Introduction to Probability | Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics PDF Download
Probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics that deals with the study chance. Probability deals with the study of experiments and their outcomes.
Probability Key Terms
- Experiment
An experiment in probability is a test to see what will happen incase you do something. A simple example is flipping a coin. When you flip a coin, you are performing an experiment to see what side of the coin you'll end up with. - Outcome
An outcome in probability refers to a single (one) result of an experiment. In the example of an experiment above, one outcome would be heads and the other would be tails. - Event
An event in probability is the set of a group of different outcomes of an experiment. Suppose you flip a coin multiple times, an example of an event would the getting a certain number of heads. - Sample Space
A sample space in probability is the total number of all the different possible outcomes of a given experiment. If you flipped a coin once, the sample space S would be given by:
S = {Head, Tail}
If you flipped the coin multiple times, all the different combinations of heads and tails would make up the sample space. A sample space is also defined as a Universal Set for the outcomes of a given experiment.
Notation of Probability
The probability that a certain event will happen when an experiment is performed can in layman's terms be described as the chance that something will happen.
The probability of an event, E is denoted by
P(E)
Suppose that our experiment involves rolling a die. There are 6 possible outcomes in the sample space, as shown below:
S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
The size of the sample space is often denoted by N while the number of outcomes in an event is denoted by n.
From the above, we can denote the probability of an event as: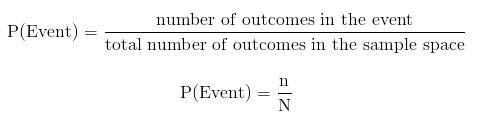
For the sample space given above, if the event is 2, there is only one 2 in the sample space, thus n = 1 and N = 6.
Thus probability of getting a 2 when you roll a die is given by
P(2) = 1/6
Understanding the Magnitude of the Probability of an Event
The largest probability an event can have is one and the smallest is zero. There are no negative probabilities and no probabilities greater than one. Probabilities are real positive numbers ranging from zero to one. The closer the probability is to 1, the more likely the event is to occur while the closer the event is to zero, the less likely the event is to occur.
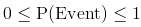
When an event has probability of one, we say that the event must happen and when the probability is zero we say that the event is impossible.
The total of all the probabilities of the events in a sample space add up to one.
Events with the same probability have the same likelihood of occurring. For example, when you flip a fair coin, you are just as likely to get a head as a tail. This is because these two outcomes have the same probability i.e.
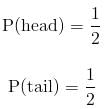
|
2 videos|45 docs|4 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Probability - Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics
| 1. What is probability mathematics? |  |
| 2. How is probability measured? |  |
| 3. What are the basic principles of probability mathematics? |  |
| 4. How is probability applied in real-life situations? |  |
| 5. What are some common probability distributions? |  |





















