Ledger (Part - 3) - Commerce PDF Download
Page No 13.62:
Question 10:
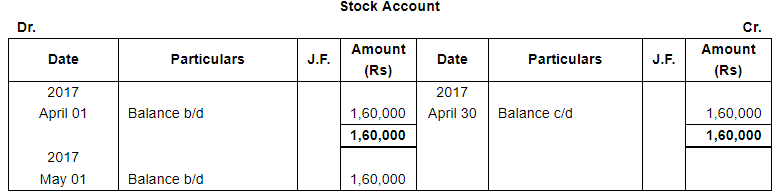
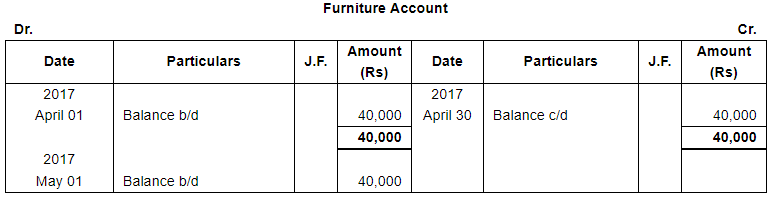
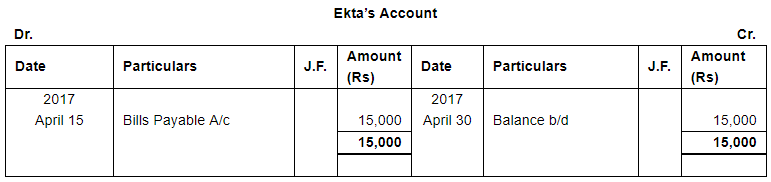
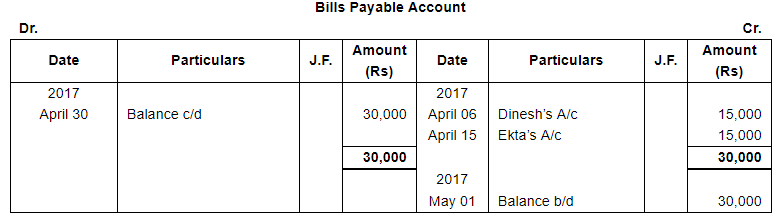
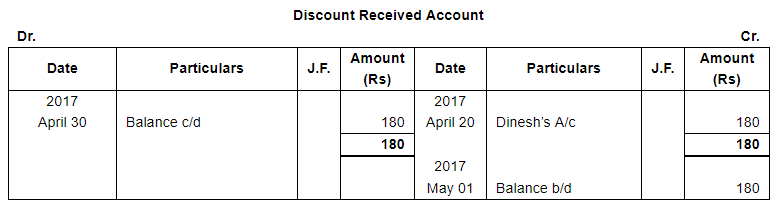
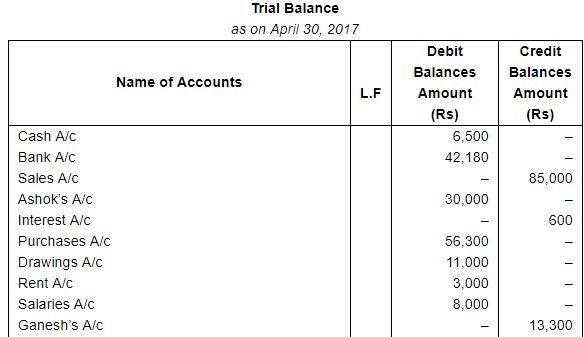
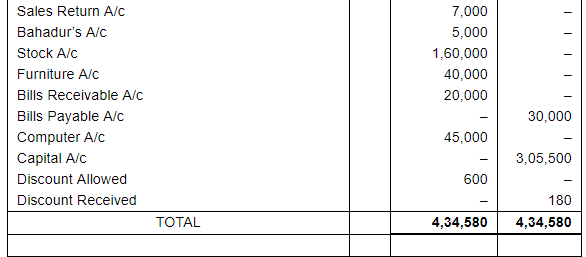
Enter the following transactions in subsidiary books, post them into Ledger and prepare a Trial Balance:
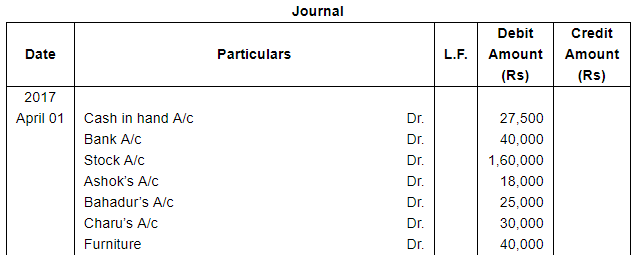
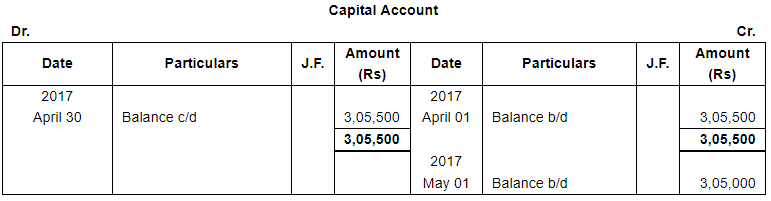
The following balances existed in Sunil Bros. books on April 1, 2017:
Assets : Cash in hand ₹ 27,500; Bank Balance ₹ 40,000;
Debtors : Ashok ₹ 18,000, Bahadur ₹ 25,000, Charu ₹ 30,000; Stock ₹ 1,60,000 and Furniture ₹ 40,000.
Liabilities : Creditors : Dinesh ₹ 20,000 and Ekta ₹ 15,000.
| 2017 | ||
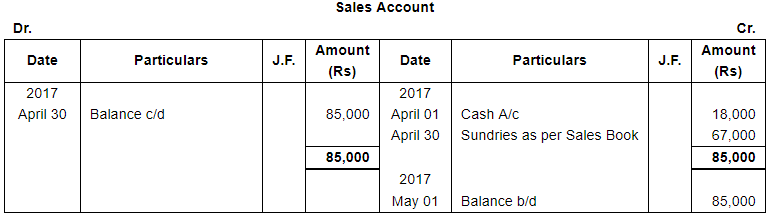
| April 1 | Cash Sales ₹ 18,000. | |
| 2 | Deposited into Bank ₹ 20,000. | |
| 3 | Purchased from Dinesh : | |
300 metres Cotton @ ₹ 60 per metre | ||
200 metres Silk @ ₹ 100 per metre | ||
| 5 | Cheque issued to Dinesh for ₹ 25,000. | |
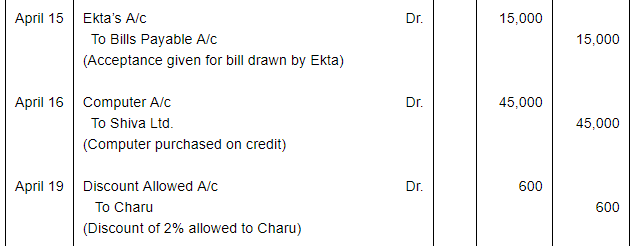
| 6 | Accepted a bill at one month for ₹ 15,000 drawn by Dinesh. | |
| 8 | Sold to Ashok : | |
400 metres Cotton @ ₹ 80 per metre | ||
250 metres Silk @ ₹ 140 per metre | ||
| 10 | Returned by Ashok 50 metres Silk. | |
| 12 | Received Cash ₹ 8,000 and a Cheque for ₹ 40,000 from Ashok. Cheque was immediately sent to Bank. | |
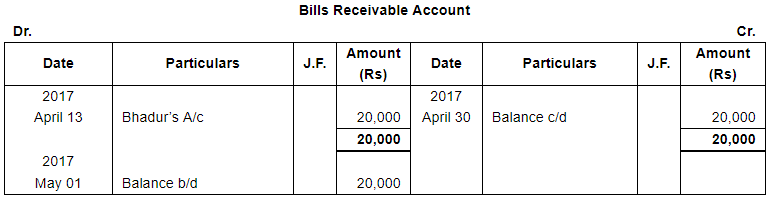
| 13 | Received a B/R from Bahadur for ₹ 20,000 at one month. | |
| 15 | Accepted a bill at two months drawn by Ekta for the amount due to her. | |
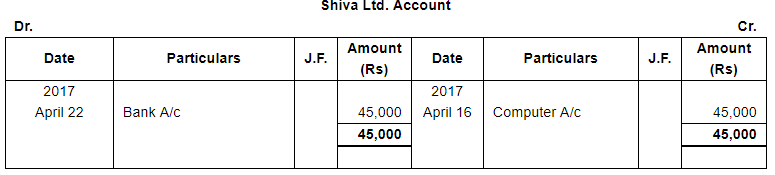
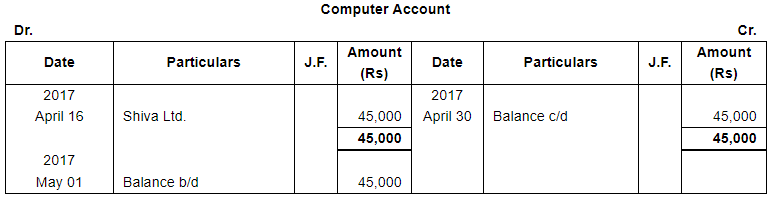
| 16 | Purchased a Computer for office use from Shiva Ltd. for ₹ 45,000 on Credit. | |
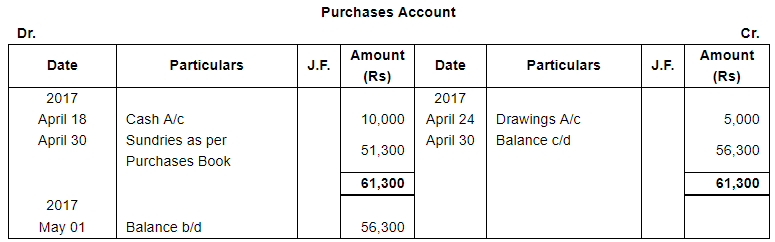
| 18 | Cash purchases ₹ 10,000. | |
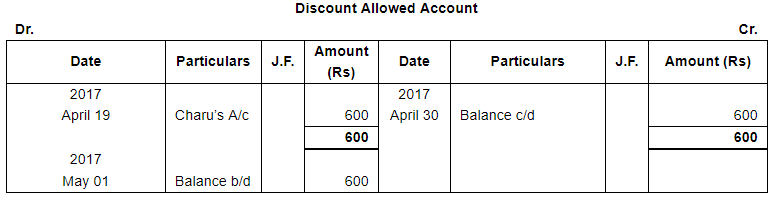
| 19 | Received full payment from Charu by cheque, sent it to Bank. Discount allowed 2%. | |
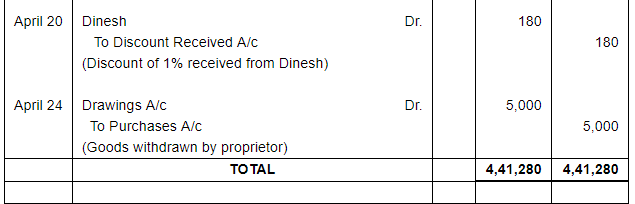
| 20 | Issued a cheque to Dinesh in full payment of his account after deducting 1% discount. | |
| 22 | Settled the account of Shiva Ltd. by a cheque. | |
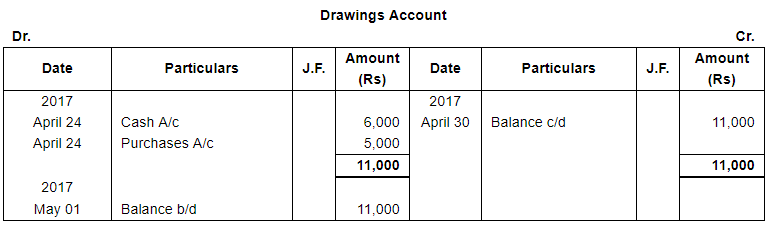
| 24 | Proprietor took away goods worth ₹ 5,000 and Cash ₹ 6,000. | |
| 25 | Purchased from Ganesh 200 metres Cotton @ ₹ 70 per metre subject to trade discount of 5%. | |
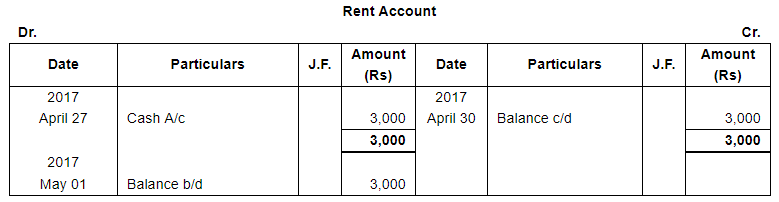
| 27 | Paid Rent ₹ 3,000 and Salaries ₹ 8,000. | |
| 30 | Interest allowed by bank ₹ 600. |
ANSWER: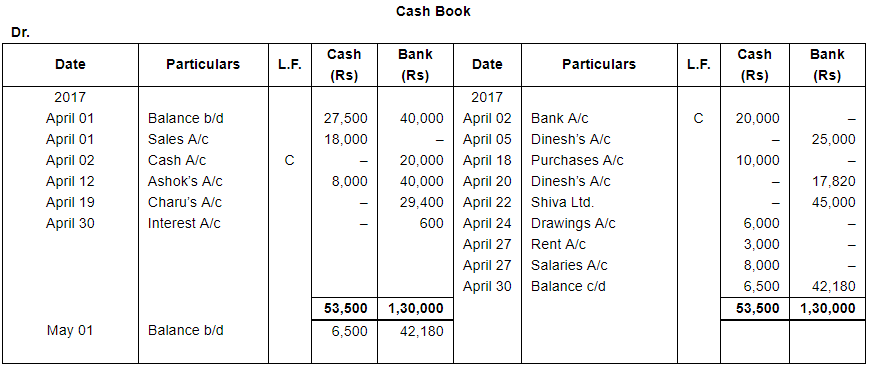
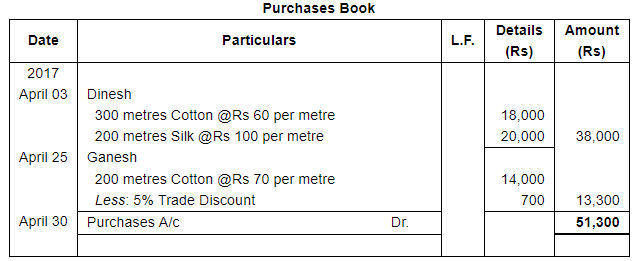
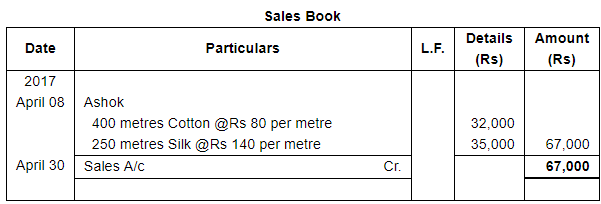
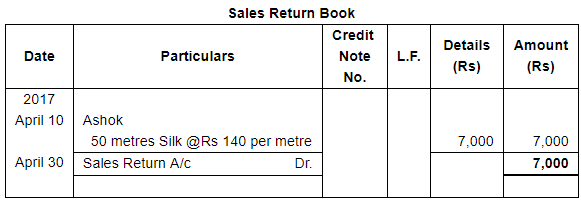

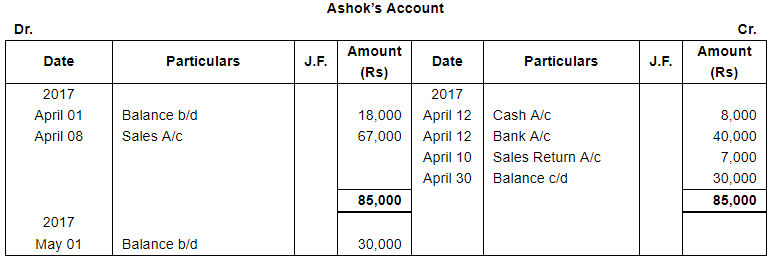
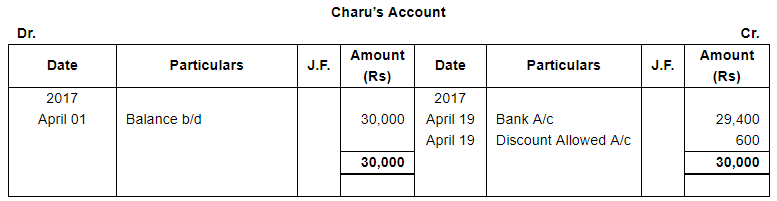
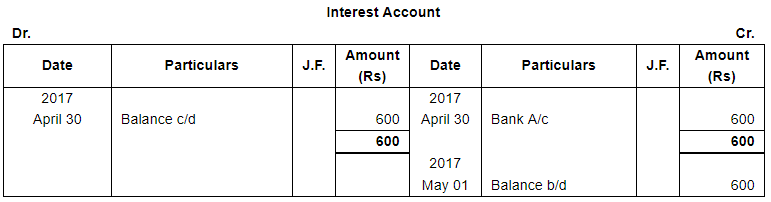
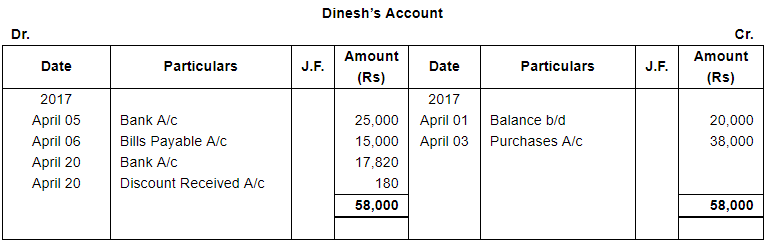
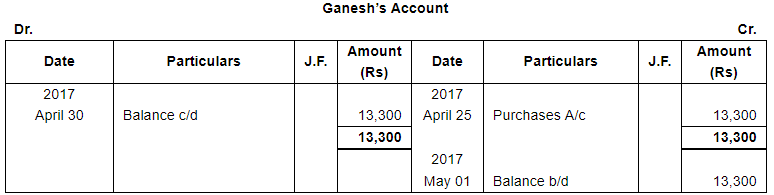
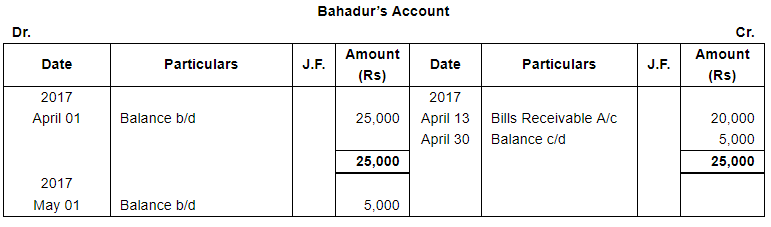
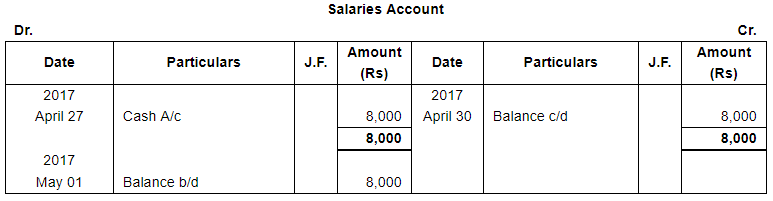
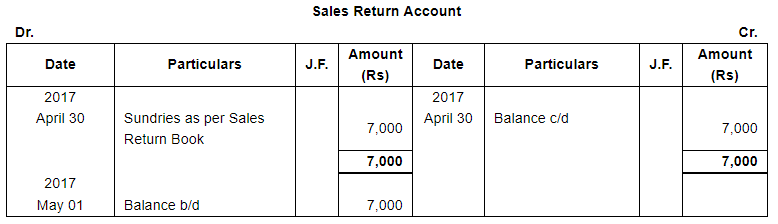
Page No 13.63:
Question 11:
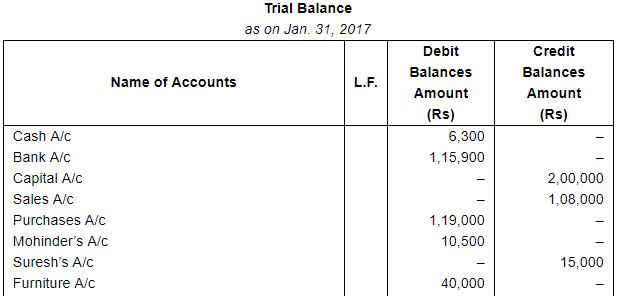
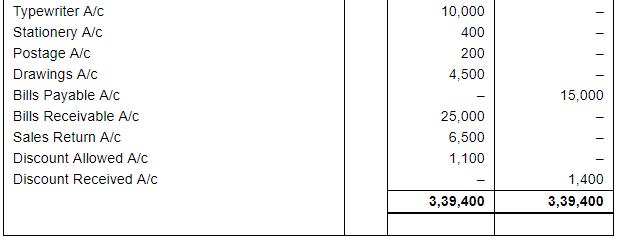
Record the following transactions of M/s Mahipal Bros. in Proper Subsidiary Books, post them into the Ledger and take out a Trial Balance:
| 2017 | ||
| Jan. 1 | Commenced business with Cash ₹ 2,00,000. | |
| 2 | Deposited into U.T.I Bank ₹ 1,75,000. | |
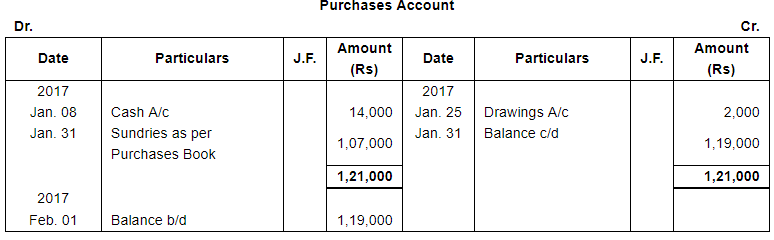
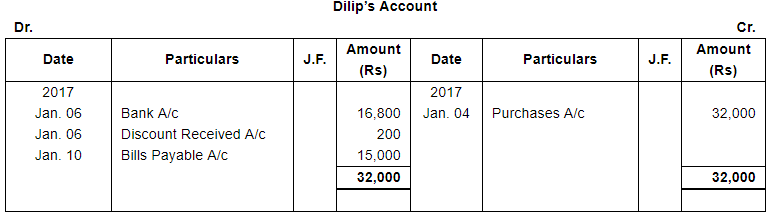
| 4 | Purchased goods from Dilip for ₹ 40,000. Trade Discount 20%. | |
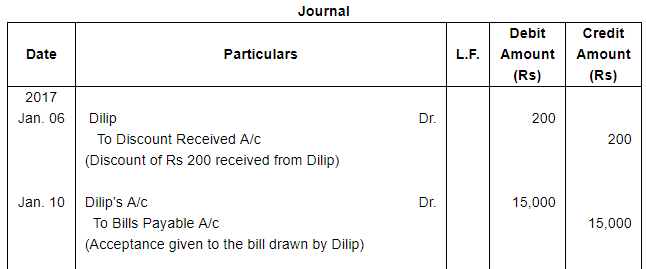
| 6 | Gave a cheque to Dilip for ₹ 16,800 and discount allowed by him ₹ 200. | |
| 8 | Goods bought from Nilesh for Cash ₹ 14,000. | |
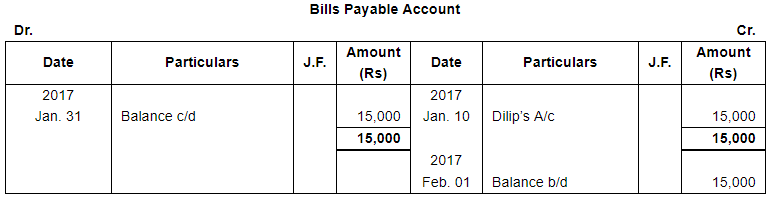
| 10 | Accepted a bill at 2 months for ₹ 15,000 drawn by Dilip. | |
| 11 | Bought goods from Suresh ₹ 75,000. | |
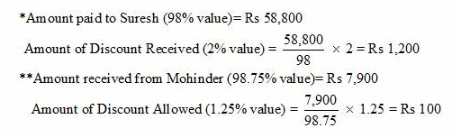
| 13 | Paid to Suresh a Cheque for ₹ 58,800 after receiving discount of 2%. | |
| 15 | Cash sales made to Jyoti Parshad ₹ 8,000. | |
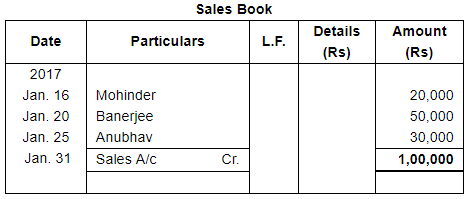
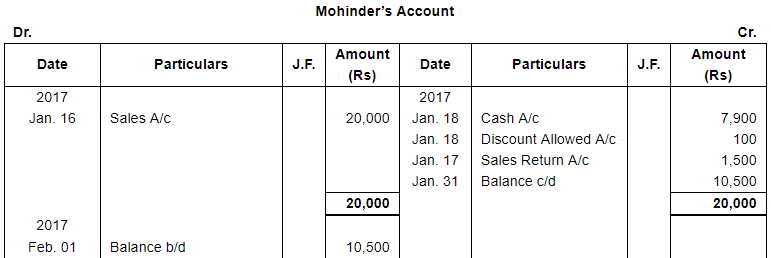
| 16 | Sold goods to Mohinder for ₹ 20,000. | |
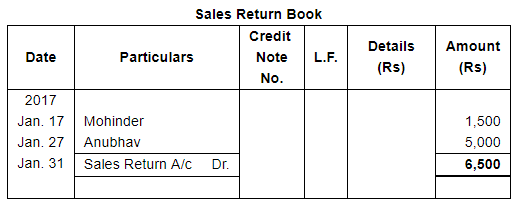
| 17 | Goods returned by Mohinder for ₹ 1,500. | |
| 18 | Received from Mohinder ₹ 7,900 after allowing a discount of 1.25%. | |
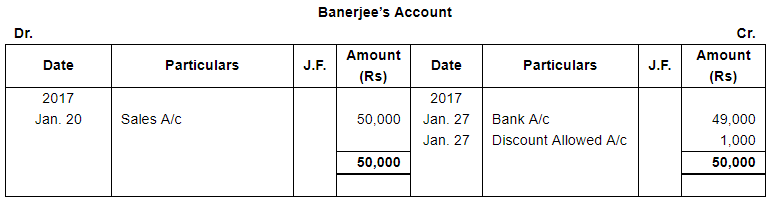
| 20 | Goods sold to Banerjee ₹ 50,000. | |
| 21 | Deposited into Bank ₹ 20,000. | |
| 25 | Goods taken for personal use ₹ 2,000. | |
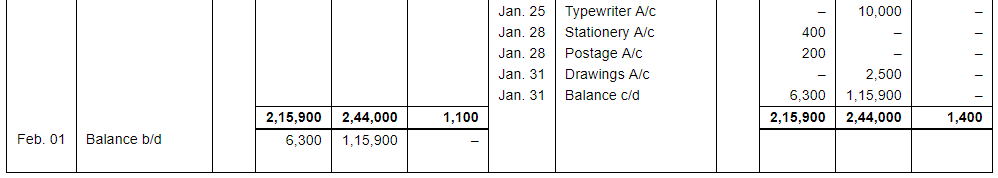
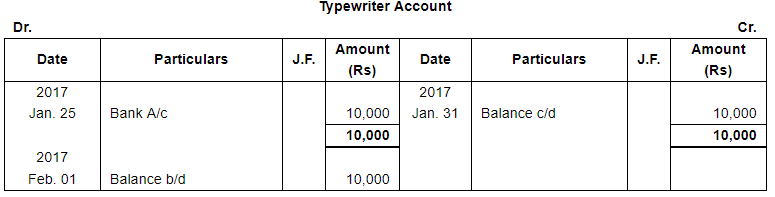
| 25 | Purchased furniture ₹ 40,000 and Typewriter ₹ 10,000 for office use. | |
| Payment for both the items is made by Cheque. | ||
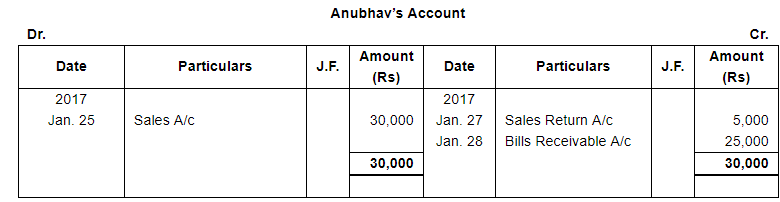
| 25 | Sold goods to Anubhav ₹ 30,000. | |
| 27 | Goods returned by Anubhav ₹ 5,000. | |
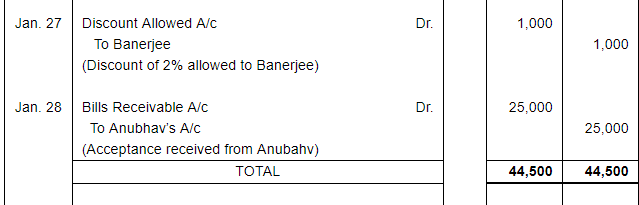
| 27 | Received full payment from Banerjee by Cheque, sent it to Bank, Discount allowed 2%. | |
| 28 | Acceptance received from Anubhav at 30 days for the amount due from him. | |
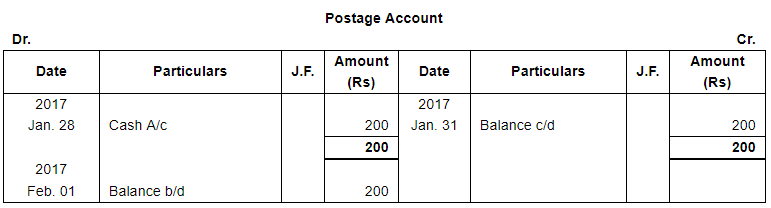
| 28 | Paid for stationery ₹ 400 and for Postage ₹ 200. | |
| 31 | Rent of proprietor's house paid by Cheque ₹ 2,500. |
ANSWER: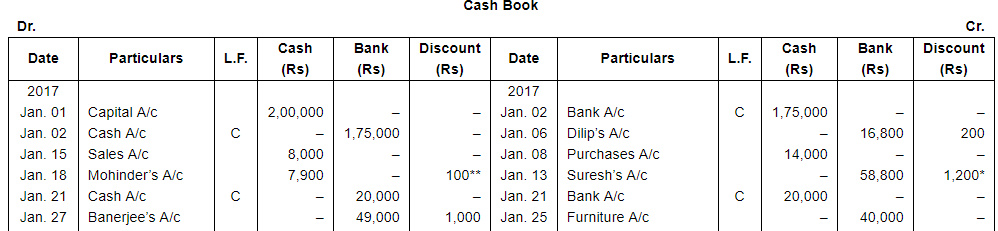


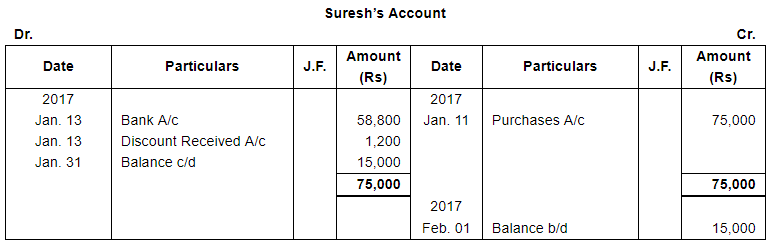
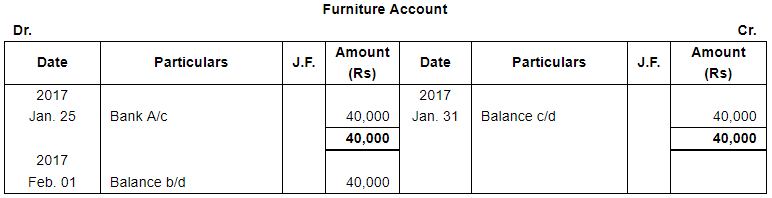
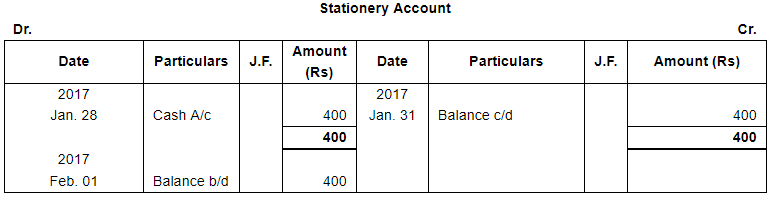
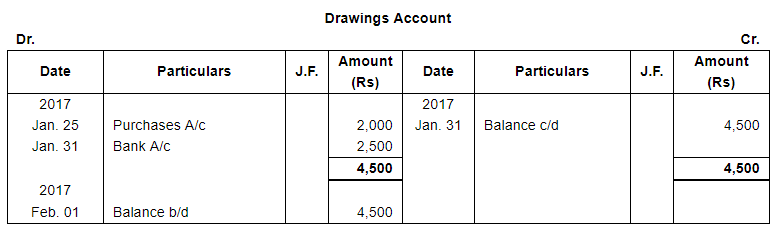
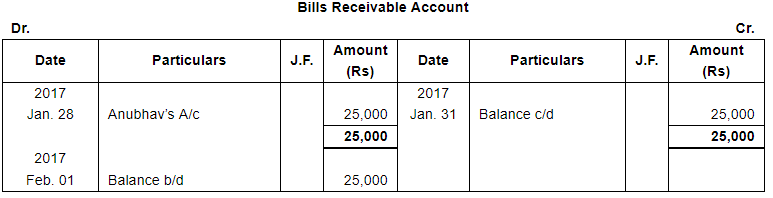
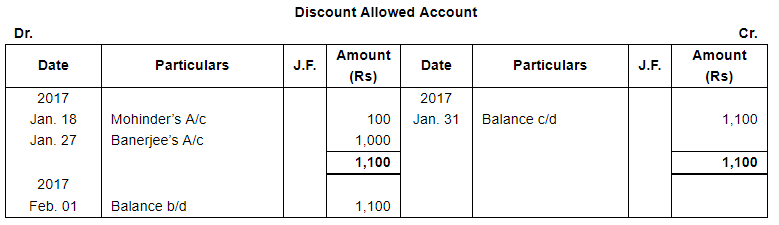
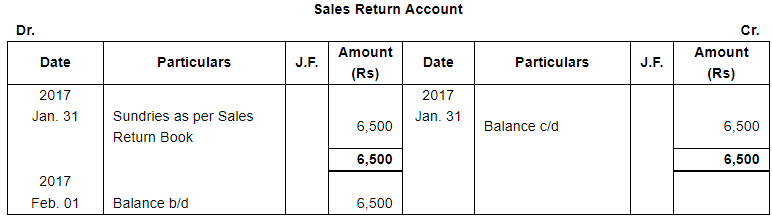
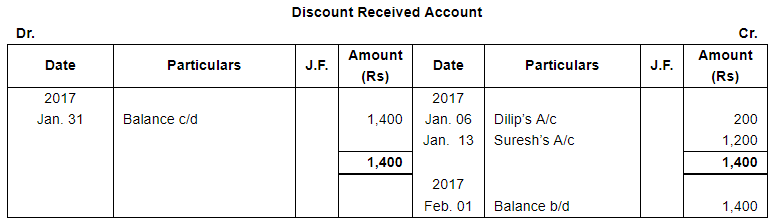
Page No 13.63:
Question 12:
Enter the following transactions in proper Subsidiary Books, post them into Ledger Accounts, balance the accounts and prepare a Trial Balance:
| 2017 | ||
| Jan. 1 | Assets : | Cash in hand ₹ 20,000; Debtors : Sri Gopal ₹ 15,000, Poonam & Co. ₹ 30,000; Stock ₹ 1,75,000, Machinery ₹ 1,20,000; Furniture ₹ 40,000. |
| Liabilities: | Bank Overdraft ₹ 33,000; Creditors : Niranjan Lal ₹ 24,000, Bombay Trading Co. ₹ 16,000. | |
| Jan. 2 | Purchased from Manohar Lal & Sons goods of the list price of ₹ 20,000 at 10% trade discount. | |
| 5 | Returned to Manohar Lal & sons goods of the list price of ₹ 2,000. | |
| 10 | Issued a Cheque to Manohar Lal & Sons in full settlement of their account. | |
| 12 | Sold to Sri Gopal, goods worth ₹ 25,000. | |
| 15 | Received Cash ₹ 10,000 and a Cheque for ₹ 8,000 from Sir Gopal. The Cheque was immediately sent to bank. | |
| 16 | Withdrew for personal use : Cash ₹ 5,000 and goods ₹ 3,000. | |
| 17 | Accepted a bill for 45 days drawn by Niranjan Lal for the amount due to him. | |
| 18 | Acceptance received from Poonam & Co. for the amount due from them payable after 30 days. | |
| 19 | Sold to Raghubir Brothers, goods valued ₹ 16,000. | |
| 20 | Cash purchases ₹ 15,000. | |
| 22 | Withdrew from bank fo office use ₹ 10,000. | |
| 23 | Purchased from Bombay Trading Co., goods valued ₹ 24,000. | |
| 24 | Sri Gopal returned goods worth ₹ 2,000. | |
| 25 | Received from Raghubir Brothers ₹ 10,000. | |
| 27 | Accepted a bill for ₹ 25,000 for 1 month drawn by Bombay Trading Co. | |
| 27 | Paid Rent by Cheque ₹ 2,800. | |
| Received Commission in Cash ₹ 800. | ||
| 31 | Paid salaries ₹ 5,000. |
ANSWER: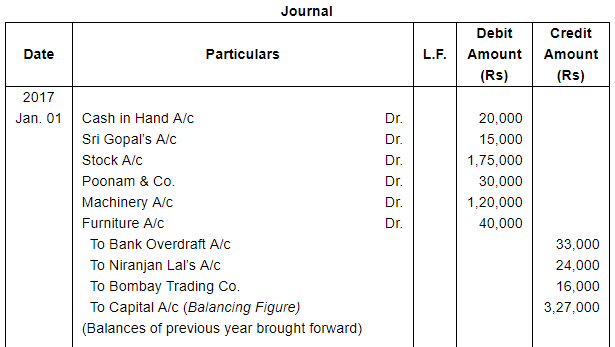
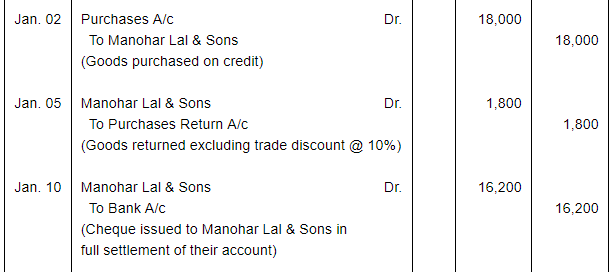
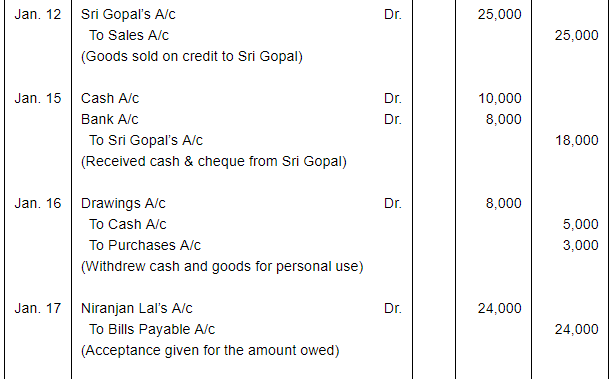
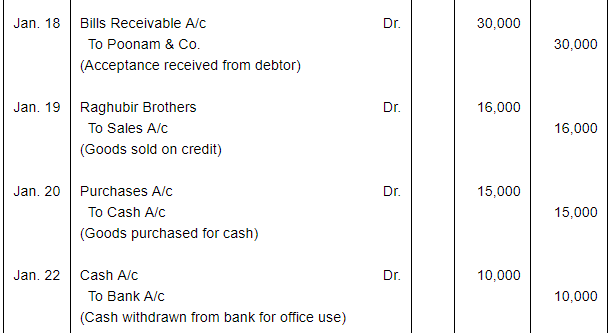

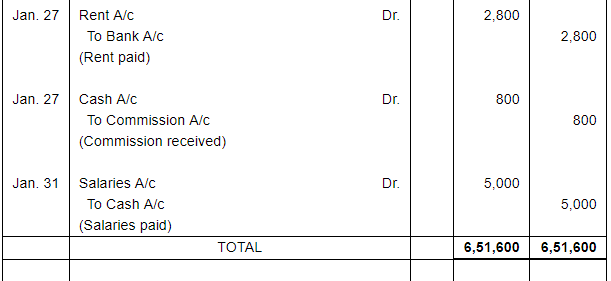
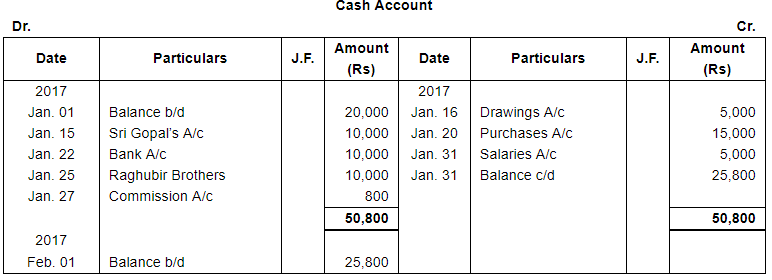
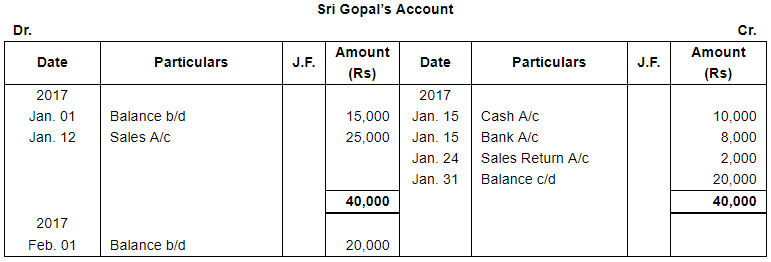
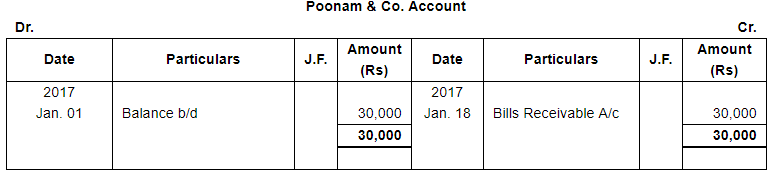
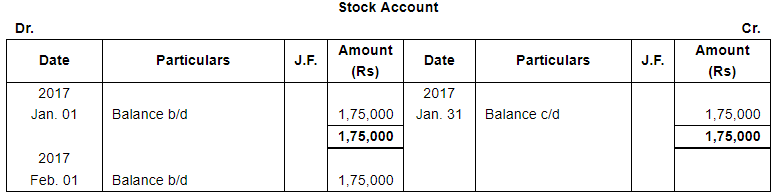
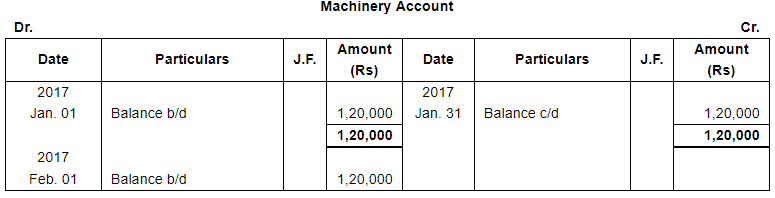
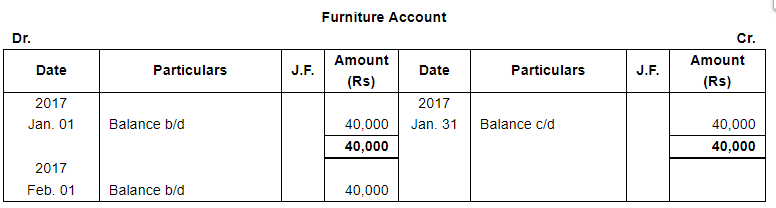
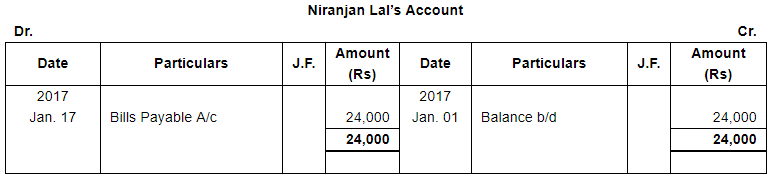
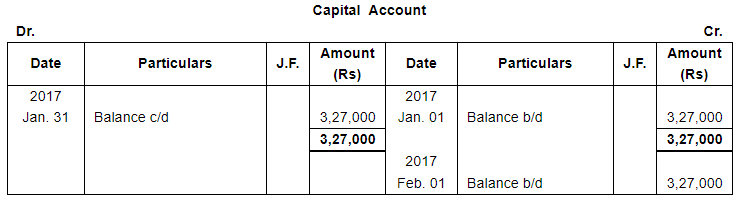
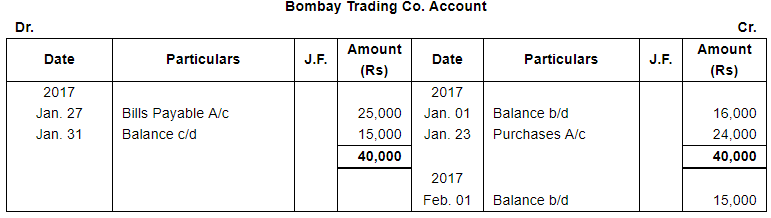
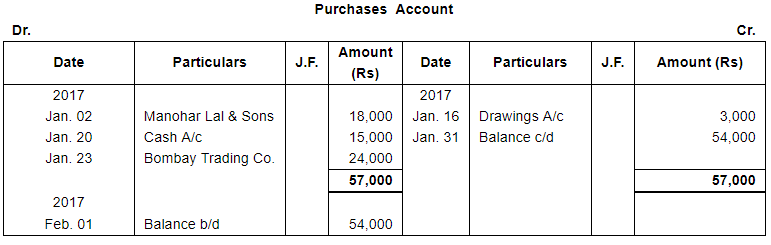
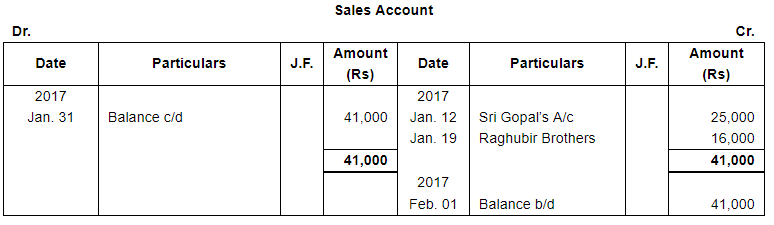
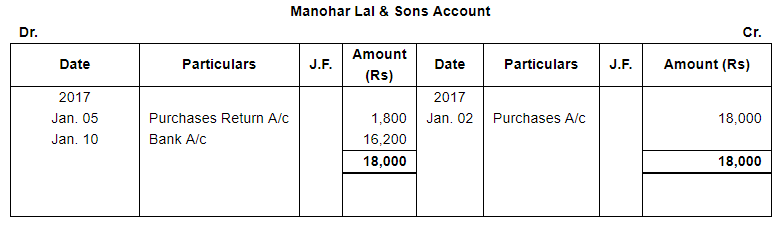
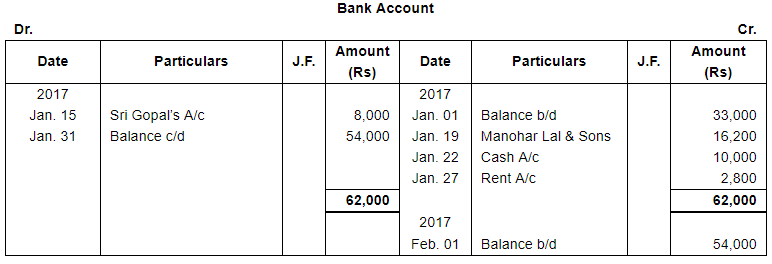
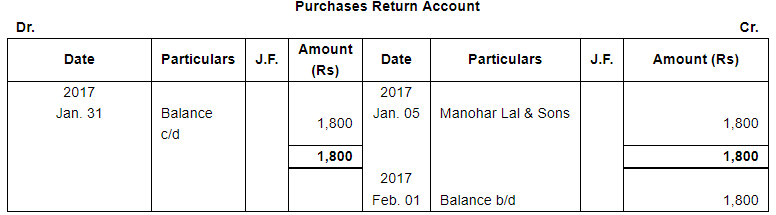
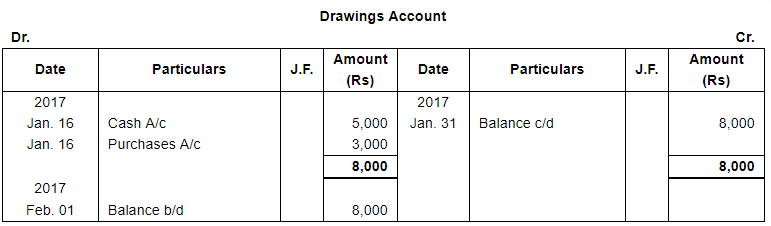
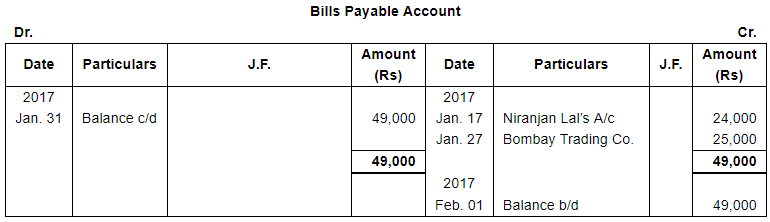
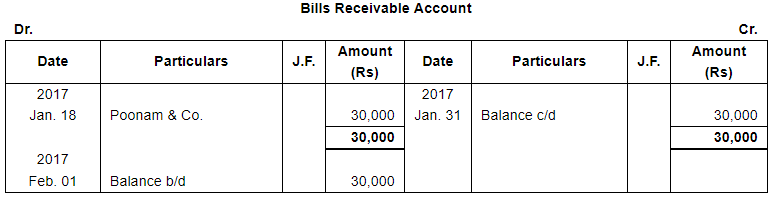
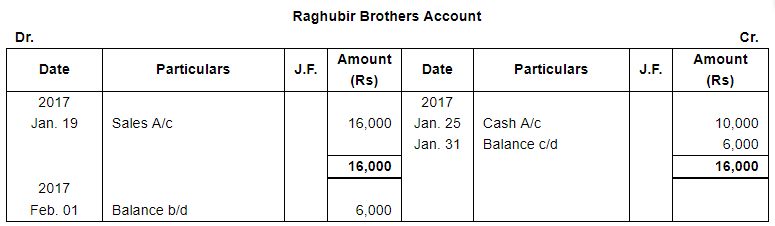
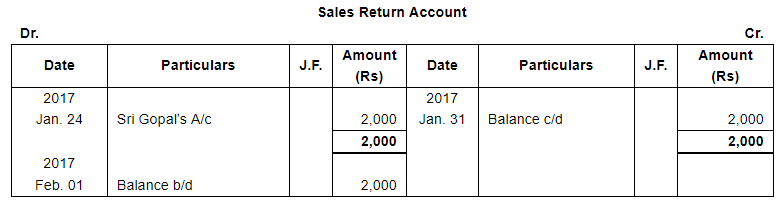
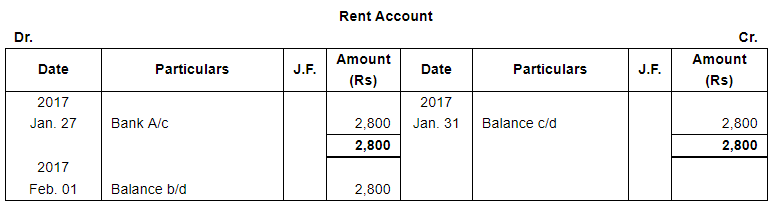
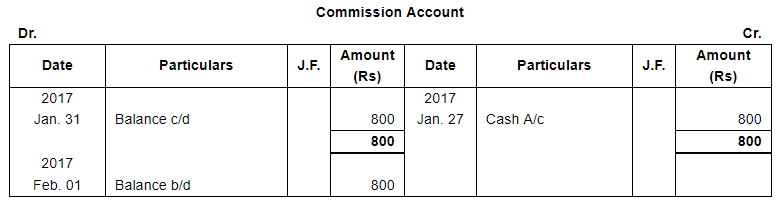
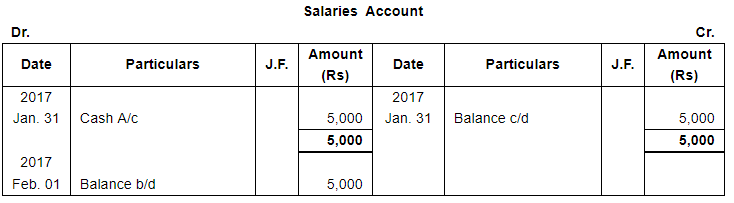
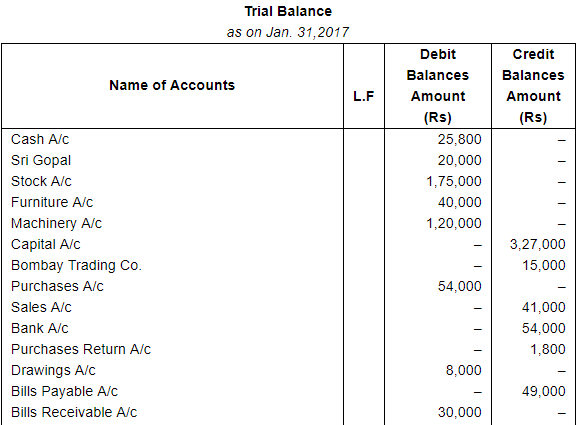

Note: Answer of Journal proper as per solution (Rs 6,51,600) is different from answer provided by the book (Rs 4,82,000)
FAQs on Ledger (Part - 3) - Commerce
| 1. What is a ledger in commerce? |  |
| 2. How is a ledger different from a journal in commerce? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of ledgers used in commerce? |  |
| 4. How does a ledger help in financial analysis? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of using a computerized ledger in commerce? |  |















