Q. 1. Define “Human Geography”.
Ans. Human geography is basically the study that deals with human activity in relation to the earth’s surface. It shows how human activity affects or is influenced by the surface of the earth. Human geography also shows an interaction between the culture of humans and their land. Examples, villages, roads , railway and agricultural farms.
Q. 2. “Leading a long and healthy life is an important aspect of human development”. Give an argument to support the statement.
Ans. Living a long and healthy life indicates access to resources, health, facilities and improved levels of nutrition intake. Hence it is an important aspect of human development.
Q. 3. Which sub-field of geography is called Demography?
Ans. Population Geography is known as Demography.
Q. 4. Which subject is called the mother of all branches of knowledge?
Ans. Geography is called the mother of all branches of knowledge.
Q. 5. ‘‘Possibilities can be created within the limit, which do not damage the environment and there is no free run without accidents’’. Analyse the statement.
Ans. Approach to development without damaging the environment :
(i) Human beings were able to develop technology after they developed better understanding of natural laws.
(ii) Obeying nature is extremely important to develop technology and technology loosens the shackles of environment on human beings.
(iii) Man has to respond to the red signals and proceed to develop when nature permits modifications.
(iv) The free run, reckless approach badly affects the environment.
(v) It has resulted in greenhouse effect, depletion of ozone layer, global warming, receding glaciers and degrading lands.
Q. 6. How are nature and human inseparable?
Ans. Nature and human are inseparable. The earth is the home of mankind. It may be in different forms. All types of life supports are provided by nature.
They directly depend on nature. Nature and humans are inseparable and should be seen holistically. Physical features are described in metaphors using symbols from the human anatomy. For example: face of earth, nose of glacier, eye of storm, mouth of river, neck of isthmus, profile of soil, etc.
Q. 7. What do you understand by humanization of nature.
Ans. Humanization of nature :
(i) People begin to understand their environment and the forces of nature with the passage of time.
(ii) With social and cultural development, humans develop better and more efficient technology.
(iii) Humans move from a state of necessity to a state of freedom.
(iv) They create possibilities with the resources obtained from the environment.
(v) The human activities create cultural landscape.
(vi) The imprints of human activities are health resorts, huge urban sprawls, fields, orchards and pastures in plains and rolling hills, ports on the coasts and satellites in the space.
Q. 8. “The nature and human beings are so intricately intertwined that they can’t be separated”. Substantiate the statement.
Ans. Nature and human beings are intertwined :
(i) The nature and humans are inseparable.
(ii) In the natural environment, man has created social and cultural environment through mutual interaction.
(iii) Physical and human phenomena are often described in metaphors like : face of the earth, eye of the storm, mouth of the river, snout of the glacier, profile of the soil, etc.
(iv) All these natural elements are inseparable from human beings.
Q. 9. “The knowledge about nature is extremely important to develop technology”. Support this statement by giving three examples.
Ans. Technology indicates the level of educational development of society. Human beings were able to develop technology after they developed better understanding of natural laws.
(i) The understanding of the concept of friction and heat helped us discover fire.
(ii) Understanding of the secrets of DNA and genetics enabled us to conquer many diseases.
(iii) The laws of aerodynamics are used to develop faster planes.
(iv) The knowledge about nature is extremely important to develop technology. Technology loosens the shackles of environment on human beings.
Q. 10. “The knowledge and understanding of the laws of nature are extremely valuable to humankind”. Explain the values that can help to use the gifts of nature in a sustainable manner.
Ans. The knowledge of laws of nature are highly valuable for mankind.
(i) Better knowledge is developed because of better knowledge of laws of nature.
(ii) The understanding of concept of friction and heat helped discover fire.
(iii) We use law of aerodynamics to develop faster planes.
(iv) Harmony with their natural environment.
(v) Thus, law of nature, if known to man are extremely valuable.
Q. 11. What is the subject matter of the study of human geography? Explain.
Ans. The subject matter of the study of human geography are :
(i) To establish relationship between the physical world and the human world.
(ii) To study the spatial distribution of human phenomenon.
(iii) To study the social and economic differences between different parts of the world.
(iv) To understand the earth as home of human beings and to study all the elements which have sustained them.
(v) Nature and human are inseparable elements and should be seen holistically.
Q.12. Explain with examples how nature gets humanized?
OR
“Nature provides opportunities and humans make use of these and slowly nature gets humanized.” Substantiate the statement.
Ans. Human starts interacting with physical environment with the help of technologies. With social and cultural development, human develops better and more efficient technologies. For example, in earlier era, people used to live in caves and were totally dependent on hunting of animals. They started developing their weapons from stones and other easily available materials. Later on, they discovered more suitable instruments. When human starts interacting with physical environment, they start forming state of necessity rather than the state of freedom.
Q. 13. “There is mutual interaction between the elements of physical geography and human geography”. Support the statement with suitable examples.
Ans. Human and physical geography is the study of the environment, people and the resources they use. Geography determines the way in which humans live, the adaptations they have developed to survive, and the alterations to the environment they have made to better their existence. The impact of human interaction with the environment has mixed results. While human life has been improved and made more comfortable, the environment has been damaged in variety of ways.
For example: Climate is a very important part in the study of human and physical geography. Climate is the usual weather patterns that occur in an area over a long period of time.
Q. 14. Define “Human Geography ” in your own words. Mention any four fields of human geography.
OR
Name some sub-fields of human geography.
Ans. Human geography is the study of many cultural aspects found throughout the world and how they relate to the spaces and places where they originate and then travel as people continually move across various areas.
Some of the main cultural phenomena studied in human geography include language, religion, different economic and governmental structures, art, music and other cultural aspects that explain how and/or why people function as they do i the areas in which they live. Globalization is also becoming increasingly important to the field of human geography as it is following these specific aspects of culture to easily travel across the globe.
Few fields of human geography are :
(i) Social geography: Its sub-fields are behavioural geography, geography of social well-being, geography of leisure, cultural geography, gender geography, historical geography and medical geography.
(ii) Urban geography: It includes the study of cities and urban processes.
(iii) Political geography: Its sub-fields are electoral geography and military geography.
(iv) Population geography: It is the study of the ways in which spatial variations in the distribution, composition, migration and growth of populations are related to the nature of the place.
(v) Settlement geography: It investigates the earth’s surface part settled by humans.
(vi) Economic geography: Its sub-fields are geography of resources, geography of agriculture, geography of industries, geography of marketing, geography of tourism and geography of international trade.
Q. 15. Explain the concept of ‘possibilism’ with three suitable examples.
Ans. Possibilism is the view of the environment as a range of opportunities from which the individual may choose. This choice is based on the individual’s needs and norms. It grants that the range of choices may be limited by the environment, but allows choices to be made, rather than thinking on deterministic lines. Few suitable examples are :
(i) Health resorts of highlands
(ii) Orchards
(iii) Ports on the coasts
(iv) Satellites in the space.
Q. 16. Explain the concept of “Determinism” with a suitable example.
Ans. (i) Determinism is the philosophical idea that every event or state of affairs, including every human decision and action, is the inevitable and necessary consequence of antecedent states of affairs.
(ii) Human dependency upon environment for sustaining is best example of it.
(iii) We use natural resources like coal, petroleum and other petroleum products for our benefits.
(iv) There is a direct dependence of human beings on nature for resources which sustain them.
(v) Determinism considers humans passive agents. Nature determines their attitudes, decisions and lifestyles.
(vi) For example : Tribals of Abujh Maad area of Central India.
Q. 17. Explain how technology indicates the level of cultural development of society.
Ans. Technology indicates the level of cultural development of society. As the technology develops cultural development takes place which is clear from the following facts:
(i) The understanding of the concepts of friction and heat helped us discover fire.
(ii) Understanding of the secrets of DNA and genetics enabled us to conquer many diseases.
(iii) We use the laws of aerodynamics to develop faster planes.
Q. 18. Define ‘Human Geography’. Give four examples of elements of material culture created by human, using the resources provided by nature. (Outside Delhi, 2012, Set I) Ans. It studies the inter-relationship between the physical environment and socio-cultural environment created by human beings through mutual interaction with each other.
Few examples of elements of material culture created by humans :
(i) Houses (ii) Villages (iii) Cities (iv) Road-rail networks (v) Industries (vi) Farms (vii) Ports (viii) Items of our daily use
Q. 19. Explain the concept of ‘Neo-determinism’.
OR
Mention three characteristics of Neo-determinism.
Ans. Concept of Neo-determinism and few of its characteristics are :
(i) It is a concept of middle path between determinism and possibilism.
(ii) The concept shows that neither is there a situation of absolute necessity nor is there a condition of absolute freedom.
(iii) It means that human beings can conquer nature by obeying it.
(iv) It also conveys that possibilities can be created within limits which do not damage the environment and there is no free run without accidents.
Detailed Answer :
(i) This concept was developed by Griffith Taylor. The main aim for ‘Neo-determinism’ is sustainable development. He believed that the best economic programme for a country to follow has in large been influenced by nature and it is geographer’s duty to interpret this programme. Human beings are capable of accelerating, slowing down or stopping the progress of a country’s development.
(ii) Neo-determinisim also refer to humans as passive agents influenced by environmental factors which determine their attitude, decision making and the lifestyle they lead.
(iii) This concept also determines that human beings follow nature’s programme only if it is wise, presuming he can act foolish, which admits the possibilities of contention within broad limits set by environment man can choose, at the very last.
Q. 20. “There is a direct dependence of human beings on nature for resources which sustain them”. Justify the statement in the light of environment determinism.
Ans. Direct dependence of human beings on nature for resources.
(i) Low level of technology
(ii) Primitive stage of human social development
(iii) Fear of nature’s fury
(iv) Nature worship
(v) Physical environment became ‘Mother Nature’
(vi) Complete harmony with natural environment.
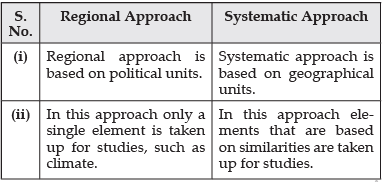
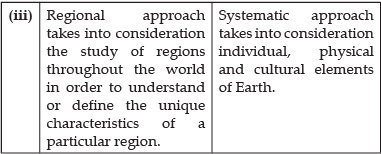
Q. 21. Distinguish between regional approach and systematic approach of geography.
Ans.


Q. 22. ‘‘The primitive communities lived in complete harmony with their natural environment and as such the humans were naturalized.’’ Support the statement.
Ans. The primitive communities lived in complete harmony with their natural environment:
(i) The primitive society live in complete harmony with their natural environment.
(ii) It is realized that in all such cases nature is a powerful force, worshipped, revered and conserved.
(iii) There is direct dependence of human beings on nature for resources which sustain them.
(iv) The people begin to understand their environment and the forces of nature with the passage of time.
(v) With social and cultural development, humans develop better and more efficient technology.
(vi) They move from a state of necessity to a state of freedom.
(vii) They create possibilities with the resources obtained from the environment.
(viii) They were afraid of the fury of nature.
(ix) Any other relevant point .
Detailed Answer:
(i) In the early stages of their interaction with their natural environment, humans were greatly influenced by the nature. They adapted the dictates of nature.
(ii) There was complete harmony with the natural environment because the level of technology was very low and the stage of human social development was primitive.
(iii) Man obeyed the nature and was afraid of her fury and worshipped the nature. This situation has been seen in several tribal areas in India and across the globe.
(iv) The tribes of Central India in Abujh Maad wears a small loin cloth and has a small axe. They practice primitive agriculture by clearing a piece of land in forest. This shows the harmonious relationship between the man and nature.
(v) There is a direct dependence of human beings on nature for resources which sustain them. The physical environment for such societies become the ‘Mother Nature’.
Q. 23. ‘Technology loosens the shackles of environment on human beings’. Justify.
Ans. With the passage of time, people began to understand their environment and the forces of nature. With social and cultural development, humans developed better and more efficient technology. They moved from a state of necessity to a state of freedom. They created possibilities with the resources they obtained from the nature. The earlier scholars termed it as ‘possibilism’ wherein humans harnessed the opportunities provided by nature and developed technology that helped them utilize the resources and loosen the shackles of nature on humans.
Q. 24. How is human geography related to other social sciences ?
Ans. Human geography attempts to explain the relationship between all elements of human life and the space they occur over. Thus, human geography assumes a highly inter-disciplinary nature. It develops close interface with other sister disciplines in social sciences in order to understand and explain human elements on the surface of the earth. With the expansion of knowledge, new subfields emerge and it has also happened to human geography.