Radiation Detection and Detectors | Modern Physics for IIT JAM PDF Download
Human Application
Becquerel’s fogged photographic plate
- The first direct detection of radiation was Becquerel’s fogged photographic plate.
- Photographic film is still the most common detector of ionizing radiation, is used routinely in medical and dental x-rays.
- Nuclear radiation is also captured on film, such as seen in. The mechanism for film exposure by ionizing radiation is similar to that of photons.
- A quantum of energy interacts with the emulsion and alters it chemically, thus exposing the film. The quantum comes from an α-particle, α-particle, or photon provided it has more than the few eV of energy needed to induce the chemical change (as does all ionizing radiation).
- The process is not 100% efficient, since not all incident radiation interacts and not all interactions produce the chemical change.
- The amount of film darkening is related to exposure, but the darkening also depends on the type of radiation, so that absorbers and other devices must be used to obtain energy, charge, and particle-identification information.
- Film badges contain film similar to that used in this dental x-ray film and are sandwiched between various absorbers to determine the penetrating ability of the radiation as well as the amount.
Geiger tube
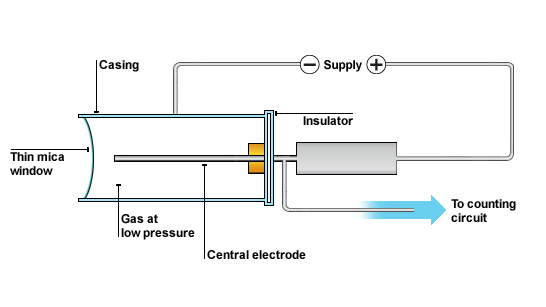
- Another very common radiation detector is the Geiger tube.
- The clicking and buzzing sound we hear in dramatizations and documentaries, as well as in our own physics labs, is usually an audio output of events detected by a Geiger counter.
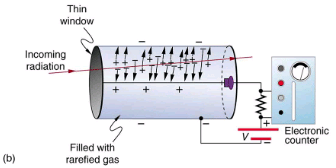
- These relatively inexpensive radiation detectors are based on the simple and sturdy Geiger tube, shown schematically in(b).
- A conducting cylinder with a wire along its axis is filled with an insulating gas so that a voltage applied between the cylinder and wire produces almost no current.
- Ionizing radiation passing through the tube produces free ion pairs that are attracted to the wire and cylinder, forming a current that is detected as a count.
- The word count implies that there is no information on energy, charge, or type of radiation with a simple Geiger counter.
- They do not detect every particle, since some radiation can pass through without producing enough ionization to be detected. However, Geiger counters are very useful in producing a prompt output that reveals the existence and relative intensity of ionizing radiation.
(a) Geiger counters such as this one are used for prompt monitoring of radiation levels, generally giving only relative intensity and not identifying the type of energy of the radiation.
(b) Voltage applied between the cylinder and wire in a Geiger tube causes ions and electrons produced by radiation passing through the gas-filled cylinder to move towards them. The resulting current is detected and registered as a count.

Scintillators and Photomultiplier
- Another radiation detection method records light produced when radiation interacts with materials.
- The energy of the radiation is sufficient to excite atoms in a material that may fluoresce, such as the phosphor used by Rutherford’s group.
- Materials called scintillators to use a more complex collaborative process to convert radiation energy into light. Scintillators may be liquid or solid, and they can be very efficient.
- Their light output can provide information about the energy, charge, and type of radiation.
- Scintillator light flashes are very brief in duration, enabling the detection of a huge number of particles in short periods of time.
- Scintillator detectors are used in a variety of research and diagnostic applications. Among these is the detection by satellite-mounted equipment of the radiation from distant galaxies, the analysis of radiation from a person indicating body burdens, and the detection of exotic particles in accelerator laboratories.
- Light from a scintillator is converted into electrical signals by devices such as the photomultiplier tube shown schematically.
- These tubes are based on the photoelectric effect, which is multiplied in stages into a cascade of electrons, hence the name photomultiplier.
- Light entering the photomultiplier strikes a metal plate, ejecting an electron that is attracted by a positive potential difference to the next plate, giving it enough energy to eject two or more electrons, and so on.
- The final output current can be made proportional to the energy of the light entering the tube, which is, in turn, proportional to the energy deposited in the scintillator.
- Very sophisticated information can be obtained with scintillators, including energy, charge, particle identification, the direction of motion, and so on.
- Photomultipliers use the photoelectric effect on the photocathode to convert the light output of a scintillator into an electrical signal.
- Each successive dynode has a more positive potential than the last and attracts the ejected electrons, giving them more energy.
- The number of electrons is thus multiplied at each dynode, resulting in an easily detected output current.
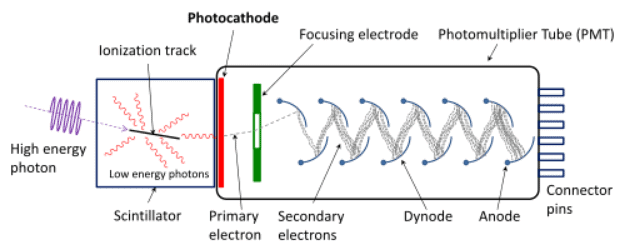 Photomultiplier tube
Photomultiplier tube
- Solid-state radiation detectors convert ionization produced in a semiconductor (like those found in computer chips) directly into an electrical signal.
- Semiconductors can be constructed that does not conduct current in one particular direction.
- When a voltage is applied in that direction, current flows only when ionization is produced by radiation, similar to what happens in a Geiger tube.
- Further, the amount of current in a solid-state detector is closely related to the energy deposited and, since the detector is solid, it can have a high efficiency (since ionizing radiation is stopped at a shorter distance in solids fewer particles escape detection).
- As with scintillators, very sophisticated information can be obtained from solid-state detectors.
Section Summary
Radiation detectors are based directly or indirectly upon the ionization created by radiation, as are the effects of radiation on living and inert materials.
Practice Questions
Q.1. Is it possible for light emitted by a scintillator to be too low in frequency to be used in a photomultiplier tube? Explain.
Q.2. The energy of 30.0 eV is required to ionize a molecule of the gas inside a Geiger tube, thereby producing an ion pair. Suppose a particle of ionizing radiation deposits 0.500 MeV of energy in this Geiger tube. What a maximum number of ion pairs can it create?
1.67104
Q.3. A particle of ionizing radiation creates 4000 ion pairs in the gas inside a Geiger tube as it passes through. What minimum energy was deposited, if 30.0eV is required to create each ion pair?
(a) Repeat, and convert the energy to joules or calories.
(b) If all of this energy is converted to thermal energy in the gas, what is its temperature increase, assuming 50.0 cm3 of an ideal gas at 0.250-atm pressure? (The small answer is consistent with the fact that the energy is large on a quantum mechanical scale but small on a macroscopic scale.)
Q.4. Suppose a particle of ionizing radiation deposits 1.0 MeV in the gas of a Geiger tube, all of which goes to creating ion pairs. Each ion pair requires 30.0 eV of energy.
(a) The applied voltage sweeps the ions out of the gas in 1.00 μs. What is the current?
(b) This current is smaller than the actual current since the applied voltage in the Geiger tube accelerates the separated ions, which then create other ion pairs in subsequent collisions. What is the current if this last effect multiplies the number of ion pairs by 900?
|
52 videos|44 docs|15 tests
|
FAQs on Radiation Detection and Detectors - Modern Physics for IIT JAM
| 1. What is Becquerel's fogged photographic plate? |  |
| 2. How did Becquerel's fogged photographic plate experiment contribute to the understanding of radiation? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of fogged photographic plates in radiation detection? |  |
| 4. How are fogged photographic plates different from modern radiation detectors? |  |
| 5. Can fogged photographic plates still be used in radiation detection today? |  |
















