Unit 1: Basic Accounting Procedures: Question & Answer - Journal Entries | Accounting for CA Foundation PDF Download
Ques 1: The rent paid to the landlord is credited to
(a) Landlord's account.
(b) Rent account.
(c) Cash account.
Ans: c
Explanation:When we pay rent to a landlord, we need to keep track of where this money goes in our accounts. Let's break down the options and understand what happens.
Therefore, the correct answer is that the rent paid to the landlord is credited to the cash account. This shows that we are spending money, and now we have less cash.
- Landlord's account: If we think of the landlord as someone we owe money to, we might think that paying rent would go into the landlord's account. But in accounting, we don't directly credit the landlord's account because we are not keeping a record of their money. Instead, we are tracking our own money.
- Rent account:The rent account is where we keep track of all the money we spend on rent. However, when we pay rent, we do not credit the rent account because this account usually reflects the expense of rent, not the payment itself. So, this option is not correct either.
- Cash account:The cash account is where we keep track of all the money we have. When we pay rent, we are using our cash, so we need to reduce the amount in our cash account. That means we credit the cash account because we are giving away cash to the landlord.
Ques 2: In case of a debt becoming bad, the amount should be credited to
(a) Trade receivables account.
(b) Bad debts account.
(c) Cash account.
Ans: a
Explanation:When a company lends money or sells goods on credit, it expects to receive that money back later. But sometimes, customers can't pay back what they owe. This is called a "bad debt."
Now, let’s look at what happens when a debt becomes bad and how it affects the accounts:
- Trade Receivables Account:
This account shows all the money that customers owe the company. When we find out that a customer can’t pay, we need to remove that amount from this account. So, we credit the Trade Receivables Account to show that this money is no longer expected to be received.
- Bad Debts Account:
This account is used to track the money that we can’t get back because a customer has not paid. While we do record bad debts here, we first remove the amount from Trade Receivables. So, even though we mention this account, the correct action is to credit Trade Receivables when we recognize a bad debt.
- Cash Account:
This account is for tracking all the cash that comes in and goes out of the business. Since a bad debt means we didn’t receive cash, we do not credit this account. So, this is not the correct choice when dealing with bad debts.
In summary, when a debt becomes bad, we need to credit the Trade Receivables Account because it helps us keep track of the money we expect to receive. By doing this, we show that we no longer expect that money to come in.
Ques 3: A Ltd. has a ₹ 35,000 account receivable from Mohan. On January 20, Mohan makes a partial payment of ₹ 21,000 to A Ltd. The journal entry made on January 20 by A Ltd. to record this transaction includes:
(a) A credit to the cash received account of ₹ 21,000.
(b) A credit to the Accounts receivable account of ₹ 21,000.
(c) A debit to the cash account of ₹ 14,000.
Ans: b
Explanation: When A Ltd. sells something to Mohan, it means Mohan owes A Ltd. some money. This money that Mohan owes is called "Accounts Receivable." In this case, Mohan owes A Ltd. ₹ 35,000.
On January 20, Mohan gives A Ltd. ₹ 21,000 as a partial payment. Let's break down what happens next:
- A credit to the Accounts Receivable account of ₹ 21,000: This means that A Ltd. is reducing the amount of money Mohan owes them. If he originally owed ₹ 35,000 and pays ₹ 21,000, now he only owes ₹ 14,000. So, A Ltd. will record this reduction by crediting (or subtracting) ₹ 21,000 from the Accounts Receivable account.
So, the correct journal entry by A Ltd. on January 20 will have:
- Debit Cash Account: ₹ 21,000
- Credit Accounts Receivable Account: ₹ 21,000
This shows that A Ltd. has received ₹ 21,000 in cash and Mohan's debt has decreased by the same amount. After this payment, Mohan still owes ₹ 14,000 to A Ltd.
Ques 4: Which financial statement represents the accounting equation - Assets = Liabilities + Owner's equity:
(a) Income Statement
(b) Statement of Cash flows
(c) Balance Sheet.
Ans: c
Explanation: The Balance Sheet is a financial statement that shows the financial position of a business at a specific point in time. It is structured around the accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity
Here's what each term means:
- Assets: These are the resources owned by the business that have economic value and can provide future benefits. Examples include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, equipment, and property.
- Liabilities: These represent the obligations or debts the business owes to outside parties, such as loans, accounts payable, and accrued expenses.
- Owner's Equity: This reflects the owner’s residual interest in the business after deducting liabilities from assets. It includes capital contributions, retained earnings, and net income or loss.
Ques 5: Which account is the odd one out?
(a) Office furniture & Equipment.
(b) Freehold land and Buildings.
(c) Inventory of materials.
Ans: c
Explanation:
- Office Furniture & Equipment and Freehold Land and Buildings are classified as fixed assets (or non-current assets). These are long-term assets used in the operations of a business and are not intended for sale.
- Inventory of materials, on the other hand, is classified as a current asset. It represents goods or raw materials that a business holds with the intention of selling or using them within a short period (usually within a year).
Thus, Inventory of materials is the odd one out because it is a current asset, while the other two are fixed assets.
Ques 6: The debts written off as bad, if recovered subsequently are
(a) Credited to Bad Debts Recovered Account
(b) Credited to Trade receivables Account.
(c) Debited to Profit and Loss Account.
Ans: a
Explanation:
- When a debt is written off as bad debt, it means the amount was considered uncollectible and recorded as an expense in the Profit and Loss Account.
- If the previously written-off debt is later recovered, it is recorded as income in the Bad Debts Recovered Account, which is credited. This ensures proper accounting treatment and reflects the recovered amount as a gain.
Why not the other options?
(b) Credited to Trade Receivables Account: This is incorrect because trade receivables have already been written off, so the recovery does not directly affect this account.
(c) Debited to Profit and Loss Account: This is incorrect because the recovered amount is not an expense; it is treated as income.
Ques 7: In the Double Entry System of Book-keeping every business transaction affects:
(a) Two accounts
(b) Two sides of the same account.
(c) The same account on two different dates.
Ans: a
Explanation: In the Double Entry System of Book-keeping, every business transaction affects two accounts because of the fundamental accounting principle:
"For every debit, there is an equal and corresponding credit."
This system ensures that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity) remains balanced.
Why not the other options?
(b) Two sides of the same account: This is incorrect because a single transaction typically affects two different accounts, not just the two sides (debit and credit) of one account.
(c) The same account on two different dates: This is incorrect because transactions are recorded in real time and affect two separate accounts simultaneously, not the same account on different dates.
Ques 8: A sale of goods to Ram for cash should be debited to:
(a) Ram
(b) Cash
(c) Sales
Ans: b
Explanation: In this transaction, goods are sold to Ram for cash, meaning the business is receiving cash immediately. According to the Double Entry System:
- Cash Account is an asset, and an increase in cash is recorded as a debit.
- Sales Account is revenue, and it is credited to reflect the income earned.
Journal Entry:
- Debit: Cash Account (Increase in asset)
- Credit: Sales Account (Income earned from the sale)
Why not the other options?
(a) Ram: This is incorrect because Ram is not involved as a debtor. The transaction is settled in cash, so there is no need to record a receivable.
(c) Sales: This account is credited, not debited, because it represents income from the sale of goods.
Theory Questions
Ques 1: Write a short note on the classification of accounts.
Ans: Accounts are broadly classified into assets, liabilities and capital. The basic accounting equation specifies broad categories, which are as follows:
(i) Assets: These are resources controlled by the enterprise as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise, namely cash, stock of goods, land, buildings, machinery etc.
(ii) Liabilities: These are financial obligations of an enterprise other than owner's equity namely long-term loans, creditors, outstanding expenses etc.
(iii) Capital: It generally refers to the amounts invested in an enterprise by its owner(s), the accretion to it or a reduction in it. Since capital is affected by expenses and incomes of a revenue nature, there are two more categories of accounts, namely expenses and incomes. The difference between income and expenses is taken into cthe apital account.
Expenses: These represent those accounts which show the amount spent or even lost in carrying on operations.
Incomes: These represent those accounts which show the revenue amounts earned by the enterprise.
However, traditionally accounts are classified as follows:
(i) Personal Accounts: These accounts relate to persons, institutions, debtors or creditors.
(ii) Impersonal Accounts: These represent accounts which are not personal. These can be further sub-divided as follows:
Real Accounts: These accounts relate to assets of the firm but not debt e.g. accounts relating to land, buildings, cash in hand etc.
Nominal accounts: These accounts relate to expenses, losses, gains, revenues etc.
Ques 2: Distinguish between Real account and nominal account.
Ans: A real account is an account relating to properties and assets, other than personal accounts of the firm. Examples are land, buildings, machinery, cash, investments etc. Nominal accounts relate to expenses or losses, incomes and gains. Examples are: wages, salaries, rent, depreciation etc. The net result of all the nominal accounts is reflected as profit or loss which is transferred to the capital account. Nominal accounts are, therefore, temporary. The real accounts are shown in the balance sheet along with personal accounts.
Practical Questions
Ques 1:Show the classification of the following Accounts under traditional and accounting equation approach: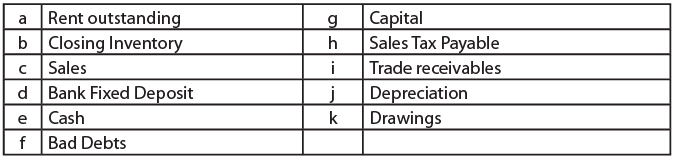 Ans:
Ans: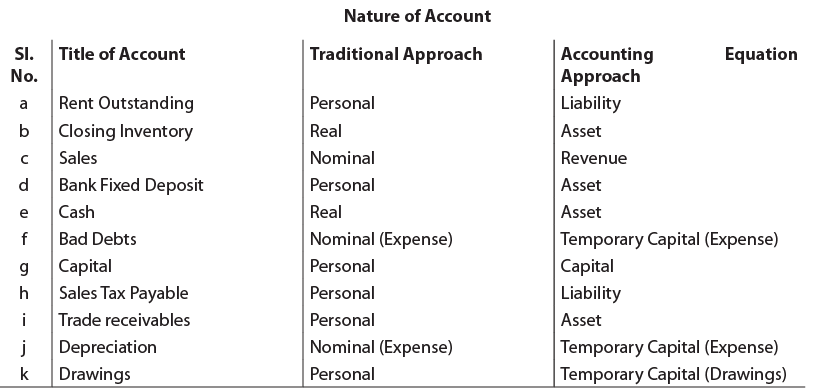
Ques 2: Pass Journal Entries for the following transactions in the books of Gamma Bros. (i) Employees had taken inventory worth ₹ 1,00,000 (Cost price ₹ 75,000) on the eve of Deepawali and the same was deducted from their salaries in the subsequent month.
(ii) Wages paid for erection of Machinery ₹ 18,000.
(iii) Income tax liability of proprietor ₹ 1,17000 was paid out of petty cash.
(iv) Purchase of goods from Naveen of the list price of ₹ 2,00,000. He allowed 10% trade discount, ₹5,000 cash discount was also allowed for quick payment.
Ans: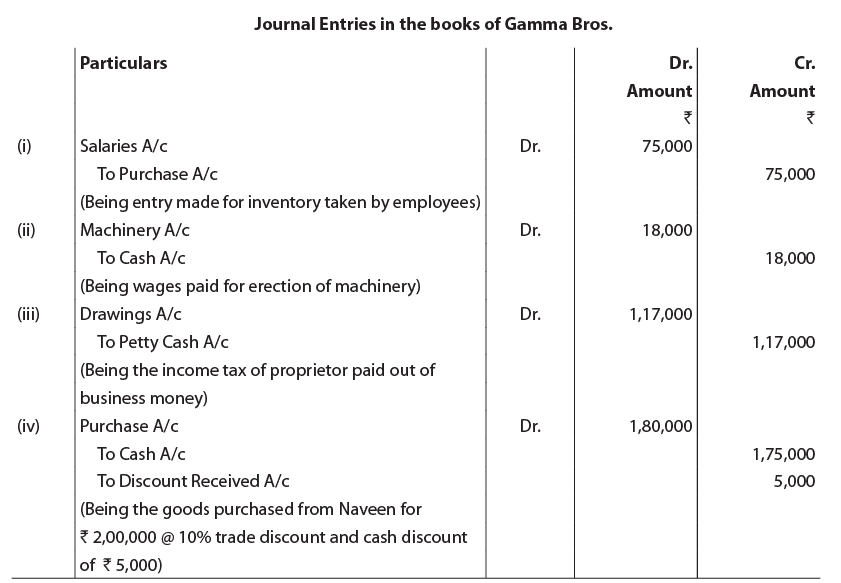 Note: (i). Here wages paid on the erection of machinery have been capitalised therefore machinery account has been debited directly instead of wages being recorded as an expenditure.
Note: (i). Here wages paid on the erection of machinery have been capitalised therefore machinery account has been debited directly instead of wages being recorded as an expenditure.
(ii). The students may also note that trade discount is allowed on the list price of goods. It is deducted to find out the invoice amount of the goods to be recorded in the books. Cash discount is a discount allowed in case of early payments to the seller. The entry is made in the books of accounts for cash discount.
Ques 3: Calculate the missing amount for the following.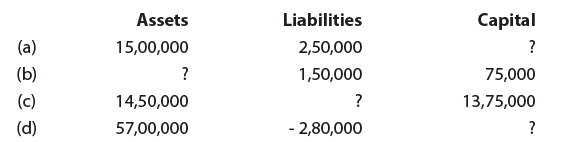 Ans: These can be solved using the Accounting Equation: Assets = Capital + Liabilities.
Ans: These can be solved using the Accounting Equation: Assets = Capital + Liabilities.
(a) 15,00,00 = 2,50,000 + Capital
Therefore, Capital = 12,50,000
The rest can also be solved similarly:
(b) 2,25,000
(c) 75,000
(d) 59,80,000
Ques 4: Show the effect of increase = (+), decrease = (-) and no change=(0) on the assets of the following transactions:
a. Purchased office furniture, payment to be made next month.
b. Collected cash for repair services
c. Goods sold on credit.
d. With drawl of cash by the owner for personal use.
e. Hired an employee as sales manager of the north wing.
f. Returned goods worth ₹ 50,000.
g. One of our debtor agreed to pay his dues to Mr. C who is a creditor of the company with the same amount being due to him.
h. Entered into an agreement with Mehta & Co. to purchase all raw materials from their company from next year. Also give reasons for your answers.
Ans:
Ques 5: Following is the information provided by Mr. Gopi pertaining to year ended 31st March 2017. Find the unknowns, showing computation to support your answer: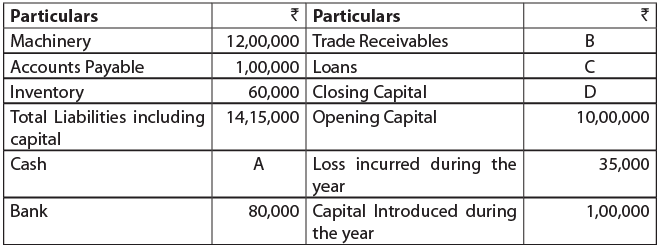 Ans: Trade Receivable Balance (B) = Sales- Amount received during the year
Ans: Trade Receivable Balance (B) = Sales- Amount received during the year
= ₹ (15,55,000 - 15,00,000)
= ₹ 55,000.
Since, we know Assets = Capital + Liabilities
Therefore, balance of assets is also ₹ 14,15,000
So, total assets: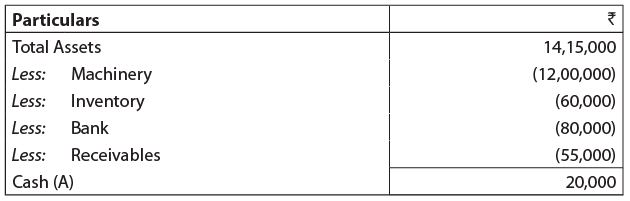 Computation of Closing Capital (D):
Computation of Closing Capital (D): So, Loan amount (C) = Total Liabilities and capital - Closing Capital - Trade Payables
So, Loan amount (C) = Total Liabilities and capital - Closing Capital - Trade Payables
= ₹ (14,15,000 - 10,65,000 - 1,00,000)
= ₹ 2,50,000
|
68 videos|160 docs|83 tests
|
FAQs on Unit 1: Basic Accounting Procedures: Question & Answer - Journal Entries - Accounting for CA Foundation
| 1. What are journal entries in accounting? |  |
| 2. How do I determine whether to debit or credit an account? |  |
| 3. What is the format of a journal entry? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a simple journal entry? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of journal entries in financial reporting? |  |























