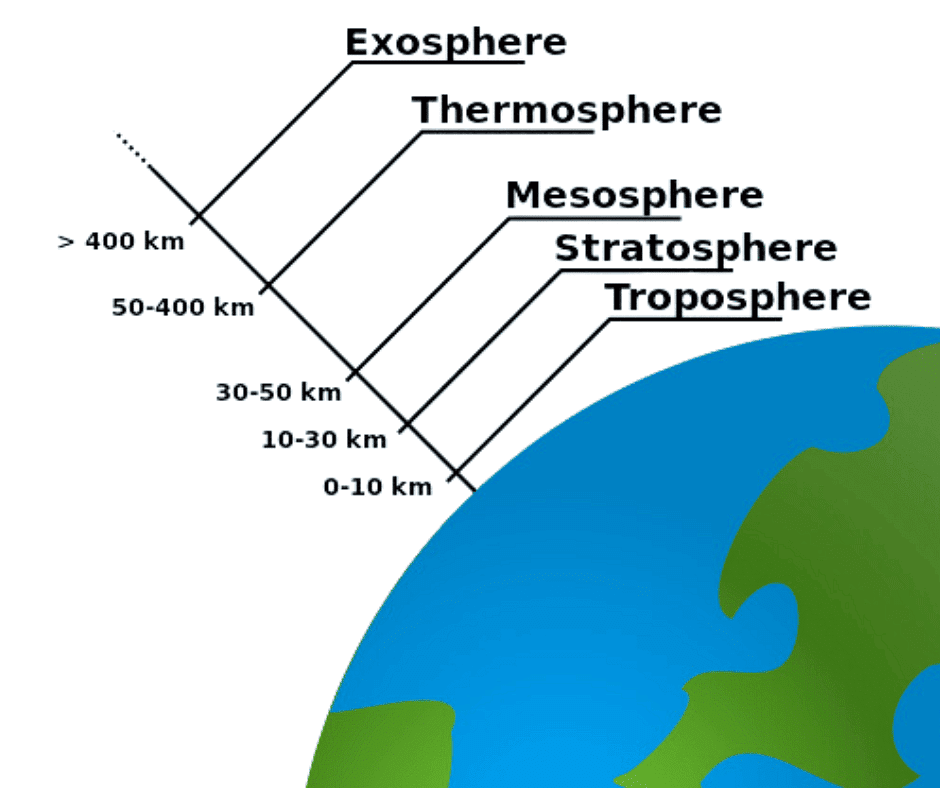
Q14: Describe the layers of the atmosphere.
Ans: The different layers of the atmosphere are:
 Layers of the Atmosphere
Layers of the Atmosphere
1. Troposphere:
- This is the first layer of atmosphere.
- The weather phenomena, such as rain, cloud formation, and wind, occur in this layer
- Living things can survive in this layer.
2. Stratosphere:
- This is the second layer of atmosphere.
- The ozone layer is present in the stratosphere which protects us from harmful UV rays radiation that can cause health problems like skin cancer.
- Many jet airplains fly in this layer.
3. Mesosphere:
- This is the third layer of atmosphere.
- It protect us from meteroids by burning them before they can reach the surface of the earth.
4. Thermosphere:
- It is the fourth layer of atmosphere.
- Space shuttles can revolve in this layer.
5. Exosphere:
- It is the last layer of the atmosphere.
- This layer separates the rest of the atmosphere from outer space.
|
42 videos|364 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Class 5 Science - Air and Water - Question Answers
| 1. What are the different states of water? |  |
| 2. Why is air important for living things? |  |
| 3. How do plants help in purifying air? |  |
| 4. What are some sources of water pollution? |  |
| 5. How can we conserve water in our daily lives? |  |

















