HC Verma Solutions: Dispersion and Spectra | HC Verma Solutions - JEE PDF Download
Page no. 441
Ques 1:The equation 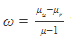 was derived for a prism having small refracting angle. Is it also valid for a prism of large refracting angle? Is it also valid for a glass slab or a glass sphere?
was derived for a prism having small refracting angle. Is it also valid for a prism of large refracting angle? Is it also valid for a glass slab or a glass sphere?
Ans: Dispersive power depends on angular deviation, and angular deviation is valid only for a small refracting angle and a small angle of incidence. Therefore, dispersive power is not valid for a prism of large refracting angle. It is also not valid for a glass slab or a glass sphere, as it has a large refracting angle.
Ques 2:Can the dispersive power 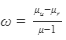 be negative? What is the sign of ω if a hollow prism is immersed into water?
be negative? What is the sign of ω if a hollow prism is immersed into water?
Ans: No, it cannot be negative, as the refractive index for violet light is always greater than that for red light. Also, refractive index is inversely proportional to 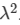 . The sign of
. The sign of 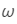 will be positive, as
will be positive, as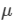 is still greater than 1 and as
is still greater than 1 and as 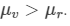
Ques 3:If three identical prisms are combined, is it possible to pass a beam that emerges undeviated? Undispersed?
Ans:No, it is not possible even when prisms are be combined with their refractive angle reversed with respect to each other. There will be at least a net deviation and dispersion equal to the dispersion and deviation produced by a single prism.
Ques 4:"Monochromatic light should be used to produce pure spectrum". Comment on this statement.
Ans:No, monochromatic light cannot be used to produce a pure spectrum. A spectrum is produced when a light of different wavelengths is deviated through different angles and gets separated. Monochromatic light, on the other hand, has a single wavelength.
Ques 5:Does focal length of a lens depend on the colour of the light used? Does focal length of a mirror depend on the colour?
Ans:Yes, the focal length of a lens depends on the colour of light.
According to lens-maker's formula,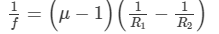 Here,
Here,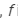 is the focal length
is the focal length 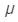 is the refractive index,
is the refractive index, 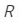 is the radius of curvature of lens.The refractive index
is the radius of curvature of lens.The refractive index 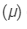 depends on the inverse of square of wavelength.The focal length of a mirror is independent of the colour of light.
depends on the inverse of square of wavelength.The focal length of a mirror is independent of the colour of light.
Ques 6:Suggest a method to produce a rainbow in your house.
Ans :A rainbow can be produced using a prism. Another way of producing a rainbow is to dip a mirror inside water, keeping it inclined along the wall of a tumbler. The light coming from water after reflecting from the mirror will give a rainbow.
Ques 1:The angular dispersion produced by a prism
(a) increases if the average refractive index increases
(b) increases if the average refractive index decreases
(c) remains constant whether the average refractive index increases or decreases
(d) has no relation with average refractive index
Ans:(a) increases if the average refractive index increases
If 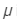 is the average refractive index and A is the angle of prism, then the angular dispersion produced by the prism is given by
is the average refractive index and A is the angle of prism, then the angular dispersion produced by the prism is given by 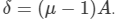
Page no. 442
Ques 1:A flint glass prism and a crown glass prism are to be combined in such a way that the deviation of the mean ray is zero. The refractive index of flint and crown glasses for the mean ray are 1.620 and 1.518 respectively. If the refracting angle of the flint prism is 6.0°, what would be the refracting angle of the crown prism?
Ans :Given:
Refractive index of the flint glass, 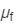 = 1.620
= 1.620
Refractive index of the crown glass,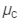 = 1.518
= 1.518
Refractive angle of the flint prism,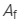 = 6°
= 6°
Now,
Let the refractive angle of the crown prism be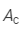 .
.
For the net deviation of the mean ray to be zero,
Deviation by the flint prism = Deviation by the crown prism
i.e., 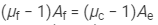
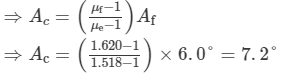
Thus, the refracting angle of the crown prism is 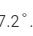
Ques 2:A certain material has refractive indices 1.56, 1.60 and 1.68 rfor red, yellow and violet lightespectively. (a) Calculate the dispersive power. (b) Find the angular dispersion produced by a thin prism of angle 6° made of this material.
Ans:Given:
Refractive index for red light,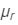 = 1.56
= 1.56
Refractive index for yellow light, 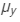 = 1.60
= 1.60
Refractive index for violet light,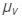 = 1.68
= 1.68
Angle of prism, 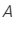 = 6°
= 6°
(a) Dispersive power 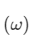 is given by
is given by
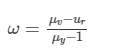
On substituting the values in the above formula, we get :
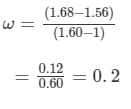
(b) Angular dispersion =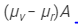
=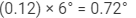
Thus, the angular dispersion produced by the thin prism is 0.72°.
Ques 3:The focal lengths of a convex lens for red, yellow and violet rays are 100 cm, 98 cm and 96 cm respectively. Find the dispersive power of the material of the lens.
Answer 3:
Focal lengths of the convex lens:
For red rays, 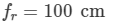
For yellow rays, 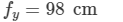
For violet rays, 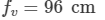
Let:
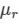 = Refractive index for the red colour
= Refractive index for the red colour
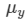 = Refractive index for the yellow colour
= Refractive index for the yellow colour
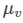 = Refractive index for the violet colour
= Refractive index for the violet colour
Focal length of a lens 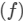 is given by
is given by
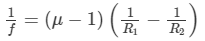
Here, 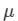 is the refractive index and R1 and R2 are the radii of curvatures of the lens.
is the refractive index and R1 and R2 are the radii of curvatures of the lens.
Thus, we have: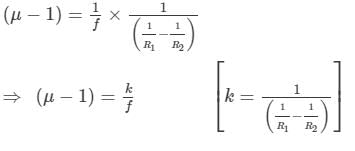
For red rays, 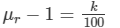
For yellow rays, 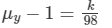
For violet rays,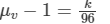
Dispersive power 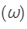 is given by
is given by
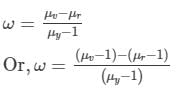
Substituting the values, we get:
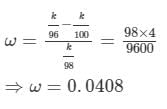
Thus, the dispersive power of the material of the lens is 0.048.
Ques 4:The refractive index of a material changes by 0.014 as the colour of the light changes from red to violet. A rectangular slab of height 2.00 cm made of this material is placed on a newspaper. When viewed normally in yellow light, the letters appear 1.32 cm below the top surface of the slab. Calculate the dispersive power of the material.
Ans:Given:
Difference in the refractive indices of violet and red lights = 0.014
Let 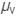 and
and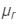 be the refractive indices of violet and red colours.
be the refractive indices of violet and red colours.
Thus, we have:
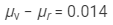
Now,
Real depth of the newspaper = 2.00 cm
Apparent depth of the newspaper = 1.32 cm
Refractive index =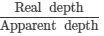
∴Refractive index for yellow light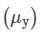 is given by
is given by
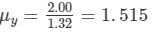
Also,
Dispersive power,
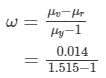
Or, 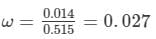
Thus, the dispersive power of the material is 0.027.
Ques 5:A thin prism is made of a material having refractive indices 1.61 and 1.65 for red and violet light. The dispersive power of the material is 0.07. It is found that a beam of yellow light passing through the prism suffers a minimum deviation of 4.0° in favourable conditions. Calculate the angle of the prism.
Ans :The refractive indices for red and yellow lights are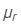 = 1.61 and
= 1.61 and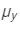 = 1.65, respectively.
= 1.65, respectively.
Dispersive power,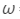 = 0.07
= 0.07
Angle of minimum deviation,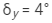
Now, using the relation,
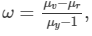
we get :
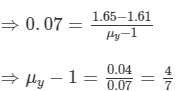
Let the angle of the prism be A.
Angle of minimum deviation, 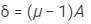
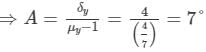
Thus, the angle of the prism is 7
Ques 6:The minimum deviations suffered by, yellow and violet beams passing through an equilateral transparent prism are 38.4°, 38.7° and 39.2° respectively. Calculate the dispersive power of the medium.
Ans: Given:
Minimum deviations suffered by
Red beam,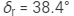
Yellow beam, 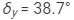
Violet beam, 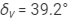
If A is the angle of prism having refractive index μ, then the angle of minimum deviation is given by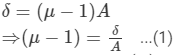
Dispersive power 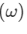 is given by
is given by
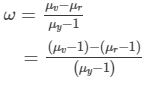
From equation (1), we ge
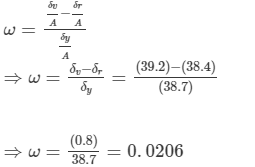
So, the dispersive power of the medium is 0.0206.
Ques 7:Two prisms of identical geometrical shape are combined with their refracting angles oppositely directed. The materials of the prisms have refractive indices 1.52 and 1.62 for violet light. A violet ray is deviated by 1.0° when passes symmetrically through this combination. What is the angle of the prisms?
Ans:Let A be the angle of the prisms.
Refractive indices of the prisms for violet light,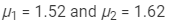
Angle of deviation,
As the prisms are oppositely directed, the angle of deviation is given by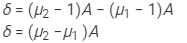
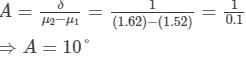
So, the angle of the prisms is 10∘.
Ques 7:Two prisms of identical geometrical shape are combined with their refracting angles oppositely directed. The materials of the prisms have refractive indices 1.52 and 1.62 for violet light. A violet ray is deviated by 1.0° when passes symmetrically through this combination. What is the angle of the prisms?
Ans:Let A be the angle of the prisms.
Refractive indices of the prisms for violet light,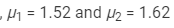
Angle of deviation, δ = 1.0°
As the prisms are oppositely directed, the angle of deviation is given by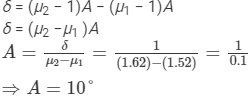
So, the angle of the prisms is 10∘.
Ques 8:Three thin prisms are combined as shown in figure. The refractive indices of the crown glass for red, yellow and violet rays are μr, μy and μv respectively and those for the flint glass are μ'r, μ'y and μ'v respectively. Find the ratio A'/A for which (a) there is no net angular dispersion, and (b) there is no net deviation in the yellow ray.
Ans:For the crown glass, we have:
Refractive index for red rays = μr
Refractive index for yellow rays = μy
Refractive index for violet rays = μv
For the flint glass, we have:
Refractive index for red rays = μ'r
Refractive index for yellow rays = μ'y
Refractive index for violet rays = μ'v
Let δcy and δfy be the angles of deviation produced by the crown and flint prisms for the yellow light.
Total deviation produced by the prism combination for yellow rays:
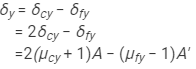
Angular dispersion produced by the combination is given by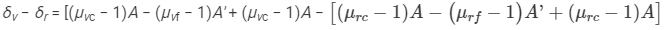
Here,
μvc = Refractive index for the violet colour of the crown glass
μvf = Refractive index for the violet colour of the flint glass
μrc = Refractive index for the red colour of the crown glass
μrf = Refractive index for the red colour of the flint glass
On solving, we get:

(b) For zero deviation in the yellow ray, δy = 0.
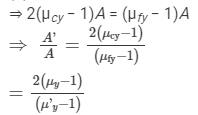
Objective I
Ques 2:If a glass prism is dipped in water, its dispersive power
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) does not change
(d) may increase or decrease depending on whether the angle of the prism is less than or greater than 60°
Ans: (b) decreases
If μ is the refractive index and A is the angle of prism, then the angular dispersion produced by the prism will be given by Aδ=(μ-1)A.
Because the relative refractive index of glass with respect to water is small compared to the refractive of glass with respect to air, the dispersive power of the glass prism is more in air than that in water.
Ques:A prism can produce a minimum deviation δ in a light beam. If three such prisms are combined, the minimum deviation that can be produced in this beam is
(a) 0
(b) δ
(c) 2δ
(d) 3δ
Ans:(b) δ
In combination (refractive angles of prisms reversed with respect to each other), the deviations through two prisms cancel out each other and the net deviation is due to the third prism only.
Ques 4:Consider the following two statements :
(A) Line spectra contain information about atoms.
(B) Band spectra contain information about molecules.
(a) Both A and B are wrong
(b) A is correct but B is wrong
(c) B is correct but A is wrong
(d) Both A and B are correct
Ans:(d) Both A and B are correct.
Because line spectra contain wavelengths that are absorbed by atoms and band spectra contain bunch wavelengths that are absorbed by molecules, both statements are correct.
Ques 5:The focal length of a converging lens are fv and fr for violet and red light respectively.
(a) fv > fr
(b) fv = fr
(c) fv < fr
(d) Any of the three is possible depending on the value of the average refractive index μ.
Ans:(c) fv < fr
Focal length is inversely proportional to refractive index and refractive index is inversely proportional to λ2. So, keeping other parameters the same, we can say: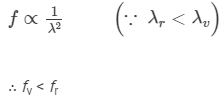
Objective II
Ques 1:A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
Ans:
(b) The emergent beam is white.
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours.
White light will split into different colours inside the glass slab because the value of refractive index is different for different wavelengths of light; thus, they suffer different deviations. But the emergent light will be white light. As the faces of the glass slide are parallel, the emerging lights of different wavelengths will reunite after refraction.
Ques 2:By properly combining two prisms made of different materials, it is possible to
(a) have dispersion without average deviation
(b) have deviation without dispersion
(c) have both dispersion and average deviation
(d) have neither dispersion nor average deviation
Ans:
(a) have dispersion without average deviation
(b) have deviation without dispersion
(c) have both dispersion and average deviation
Consider the case of prisms combined such that the refractive angles are reversed w.r.t. each other. Then, the net deviation of the yellow ray will be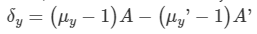
And, the net angular dispersion will be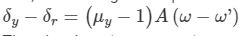
Thus, by choosing appropriate conditions, we can have the above mentioned cases.
Ques:In producing a pure spectrum, the incident light is passed through a narrow slit placed in the focal plane of an achromatic lens because a narrow slit
(a) produces less diffraction
(b) increases intensity
(c) allows only one colour at a time
(d) allows a more parallel beam when it passes through the lens
Ans:(d) allows a more parallel beam when it passes through the lens
To produce a pure spectrum, a parallel light beam is required to be incident on the dispersing element. So, the incident light is passed through a narrow slit placed in the focal plane of an achromatic lens.
Ques 4:Which of the following quantities related to a lens depend on the wavelength or wavelengths of the incident light?
(a) Power
(b) Focal length
(c) Chromatic aberration
(d) Radii of curvature
Ans:
(a) Power
(b) Focal length
(c) Chromatic aberration
The focal length, power and chromatic aberration are dependent on the refractive index of the lens, which itself is dependent on the wavelength of the light.
Ques 5:Which of the following quantities increase when wavelength is increased? Consider only the magnitudes.
(a) The power of a converging lens
(b) The focal length of a converging lens
(c) The power of a diverging lens
(d) The focal length of a diverging lens
Ans:
(b) The focal length of a converging lens
(d) The focal length of a diverging lens
The focal length of a lens is inversely proportional to the refractive index of the lens and the refractive index of the lens is inversely proportional to the square of wavelength. Therefore, the focal length is directly dependent on wavelength; it increases when the wavelength is increased.
Page 443
Ques 9:A thin prism of crown glass (μr = 1.515, μv = 1.525) and a thin prism of flint glass (μr = 1.612, μv = 1.632) are placed in contact with each other. Their refracting angles are 5.0° each and are similarly directed. Calculate the angular dispersion produced by the combination.
Ans:
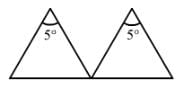
For crown glass, we have:
Refractive index for red colour, μcr = 1.515
Refractive index for violet colour, μcv = 1.525
For flint glass, we have:
Refractive index for red colour, μfr = 1.612
Refractive index for violet colour,μfv = 1.632
Refracting angle, A = 5°
Let:
δc = Angle of deviation for crown glass
δf = Angle of deviation for flint glass
As prisms are similarly directed and placed in contact with each other, the total deviation produced (δ) is given by
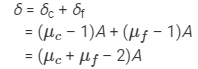
For violet light, δv = (μcv + μfv – 2)A
For red light, δr = (μcr + μfr – 2)A
Now, we have:
Angular dispersion of the combination: 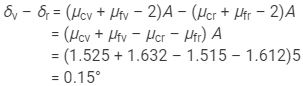
So, the angular dispersion produced by the combination is 0.15°.
Ques 10:A thin prism of angle 6.0°, ω = 0.07 and μy = 1.50 is combined with another thin prism having ω = 0.08 and μy = 1.60. The combination produces no deviation in the mean ray. (a) Find the angle of the second prism. (b) Find the net angular dispersion produced by the combination when a beam of white light passes through it. (c) If the prisms are similarly directed, what will be the deviation in the mean ray? (d) Find the angular dispersion in the situation described in (c).
Ans: Given:
For the first prism,
Angle of prism, A' = 6°
Angle of deviation, ω' = 0.07
Refractive index for yellow colour, μ'y = 1.50
For the second prism,
Angle of deviation, ω = 0.08
Refractive index for yellow colour, μy= 1.60
Let the angle of prism for the second prism be A.
The prism must be oppositely directed, as the combination produces no deviation in the mean ray.
(a) The deviation of the mean ray is zero.
Thus, we have:
Thus, we have:
δy = (μy – 1)A – (μ'y – 1)A' = 0
∴ (1.60 – 1)A = (1.50 – 1)A'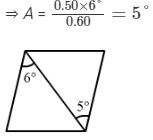
(b) Net angular dispersion on passing a beam of white light:
(μy – 1)ωA – (μy – 1)ω'A'
⇒ (1.60 – 1)(0.08)(5°) – (1.50 – 1)(0.07)(6°)
⇒ 0.24° – 0.21° = 0.03
(c) For the prisms directed similarly, the net deviation in the mean ray is given by
δy = (μy – 1)A + (μy – 1)A'
= (1.60 – 1)5° + (1.50 – 1)6°
= 3° + 3° = 6°
(d) For the prisms directed similarly, angular dispersion is given by
δv – δr = (μy – 1)ωA – (μy – 1)ω'A'
= 0.24° + 0.21°
= 0.45°
Ques 11:The refractive index of a material M1 changes by 0.014 and that of another material M2 changes by 0.024 as the colour of the light is changed from red to violet. Two thin prisms, one made of M1(A = 5.3°) and the other made of M2(A = 3.7°) are combined with their refracting angles oppositely directed. (a) Find the angular dispersion produced by the combination. (b) The prisms are now combined with their refracting angles similarly directed. Find the angular dispersion produced by the combination.
Answer 11:
If μ'v and μ'r are the refractive indices of material M1, then we have:
μ'v – μ'r = 0.014
If μv and μr are the refractive indices of material M2, then we have:
μv – μr = 0.024
Now,
Angle of prism for M1, A' = 5.3°
Angle of prism for M2, A = 3.7°
(a) When the prisms are oppositely directed, angular dispersion (δ1) is given by
δ1 = (μv – μr)A – (μ'v – μ'r)A'
On substituting the values, we get:
δ1 = 0.024 × 3.7° – 0.014 × 5.3°
= 0.0146°
So, the angular dispersion is 0.0146°.
(b) When the prisms are similarly directed, angular dispersion(δ2) is given by
δ2 = (μv – μr)A + (μ'v – μ'r)A'
On substituting the values, we get:
δ2 = 0.024 × 3.7° + 0.014 × 5.3°
= 0.163°
So, the angular dispersion is 0.163°.
|
134 docs
|
FAQs on HC Verma Solutions: Dispersion and Spectra - HC Verma Solutions - JEE
| 1. What is dispersion in physics? |  |
| 2. How does a prism create a spectrum? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between the angle of deviation and the refractive index in dispersion? |  |
| 4. How does dispersion affect the formation of rainbows? |  |
| 5. How is dispersion used in spectroscopy? |  |
















