Class 12 Geography Short Questions with Answers- Water Resources
Q1: Define catchment area.
Ans: The area from which rainfall flows into a river, lake, or reservoir is known as a catchment area.
Q2: Define a lagoon.
Ans: A lagoon is a shallow body of water that is separated from the sea by:
- Barrier islands
- Reefs
These features help create a calm environment, making lagoons important for various ecological and economic activities.
Q3: Define groundwater.
Ans: Groundwater is the water that is stored beneath the Earth's surface. It is found in:
- Soil - Water held in the spaces between soil particles.
- Pores - Water located in the small openings within rocks.
- Crevices - Water trapped in cracks and fissures in rock formations.
This vital resource plays a crucial role in supporting ecosystems, agriculture, and drinking water supplies.
Q4: India accounts for how much of the world’s water resource?
Ans: India accounts for 4 per cent of the world's water resources.
Q5: Name any two major sources of water resources.
Ans: Major sources of water resources include:
- Rivers
- Lakes
- Ponds
- Tanks
Q6: Water flow in the river depends on what basic factor?
Ans: Water flow in a river is influenced by several key factors:
- The size of its catchment area or river basin.
- The amount of rainfall within that catchment area.
These elements determine how much water can flow through the river, affecting its overall health and sustainability.
Q7: Name any two rivers which have huge catchment areas.
Ans: Ganga and Brahmaputra are two rivers with significant catchment areas.
- The Ganga River has a vast catchment area that supports extensive water resources.
- The Brahmaputra River also boasts a large catchment, contributing to its substantial flow.
Q8: Name the states where the groundwater utilisation is very high. OR Mention any two states where groundwater level utilisation is very high.
Ans: The states with very high groundwater utilisation include:
- Punjab
- Haryana
- Rajasthan
- Tamil Nadu
Q9: Name the states which utilise very small proportion of their groundwater potentials.
Ans: States that utilise a very small proportion of their groundwater potentials include:
- Chhattisgarh
- Odisha
- Kerala
Q10: What is the percentage of Earth covered with water?
Ans: Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered with water.
Q11: Which sector grounds for most of the surface and groundwater utilisation?
Ans: Agriculture is the primary sector responsible for the majority of surface and groundwater utilisation in India.
- It accounts for 89% of surface water use.
- It also represents 92% of groundwater utilisation.
- The industrial sector uses only 2% of surface water and 5% of groundwater.
- Domestic use is higher in surface water at 9% compared to groundwater.
- Agriculture's share in total water use is significantly greater than that of other sectors.
- Future developments may increase the shares of the industrial and domestic sectors.
Q12: Explain the importance of irrigation for agriculture in India.
Ans: Importance of irrigation:
- Control of drought and famines: Unpredictable rainfall can lead to droughts, especially when the monsoon is delayed or ends early. Irrigation helps manage these risks effectively.
- Higher productivity: Irrigated land produces significantly more than unirrigated land, boosting overall agricultural output.
- Multiple cropping: With irrigation, farmers can grow two or three crops each year, greatly increasing production and productivity.
- Support for agricultural strategies: The success of the High Yielding Programme relies heavily on expanded irrigation facilities, contributing to increased agricultural production.
Q13: Study the given diagram and answer the questions that follow:
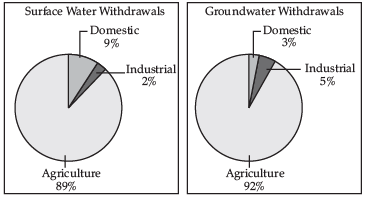
Ans: The agricultural sector is the largest user of water in India, as the country relies heavily on agriculture. 2: Many regions lack access to underground water, which limits irrigation options.
Q14: What factors are responsible for the highest groundwater development in the states of Punjab, Haryana and Tamil Nadu?
Ans: The high groundwater development in Punjab, Haryana, and Tamil Nadu is due to several factors:
- Advanced agriculture: These states are known for their developed agricultural practices.
- Irrigation needs: Water is primarily used for irrigation, which is crucial due to the variability in rainfall.
- Drought-prone areas: Many regions face deficient rainfall, necessitating a reliable irrigation system.
- High-yield crops: The cultivation of high-yield varieties requires consistent moisture, supported by developed irrigation.
Q15: Why has development of irrigation assigned a very high priority in the Five Year Plans?
Ans: About two-thirds of India's population relies on agriculture. Therefore, the development of irrigation is crucial for:
- Increasing agricultural production.
- Ensuring reliable water supply for crops.
- Facilitating multiple cropping opportunities.
- Enhancing productivity on irrigated lands compared to unirrigated ones.
Moreover, high-yielding crop varieties require consistent moisture, which can only be provided through effective irrigation systems. This focus on irrigation has significantly contributed to the success of the Green Revolution in regions like Punjab, Haryana, and western Uttar Pradesh.
Q16: Name any two multipurpose river valley projects.
Ans: Multipurpose river valley projects are essential for managing water resources in India. Here are two notable examples:
- Bhakra-Nangal Project
- Hirakud Dam
Other significant projects include:
- Damodar Valley
- Nagarjuna Sagar
- Indira Gandhi Canal Project
Q17: What accounts for most surface and groundwater utilisation?
Ans: Agriculture is the primary driver of surface and groundwater use in India.
- It accounts for 89% of surface water utilisation.
- It also represents 92% of groundwater utilisation.
- The industrial sector uses only 2% of surface water and 5% of groundwater.
- Domestic use is higher in surface water at 9% compared to groundwater.
- As development progresses, the shares of the industrial and domestic sectors are expected to rise.
Water is mainly used for irrigation in agriculture, necessary due to varying rainfall patterns across the country.
Q18: Why is irrigation needed in our country?
Ans: Irrigation is essential in our country due to the uneven distribution of rainfall.
- Many regions experience drought and insufficient rainfall.
- Dry seasons make it challenging to grow crops without reliable irrigation.
- High water-demand crops like rice, sugarcane, and jute require consistent moisture.
- Irrigation enables multiple cropping, increasing agricultural productivity.
- Irrigated lands yield better results compared to unirrigated areas.
Overall, irrigation is crucial for ensuring food security and agricultural success across diverse climates.
Q19: What has intensive irrigation in Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh resulted into?
Ans: Intensive irrigation in Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh has led to significant environmental issues:
- Increased salinity in the soil, which affects crop growth.
- Depletion of groundwater, reducing the availability of water for irrigation.
These factors can negatively impact agricultural productivity and sustainability in the region.
Q20. What are the implications of using groundwater resources water in drought prone area of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu?
Ans: The overuse of groundwater resources in drought-prone areas like Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu has significant implications:
- Increased fluoride concentration in groundwater.
- Decline in the groundwater table due to excessive extraction.
- Potential rise in arsenic levels in certain regions, such as West Bengal and Bihar.
- Overall depletion of groundwater resources, threatening future water availability.
Q21: Which state makes use of highest percentage of tubewell water? [Old NCERT]
Ans: Gujarat utilises the highest percentage of tubewell water in India, with an impressive 86.6% of its total water supply coming from this source.
Q22: Why is irrigation required? Give one reason.
Ans: Irrigation is essential due to the inconsistent rainfall across the country.
- Many regions experience drought or insufficient rainfall.
- Dry seasons make it challenging to grow crops without reliable water supply.
- Crops like rice and sugarcane require a lot of water, which can only be provided through irrigation.
Q23: Why the share of agriculture sector in total water used in the country is expected to decline?
Ans: The share of the agricultural sector in total water usage is expected to decline due to several factors:
- Other sectors, particularly industry, are growing rapidly.
- Water consumption in these sectors is likely to increase.
- As industries expand, they will require more water, reducing agriculture's share.
Overall, the shift in water demand from agriculture to other sectors reflects broader economic development.
Q24: Study the data of percentage of net irrigated area to total by wells and tube-wells given below and answer the questions:
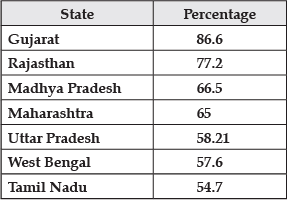
Ans:Gujarat has seen a significant decline in its groundwater resources due to over-extraction. This situation is evident in several states:
- Over-use of groundwater has led to a drop in the groundwater table.
- States like Rajasthan and Maharashtra have reported increased fluoride levels in their groundwater.
- This excessive withdrawal has also raised arsenic concentrations in regions of West Bengal and Bihar.
Q25: Mention any two sources of water pollutants created by humans. OR Mention any two sources of water pollution in India. OR Name any two natural sources of water pollutants.
Ans: Sources of water pollutants created by humans:
- Sewage disposal - Wastewater from households and industries.
- Urban run-off - Rainwater that collects pollutants from streets and buildings.
- Toxic effluents - Harmful chemicals released by industries.
- Run-off from cultivated lands - Fertilisers and pesticides washed into water bodies.
Q26: Name any two natural sources of water pollutants. [Old NCERT]
Ans: Natural sources of water pollutants include:
- Erosion: This process can wash away soil and debris into water bodies, leading to contamination.
- Landslides: When landslides occur, they can introduce sediments and pollutants into nearby water sources.
Q27: Why is the per capita availability of water dwindling day by day?
Ans: The per capita availability of water is decreasing due to several key factors:
- Population Growth: The increasing population leads to higher demand for water.
- Pollution: Water sources are becoming contaminated by industrial, agricultural, and domestic waste, reducing the amount of clean water available.
- Overuse: Excessive extraction of water from rivers and aquifers further limits supply.
These factors combined contribute to the ongoing decline in the availability of usable water resources.
Q28: What does water quality refer to?
Ans: Water quality refers to the purity of water and its suitability for various uses. It is determined by the presence of unwanted substances, which can include:
- Micro-organisms that can cause diseases.
- Chemicals from industrial processes.
- Pollutants from agricultural runoff.
When these substances contaminate water, they can:
- Make it unsafe for drinking.
- Affect aquatic life.
- Pollute groundwater sources.
Maintaining good water quality is essential for health and the environment.
Q29: How do the toxic substances pollute the water?
Ans: Toxic substances pollute water bodies through various means:
- They enter lakes, streams, rivers, and oceans.
- These substances can either dissolve in water or remain suspended.
- This process leads to water pollution, degrading its quality.
- Polluted water affects aquatic life and can seep into groundwater.
Q30. Mention any two uses of river water in the plains.
Ans: River water serves several essential purposes in the plains:
- Irrigation: It is primarily used to irrigate crops, ensuring adequate water supply for agricultural activities.
- Drinking: River water is a vital source of drinking water for local communities.
- Domestic Use: It is used for various household needs, including cleaning and cooking.
- Industrial Purposes: Industries rely on river water for processes and cooling.
Q31: Name the two boards that have been monitoring the water quality of national aquatic resources.
Ans: The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Boards are responsible for monitoring the water quality of national aquatic resources.
Q32: Mention any two cultural activities that are responsible for water pollution in India.
Ans:
- The cultural activities responsible for water pollution include:
- Pilgrimage and religious fairs held near riverbanks.
- Dispersal of idols, ashes, and dead bodies.
Q33: Mention two highly polluted rivers in India.
Ans: Highly polluted rivers in India include:
- Ganga - Known for severe pollution, especially in areas like Kanpur and Varanasi.
- Yamuna - The most polluted river in India, particularly between Delhi and Etawah.
Q34: Which is the most significant contributor of water pollution in India?
Ans: The most significant contributor to water pollution in India is untreated sewage.
Q35: Mention any two sources of water pollution by human beings in India.
Ans: The two main sources of water pollution caused by human activities in India are:
- Urban sources: This includes polluted water and sewage, along with municipal and domestic waste, which are often dumped into water bodies.
- Industrial effluents: Factories frequently discharge harmful waste into rivers, leading to severe degradation and toxicity of the water.
Q36: Name any two water conservation techniques adopted in India.
Ans: Two water conservation techniques are:
- Rainwater harvesting: This technique captures and stores rainwater for various uses, helping to recharge groundwater. It is cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
- Watershed development: This involves managing and conserving water resources in a specific area to improve water availability sustainably. It relies on community participation for success.
Q37: “The assessment, efficient use and conservation of water are necessary to ensure development.” Explain in the light of values regarding conservation of water resources.
Ans: Conservation of water resources is essential for several reasons:
- India has about 16% of the world’s population but only 4% of its water resources.
- The total utilisable water resources in India are very limited.
- Population growth is rapid, leading to an increasing demand for water.
- Pollution is rendering many water sources unusable.
To effectively conserve water, we need to embrace human values such as:
- Responsibility
- Awareness
- Cooperation
- Active citizenship
These values are crucial for the sustainable management of our water resources.
Q38: Explain with examples, how the industries are responsible for polluting water resources in India.
Ans: The dumping of industrial waste into rivers is a major cause of water pollution in India. Key points include:
- Industries produce ordinary domestic sewage, which can be treated by municipal facilities.
- However, industries generating wastewater with high concentrations of pollutants (e.g., oil, grease, heavy metals) significantly contribute to pollution.
- When these substances enter water resources, they degrade water quality, making it unsafe for human use.
- This limits the availability of clean water for communities.
- Many industries fail to follow regulations, allowing untreated wastewater to flow into rivers.
- For example, the Yamuna River is the most polluted river in India, particularly between Delhi and Etawah, due to industrial discharges.
Overall, industrial practices are a primary factor in the ongoing water pollution crisis in India.
Q39: Examine any three causes for the deterioration of ‘quality of water’ in India.
Ans:
- Urbanisation and industrialisation produce large amounts of waste, which contaminate water sources.
- Excessive use of pesticides in agriculture leads to chemical runoff, polluting nearby water bodies.
- Many rivers receive millions of litres of sewage and industrial waste, significantly degrading water quality.
Q40. Why is conservation of water resources necessary? Explain any three reasons.
Ans: Conservation of water resources is crucial for several reasons:
- Essential for life: Water is vital for all living beings. Without it, humans, plants, and animals cannot survive.
- Decreasing groundwater: Groundwater levels are dropping, leading to a shortage of clean drinking water.
- Wildlife dependence: Wildlife relies on nearby water sources, which may be polluted. This pollution can harm both wildlife and human health.
By conserving water, we can ensure that our watersheds remain healthy and can support both wildlife and human needs.
Q41: Describe any three major problems related to water in India.
Ans: Major problems related to water in India include:
- Water scarcity: The demand for water is primarily from agriculture (90%), with industry (5-6%) and domestic use making up the rest. As the economy and population grow, the demand from domestic and industrial sources is expected to rise.
- Depletion of groundwater: Groundwater supplies nearly 50% of irrigation and most rural domestic needs. When extraction exceeds replenishment, aquifers become depleted.
- Water pollution: This is a serious issue, with over 70% of surface water and many groundwater sources contaminated by toxic biological, organic, and inorganic waste.
Q42: What can be possible impacts of consumption of contaminated/unclean water on the people?
Ans: Impacts of consumption of contaminated/unclean water on the people:
- Water-borne diseases are primarily spread through contaminated water. In India, approximately 80% of stomach diseases are linked to unclean water.
- Most intestinal diseases arise from consuming contaminated water.
- Consuming unclean water can lead to serious illnesses such as hepatitis, cholera, dysentery, and typhoid.
Q43: How can we conserve water resources?
Ans:
- Recycling and reusing water can greatly enhance its availability.
- Implementing rainwater harvesting helps meet water needs.
- Utilising drip irrigation and sprinkler systems optimises water use in agriculture.
- In urban areas, water from bathing and washing dishes can be repurposed for gardening.
Detailed Answer
Q44: ‘Indiscriminate use of water by increasing population and industrial expansion has led to degradation of the quality of water considerably.’ Evaluate the statement.Ans: Increasing population and industrial expansion are responsible for water pollution:
- Untreated domestic and sewage waste: Rapid urban expansion has led to poor waste disposal, allowing untreated waste to contaminate water resources.
- Excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides: These agricultural chemicals can leach into water bodies, causing significant pollution. Adopting environmentally friendly practices is essential.
- Cultural activities: Events like fairs and pilgrimages contribute to water pollution by introducing various pollutants into water sources.
- Industrial waste: Factories release toxic substances that adversely affect nearby water bodies. Emissions and waste can introduce harmful chemicals into the water.
- Chemical residues: Contaminants from fossil fuels can lead to dangerous levels of lead in water, posing risks to both marine life and human health.
- Major polluting industries: Industries such as leather, pulp, paper, textiles, and chemicals significantly increase pollution levels, often raising water temperatures and promoting bacterial growth.
Q45: Define the term ‘watershed management.’
Ans: Watershed management refers to the careful handling of land and water resources within a watershed. Its main goals include:
- Conservation of surface and groundwater resources.
- Preventing runoff and promoting the storage and recharge of groundwater.
- Regulating the use of natural resources, such as land, water, and plants.
- Encouraging community participation in sustainable practices.
This approach aims to balance the needs of the environment and society while ensuring the availability of water resources.
Q46: Define rainwater harvesting.
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is a method used to capture and store rainwater for various purposes. It can also help recharge groundwater aquifers.
- It is a cost-effective and eco-friendly technique.
- Helps preserve every drop of water by directing it to borewells, pits, and wells.
- Increases water availability and combats the declining groundwater table.
- Improves groundwater quality by diluting contaminants such as fluoride and nitrates.
- Prevents soil erosion and flooding.
- Can stop saltwater intrusion in coastal areas when used for aquifer recharge.
Various communities have practised rainwater harvesting for a long time, using methods like:
- Surface storage bodies, such as lakes and ponds.
- In Rajasthan, structures known as Kund or Tanka (covered underground tanks) are built to store rainwater.
There is significant potential for rainwater harvesting to conserve water resources:
- Can be implemented on rooftops and open spaces.
- Reduces community reliance on groundwater for domestic use.
- Helps bridge the demand-supply gap and saves energy needed for pumping groundwater.
Urban areas particularly benefit from rainwater harvesting due to high water demand. However, awareness of its benefits is still limited, and many programmes are in the early stages of development.
Q47: What determines the success of watershed development?
Ans: Community participation is crucial for the success of watershed development.
- It encourages local involvement and ownership of projects.
- Active participation leads to better decision-making and resource management.
- Community-led initiatives often result in sustainable practices.
Government programmes at both the Central and State levels support these efforts, often in collaboration with non-governmental organisations.
Q48: What do you know about Haryali?
Ans: Haryali is a watershed development project initiated by the Central Government aimed at helping rural communities manage their water resources effectively. Its key objectives include:
- Conserving water for drinking, irrigation, fisheries, and afforestation.
- Encouraging community participation through local governance by Gram Panchayats.
- Promoting sustainable practices to enhance water availability.
This project plays a vital role in improving the livelihoods of rural populations by ensuring access to essential water resources.
Q49: What projects have been taken up by Neeru-Meeru and Arvary Pani Sansad?
Ans: Neeru-Meeru and Arvary Pani Sansad have initiated various projects focused on water conservation. Their efforts include:
- Construction of percolation tanks
- Development of dug-out ponds (Johads)
- Building check dams
These projects are carried out with active community participation.
Q50. What does watershed management include?
Ans: Watershed management involves the careful handling of resources within a watershed. It includes:
- Conservation of natural resources like land, water, and biodiversity.
- Regeneration of ecosystems to restore their health and productivity.
- Judicious use of both natural and human resources to ensure sustainability.
This approach aims to balance the needs of the environment with those of the community.
Q51: How can the quality of water be improved?
Ans: Quality of water can be improved by:
- Judicious use of water resources.
- Creating awareness about the importance of water.
Q52: Who sponsored Hariyali programme?
Ans: The Hariyali programme is a watershed development project. It is sponsored by the Central Government of India. The main goals of this programme include:
- Enabling rural communities to conserve water for various uses such as drinking, irrigation, and fisheries.
- Promoting afforestation efforts.
- Encouraging participation from local Gram Panchayats and the community.
Q53: What is the local name of rainwater harvesting structure in Rajasthan?
Ans: Kund and Tanka are the local names for rainwater harvesting structures in Rajasthan. These are:
- Kund: A traditional structure for collecting rainwater.
- Tanka: A covered underground tank designed to store rainwater.
These systems help conserve water and reduce reliance on groundwater.
Q54: Explain watershed management. What is its aim? OR What is watershed management ? Do you think it can play an important role in sustainable development ?
Ans: Watershed management involves the careful management and conservation of both surface and groundwater resources. Its key components include:
- Preventing runoff and enhancing water storage.
- Recharging groundwater through methods such as percolation tanks and recharge wells.
- Conserving and judiciously using natural resources like land, water, plants, and animals.
The main aim of watershed management is to achieve a balance between natural resources and human needs. This approach is crucial for:
- Ensuring sustainable water availability.
- Supporting environmental health and economic stability.
- Encouraging community participation in conservation efforts.
Effective watershed management can significantly contribute to sustainable development by promoting responsible resource use and enhancing ecosystem resilience.
Q55: Define the term ‘Rainwater Harvesting’. Mention any four advantages of rainwater harvesting.
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is the practice of collecting and storing rainwater for reuse, rather than letting it flow away. This method can also help recharge groundwater supplies. The four advantages of rainwater harvesting include:
- Cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to save water.
- Increases water availability and helps maintain groundwater levels.
- Reduces soil erosion and the risk of flooding.
- Can save energy by reducing the need to pump groundwater.
Detailed Answer
Q56: What values can help us in maintaining the quality of water?Ans: The values that can help in maintaining the quality of water include:
- Judicious use of water
- Controlling population
- Recycle and reuse of water
- Watershed management
- Rainwater harvesting
- Rules and regulations
Recycle and reuse of water: Improving the availability of fresh water can be achieved through recycling and reusing water. Industries can use lower quality water, such as reclaimed wastewater, for cooling and fire fighting, which helps reduce costs. In urban areas, water from bathing and washing dishes can be reused for gardening, conserving higher quality water for drinking. Watershed management: This involves the effective management and conservation of surface and groundwater resources. It includes preventing runoff and storing water through methods like percolation tanks and recharge wells. Watershed management aims to conserve and judiciously use all resources—natural and human—within a watershed. Rainwater harvesting: This technique captures and stores rainwater for various uses, including recharging groundwater aquifers. It is a cost-effective and eco-friendly method that helps preserve water by directing rainwater to bore wells and pits. This practice increases water availability, improves groundwater quality, prevents soil erosion, and reduces flooding.
Q57: What are the aims of rainwater harvesting?
Ans:
- Increase water availability.
- Check the declining groundwater table.
- Improve groundwater quality by diluting contaminants, such as fluoride and nitrate.
- Prevent soil erosion and flooding.
- Reduce community dependence on groundwater for domestic use.
|
50 videos|273 docs|37 tests
|
FAQs on Class 12 Geography Short Questions with Answers- Water Resources
| 1. What are the main sources of water resources? |  |
| 2. How are water resources managed? |  |
| 3. What are the effects of water scarcity? |  |
| 4. What are the factors contributing to water pollution? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to water resource conservation? |  |






















