Free Body Diagram | Basic Physics for IIT JAM PDF Download
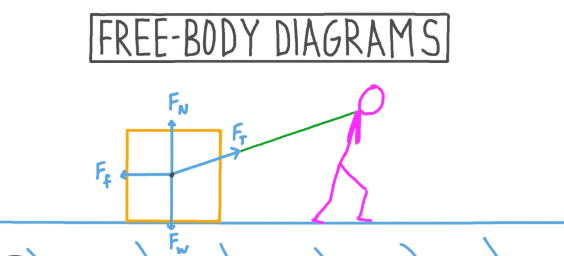
Free Body Diagram
The Free body diagram (FBD) is representation of all forces acting on independent bodies. To draw FBD we assume the body to be a point mass and then we mark all forces acting on it. A suitable coordinate axis may be drawn to resolve the forces along X and Y direction. Some common external forces are discussed below:
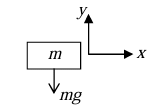
- Weight: The weight of body is w = mg as shown in figure
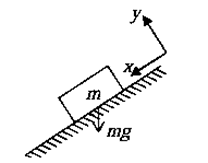
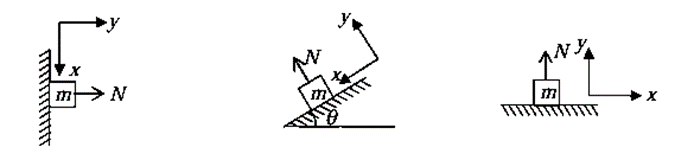
- Normal forces: When a body is in contact with any surface then the surface will exert normal force N ( reaction force). The direction of normal force is perpendicular to the plane of surface. If a Block of mass m is lying on any surface, the surface will push the block in perpendicular direction w.r.t. the plane of the surface with magnitude N and at the same time by Newtons third law the block will push the contact surface with same magnitude but opposite in direction.
Example 1: A Force F of 20N acts on a block m1 = 5 kg such that m2 = 3 Kg is in contact with m1 and m3 = 2 Kg as shown in figure.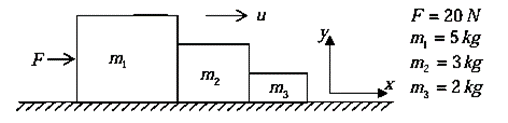
(i) Find acceleration of each block
(ii) Find contact force in each block
Sol: (i) All are moving with same acceleration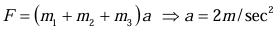 (ii) Free body diagram
(ii) Free body diagram 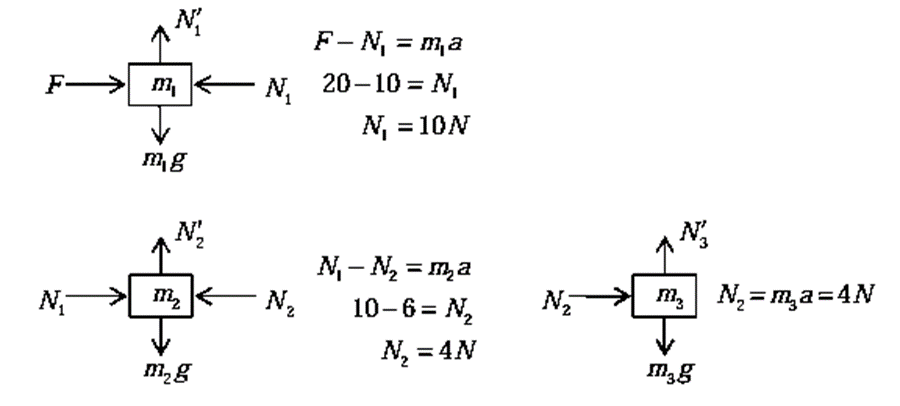
- Tension: Force F is exerted on mass m through string .Then any section of the string is pulled by two equal and opposite forces. Any one of these forces is called tension. Tension always gives pulling effect to mass. In the Figure, the force F is acted on mass m through string so there is tension T in the string giving pulling effect.
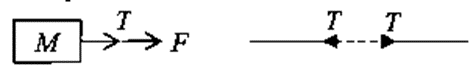
Now let us analyze another system in which two masses m1 and m2 are attached with a string and force F is acted on the mass m1 as shown in figure. Due to force F tension T is developed in the string. If one will draw free body diagram for m1 the tension will act towards left and if free body diagram draw for m2 the tension will act towards right. In both the case tension will produce pulling effect on mass m1 and m2.
String is massless show there is same tension acts on is part of the string.
Free body diagram for mass m1 and m2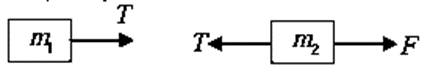
If the rope is massless the tension in string is same for all sections of string other wise it will depend on mass of segment of the rope.
Example 2: Figure shows a block of mass m1 and m2 attached to mass less string. Another mass m3 attached to mass m2 with different mass less string . All contact surface are Smooth. Mass m2 can move vertical downward direction under influence of Gravitation field g. Find the acceleration of each mass and tension in both string.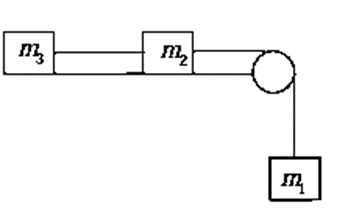
Sol: All forces act on the system shown in figure T and T1 are Tension in first and second string, m1g is weight of mass m1 . The weight of other particle will balanced with their normal force exerted by the surface . Hence length of each string is fixed so all three particle will move will same acceleration .
The free body diagram and equation of motion for mass m1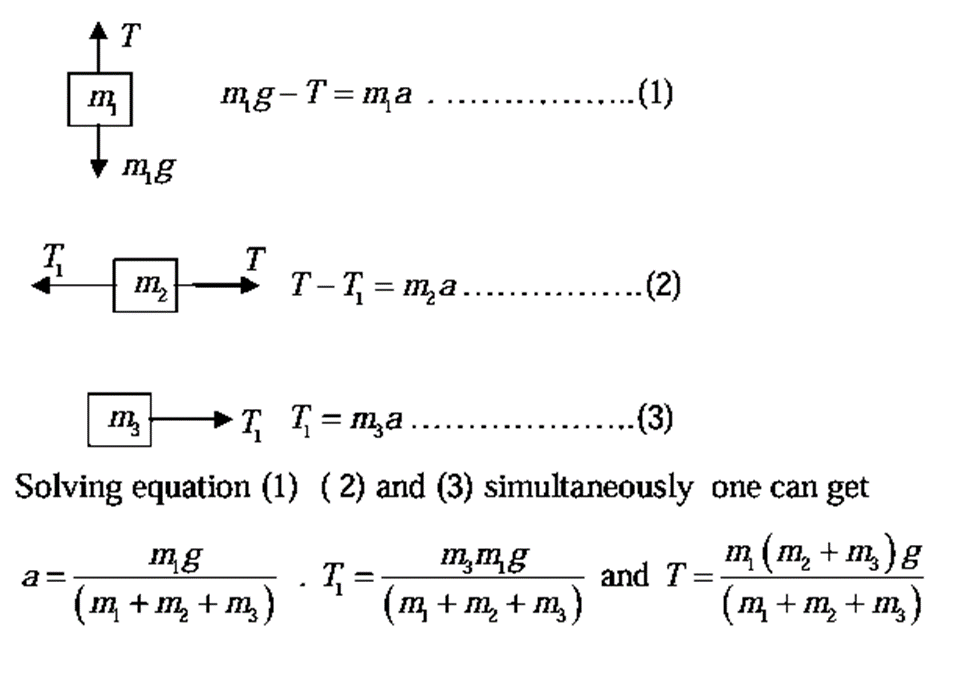
|
217 videos|156 docs|94 tests
|
FAQs on Free Body Diagram - Basic Physics for IIT JAM
| 1. What is a free body diagram and why is it important in physics? |  |
| 2. How do you draw a free body diagram? |  |
| 3. What are common forces represented in a free body diagram? |  |
| 4. How can free body diagrams help in solving physics problems? |  |
| 5. Can free body diagrams be used in real-life situations? |  |

















