Class 12 Economics Long Questions With Answers - Introduction (Macroeconomics)
Q1. What are macroeconomics and microeconomics? What is the connection between the two?
Ans:
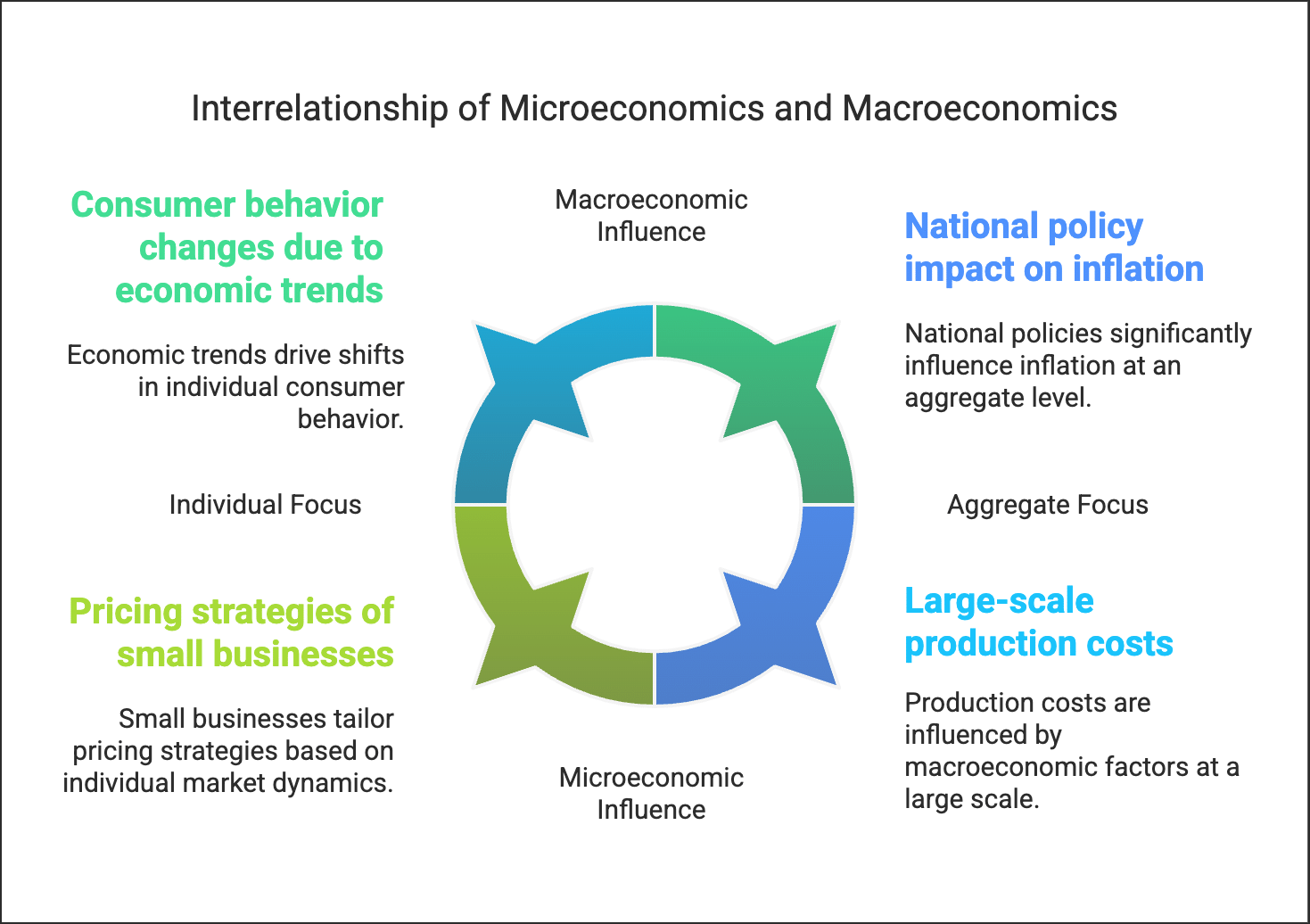
Microeconomics focuses on individual and business decisions regarding resources and pricing. It examines supply and demand, along with factors that influence prices.
Macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole, analysing national trends rather than individual markets.
Despite their differences, the two fields are interconnected:
- For example, higher inflation can increase raw material costs for businesses, affecting consumer prices.
- Professor Ackley highlights the relationship between macroeconomic trends and individual behaviours.
- Microeconomic theories help shape macroeconomic understanding, while macroeconomic patterns can inform microeconomic theories.
Q2. Explain the scope of macroeconomics.
Ans: The scope of Macroeconomics is as follows:
- To comprehend the operation of the economy: Understanding how the economy works require an understanding of macroeconomic variables. Macroeconomic challenges are related to the behaviour of total income, output, employment, and the overall price level of the economy.
- Economic Policies: Macroeconomics is especially useful for economic policy. Modern governments, particularly those in developing countries, are confronted with a plethora of domestic issues. For example, overcrowding, inflation, the balance of payments, general underproduction, and so on.
- Unemployment in General: Unemployment is thus, caused by a lack of effective demand. Total investment, total output, total income, and total consumption should all be increased to boost effective demand. As a result, macroeconomics is particularly important in studying the causes, consequences, and treatments of general unemployment.
- National Income: Understanding macroeconomics is essential for assessing the economy’s overall performance in terms of national income. When the Great Depression of the 1930s began, it became necessary to investigate the causes of general overproduction and general unemployment.
- Economic Growth: A subfield of macroeconomics focuses on growth, and is known as growth economics. Macroeconomic principles are used to assess an economy’s resources and capacities. To boost the economy’s overall level of economic development, plans for overall increases in national income, output, and employment are developed and implemented.
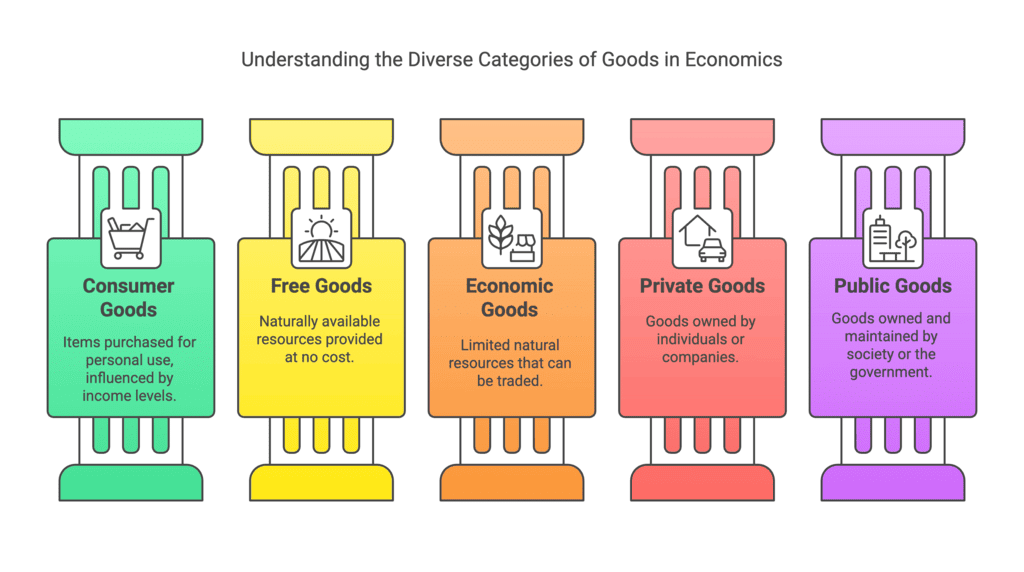
Q3. What are the different types of goods produced in an economy?
Ans: The different types of goods produced in an economy can be categorized as follows:
- Consumer Goods: These are items that people buy for personal use. When people have more money, they buy more of these goods, and when they have less money, they buy fewer. Examples include bread, biscuits, butter, jam, rice, fish, eggs, shoes, clothing, fans, books, and pens.
- Free Goods: These goods are available in unlimited quantities and are provided by nature for free. Examples include air, seawater, sunlight, and desert sand.
- Economic Goods: These are natural resources that are limited in supply and can be bought and sold in the market. Examples include vegetables, cereals, minerals, fruits, and fish.
- Private Goods: These are goods owned by individuals or private companies. Examples include cars, houses, motorcycles, mobile phones, books, and televisions.
- Public Goods: These are goods owned by society, the general public, or the government. Examples include roads, bridges, hospitals, and government schools.
- Capital Goods: Also known as producer goods, these items are not used immediately but are used in the production of other goods. Examples include seeds, fertilizers, tools, machinery, and raw materials.
Q4. Define and explain the importance of ‘scarcity’ and ‘opportunity costs’ in economics.
Ans:
Scarcity
Scarcity is the situation where there are not enough resources to satisfy all the wants and needs of individuals or society. Any resource that costs something is considered scarce to some extent, but what really matters is relative scarcity.
- Scarcity is also known as "paucity."
- Economics studies how people use limited resources to fulfil their unlimited desires.
- The main idea in economics is that our world faces scarcity, meaning we cannot access all the resources we want. Hence, we must make choices.
Importance of Scarcity:
- Scarcity affects the levels of supply and demand in the economy.
- The production of goods and services depends on the scarcity of input resources. If resources are scarce, it becomes harder for producers to create the necessary amount of goods and services.
Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that we give up when we make a decision. It's the cost of what we forego to do something else.
- Economists define opportunity cost as the next best or highest-valued alternative to the chosen option. For example, if we use resources to make one product, the opportunity cost is what we could have made instead.
- Opportunity costs occur when choosing between different alternatives. Every resource used in the economy has a limited quantity.
- This concept leads to the pricing of all goods and services. If resources weren't scarce, everything would be free, and there would be no opportunity cost of choosing one option over another. Because resources are limited, both customers and producers must consider opportunity costs when making decisions.
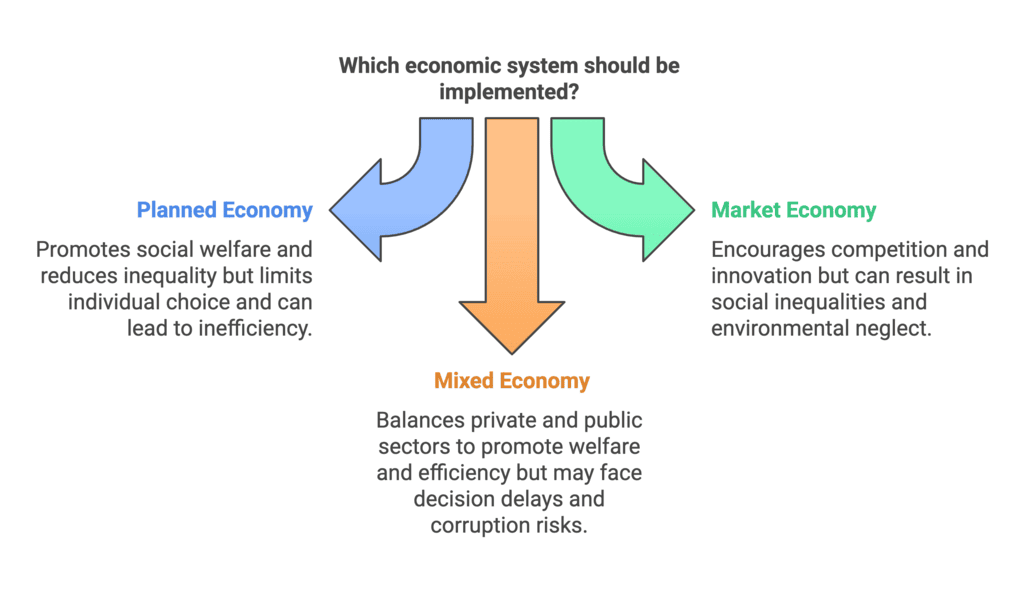
Q5. What are the different ways in which resources can be allocated, and what are their respective advantages and disadvantages?
Ans: Resources can be allocated through free individual interaction or a government-controlled system. The three major market systems for resource allocation are:
Planned Economy: In a centrally planned economy, the government or a central authority controls all major economic activities, including the production, exchange, and consumption of goods and services. The goal is to achieve specific resource allocation and distribute goods and services to promote social welfare.
Advantages:
- Promotes higher economic growth and development with a focus on social welfare.
- Reduces income and social inequalities.
- Minimizes resource duplication.
- Optimizes resource utilization.
Disadvantages:
- Limits individual choice and rights.
- Individuals have no say in economic decisions.
- This can lead to inefficiency as products may not align with consumer preferences.
Market Economy: In a market economy, economic activities are organized by the market through the free interaction of individuals. There is no government interference, and the economy is driven by demand, supply, and the behaviour of economic participants. The primary goal is profit maximization.
Advantages:
- Higher efficiency due to competition.
- Offers a wide variety of products to gain competitive advantage.
- Encourages innovation to boost consumer demand.
- Ensures efficient resource production and utilization.
Disadvantages:
- Little concern for society or the environment.
- This can lead to exploitation and competitive disadvantages.
- Results in social, economic, and income inequalities.
Mixed Economy: A mixed economy combines elements of both government and private sector control. The private sector aims for profit maximization, while the public sector focuses on social welfare. Major economic issues are addressed by both central planning and the price mechanism.
Advantages:
- Efficient resource allocation.
- Promotes social welfare.
- Encourages private sector involvement.
- Reduces economic disparities.
Disadvantages:
- Decision-making delays.
- Potential for resource wastage.
- Higher risk of corruption and black marketing.
- Often lacks proper economic planning.
Q6. Define intermediate goods and final goods. Can milk be an intermediate good? Give a reason for your answer.
Ans:
- Intermediate goods: These are goods that a firm buys to use in the production of other goods or to resell. For example, steel is used to make cars or milk bought by a milk seller.
- Final goods: These are goods that have completed the production process and are ready to be used by the final consumer. Examples include clothes or milk consumed by a household.
- Milk can be both a final good and an intermediate good, depending on its use. If a household consumes milk, it is a final good. However, if a firm uses milk to make products like ice cream, it is an intermediate good.
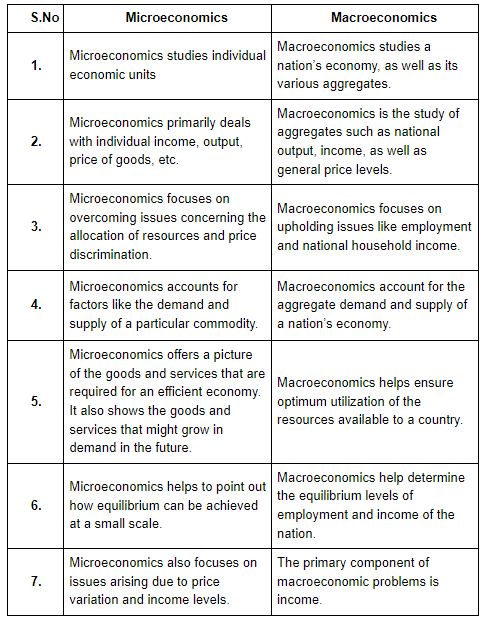
Q7. What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?
Ans. The following points explain the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics:
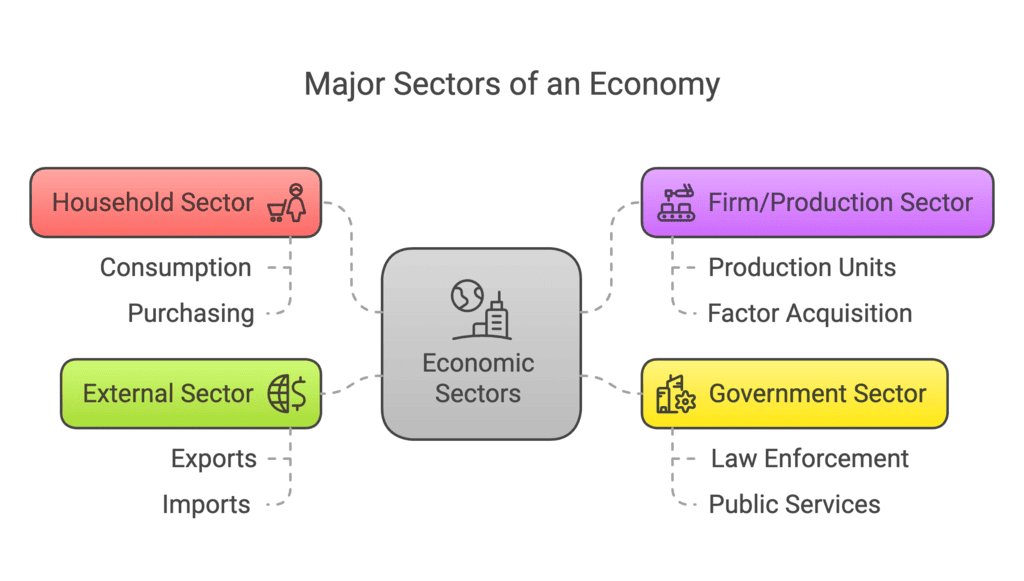
Q8. Describe the four major sectors in an economy according to the macroeconomic point of view.
Ans. The following are the four major sectors of an economy:
(a) Household Sector: By household sector, we mean a group of individuals who purchase goods and services for consumption.
(b) Firm/Production Sector: The production units are called firms. The firm sector includes all the units that buy factors of production from households.
(c) Government Sector: The role of the government sector includes framing laws, enforcing them and delivering justice. The government, in many instances, undertakes production apart from imposing taxes and spending money on building public infrastructure, running schools, and colleges, providing health services, etc.
(d) External Sector: The external sector includes exports and imports of goods and services. Capital from foreign countries may also flow into the domestic country, or the domestic country may be ; exporting capital to foreign countries.
 Q9. Describe the Great Depression of 1929.
Q9. Describe the Great Depression of 1929.
Ans. The Great Depression lasted from 1929 to 1933 and had significant impacts worldwide. Key points include:
- Severe decline in output and employment across Europe and North America.
- In the USA, the unemployment rate soared from 3% to 25%.
- Aggregate output in the USA fell by about 33%.
- Many factories were idle, and demand for goods dropped sharply.
- This crisis led economists to rethink economic theories, paving the way for macroeconomics.
John Maynard Keynes' work during this time focused on understanding these economic failures and proposed new ideas on how economies function.
Q10. Discuss the contributions of Adam Smith to modern economics and explain how his ideas differed from those of the Physiocrats of France. Also, explain his advocacy for a free market economy with reference to the famous passage from An Enquiry into the Nature and Cause of the Wealth of Nations (1776).
Ans. Adam Smith is regarded as the founding father of modern economics, which was known as political economy during his time. He was a Scotsman and a professor at the University of Glasgow. Smith was a philosopher by training, and his most well-known work is An Enquiry into the Nature and Cause of the Wealth of Nations (1776), which is considered the first major comprehensive book on economics.
One of the most famous passages from this book is: “It is not from the benevolence of the butcher, the brewer, of the baker, that we expect our dinner, but from their regard to their own interest. We address ourselves, not to their humanity but to their self-love, and never talk to them of our own necessities but of their advantage.”
This quote explains that people engage in business not out of kindness but for their own benefit. For example, a butcher, brewer, or baker provides products to earn money, not out of generosity. When we buy their products, we appeal to their desire for profit, not kindness.
Smith’s point is that self-interest when directed properly, benefits everyone. As individuals pursue their own gain, they end up providing goods and services that others need, which is the basis of a free market economy.
Before Adam Smith, the Physiocrats of France were prominent thinkers in political economy.
|
69 videos|377 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Class 12 Economics Long Questions With Answers - Introduction (Macroeconomics)
| 1. What is macroeconomics? |  |
| 2. What are the key topics studied in macroeconomics? |  |
| 3. Why is macroeconomics important? |  |
| 4. How does macroeconomics differ from microeconomics? |  |
| 5. How does macroeconomics impact individuals and businesses? |  |






















