Bills of Exchange (Part - 2) - Commerce PDF Download
Page No 18.60:
Question 12:
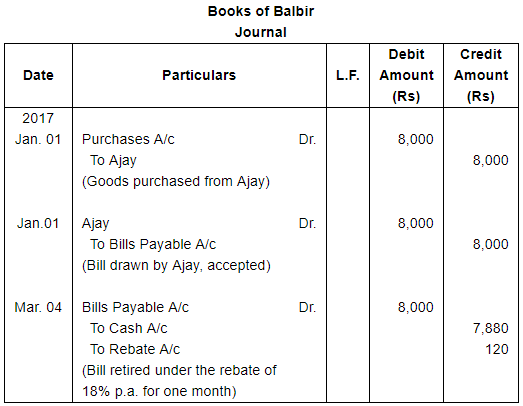
On January 1, 2017, Ajay sold goods to Balbir for ₹ 10,000 at a discount of 20%. On that date, Balbir accepted a bill, drawn on him by Ajay for ₹ 8,000 payable 3 months after sight. Having surplus funds, Balbir paid off the bill on 4th March, 2017 and was allowed a rebate of 18% per annum. Show Journal entries in the books of Ajay and Balbir.
ANSWER: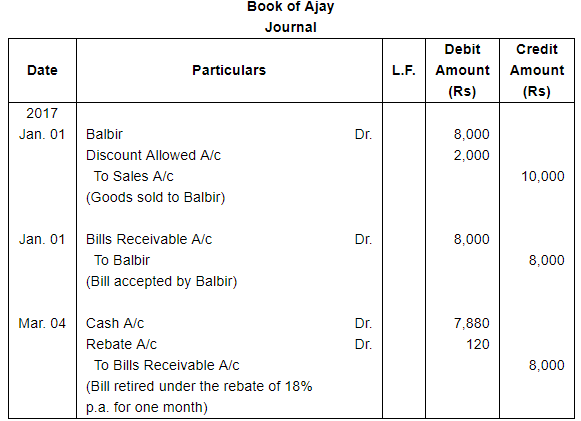
Working Note: Calculation of amount of Rebate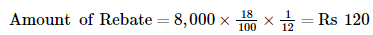
Question 13:
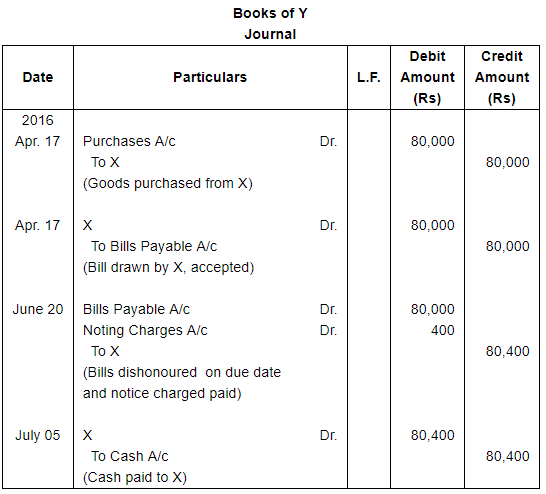
On 17th April, 2016, X sold goods to Y for ₹ 80,000 and draws a bill for 2 months upon Y for the amount due. Y accepted the bill and returned it to X. On due date the bill became dishonoured and X paid ₹ 400 as Noting Charges. Fifteen days later Y pays the amount due to X. Pass Journal entries in the books of both the parties.
ANSWER: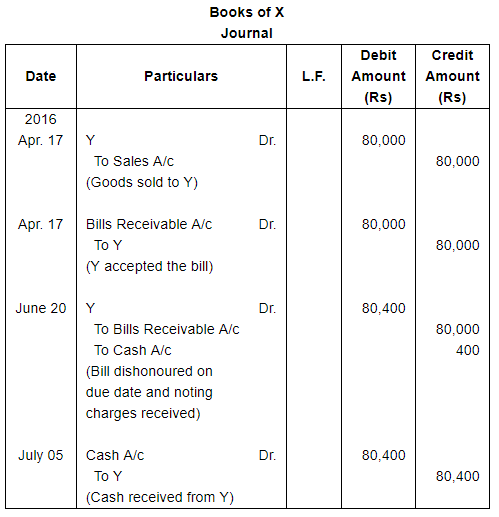
Page No 18.61:
Question 14(A):
On 1st April, 2016, B accepts a bill drawn by A at three months for ₹ 8,000 in payment of debt. On the due date the acceptance is dishonoured and A gets the bill noted paying ₹ 100. On 4th July, 2016 A draws a new bill payable after 73 days provided interest is paid in cash @ 15% p.a. To this B is agreeable. The bill is met on maturity.
Record these transactions in the Journal of both the parties.
ANSWER: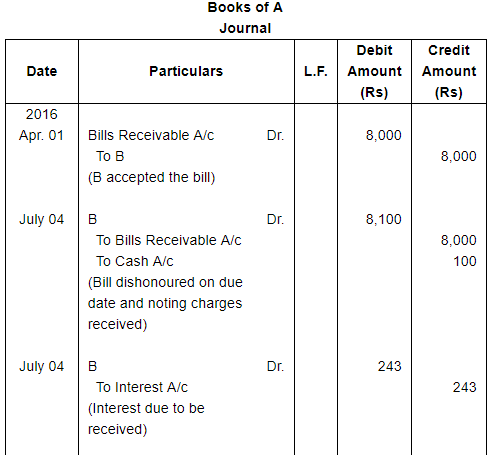
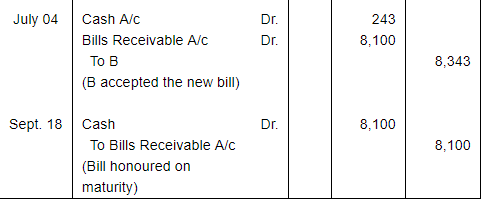
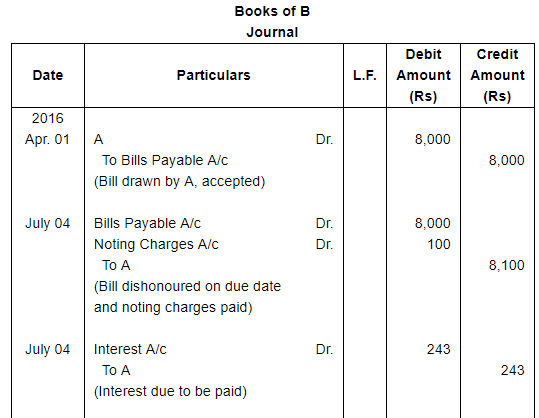
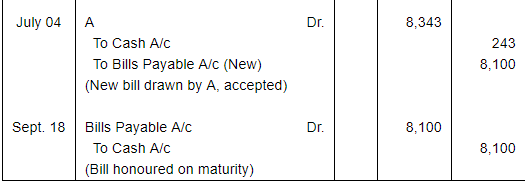
Working Note: Calculation of amount of Interest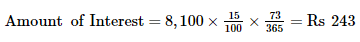
Question 14(B):
On 15th October, 2016, Y purchased goods worth ₹ 75,000 from X, and accepted a three months bill for this amount drawn by X. On the due date, it was dishonoured. Noting charges paid by X ₹ 600. On 18th January, 2017, Y requested X for renewal of the bill for another two months, for which X agrees, provided that interest is paid @ 15% p.a. in cash. Make Journal entries of these transactions in the books of X and Y.
ANSWER: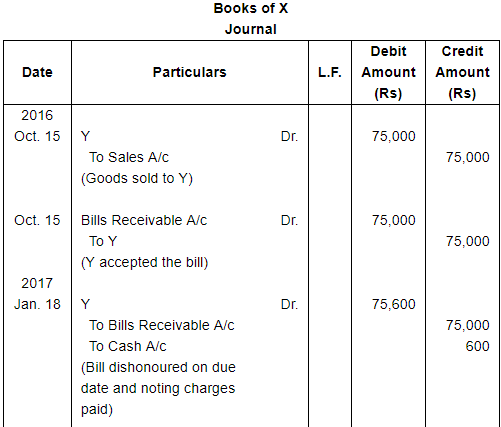
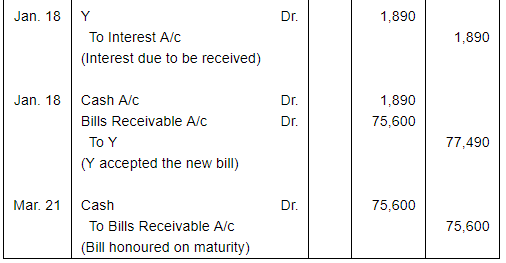
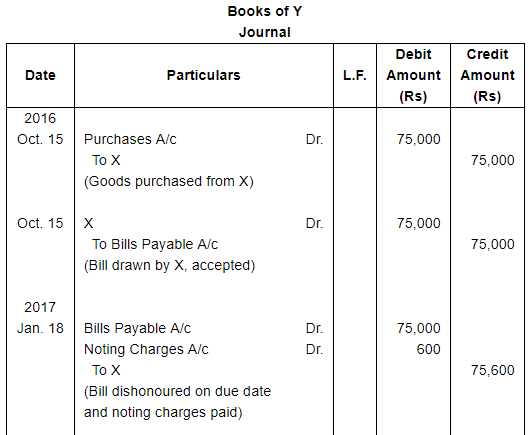
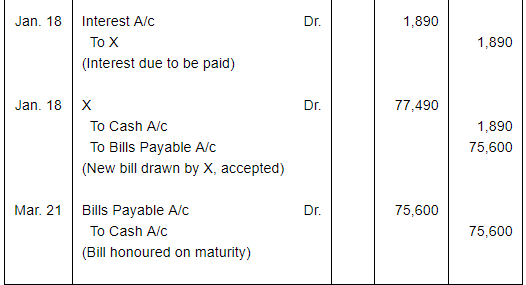
Working Note:Calculation of amount of Interest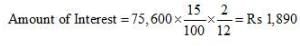
Question 15:
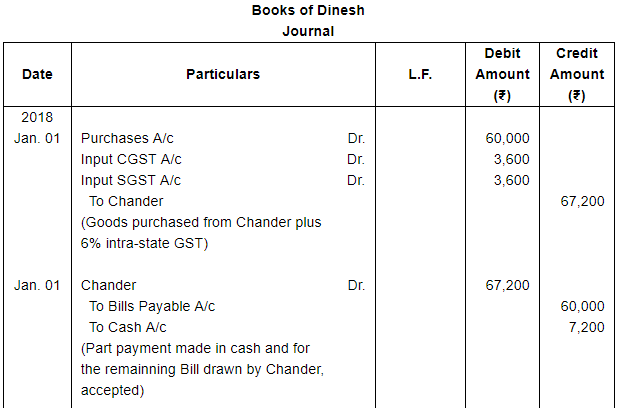
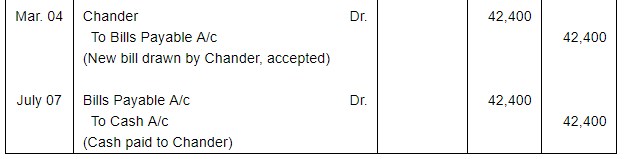
On 1st January, 2018, Dinesh purchased goods from Chander for ₹ 60,000 plus CGST and SGST @ 6% each. Dinesh pays ₹ 7,200 in cash and accepts a bill drawn by Chander for the balance amount payable after two months. On the due date Dinesh is able to manage ₹ 20,000 in cash and he arranges with Chander for the retirement of the bill in consideration of this payment and a fresh bill at four months for the balance plus interest at 18% per annum. The second bill is duly met on maturity.
make the necessary Journal entries in the books of Chander and Dinesh.
ANSWER: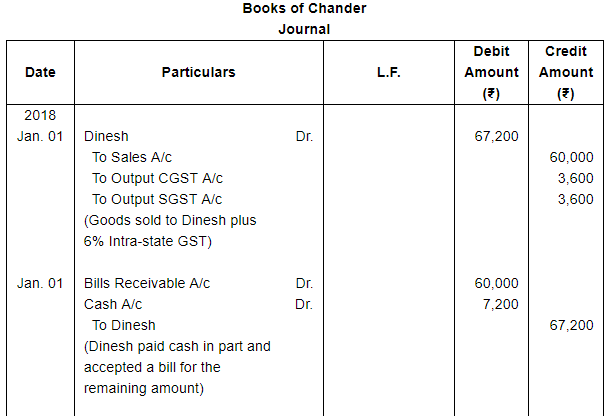
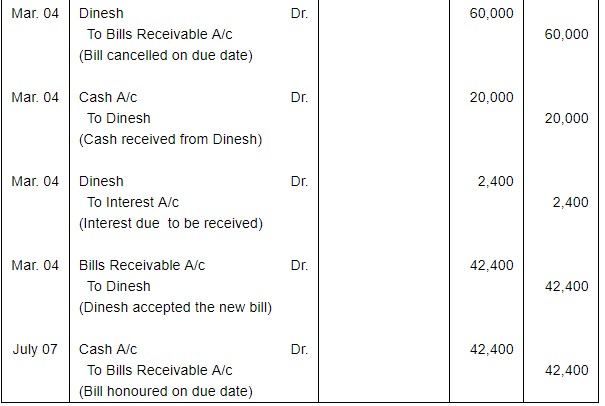

Working Note: Calculation of amount of Interest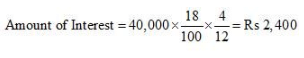
Question 16:
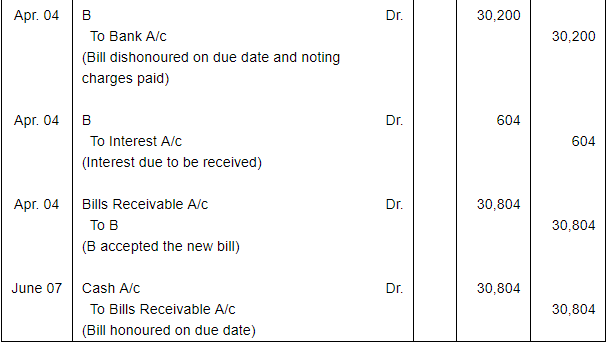
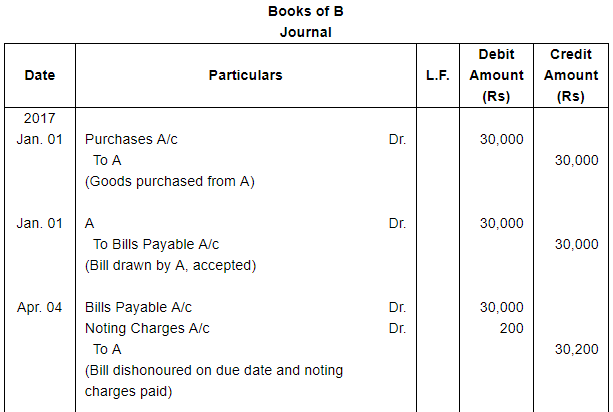
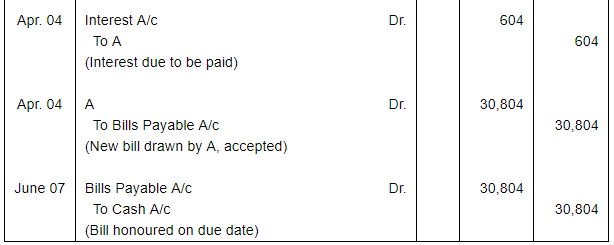
A sells goods for ₹ 30,000 to B on 1st January, 2017 and on the same day draws a bill on B at three months for the amount. B accepts it and returns it to A, who discounts it on 4th February, 2017 with his bank at 18% per annum. The acceptance is dishonoured on the due date, the noting charges paid by the bank being ₹ 200.
On 4th April, 2017, B accepts a new bill at two months for the amount then due to A together with interest at 12 per cent per annum.
Make Journal entries to record these transactions in the books of A and B.
ANSWER: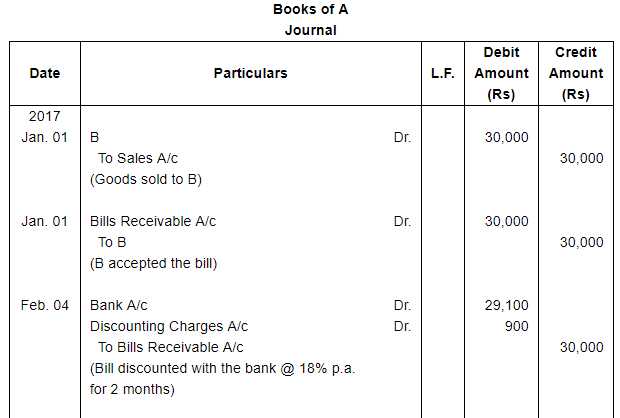
Working Note: WN1 Calculation of Discounting Charges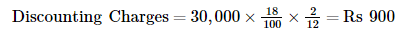
WN2 Calculation of amount of Interest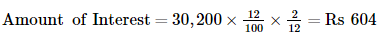
Question 17:
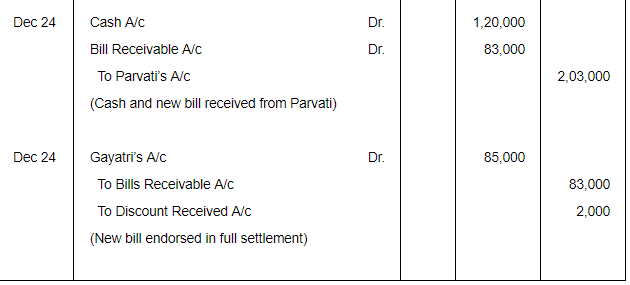
On 21st Sept. 2017, Radhika sold goods for ₹ 2,00,000 to Parvati and drew upon later a bill for the same amount payable after 3 months. The bill was accepted by Parvati, Radhika discounted the bill from bank at a discount of 15% p.a. on 21st Oct., 2017. On maturity, the bill was dishonoured. Parvati agreed to pay ₹ 1,20,000 in cash including ₹ 3,000 interest and accepted a new bill for 3 months. The new bill was endorsed to Gayatri in full settlement of his account ₹ 85,000. It was duly met on maturity. Pass entries in the books of Radhika.
ANSWER: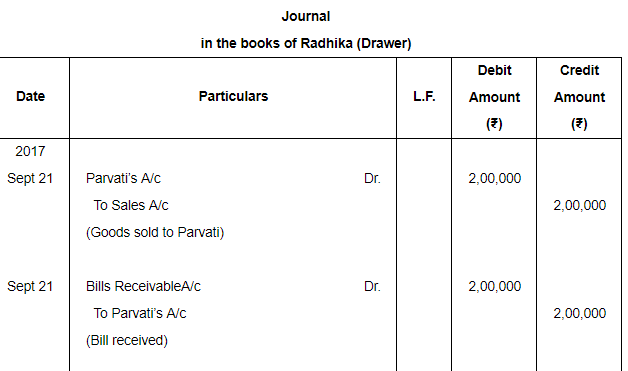
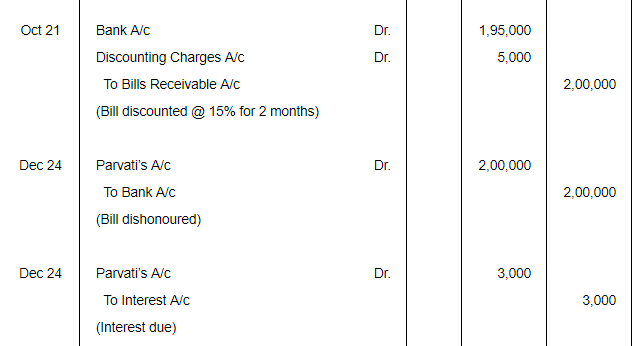
Page No 18.62:
Question 18:
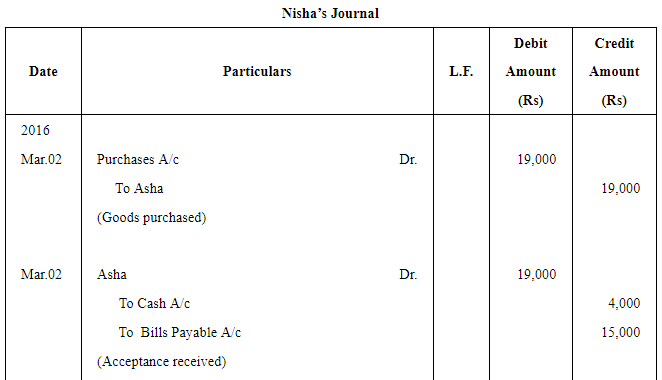
Asha sold goods worth ₹ 19,000 to Nisha on March 2, 2016. ₹ 4,000 were paid by Nisha immediately and for the balance she accepted a bill of exchange drawn upon her by Asha payable after three months. Asha discounted the bill immediately with her bank @ 10% p.a. On the due date Nisha dishonoured the bill and the bank paid ₹ 30 as noting charges.
On 5th June, Nisha paid ₹ 3,030 (including noting charges) in cash and accepted a new bill at one month for the amount due to Asha together with interest @ 15% p.a.
Record the necessary journal entries in the books of Asha and Nisha.
ANSWER: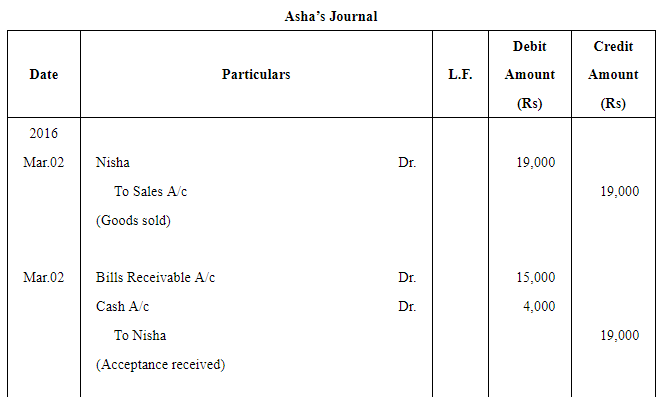
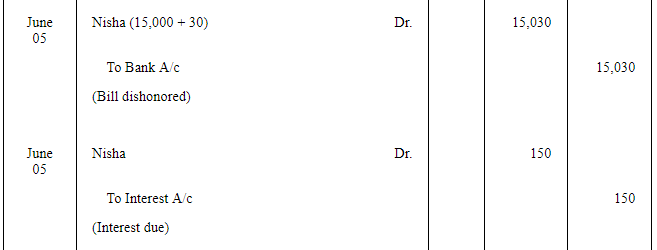



 Question 19:
Question 19:
A sold goods for ₹ 40,000 to B on Jan. 01, 2017. He drew upon B a bill of exchange for the same amount payable after 1 month. B accepted the bill and sent it back to A. A discounted the bill immediately with his bank @ 9% p.a. On the due date B dishonoured the bill of exchange and the bank paid ₹ 200 as noting charges. B requested A to draw a new bill upon him with interest @ 12% p.a. which he agreed. The new bill was payable after 1 month. One week before the maturity of the second bill B requested A to cancel the second bill. He further requested to accept ₹ 15,000 in cash immediately and draw a third bill upon him including interest of ₹ 1,000. A agreed to B's request. The third bill was payable after one month. B met the third bill on its maturity. Record the necessary journal entries in the books of A and B and also prepare B's account in the books of A and A's account in the books of B.
ANSWER: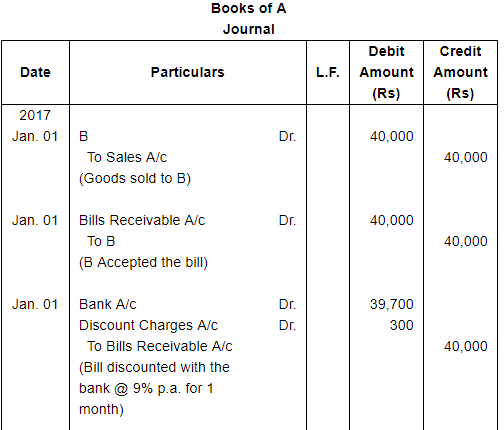
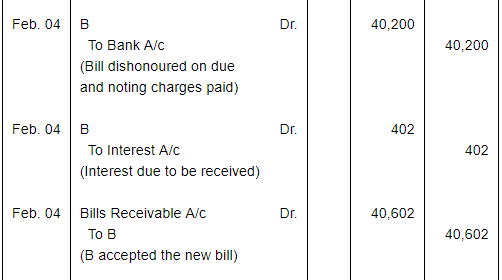

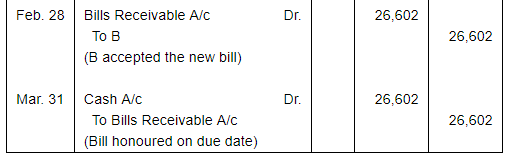
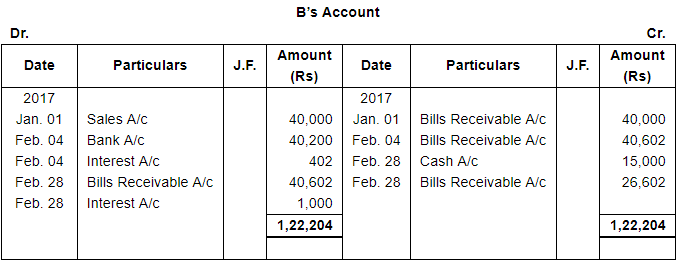
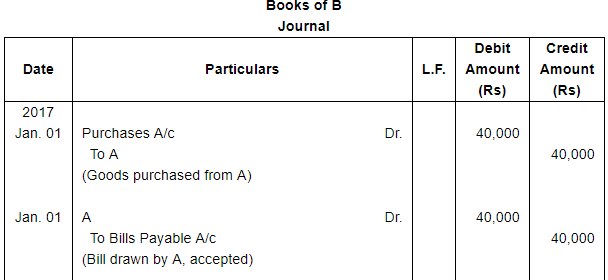


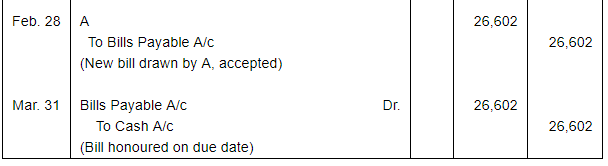
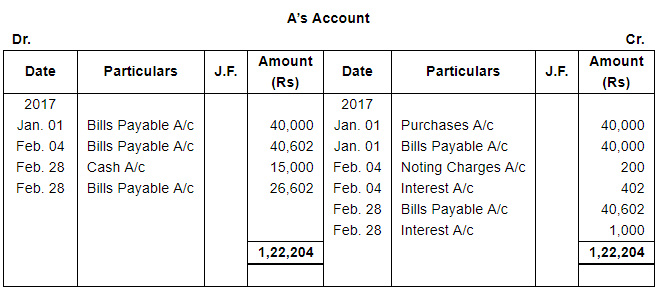
Working Notes: WN1 Calculation of Discounting Charges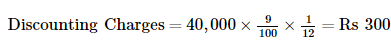
WN2 Calculation of amount of Interest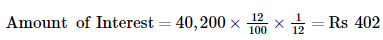
FAQs on Bills of Exchange (Part - 2) - Commerce
| 1. What is a bill of exchange? |  |
| 2. How does a bill of exchange work? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using bills of exchange in commerce? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a bill of exchange and a promissory note? |  |
| 5. What are the legal requirements for a bill of exchange to be valid? |  |















