Depreciation (Part - 1) | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
In accounting, depreciation is the process of spreading out the cost of a physical asset—like a machine or furniture—over the years it’s expected to be used. Since these assets wear out or lose value over time, depreciation helps show this gradual decrease in value on the books.
Key Terms
- Depreciation: The systematic allocation of an asset’s cost over its useful life.
- Straight Line Method (SLM): A depreciation method where the cost is evenly spread over the asset’s life.
- Annual Depreciation: The fixed amount deducted yearly, calculated as (Cost - Residual Value) ÷ Useful Life.
- Rate of Depreciation: The percentage of depreciation relative to the asset’s cost, expressed as (Annual Depreciation ÷ Cost) × 100.
- Residual Value: The estimated value of an asset at the end of its useful life.
- Cost of Asset: Purchase price plus additional expenses (e.g., installation, repairs to make it serviceable).
- Machinery/Furniture Account: Ledger account tracking an asset’s cost, depreciation, and balance over time.
- Net Book Value: The asset’s value after subtracting accumulated depreciation (Cost - Total Depreciation).
- Gain/Loss on Sale: Profit or loss when an asset is sold, calculated as Sale Price - Net Book Value.
- Working Notes: Calculations supporting depreciation amounts, especially for multiple assets or partial years.
Page No 14.48:
Question 1: Calculate the Amount of annual Depreciation and Rate of Depreciation under Straight Line Method (SLM) from the following:
Purchased a second-hand machine for ₹ 96,000, spent ₹ 24,000 on its cartage, repairs and installation, estimated useful life of machine 4 years. Estimated residual value ₹ 72,000.
ANSWER: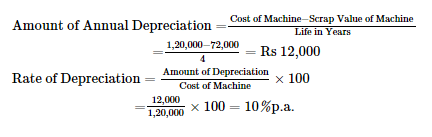
Page No 14.48:
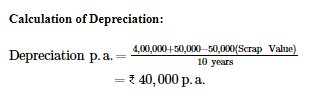
Question 2: On 1st April, 2016, X Ltd. purchased a machine costing ₹ 4,00,000 and spent ₹ 50,000 on its installation. The estimated life of the machinery is 10 years, after which its residual value will be ₹ 50,000 only. Find the amount of annual depreciation according to the Fixed Instalment Method and prepare the Machinery Account for the first three years. The books are closed on 31st March every year.
ANSWER: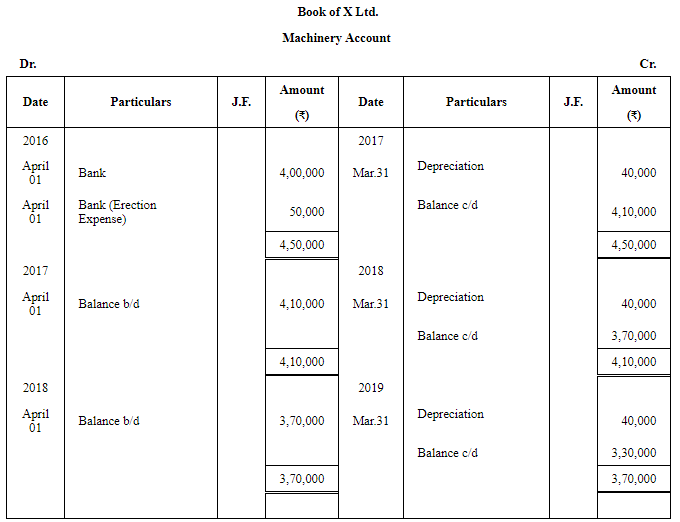
Page No 14.48:
Question 3: On 1st April, 2015, furniture costing ₹ 55,000 was purchased. It is estimated that its life is 10 years at the end of which it will be sold for ₹ 5,000. Additions are made on 1st April 2016 and 1st October, 2018 to the value of ₹ 9,500 and ₹ 8,400 (Residual values ₹ 500 and ₹ 400 respectively). Show the Furniture Account for the first four years, if Depreciation is written off according to the Straight Line Method.
ANSWER: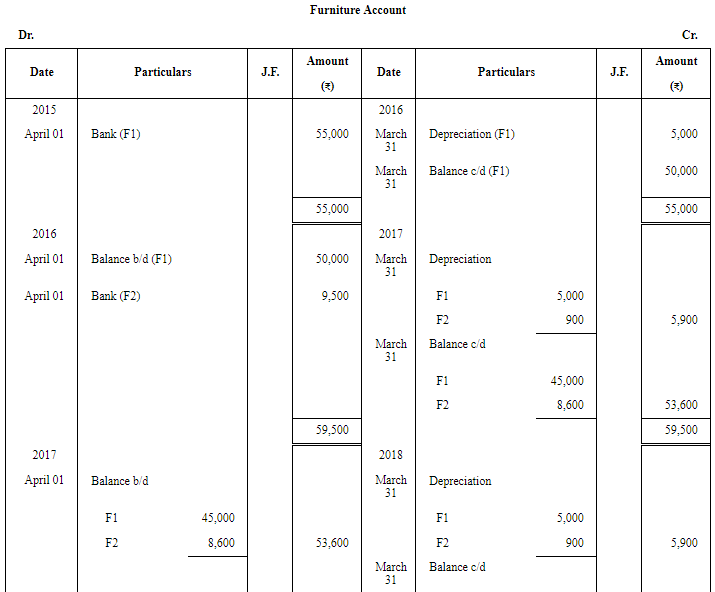
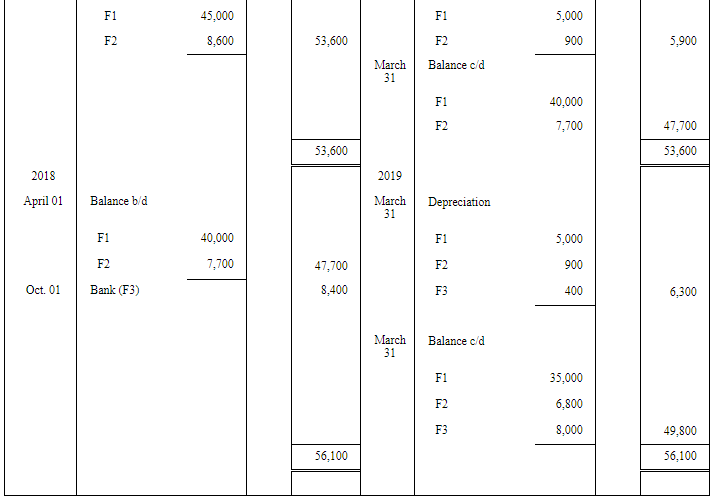
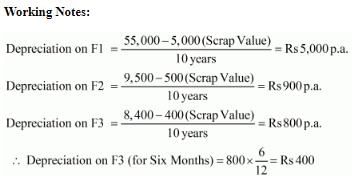
Page No 14.48:
Question 4: From the following transactions of a concern, prepare the Machinery Account for the year ended 31st March 2019:
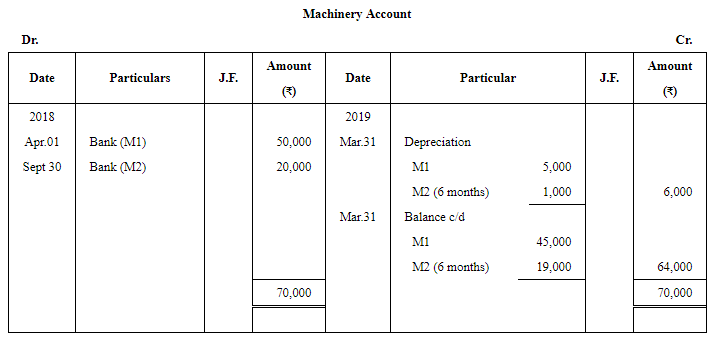 Note:
Note:
The repair and renewal made on December 31, 2018, will not be recorded inthe Machinery Account because this repair was made after putting the Machinery into use.
Page No 14.48:
Question 5: An asset was purchased for ₹ 10,500 on 1st April, 2012. The scrap value was estimated to to be ₹ 500 at the end of asset's 10 years' life. Straight Line Method of depreciation was used. The accounting year ends on 31st March every year. The asset was sold for ₹ 600 on 31st March, 2019. Calculate the following.
(i) The Depreciation expense for the year ended 31st March, 2013.
(ii) The net book value of the asset on 31st March, 2017.
(iii) The gain or loss on sale of the asset on 31st March, 2019.
ANSWER: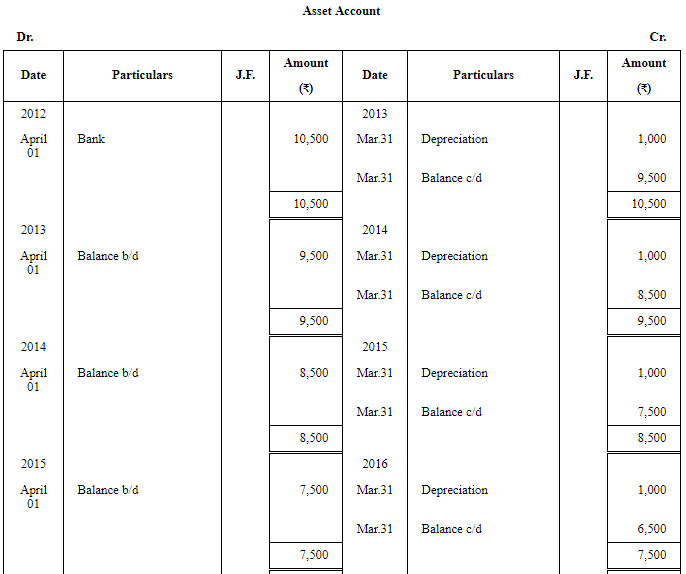
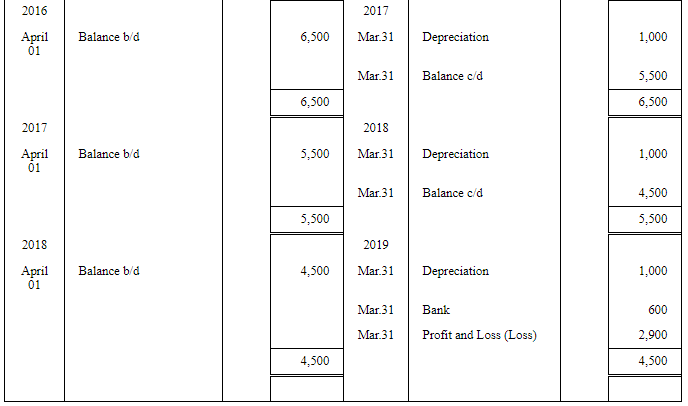
(i) Depreciation Expense for the year ended March 31, 2013, is Rs 1000
(ii) The Net Book Value of the asset on March 31, 2017, is Rs 5,500
(iii) Loss on Sale of the asset on March 31, 201,9 is Rs 2,900
|
61 videos|226 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Depreciation (Part - 1) - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is depreciation in commerce? |  |
| 2. How is depreciation calculated? |  |
| 3. Why is depreciation important in accounting? |  |
| 4. What factors affect the depreciation of an asset? |  |
| 5. How does depreciation impact taxes? |  |






















