Class 11 Political Science Short Questions with Answers- Equality
Q1. What is equality?
Ans: Equality refers to a situation where all individuals are treated fairly and enjoy the same rights, opportunities, and access to necessities.
 Equality for allIt aims to eliminate disparities caused by caste, gender, wealth, or social status and seeks to create a just society where everyone can develop their potential.
Equality for allIt aims to eliminate disparities caused by caste, gender, wealth, or social status and seeks to create a just society where everyone can develop their potential.
- Ensures equal treatment and non-discrimination.
- Promotes fairness in access to education, jobs, and resources.
- Seeks to remove social, economic, and political barriers.
- Provides a foundation for dignity and freedom for all individuals.
- Builds a society where everyone can contribute according to their abilities.
Q2. What is equality of opportunities?
Ans: Equality of opportunity means providing every individual with the same chances to develop their talents and achieve personal goals. It focuses on fairness in access rather than guaranteeing identical outcomes for everyone.
- Ensures access to education, jobs, and public participation.
- No discrimination based on caste, religion, gender, or social status.
- Differences in outcome due to talent, effort, or choice are acceptable.
- Encourages a merit-based society while removing systemic barriers.
- Supports social mobility and empowerment of disadvantaged groups.
Q3. What do you mean by social inequality?
Ans: Social inequality refers to the unfair treatment of people within society based on factors like caste, gender, religion, colour, or social status. Unlike natural differences, these inequalities are man-made and can be corrected through reforms and awareness.
- Arises from societal customs, traditions, and prejudices.
- Manifests as unequal access to education, jobs, or social participation.
- Includes practices like untouchability, gender discrimination, and caste-based exclusion.
- It can be reduced through social reforms, education, and awareness campaigns.
- Affects social cohesion and limits the development of marginalised groups.
Q4. What is political inequality?
Ans: Political inequality occurs when certain groups are denied equal rights to participate in governance and political processes. Historically, factors like property ownership, education, gender, and race restricted political participation.
- Denial of voting, contesting elections, or expressing political opinions constitutes inequality.
- Political equality requires that every citizen have equal political rights.
- Ensures representation for marginalised and disadvantaged groups.
- Promotes democratic values and prevents domination by elite classes.
- Supports accountability and inclusivity in governance.
Q5. What is social equality?
Ans: Social equality means equal status and treatment for all individuals in society, without discrimination based on caste, religion, gender, or region. It aims to remove social hierarchies and promote dignity for everyone.
- Eliminates discrimination such as untouchability and gender bias.
- Ensures equal access to social institutions, public spaces, and services.
- Promotes respect, fairness, and inclusion in daily life.
- Encourages social cohesion and unity.
- Forms a basis for building just and democratic societies.
Q6. How is social equality ensured in the Indian Constitution?
Ans: The Indian Constitution enshrines social equality through specific provisions that guarantee equal rights and prohibit discrimination:
- Article 14: Equality before law and equal protection under the law.
- Article 15: Prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.
- Article 17: Abolishes untouchability and its practice in any form.
- These legal safeguards ensure that all citizens enjoy equal status and opportunities in public life.
- Strengthens social justice and inclusion in India’s democratic framework.
Q7. What is the reason for economic inequality according to Marx?
Ans: According to Karl Marx, economic inequality arises from the unequal ownership of property and the exploitation of labour by the capitalist class. This economic divide creates social and political inequalities as well.
- Capitalists own means of production (factories, land, resources), while workers sell their labour.
- Surplus value generated by workers is appropriated by capitalists as profit.
- Creates a widening gap between the rich (bourgeoisie) and the poor (proletariat).
- Leads to class conflict and social tensions.
- Marx argued that this exploitation is the root cause of systemic inequality in society.
Q8. How can formal equality be achieved?
Ans: Formal equality can be ensured by treating every individual equally before the law and removing discriminatory practices that privilege some over others.
- Abolish laws that discriminate based on caste, religion, gender, or wealth.
- Ensure everyone has equal legal rights and responsibilities.
- State intervention through constitutional safeguards and legal reforms.
- Focus is on equal status rather than outcomes.
- Provides a framework for justice but does not automatically eliminate social or economic disparities.
Q9. What is socialism?
Ans: Socialism is an economic and social philosophy that seeks to create an egalitarian society based on cooperation, justice, and welfare. It emphasises reducing inequality and providing equal opportunities for all.
- Promotes collective ownership of resources and means of production.
- Reduces exploitation and ensures fair distribution of wealth.
- Encourages social welfare schemes and public services for all.
- Aims to create a society where inequalities in wealth, status, and opportunity are minimised.
Q10. What is affirmative action?
Ans: Affirmative action refers to policies that provide special support to disadvantaged groups to promote real equality in opportunities.
- Examples include reservations in education and public employment for SCs, STs, and OBCs.
- Compensates for historical discrimination and social disadvantages.
- Helps marginalised groups access education, jobs, and political participation.
- Aims to reduce inequality and promote social justice.
- Ensures that formal equality translates into substantive equality in practice.
Q11. Why is equality necessary for human life?
Ans: Equality is essential because all human beings have equal moral worth. Without it, societies allow oppression and exploitation based on caste, gender, or status.
- Ensures freedom, dignity, and respect for every individual.
- Reduces social tensions and promotes harmony.
- Forms the foundation of democratic societies.
- Allows people to develop their abilities and contribute meaningfully.
- Promotes justice and fairness in all spheres of life.
Q12. How has the concept of equality influenced political movements in the world?
Ans: The idea of equality has inspired social and political movements worldwide, demanding rights, justice, and fair treatment for all.
- French Revolution: “Liberty, equality, fraternity” became a guiding principle.
- Anti-colonial movements emphasised equality against imperial domination.
- Civil rights movements in the U.S. fought racial inequality.
- Anti-untouchability and women’s movements in India promoted social equality.
- These movements made equality a universal political and social value.
Q13. Give some factual position about global inequalities.
Ans: Global inequalities highlight the uneven distribution of wealth, resources, and opportunities between countries and social groups. Understanding these facts helps in addressing poverty and development challenges.
- The world’s richest individuals earn more than the poorest hundreds of millions combined.
- The poorest 40% of the population receive only a small fraction of global income.
- Industrialised nations, though fewer in population, consume most of the world’s energy and resources.
- These figures reveal stark differences in living standards and opportunities between rich and poor countries.
- Addressing global inequality requires coordinated policies, social welfare, and equitable resource distribution.
Q14. What is the liberal view of equality?
Ans: Liberals believe equality should be ensured through free and fair competition rather than identical outcomes. They focus on providing equal opportunities for all individuals.
- Guarantees equal chances to access education, jobs, and public services.
- Accepts differences in outcomes based on talent, effort, and personal choice.
- Opposes inherited privileges or discrimination.
- Emphasises legal equality and individual rights.
- Encourages merit-based progress while removing systemic barriers.
Q15. Can treating people differently sometimes promote equality? Explain.
Ans: Yes, differential treatment can promote equality when it compensates for disadvantages faced by certain groups. Such measures help achieve substantive equality in practice.
- Providing ramps and accessible facilities for persons with disabilities.
- Maternity leave and childcare support for women.
- Reservations in education and employment for disadvantaged groups.
- Special programmes for marginalised communities to ensure participation.
- These measures help remove historical and social barriers, allowing everyone to enjoy equal rights and opportunities.
Q16. Do you think that equality means always treating all identically?
Ans: No, equality does not require identical treatment. People differ in abilities, needs, and circumstances, and real equality recognises these differences while ensuring fairness.
- Treatment should be based on need and context rather than uniformity.
- Different measures may be required for disadvantaged groups.
- Focus is on fairness, dignity, and equal opportunity.
- Ensures social, economic, and political inclusion for all.
- Promotes harmony while respecting individual differences.
Q17. What is the difference between natural inequalities and social inequalities?
Ans: Inequalities in society can arise naturally or be socially constructed, and understanding the difference helps in addressing injustices.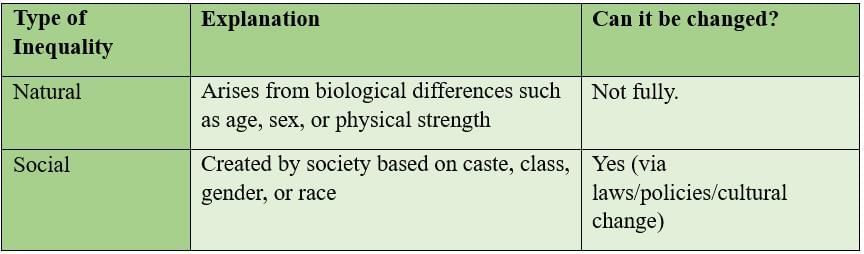
- Natural inequalities are inherent and unavoidable, and cannot be changed fully; effects can often be mitigated with support and technology, and they should not justify unequal rights
- Social inequalities are man-made and can be corrected through reforms, education, and legal measures.
Q18. Discuss social inequality as prevailing in India.
Ans: Social inequality in India has historically been shaped by caste, gender, region, and religion, leading to discrimination and exclusion.
- Practices like untouchability and denial of education or property rights targeted certain groups.
- Women and lower-caste communities were often excluded from public life.
- Social reforms and legal measures, like the abolition of untouchability and affirmative action, aim to reduce inequalities.
- Disparities continue in access to education, employment, and resources for marginalised groups.
- Addressing these inequalities is essential for social justice and inclusive development.
Q19. Explain Economic Equality?
Ans: Economic equality aims to reduce extreme differences in wealth, income, and living standards while ensuring fair access to resources. It does not demand identical incomes but focuses on opportunity and fairness.
- Ensures equitable access to jobs, education, and social security.
- Reduces poverty and bridges the gap between the rich and the poor.
- Encourages rational distribution of resources and wealth.
- Supports policies that uplift marginalised and disadvantaged groups.
- Promotes social justice and contributes to overall societal stability.
Q20. Show the relationship between education inequality and socio-economic status in urban India.
Ans: Educational opportunities in urban India are closely linked to family income and social status, leading to disparities in learning outcomes.
- Wealthier families can afford better schools, coaching, and study resources.
- Poorer families face limited access to quality education, affecting performance and future opportunities.
- Socio-economic status influences enrolment, retention, and academic achievement.
- This cycle reinforces inequality across generations.
- Addressing educational inequality requires scholarships, government schools, and targeted programmes for disadvantaged children.
The following table shows the above situation:
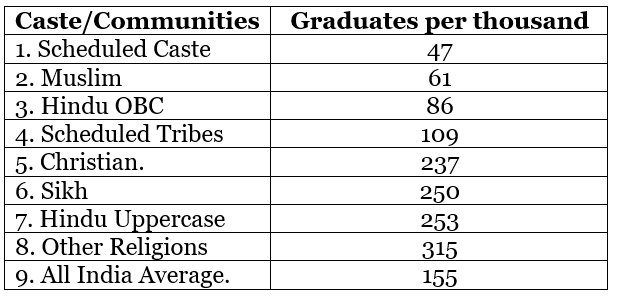 Source: NSSO 55th Round Survey, 1999-2000.
Source: NSSO 55th Round Survey, 1999-2000.
Q21. Discuss the meaning and need for Feminism.
Ans: Feminism is a social and political movement that advocates for equal rights, opportunities, and status for women. It challenges patriarchal structures and gender-based discrimination.
- Seeks equal participation in education, employment, and decision-making.
- Opposes social norms that subordinate women.
- Promotes legal and social reforms for gender justice.
- Strives to eliminate violence, discrimination, and exploitation against women.
- Aims to create a society where men and women can develop their potential equally.
Q22. What is a Marxist view of Equality?
Ans: Marxists view inequality as rooted in private property and the exploitation of labour. Economic inequality leads to social and political inequality, which perpetuates class dominance.
- Capitalist ownership creates a divide between rich and poor.
- Labour is exploited to generate surplus value for the ruling class.
- Inequality is systemic and structural, not merely individual.
- Social and political power is concentrated with those who control property.
- Marxists advocate collective ownership to achieve true equality.
Q23. What is a Marxist view of establishing equality?
Ans: Marxists propose that equality can be achieved only in a classless, stateless society where private property is abolished.
- Collective ownership replaces capitalist ownership of resources.
- Exploitation of labour ends, eliminating economic inequality.
- Social and political equality follows once class divisions are removed.
- Aims for a society where each contributes according to ability and receives according to need.
- Establishing equality requires systemic restructuring rather than superficial reforms.
Q24. Explain the Socialist view of Equality.
Ans: Socialists oppose inequalities created by capitalism and seek an egalitarian society based on cooperation and welfare. They emphasise correcting historical and social disadvantages.
- Focuses on gender, caste, colour, and colonial inequalities.
- Advocates collective welfare and redistribution of resources.
- Promotes social justice through policies that uplift disadvantaged groups.
- Encourages cooperation over competition for societal well-being.
Q25. Distinguish between Formal Equality and Substantive Equality.
Ans: 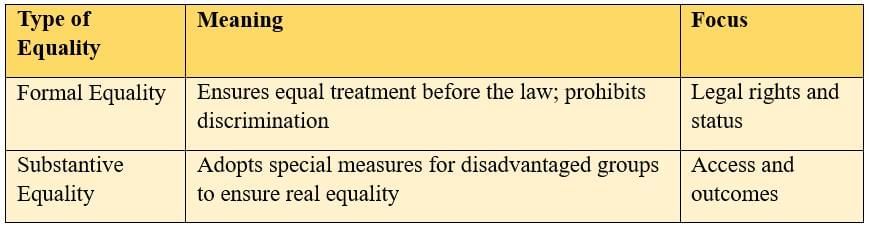
- Formal equality provides equal status but may ignore historical disadvantages.
- Substantive equality ensures that equality becomes effective in practice.
- Both are essential: formal equality guarantees legal fairness, while substantive equality ensures social justice.
|
44 videos|392 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Class 11 Political Science Short Questions with Answers- Equality
| 1. What is the concept of equality? |  |
| 2. How is equality important in society? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of inequality in the world today? |  |
| 4. How can individuals promote equality in their daily lives? |  |
| 5. Why is it important for governments to enforce laws that promote equality? |  |

















