Financial Statements Of Sole Proprietorship - (Part - 1) | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
Financial statements for a sole proprietorship focus on recording and analyzing the financial activities of a single-owner business. This involves distinguishing between capital and revenue expenses, calculating gross profit, and preparing trading accounts, using examples to classify expenses and determine stock values with profit rates.
Key Concepts
- Capital Expenditure: Money spent on acquiring or improving assets for long-term use (e.g., painting a building to make it usable).
- Revenue Expenditure: Costs for daily operations or maintenance (e.g., repairs on an existing car).
- Gross Profit: Profit from sales after subtracting the cost of goods sold, found by Sales + Closing Stock - (Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses).
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Total cost of goods available minus closing stock, showing what was sold in the period.
- Trading Account: A statement comparing net sales (after returns) with the cost of goods sold and direct expenses like carriage inwards to find gross profit.
- Opening Stock: Value of goods at the period’s start.
- Closing Stock: Value of unsold goods at the period’s end.
- Purchases Return: Goods sent back to suppliers, lowering the purchase total.
- Sales Return: Goods returned by customers, reducing sales.
- Direct Expenses: Costs tied to producing or acquiring goods (e.g., freight), part of COGS, unlike indirect expenses (e.g., depreciation).
Page No 18.62:
Question 1: State whether the following expenses are capital or revenue in nature:
(i) Expenses on whitewashing and painting of a building purchased to make it ready for use.
(ii) ₹ 10,000 spent on constructing platform for a new machine.
(iii) Repair expenses of ₹ 25,000 incurred for whitewashing of factory building.
(iv) Insurance premium paid as renewal premium.
(v) Purchased a new car.
ANSWER:
(i) Expenses on whitewashing and painting of a building purchased to make it ready for use: Capital expenditure. This is spent to prepare a newly bought building for use, adding to its value as a long-term asset.
(ii) ₹ 10,000 spent on constructing platform for a new machine: Capital expenditure. Building a platform is a one-time cost to set up the new machine, making it ready for long-term use in the business.
(iii) Repair expenses of ₹ 25,000 incurred for whitewashing of factory building: Revenue expenditure. This is for maintaining an existing factory building, keeping it in good shape, not creating or improving an asset.
(iv) Insurance premium paid as renewal premium: Revenue expenditure. This is a recurring cost to keep the business running smoothly, part of normal operations, not tied to a long-term asset.
(v) Purchased a new car: Capital expenditure. Buying a new car is an investment in a long-term asset that will be used in the business for several years.
Page No 18.62:
Question 2: State with reasons whether the following are Capital or Revenue Expenses:
(i) Excise duty paid on purchase of new machine.
(ii) Wages paid to install a machine.
(iii) Repairs carried out on existing car.
(iv) Office block of building repainted for ₹ 50,000.
(v) Paid telephone bill ₹ 2,500.
ANSWER:
(i) Excise duty paid on purchase of new machine: This is a capital expenditure because it’s part of the cost of buying a new machine, an asset that will be used in the business for years. It increases the machine’s total cost, not just a daily expense.
(ii) Wages paid to install a machine: This is a capital expenditure since it’s spent to set up the machine and make it ready for use. It’s a one-time cost tied to getting a long-term asset operational, not a recurring expense.
(iii) Repairs carried out on existing car: This is a revenue expenditure because it’s money spent to maintain or fix an asset already in use. It keeps the car running but doesn’t add to its value or extend its life significantly.
(iv) Office block of building repainted for ₹ 50,000: This is a revenue expenditure as it’s for maintaining the building, keeping it in good condition. Repainting doesn’t create a new asset or improve the building’s long-term value, so it’s a regular upkeep cost.
(v) Paid telephone bill of ₹ 2,500: This is a revenue expenditure because it’s a normal operating cost of the business. Telephone bills are routine expenses needed to keep the business going day-to-day, not tied to any long-term asset.
Page No 18.62:
Question 3: From the following information, determine Gross Profit for the year ended 31st March 2019: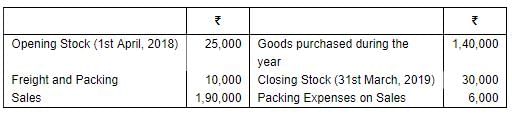
ANSWER:
Gross Profit
= Sales + Closing Stock – (Opening Stock + Freight and Packing + Goods Purchased)
=1,90,000 + 30,000 – (25,000 + 10,000 + 1,40,000)
=2,20,000 – 1,75,000 = ₹45,000
Alternatively,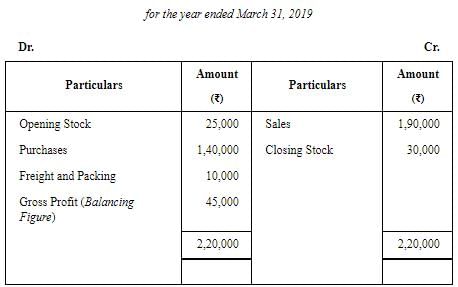
Note: Packing Expenses (Rs 6,000) on Sales is an Indirect Expense, therefore, it is not considered to compute the amount of Gross Profit
Page No 18.62:
Question 4: Calculate Closing Stock from the following details: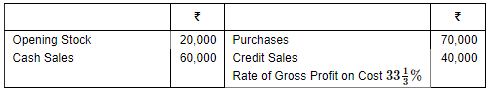
ANSWER: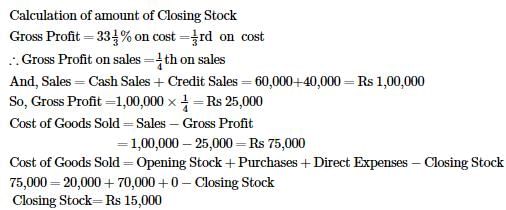
Page No 18.62:
Question 5: Prepare Trading Account from the transactions givne below: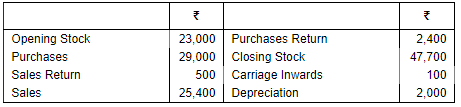
Also pass the Journal entries.
ANSWER: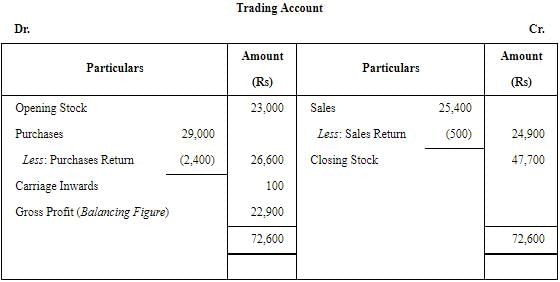
Note: Depreciation is an Indirect Expense, therefore it is not shown in the Trading Account.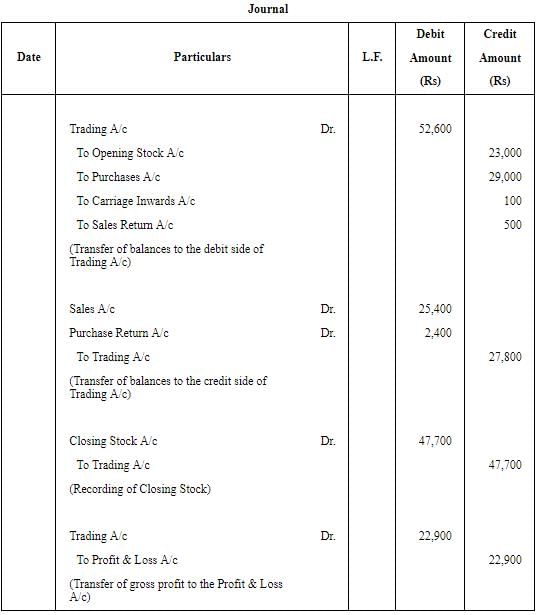
|
61 videos|227 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Financial Statements Of Sole Proprietorship - (Part - 1) - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are financial statements of a sole proprietorship? |  |
| 2. Why are financial statements important for a sole proprietorship? |  |
| 3. How often should financial statements be prepared for a sole proprietorship? |  |
| 4. What information is included in an income statement for a sole proprietorship? |  |
| 5. How can a sole proprietorship use financial statements to evaluate its performance? |  |





















