Q. 1. Define the term ‘commercial livestock rearing’. Explain any four characteristics.
OR
Describe any five characteristics of commercial livestock rearing practiced in the world.
Ans. Commercial livestock rearing is the practice of nurturing the animals for food and for other human uses. The word ‘livestock’ applies to dairy cows, chickens, goats, pigs, horses and sheep. Today, even animals like donkeys, mules, rabbits and insects such as bees are being raised as part of commercial livestock rearing.Characteristics of commercial livestock rearing are :
(i) Commercial livestock rearing is practiced in the western cultures.
(ii) Ranches cover large areas and are divided into parcels.
(iii) The number of animals in the pastures is kept according to the carrying capacity of the pasture.
(iv) Rearing of animals in ranching is organised on the scientific basis.
(v) It has emphasis on breeding, genetic improvement, disease control and health care of the animals.
Q. 2. Define the term ‘nomadic herding’. Explain its any four characteristics.
OR
Explain any five features of nomadic herding in the world.
Ans. Nomadic herding can be defined as primitive subsistence activity in which the herders rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport. They move from one place to another along with their livestock.
Characteristics :
(i) Simple form of pastoralism in which herds and flocks graze on natural vegetation called pastures.
(ii) It is an ancient activity where each nomadic community occupies a well-defined territory as per their tradition and culture.
(iii) Animals of the nomads differ according to the cultural and physical characteristics. The camel is the most desired animal in North Africa and the Middle-East followed by sheep and goats. Horses, yaks, reindeers and llamas are other important animals.
(iv) The nomadic herders are very much dependent on their animals as they provide them with food, clothing, transport and for materials from which their houses can be made.
(v) They move their herds from one place to another with change in seasons. This is known as transhumance. For example: Sheep or other animals may graze in Alpine meadows in the summers and be heralded back down into valleys for the winters.
(vi) Nomadic herding as a way of life is declining because of natural disasters such as droughts, loss of land area due to urban development and pressure from government to lead a settled existence.
Q. 3. Describe any five characteristics of the economic activities of hunting and gathering practised in the world.
Ans. Characteristics of hunting and gathering:
(i) These are carried out at different levels with different orientations.
(ii) This is practised in regions with harsh climatic conditions.
(iii) It often involves primitive societies, who extract both plants and animals to satisfy their needs for food, shelter and clothing.
(iv) This type of activity requires a small amount of capital investment and operates at very low level of technology.
(v) The yield per person is very low and little or no surplus is produced.
(vi) In some regions gathering has become market- oriented.
(vii) Gathering activity faces stiff competition from the synthetic products.
Q. 4. Why is a wide variety of animals kept by pastoral nomads in different regions of the world? Explain the process of transhumance with an example.
Ans. Pastoral nomadism is a primitive subsistence activity, in which the herders keep a large variety of animals as they rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport. Each nomadic community occupies a well-identified territory as a matter of tradition.
They move from one place to another along with their livestock, depending on the amount and quality of pastures and water.
Nomads living in different climatic conditions select and domesticate animals found in those regions.
The process of migration from plain areas to pastures on mountains during summers and again from mountain pastures to plain areas during winters is known as transhumance. For example: In mountain regions, such as Himalayas, Gujjars, Bakarwals, Gaddis and Bhotiyas migrate from plains to the mountains in summers and to the plains from the high altitude pastures in winters. Similarly, in the Tundra regions, the nomadic herders move from South to North in summers and from North to South in winters.
Q. 5. Differentiate between nomadic herding and commercial livestock rearing, stating any five points of distinction.
OR
Differentiate between nomadic herding and commercial livestock rearing.
Ans. Nomadic herding :
(i) It is practiced by nomads who live a migratory life.
(ii) They keep on moving from one place to another in search of pasture , food and water
(iii) The animals that they rear are of poor quality and the produce meets the local requirements of the nomads.
(iv) It is practised mostly in the tropical grasslands of Savannahs and the pastures are not permanent.
(v) Types of animals reared vary from region to region. In Tropical Africa, cattle are the most important livestock, while in Sahara and Asiatic deserts, sheep, goats and camel are reared. In the mountainous areas of Tibet and Andes, yak and llamas and in the Arctic and sub-Arctic areas, reindeer are the most important animals.
Commercial livestock rearing :
(i) It is practiced by people who are well-settled.
(ii) Ranches are built to rear animals. The animals are taken care of.
(iii) The quality of animals is very good, the produce from the animals is large and the products are processed and exported.
(iv) I t is mostly practised in temperate grasslands Pampas, Prairies.
(v) This type of activity is a specialised activity in which only one type of animal is reared. Important animals include sheep, cattle, goats and horses. Products such as meat, wool, hides and skin are processed and packed scientifically and exported to different world markets.
Q. 6. Explain any three characteristics of hunting and gathering. Give two reasons why gathering has little chance to become important at global level.
OR
Describe any five characteristics of the economic activities of hunting and gathering practised in the world.
Ans. Characteristics of hunting and gathering :
(i) G athering and hunting are the oldest economic activities known. These are carried out at different levels with different orientations.
(ii) Gathering is practised in regions with harsh climatic conditions. It often involves primitive societies, who extract, both plants and animals to satisfy their needs for food, shelter and clothing.
(iii) Gathering is practised in :
(a) high latitude zones which include northern Canada, northern Eurasia and southern Chile;
(b) Low latitude zones such as the Amazon Basin, tropical Africa, Northern fringe of Australia and the interior parts of Southeast Asia.
(iv) Gathering has little chance of becoming important at global level because it operates at very low level of technology.
(v) The yield per person is very low and little or no surplus is produced.
Q. 7. What type of agriculture is mainly practised in the interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid latitudes? Describe the main features of such type of agriculture.
OR
Where is extensive commercial grain cultivation practiced? Mention its main features.
OR
Explain any five characteristics of ‘extensive commercial grain cultivation’ practised in the world.
Ans. Extensive commercial grain cultivation is practised in the interior parts of semi-arid lands of midlatitudes.
Features :
(i) The size of farm is very large.
(ii) Entire operations of cultivation from ploughing to harvesting is mechanized.
(iii) There is low yield per acre but high yield per person.
(iv) Wheat is the principal crop. Corn, oats, barley and rye are also grown.
Q. 8. How many types of subsistence agriculture are practised in the world? Mention the main features of each type.
Ans. Two types of Subsistence Agriculture :
(i) Primitive Subsistence agriculture
(ii) Intensive Subsistence agriculture
(i) Main features of Primitive Subsistence Agriculture :
(a) It is also called shifting agriculture /slash and burn / Jhuming / Milpa /Ladang.
(b) It is widely practised by tribes in tropics : Africa, South and Central America, Southeast Asia.
(c) Vegetation is cleared by fire and ashes add to soil fertility.
(d) Farms are small.
(e) They use primitive tools.
(ii) Main features of Intensive Subsistence Agriculture :
(a) It is practised in densely populated regions of monsoon Asia.
(b) Land holdings are small.
(c) Farmers work with family workers.
(d) Use of machinery is limited.
(e) Farm yard manure is used for soil fertility.
Q. 9. What are the features of plantation agriculture?
OR
Describe any five characteristics of plantation agriculture in the world.
OR
Discuss the important characteristic features of plantation agriculture. Name a few important plantation crops from different countries.
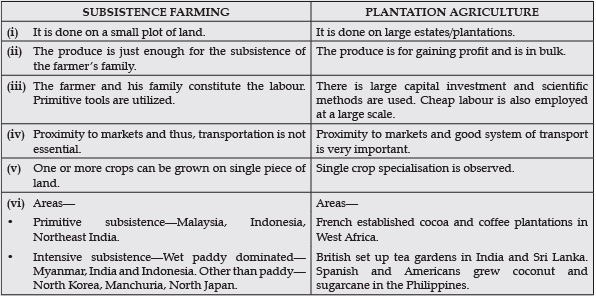
Ans. Features of Plantation Agriculture :
(i) Introduced by Europeans in their colonies in tropics.
(ii) Plantation crops are coffee, tea, banana, sugarcane, pineapples, etc.
(iii) They are large estates.
(iv) They require large capital investment.
(v) Cheap labour.
(vi) Single crop specialization.
(vii) Good transport network.
(viii) Scientific methods of cultivation are used.
(ix) Tea, coffee, cocoa, cotton, sugarcane, etc., are the examples of plantation crops.
Detailed Answer :
(i) Introduced by Europeans in their colonies in tropics : Plantation agriculture was introduced by Europeans which rapidly gained popularity and helped them gain profit due to increased international demand.
(ii) They are large estates : Plantation agriculture is practised on large scale, it is highly capitalised and export oriented in its approach.
(iii) They require large capital investment : Large capital investment is required to purchase the land, machinery involved and estates have to be scientifically managed.
(iv) Cheap labour : This type of cultivation gives employment to locally available labour or immigrants who belong to economically lower strata of the society.
(v) Single crop specialization : This type of agriculture is dedicated to single crop specialization as its main motive is large scale production in order to generate profit by selling the produce in the market.
(vi) Good transport network : Plantation agriculture is done is places which have a good transport network in terms to road and rail transportation because this type of agriculture is done on commercial basis.
(vii) Scientific methods of cultivation are used : In order to increase the produce and manage the cultivation on large scale, scientific method of cultivation are used.
(viii) Tea, coffee, cocoa, cotton, sugarcane, etc., are the examples of plantation crops : These produces are cultivated in order to be sold in local as well as international market.
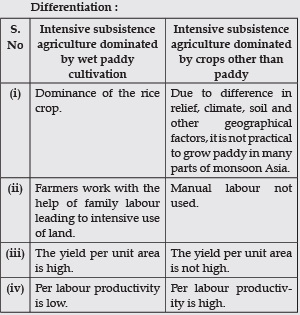
Q. 10. Classify and differentiate between two types of intensive subsistence agriculture.
Ans. Classification of intensive subsistence agriculture :
(i) Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by wet paddy cultivation.
(ii) Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by crops other than paddy.
Q. 11. Differentiate between co-operative and collective farming, stating any five points of distinction.
Ans. Differences :
(i) In co-operative farming, the farmers pool their resources together voluntarily and practise farming whereas in collective farming, there is social ownership of production and collective labour.
(ii) In case of co-operative farming individual ownership remains intact but in collective farming, farmers pool all their resources but they can keep a small portion of land.
(iii) Co-operative societies help farmers to procure all inputs of farming but in collective farming, the government procures the inputs for them.
(iv) Co-operative societies sell their products at favourable terms while in collective farming the product is sold at the price fixed by the state.
(v) European countries like Denmark, Netherlands, Belgium, Sweden, etc. follow co-operative system but Russia follows collective farming.
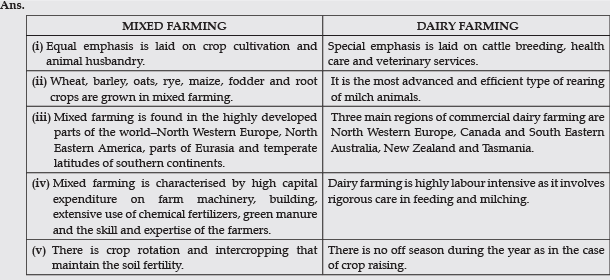
Q.12. Differentiate between mixed farming and dairy farming, stating any five points of distinction.
OR
Compare the features of mixed farming and dairy farming in five points each.
Ans:
Q. 13. Explain how dairy farming is highly capital intensive and labour intensive.
Ans. Dairy farming is highly capital intensive and labour intensive :
(i) Animal sheds, storage facilities for fodder involve big capital investment.
(ii) Feeding and milching machines add to the cost of dairy farming.
(iii) Cattle breeding, health care and veterinary services also requires large sum of capital. (iv) It is highly labour intensive as it involves rigorous care in feeding and milching.
(v) There is no off season for the workers during the year.
(vi) The transportation/refrigeration/pasteurization and other preservation processes involve huge manpower.
Q. 14. Why is dairy farming known as the most advanced and efficient type of farming in the world? Explain any five reasons.
Ans. Dairy farming is the most advanced and efficient type of rearing of milch animals :
(i) It is highly capital intensive. Animal sheds, storage facilities for fodder, feeding and milching machines add to the cost of dairy farming.
(ii) Special emphasis is laid on cattle breeding, health care and veterinary services.
(iii) It is highly labour intensive as it involves rigorous care in feeding and milching. There is no off season during the year as in the case of crop raising.
(iv) Huge market for fresh milk and dairy products. The development of transportation, refrigeration, pasteurisation and other preservation processes have increased the duration of storage of various dairy products.
(v) It is practised mainly near urban and industrial centres.
Q. 15. Define the term ‘mixed farming’. Explain any four characteristics of mixed farming practised in the world.
Ans. Characteristics of mixed farming practised in the world :
(i) This form of agriculture is found in the highly developed parts of the world, e.g. North-Western Europe, Eastern-North America, parts of Eurasia and the temperate latitudes of Southern continents.
(ii) Mixed farms are moderate in size and usually the crops associated with it are wheat, barley, oats, rye, maize, fodder and root crops.
(iii) Crop rotation and intercropping play an important role in maintaining soil fertility.
(iv) Mixed farming is characterised by high capital expenditure on farm machinery and building, extensive use of chemical fertilisers and green manures and also by the skill and expertise of the farmers.
(v) Equal emphasis is laid on crop cultivation and animal husbandry. Animals like cattle, sheep, pigs and poultry provide the main income along with crops.
Q. 16. Explain any five characteristics of ‘Market Gardening and Horticulture’ practised in the world.
OR
What is the meaning of market gardening and horticulture? Describe any four characteristics of this type of agriculture in the world.
Ans. Market gardening and horticulture specialize in the cultivation of high value crops such as vegetables, fruits and flowers solely for the urban markets. Characteristics of ‘Market Gardening’ and ‘Horticulture’:
(i) Market gardening and horticulture specialise in the cultivation of high value crops such as vegetables, fruits and flowers, solely for the urban markets.
(ii) It is both labour and capital intensive and lays emphasis on the use of irrigation, HYV seeds, fertilisers, insecticides, greenhouses and artificial heating in colder regions.
(iii) This type of agriculture is well developed in densely populated industrial districts of North West Europe, North Eastern United States of America and the Mediterranean regions.
(iv) Farms are small and are located where there are good transportation links with the urban centre where high income group of consumers is located.
(v) Netherlands specialises in growing flowers and horticultural crops especially tulips, which are flown to all major cities of Europe.
Q. 17. Where is intensive subsistence agriculture practiced in the world? What are its two types? Describe any two characteristics of each type.
Ans. Intensive subsistence agriculture is practiced mainly in densely populated regions of monsoon Asia. Basically, there are two types of intensive subsistence agriculture :
(i) Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by wet paddy cultivation :
(a) This type of agriculture is characterised by dominance of the rice crop.
(b) Use of machinery is limited and most of the agricultural operations are done by manual labour. Farm yard manure is used to maintain the fertility of the soil.
(ii) Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by crops other than paddy :
(a) Wheat, soyabean, barley and sorghum are grown.
(b) Yield per unit area is very high.
Q. 18. What is subsistence agriculture? Describe four features of primitive subsistence agriculture.
Ans. Subsistence agriculture refers to the type of farming in which farmers produce crops and rear animals to fulfil their needs and the requirements of their family only and not for the market.
Features of primitive subsistence agriculture :
(i) Primitive subsistence agriculture is also known as shifting agriculture.
(ii) This method involves the shifting of agricultural land from one part to the other by clearing forests which is done by felling of trees and burning them.
(iii) Cultivation is usually done by primitive implements without the aid of machine. Only manual labour is employed in clearing the forests.
(iv) Food crops such as yams, tapioca, maize, millets, beans, upland rice are the main crops grown by this method.
(v) This method results in deforestation and soil erosion.
Q. 19. Compare the features of Subsistence and Plantation Agriculture in five points each.
Ans.
Q. 20. ‘‘Gathering and hunting are the primitive economic activities meant for the subsistence of tribal societies, but in modern times gathering is market oriented and has become commercial.’’ Examine the statement.
Ans. Gathering activities :Gatherers collect valuable plants, leaves, bark and medicinal herbs for different uses and sell in market. The barks are used for making quinine, tannin etc., in different ways; leaves for beverages, drugs, cosmetics, fibers, thatch, fabrics. Edible nuts and their oils are also collected. Tree trunks for latex, balata, gums and resins are used as raw materials in various industries.
Q. 21. How did the Europeans introduce important plantation crops in the colonies situated in different parts of the tropics? Explain.
Ans. Plantation agriculture was introduced by the Europeans in colonies situated in the tropics. Some of the important plantation crops are tea, coffee, cocoa, rubber, cotton, oil palm, sugarcane, bananas and pineapples. The characteristic features of this type of farming are large estates or plantations, large capital investment, managerial and technical support, scientific methods of cultivation, single crop specialisation, cheap labour, and a good system of transportation which links the estates to the factories and markets for the export of the products. The French established cocoa and coffee plantations in West Africa. The British set up large tea gardens in India and Sri Lanka, rubber plantations in Malaysia and sugarcane and banana plantations in West Indies. Spanish and Americans invested heavily in coconut and sugarcane plantations in the Philippines. The Dutch once had monopoly over sugarcane plantation in Indonesia. Some coffee fazendas (large plantations) in Brazil are still managed by Europeans. Today, ownership of the majority of plantations has passed into the hands of the government or the nationals of the countries concerned.
Q. 22. Classify mining methods on the basis of mode of occurrence and the nature of the ore, into two categories. How are they different from each other?
Explain with examples.
Ans. Classification of mining :
(i) Surface Mining
(ii) Underground Mining Differences :
(i) Surface mining is known as open-cast mining whereas, underground mining is known as shaft method.
(ii) Surface mining is the cheapest way of mining, contrary to the underground mining which is expensive.
(iii) The former occurs close to the surface whereas, in the latter method vertical shafts have to be sunk, from where underground galleries radiate to reach the minerals.
(iv) Overhead cost for equipment is relatively low in open-cast, but for underground mining the equipment such as lifts, drills, etc. used are expensive.
(v) Open-cast mining is less risky than the underground mining which has more possibility of people becoming victim of poisonous gases, fire, floods, etc.

























