Accounts From Incomplete Records Single Entry System (Part - 1) | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Page No 20.38:
Question 1:
Following information of an accounting year is given:
Opening Capital ₹ 60,000; Drawings ₹ 5,000; Capital added during the year ₹ 10,000 and Closing Capital ₹ 90,000. Calculate the Profit or Loss for the year.
ANSWER: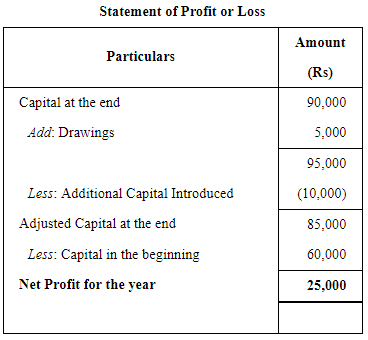
Question 2:
Mayank does not keep proper records of his business, he gives you the following information: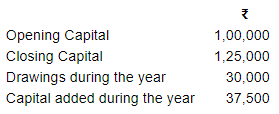
Calculate the profit or loss for the year. 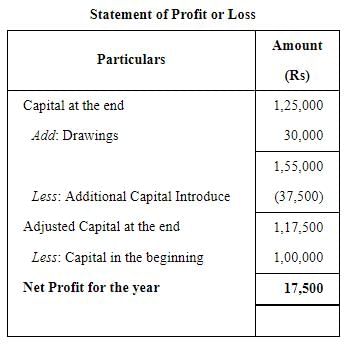
Page No 20.39:
Question 3:
Capital of Ganesh Gupta in the beginning of the year was ₹ 70,000. During the year his business earned a profit of ₹ 20,000, he withdrew ₹ 7,000 for his personal use. He sold ornaments of his wife for ₹ 20,000, and invested that amount into the business. Find out his Capital at the end of the year.
ANSWER:
Capital at the end = Opening Capital + Additional Capital + Profit − Drawings
= 70,000 + 20,000 + 20,000 − 7,000 = Rs 1,03,000
Question 4:
Vikas maintains his books of account on Single Entry System. He provides following information from his books. Find out additional capital introduced in the business during the year 2018–19.
Opening Capital − ₹ 1,30,000 Drawings during the year ₹ 50,000
Closing Capital − ₹ 2,00,000 Profit made during the year ₹ 1,00,000
ANSWER:
Additional Capital = Capital at the End + Drawings − (Capital in the Beginning + Profit) = 2,00,000 + 50,000 − (1,30,000 + 1,00,000)
= 2,50,000 − 2,30,000 = Rs 20,000
Question 5:
Mohan maintains books on Single Entry System. He gives you the following information: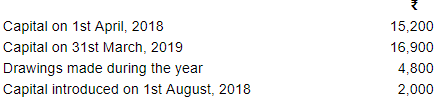
You are required to calculate the Profit or Loss made by Mohan.
ANSWER: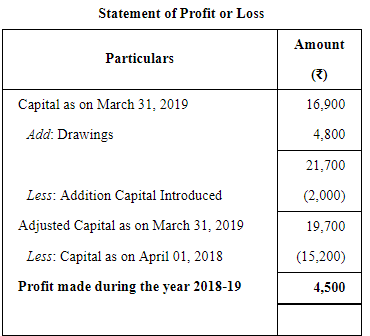
Page No 20.39:
Question 6:
Mahesh who keeps his books on Single Entry System sells goods at Cost plus 50%. On 1st April, 2018 his Capital was ₹ 4,00,000 and on 31st March, 2019 it was ₹ 3,50,000. He had withdrawn ₹20,000 per month besides goods of the sale value of ₹ 60,000. How much did he earn in 2018-19?
ANSWER: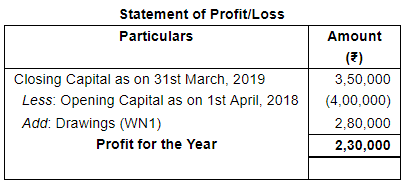
Working Notes:
Question 7:
Krishan started his business on 1st April, 2018 with a Capital of ₹ 1,00,000. On 31st March, 2019, his assets were: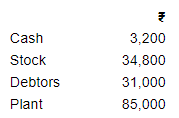
He owed ₹ 12,000 to sundry creditors and ₹ 10,000 to his brother on that date. He withdrew ₹ 2,000 per month for his personal expenses. Ascertain his profit.
ANSWER: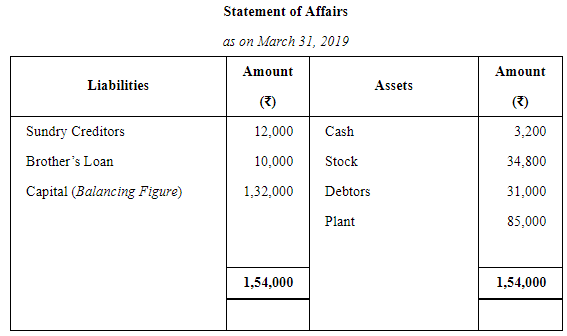
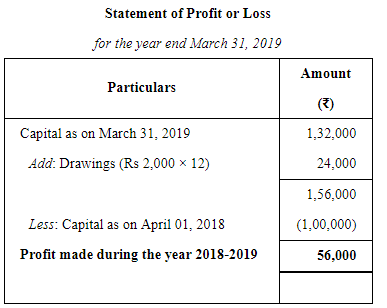
Question 8:
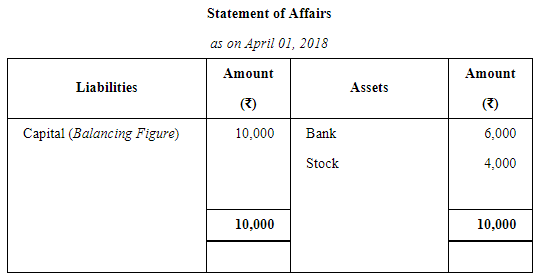
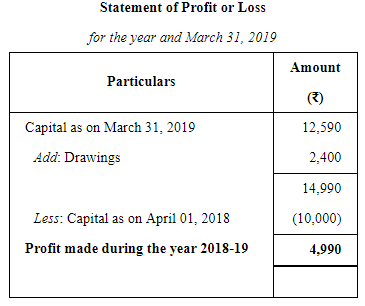
Ram Prashad keeps his books on Single Entry System and from them and the particulars supplied, the following figures were gathered together on 31st March, 2019:
Book Debts ₹ 10,000; Cash in Hand ₹ 510; Stock-in-Trade (estimated) ₹ 6,000; Furniture and Fittings ₹ 1,200; Trade Creditors ₹ 4,000; Bank Overdraft ₹ 1,000; Ram Prashad stated that he started business on 1st April, 2018 with cash ₹ 6000 paid into bank but stocks valued at ₹ 4,000. During the year he estimated his drawings to be ₹ 2,400. You are required to prepare the statement, showing the profit for the year, after writing off 10% for Depreciation on Furniture and Fittings.
ANSWER: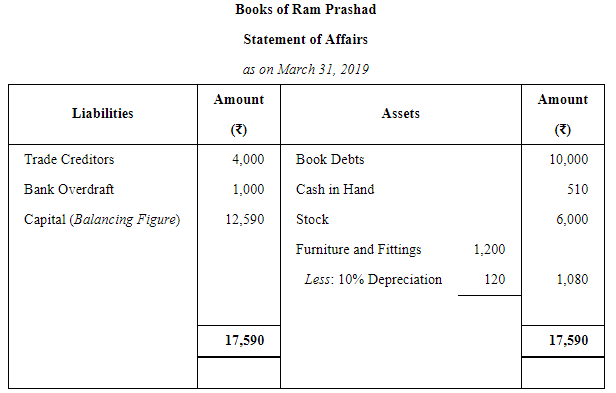
Page No 20.40:
Question 9:
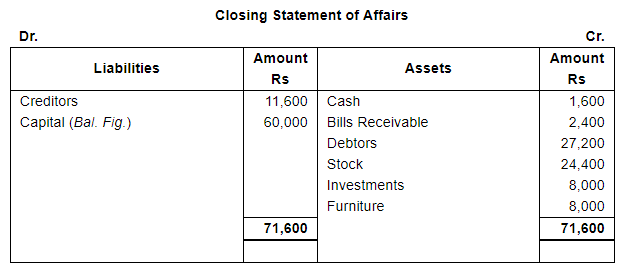
Shruti maintains her books of account from Incomplete Records. Her books provide the following information: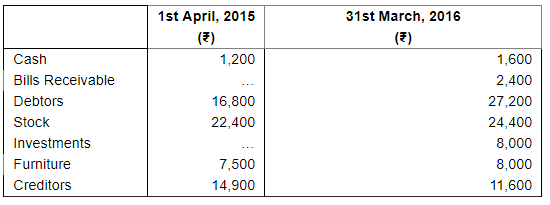
She withdrew ₹ 500 per month for personal expenses. She sold her Investments of ₹ 16,000 at 5% premium and introduced the amount into business.
You are required to prepare a Statement of Profit or Loss for the year ending 31st March, 2016.
ANSWER: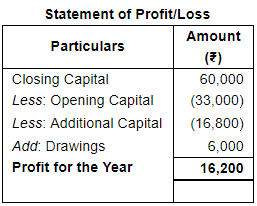
Working Notes: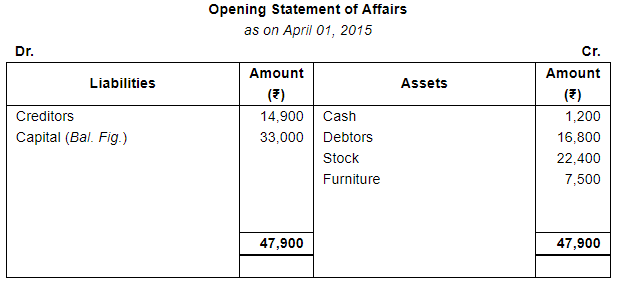
Page No 20.40:
Question 10:
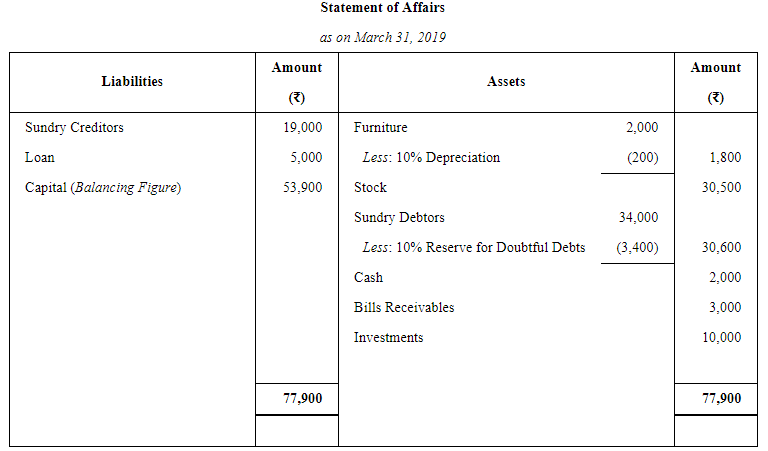
Hari maintains his books of account on Single Entry System. His books provide the following information: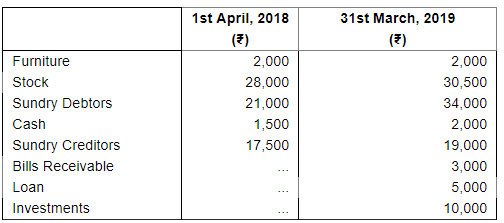
His drawings during the year were ₹ 5,000 Depreciate furniture by 10% and provide a reserve for Bad and Doubtful Debts at 10% on Sundry Debtors.
Prepare the statement showing the profits for the year.
ANSWER: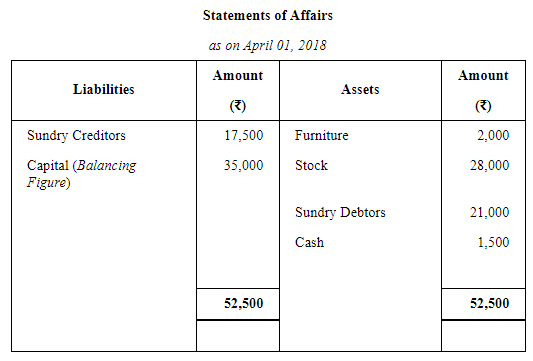
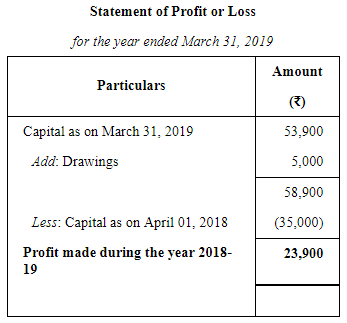
Question 11:
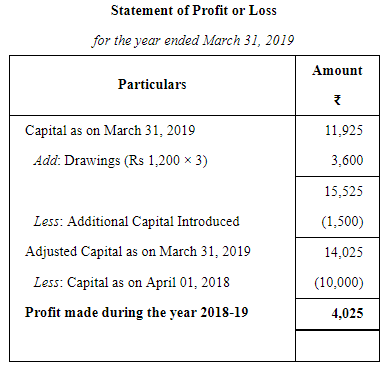
A commenced business on 1st April, 2018 with a capital of ₹ 10,000. He immediately bought Furniture and Fixtures for ₹ 2,000. On 1st October, 2018, he borrowed ₹ 5,000 from his wife @ 9% p.a. (interest not yet paid) and introduced a further capital of his own amounting to ₹ 1,500. A drew @ ₹ 300 per month at the end of each month for household expenses. On 31st March, 2019 his position was as follows:
Cash in Hand ₹ 2,800; Sundry Debtors ₹ 4,800; Stock ₹ 6,800; Bills Receivable ₹ 1,600; Sundry Creditors ₹ 500 and owing for Rent ₹ 150. Furniture and Fixtures to be depreciated by 10%.
Ascertain the profit or loss made by A during 2018–19.
ANSWER: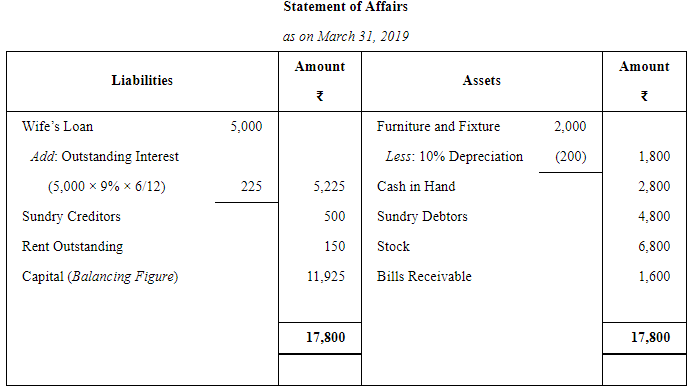
|
61 videos|227 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Accounts From Incomplete Records Single Entry System (Part - 1) - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is an incomplete records single entry system? |  |
| 2. How is an incomplete records single entry system different from a double-entry system? |  |
| 3. What are the limitations of an incomplete records single entry system? |  |
| 4. How can businesses overcome the limitations of an incomplete records single entry system? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of an incomplete records single entry system? |  |

















