Accounting from Incomplete Records (Part - 2) - Commerce PDF Download
Page No 23.47
Ques 13: From the details given below find out the Credit Sales and Total Sales: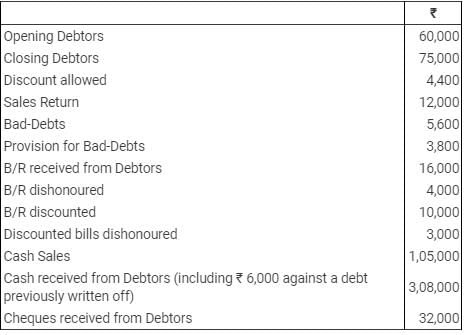
Ans:
Debtors Account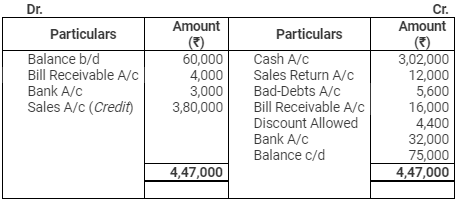
Total Sales = Cash Sales + Credit Sales
Total Sales = 1,05,000 + 3,80,000 = 4,85,000
Question 14: Find out the Credit Purchases from the details given below: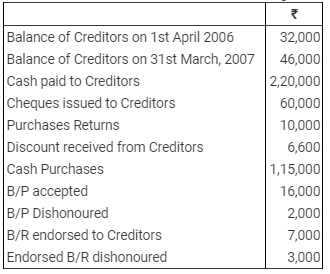
Ans:
Creditors Account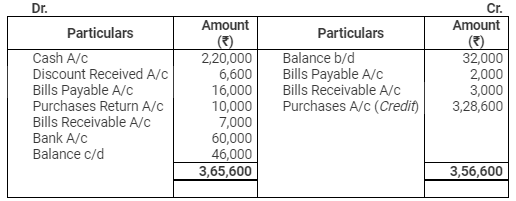
Question 15: Anand Mohan has kept incomplete books. From the following particulars, prepare his Final Accounts for the year ending 31st March, 2012 :
Receipts:- Received from Debtors ₹ 37,000; Fresh Capital brought in cash ₹ 20,000; Commission received ₹ 2,800; Cash Sales ₹ 95,000.
Payments:- Paid to Creditors ₹ 35,000; Cash Purchases ₹ 26,500; Ornaments for his wife ₹ 22,000; Wages ₹ 18,800; Rent ₹ 8,400; Salary ₹ 12,000.
His Other Assets and Liabilities:-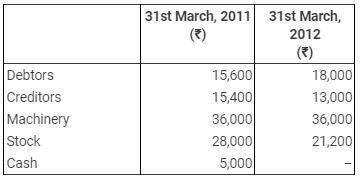
Adjustments :-
(1) Unpaid wages ₹1,500.
(2) Provide for Doubtful Debts at 5% on Debtors.
Ans:
Trading Account
for the year ended March 31, 2012
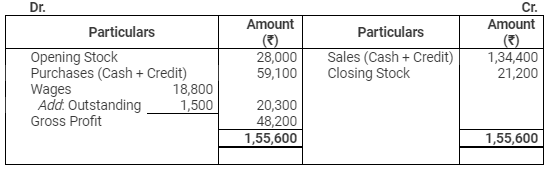
Profit & Loss Account
for the year ended March 31, 2012
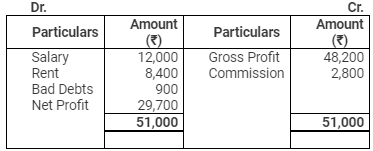
Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2012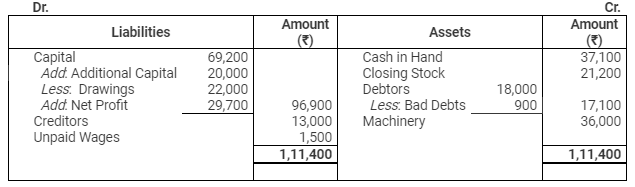
Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2011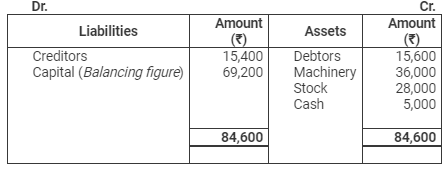
Cash Account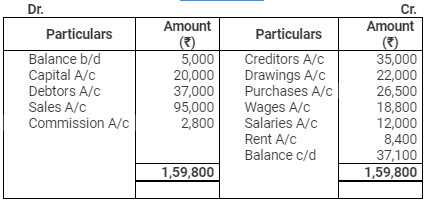
Debtors Account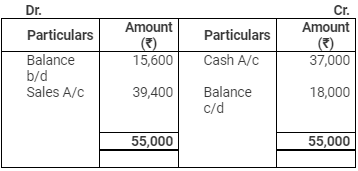
Creditors Account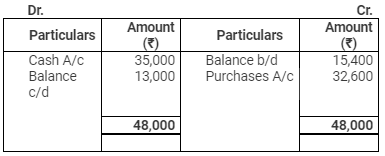
Page No 23.48
Question 16: Mukesh Khanna has not kept proper books. However, he gives you the following information relating to the year 2011-12:
Summary of his Cash Book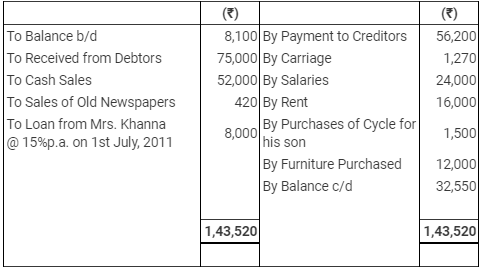
The following balances existed on 1st April, 2011 - Debtors ₹ 24,200; Furniture ₹ 18,000; Stock ₹ 30,000; Creditors ₹ 18,000.
The following balances existed on 31st March, 2012 - Debtors ₹ 20,800; Furniture ₹ 30,000; Stock ₹ 35,950; Creditors ₹ 34,600.
Adjustments:-
(1) Depreciate Furniture by 10%.
(2) Provide upto-date interest on Mrs. Khanna's Loan.
Prepare trading and Profit and Loss A/c for the year ending 31st March, 2012 and a Balance Sheet as at that date.
Ans:
Trading Account
for the year ended March 31, 2012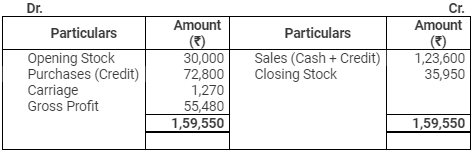
Profit & Loss Account
for the year ended March 31, 2012
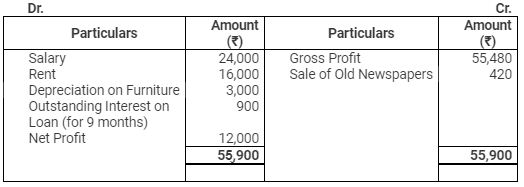
Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2012

Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2011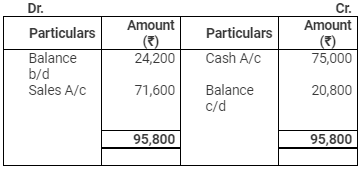
Debtors Account 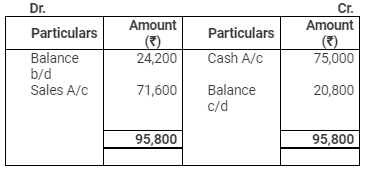
Creditors Account 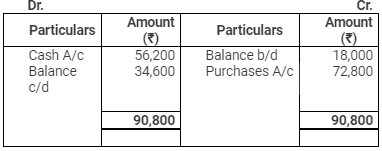
Question 17: Mr. Asif Ali, a retail trader, who keeps Incomplete Records gives you the following information for the year 2011-12:
Summary of Cash Transactions 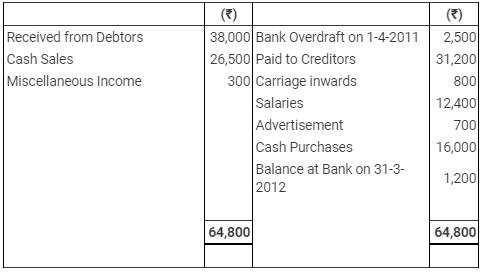
The Assets and Liabilities were as follows: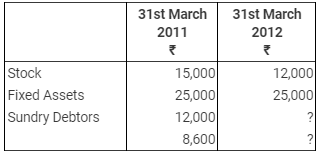
Other Informations:
(1) Credit Sales during the year were ₹ 35,100.
(2) Sales returns ₹ 800.
(3) Credit Purchases during the year were ₹ 30,000.
(4) Discount allowed to Debtors ₹ 300.
(5) Discount received from Creditors ₹ 130.
Adjustments:-
(1) Make a provision for doubtful debts @ 5% on Debtors.
(2) Also make a provision for discount @ 2% on Debtors.
Prepare his Trading, P & L A/c and a Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2012.
Ans:
Trading Account
for the year ended March 31, 2012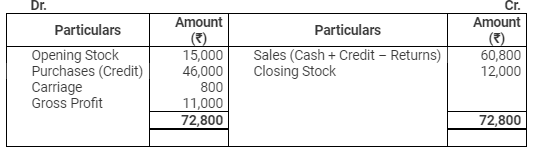
Profit & Loss Account
for the year ended March 31, 2012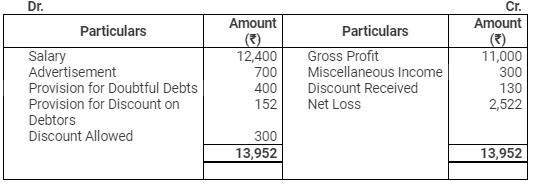
Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2012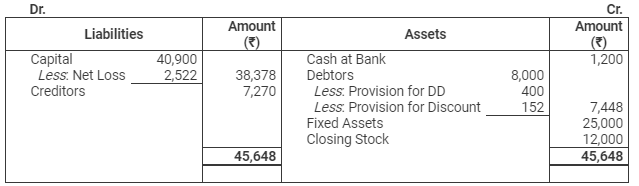
Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2011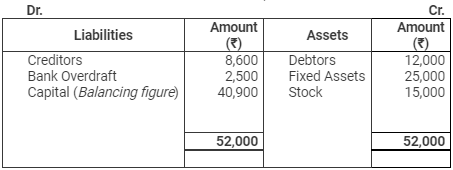
Debtors Account 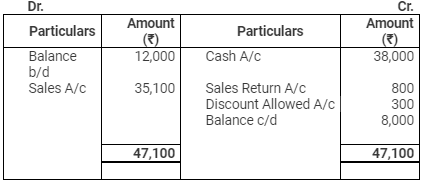
Creditors Account 
Page No 23.49
Ques 18: Lalit Mohan keeps incomplete records. From the following information provided by him, prepare a Trading and Profit & Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2015 and a Balance Sheet as at that date: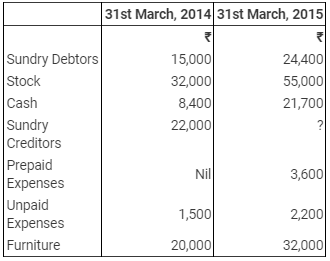
Summary of cash transactions during the year: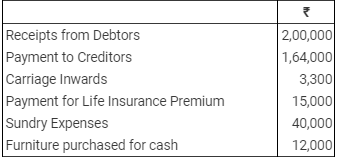
You are informed that there were considerable amount of cash sales during the year. Credit purchases during the year amounted to ₹ 1,80,000. Provide 5% for doubtful debts on debtors.
Ans:
Trading Account
for the year ended March 31, 2015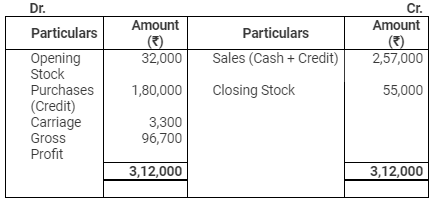
Profit & Loss Account
for the year ended March 31, 2015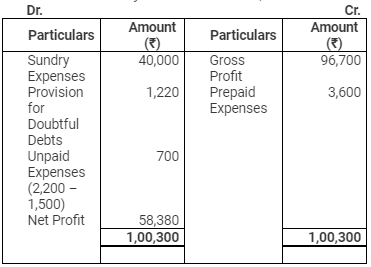
Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2015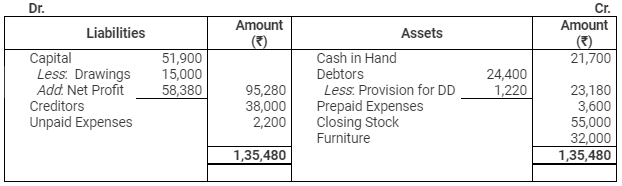
Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2014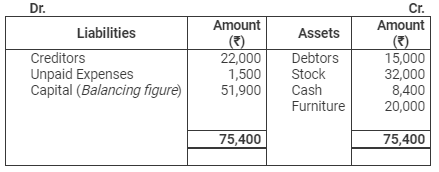
Cash Account 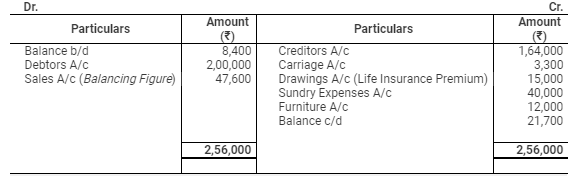
Debtors Account 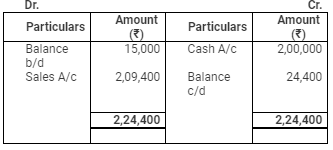
Creditors Account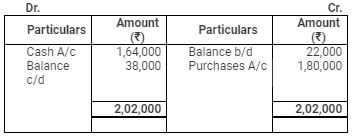
Page No 23.50
Quest 19: Vardhman commenced business on 1st April, 2008, with a capital of ₹ 50,000. He immediately purchased furniture of ₹ 20,000. During the year he received from his uncle a gift of ₹ 3,000 and he borrowed from his father a sum of ₹ 5,000. He had withdrawn ₹ 600 per month for his household expenses. He had no Bank account and all dealings were in cash. He did not maintain any books but following information is given: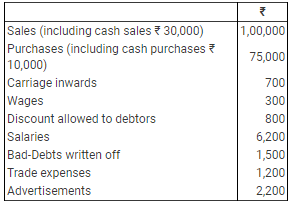
He used goods worth ₹ 1,300 for personal purposes and paid ₹ 500 to his son for examination and college fees.
On 31st March, 2009, his Debtors were worth ₹ 21,000 and Creditors ₹ 15,000. Stock in trade was valued at ₹ 10,000. Furniture to be depreciated by 10% p.a.
Prepare trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ended on 31st March, 2009, and Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2009.
Ans:
Trading Account
for the year ended March 31, 2009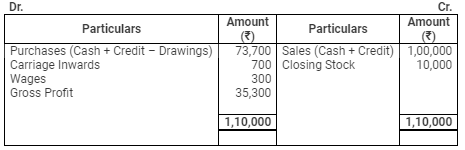
Profit & Loss Account
for the year ended March 31, 2009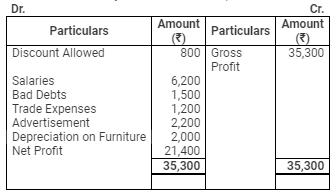
Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2009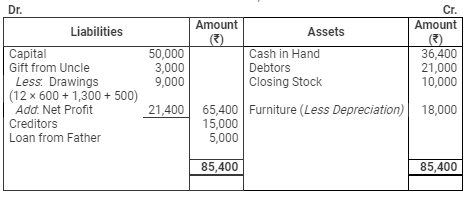
Debtors Account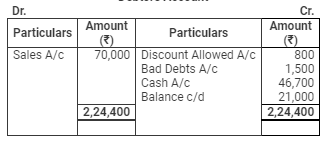
Creditors Account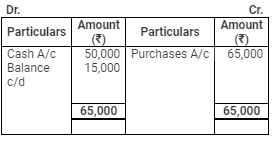
Cash Account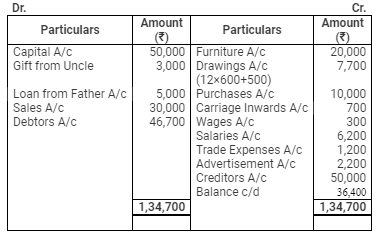
Page No 23.51
Ques 20: Calculate the value of Closing Stock from the following particulars: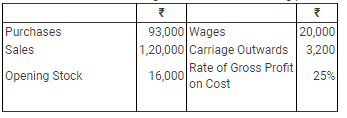
Ans:
Rate of Gross Profit (on cost) = 25%
Rate of Gross Profit (on sales) = 20%
Gross Profit = 20% of 1,20,000 = 24,000
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
24,000 = 1,20,000 – Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold = 1,20,000 – 24,000 = Rs 96,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
96,000 = 16,000 + 93,000 + 20,000 – Closing Stock
Closing Stock = 16,000 + 93,000 + 20,000 – 96,000 = Rs 33,000
Ques 21: Calculate the value of Opening Stock from the following: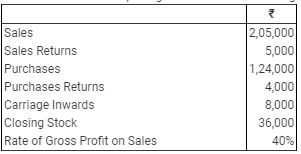
Answer 21:
Rate of Gross Profit (on sales) = 40%
Gross Profit = 40% of (2,05,000 – 5,000) = 80,000
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
80,000 = 2,00,000 – Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold = 2,00,000 – 80,000 = ₹ 1,20,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
1,20,000 = Opening Stock + (1,24,000 – 4,000) + 8,000 – 36,000
Opening Stock = 1,20,000 – 1,20,000 – 8,000 + 36,000 = ₹ 28,000
Question 22: Chakravarti does not maintain proper books of accounts. Following information is obtained from his books for the year ended 31st March, 2008:
Cash Transactions: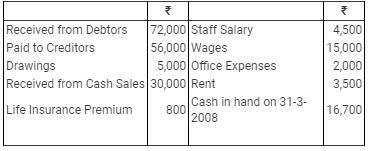
Assets and Liabilities: 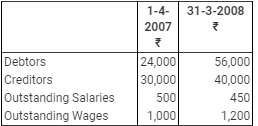
The Stock on 31st March, 2008 was valued at ₹ 20,000 but Chakravarti has no record of the Stock on 1st April, 2007. However, he informs you that he sells his goods at cost plus 25%. Prepare his Cash Book, Trading and P & L A/c for the year ended 31st March, 2008 and a Balance Sheet as at that date.
Ans:
Trading Account
for the year ended March 31, 2008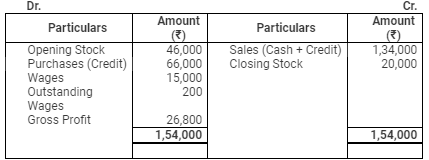
Profit & Loss Account
for the year ended March 31, 2008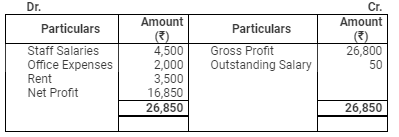
Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2008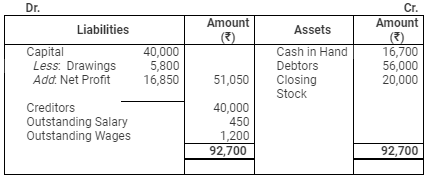
Balance Sheet
as on March 31, 2007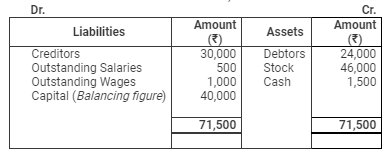
Cash Account 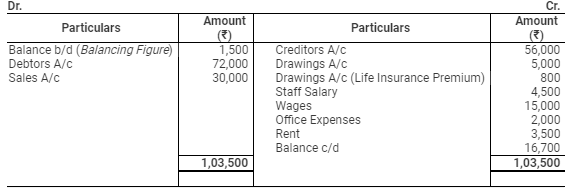
Debtors Account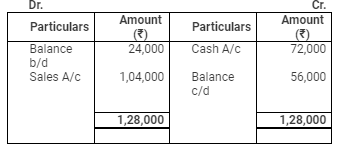
Creditors Account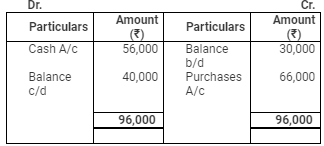
Rate of Gross Profit (on cost) = 25%
Rate of Gross Profit (on sales) = 20%
Gross Profit = 20% of (30,000 + 1,04,000) = 26,800
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
26,800 = 1,34,000 – Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of Goods Sold = 1,34,000 – 26,800 = ₹ 1,07,200
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
1,07,200 = Opening Stock + 66,000 + (15,000 + 200) – 20,000
Opening Stock = 1,07,200 – 66,000 – 15,200 + 20,000 = ₹ 46,000
FAQs on Accounting from Incomplete Records (Part - 2) - Commerce
| 1. What is accounting from incomplete records? |  |
| 2. What are the challenges of accounting from incomplete records? |  |
| 3. How can one reconstruct financial statements from incomplete records? |  |
| 4. What are the limitations of accounting from incomplete records? |  |
| 5. How does accounting from incomplete records affect financial analysis? |  |




















