Experiments with Water - 1 Class 5 Worksheet EVS Chapter 7
Q1: Which of the following objects dissolve in water?
Write yes for the dissolved one.
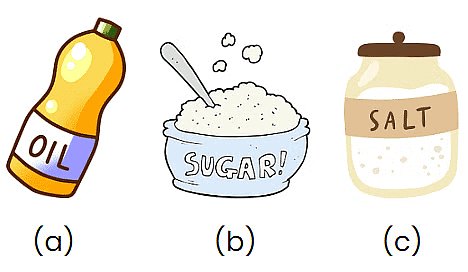
Ans:
(a) No
 View Answer
View Answer 
Oil does not dissolve in water. Instead of mixing, oil floats on top because they have different properties.
(b) Yes
 View Answer
View Answer 
Sugar dissolves in water, meaning it mixes well. When you stir sugar into water, it disappears and makes the water sweet!
(c) Yes
 View Answer
View Answer 
Salt also dissolves in water. When you add salt to water and stir, it breaks down into tiny pieces and makes the water salty and clear.
Q2: Fill in the blanks
(i) Ayesha saw that at first puri ____________ to the bottom of the pan; as puffed up, it started ____________ on the oil.
Ans: Ayesha saw that at first puri sank to the bottom of the pan; as it puffed up, it started floating on the oil.
 View Answer
View Answer 
When Ayesha first dropped the puri into the hot oil, it sank because it was heavy. But as it cooks, air gets inside it, making it lighter and allowing it to float.
(ii) When Ayesha put salt in the boiling water; eggs started ____________.
Ans: When Ayesha put salt in the boiling water, eggs started floating.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Adding salt to water makes the water denser. This means that objects like eggs can float instead of sinking!
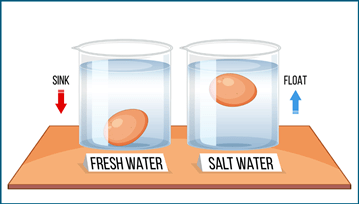 Floating Egg Experiment
Floating Egg Experiment
(iii) On ____________ sugar gets quickly dissolved in water.
Ans: On stirring, sugar gets quickly dissolved in water.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Stirring helps sugar mix better with water. It speeds up the process, making it dissolve faster.
(iv) Oil does not ____________ in water.
Oil does not dissolve in water.
 View Answer
View Answer 
This means that oil and water can’t mix together; they remain separate.
(v) The ____________ made a law that people could not make ____________ even for use at home.
The British made a law that people could not make salt even for use at home.
 View Answer
View Answer 
This law was unfair, as salt is essential for cooking, and it made life difficult for many people.
(vi) The ____________ can be used to make salt.
The seawater can be used to make salt.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Seawater contains a lot of salt. We can extract it to use for cooking and other purposes!
 Sea Water is Salty
Sea Water is Salty
(vii) For making salt, water is allowed to dry in ____.
For making salt, water is allowed to dry in the sun.
 View Answer
View Answer 
When seawater is left out in the sun, the water evaporates, leaving behind salt.
(viii) Dead Sea is the _______ of all.
The Dead Sea is the saltiest of all.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The Dead Sea has a very high concentration of salt, making it much saltier than any ocean or sea!
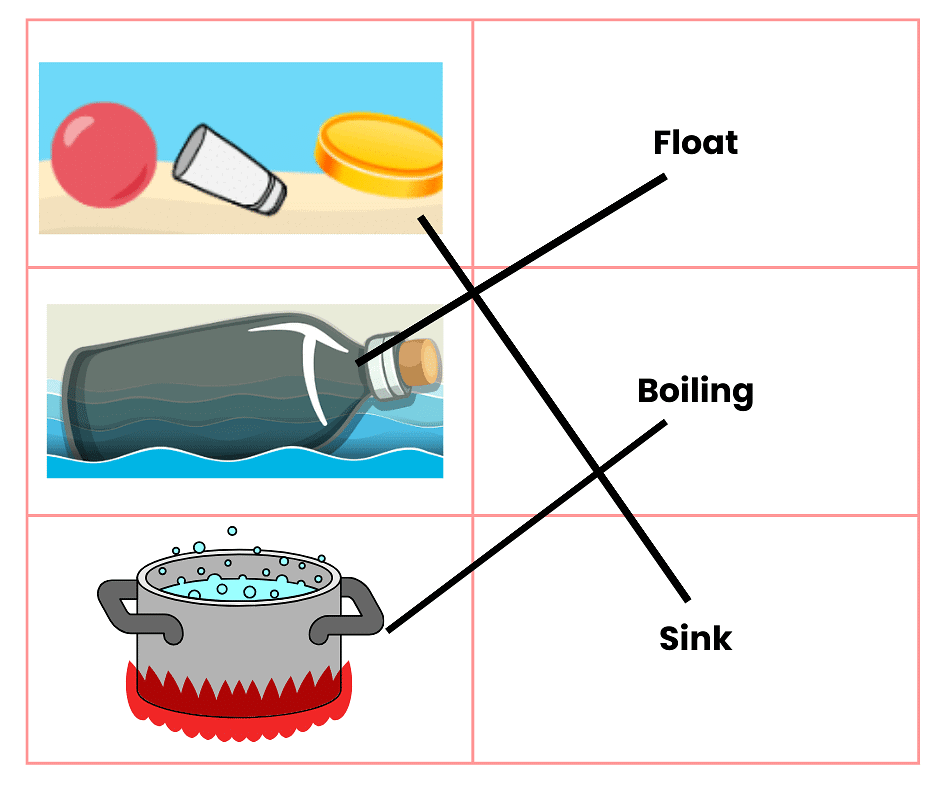
Q3: Match the following
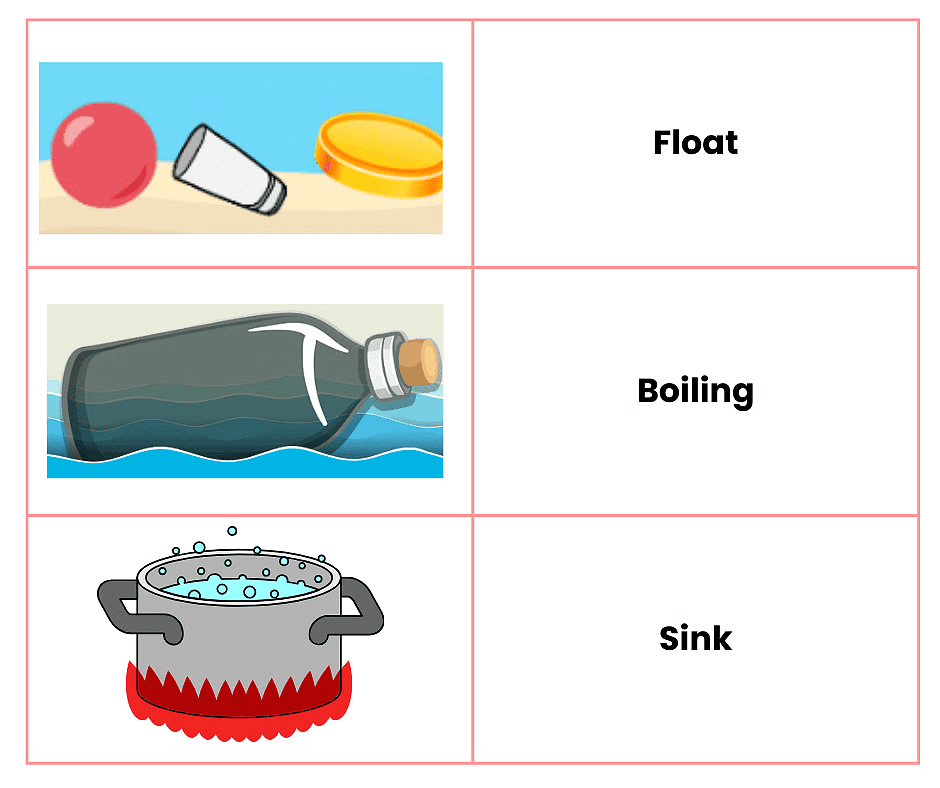 Ans:
Ans:
Q4: True/False
(i) A puffed-up puri will float in water.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Puffed-up puris are light and will float!
(ii) A steel plate sinks in water.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Steel is heavy, so it sinks in water.
(iii) A plastic bottle cap floats in water.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
Plastic is lighter than water, so it floats.
(iv) The Dead Sea has the saltiest water of all seas.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
The Dead Sea is known for its high salt concentration.
 Floating in Dead Sea
Floating in Dead Sea
(v) Oil can easily mix with water.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer 
Oil and water do not mix; they stay separate.
(vi) Sugar and salt do not dissolve in water.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer 
Both sugar and salt dissolve in water and give clear solution.
(vii) Salt is made from seawater.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View Answer 
We can obtain salt from seawater through evaporation.
(viii) Sugar and salt do not dissolve in hot water.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View Answer 
In fact, sugar and salt dissolve even faster in hot water!
Q5: Short answer questions
(i) How would you separate
(a) Salt from water?
Ans:
- You can separate salt from water by boiling it or letting the water evaporate.
- When the water heats up, it turns into steam, and the salt remains behind
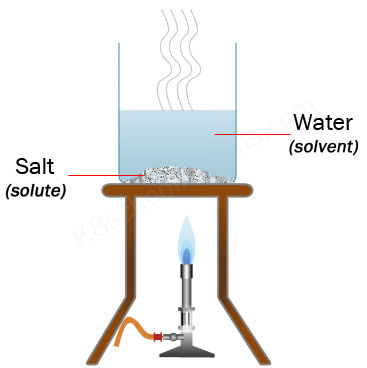 Evaporation: Separating Salt and Water
Evaporation: Separating Salt and Water
(b) Chalk powder from water?
Ans:
- To separate chalk powder from water, you can use evaporation to dry out the water.
- You could also use filtration, where the chalk settles at the bottom, and you pour off the clear water.
(c) Mud from water?
Ans:
- Decantation: You can separate mud from water using decantation. This means letting the mud settle at the bottom and carefully pouring out the clear water.
- Filtration: You can also use filtration, which uses a filter to trap the mud while letting the water pass through.
(ii) Name two factors that help the sugar dissolve in water.
Ans:
- Two important factors that help sugar dissolve in water are stirring and heating (boiling) the water.
- Stirring mixes the sugar evenly, while heat makes the water molecules move faster, helping the sugar dissolve more quickly.
(iii) Does oil dissolve in water? Why?
Ans:
- No, oil does not dissolve in water because it is less dense than water.
- Instead of mixing, oil floats on top of the water because the two liquids have different properties.
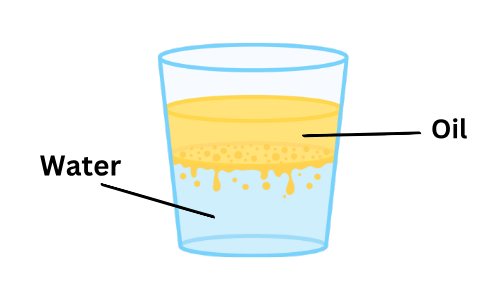 Oil & Water
Oil & Water
Q6: Long answer questions
(i) Why do puris float on oil while frying?
Ans:
- Hot Oil: When puris are fried, the oil is hot.
- Air Inside: As the puris cook, they puff up and get filled with air.
- Lighter Than Oil: The air is lighter than the oil, causing the puris to rise and float on the surface of the oil.
(ii) Why does a soap case float in water while a cake of soap sinks?
Ans:
- Material of Soap Case: The soap case is made of plastic, which is less dense than water.
- Density of Soap Cake: The cake of soap is denser than water.
- Result: Because the soap case is lighter and less dense, it floats, whereas the denser cake of soap sinks.
(iii) Why does an iron nail sink in water while an iron ship floats?
Ans: The density of nails (as of iron) is much larger than that of water. So it sinks easily.
- Density of Nail: An iron nail has a higher density than water, causing it to sink easily.
- Density of Ship: A ship made of iron has a larger volume, which spreads its weight over a greater area.
- Buoyancy: The shape of the ship allows it to displace enough water to create upward buoyant force, making it float, despite being made of the same material as the nail.
(iv) What happens when salt is added to water in which eggs are boiled? Why?
Ans:
- Density of Egg: Eggs are denser than plain tap water, so they sink.
- Adding Salt: When enough salt is added to the water, it increases the density of the water.
- Result: The increased density allows the eggs to float, as the water becomes denser than the eggs themselves.
(v) Which handkerchief will dry faster: one kept in the sun or one kept in the shade? Why?
Ans:
- Handkerchief in the Sun: The handkerchief in the sun dries faster.
- Reason: Sunlight provides heat, which helps evaporate the moisture quickly.
- Handkerchief in the Shade: The one in the shade does not receive sunlight, leading to slower evaporation.
(vi) Why do clothes dry faster on a sunny day than on a cloudy day?
Ans:
- Sunlight and Heat: On sunny days, the sun’s heat helps evaporate the water in clothes faster.
- Molecule Movement: Heat makes water molecules move faster, allowing them to escape as vapor.
- Saturation Levels: The air is less saturated with moisture on sunny days, which also aids in quicker drying compared to cloudy days.
(vii) Look at the picture and write how salt can be obtained from seawater. Ans:
Ans:
- Evaporation Process: Common salt is obtained from seawater through evaporation.
- Setting Up Pools: Seawater is collected in large, shallow pools.
- Sun’s Heat: The sun's heat evaporates the water slowly, leaving behind the salt as it crystallizes.
(viii) Mahatma Gandhi was picking up salt in the picture. In which march (or) movement he did do it? Why did he undertake this march?
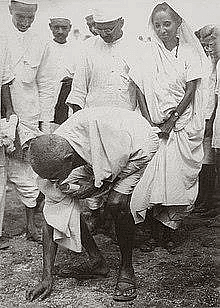 Ans:
Ans:
- March Name: Mahatma Gandhi picked up salt during the Dandi March.
- Reason for the March: The British had imposed a tax on salt, which was an essential item for common people.
- Purpose: The march was organized as a protest against the salt tax, aiming to compel the British government to withdraw it.
(ix) In the given picture a person is floating on water in a lake. What is that lake called? How he can float on water? (or) Why do a person who cannot swim, will not drown in the Dead sea?

Ans:
- High Salt Concentration: The Dead Sea has an extremely high concentration of dissolved mineral salts.
- Density of Water: This makes the water denser than plain fresh water.
- Buoyancy: Since the body’s density is lighter than the water, it becomes more buoyant, making it easy to float.
(x) Ayesha put two drops each of groundnut oil, sugar solution, and water on a stainless steel plate. She tilted the plate and found that some of the drops slid down quickly while some lagged behind. Now answer the following questions.
Which drops slid down faster? Ans:
Ans:
- Faster Sliding Drop: The drop of water slides down the plate the fastest.
- Reason: Water does not stick to the stainless steel plate as much as the sugar solution and oil do, allowing it to move quickly.
(xi) Encircle the things that dissolve in water.
Sugar, Lemon juice, Oil, Fruit juice, Pepsi, Salt, Chalk powder, Mud, Ghee, Mishri (sugar lumps), and Milk.
Ans: Items that Dissolve: The following items dissolve in water:
- Sugar
- Lemon Juice
- Fruit Juice
- Pepsi
- Salt
- Mishri (sugar lumps)
- Milk
(xii) A lemon sinks in a glass of plain water but floats on adding salt in the water. Why?
Ans:
- Sinking in Plain Water: The lemon sinks in plain water because it is denser than the water.
- Floating in Salt Water: When salt is added, it increases the density of the water.
- Result: The lemon floats because the denser saltwater supports it better.
(xiii) Suggest some ways to quickly dissolve sugar in water for making shakkarpara.
Ans:
- Stirring: Stir the mixture of sugar and water thoroughly to help the sugar dissolve faster.
- Heating: Warm the mixture over a flame, which speeds up the dissolving process.
|
37 videos|244 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Experiments with Water - 1 Class 5 Worksheet EVS Chapter 7
| 1. What types of substances typically dissolve in water? |  |
| 2. How can I test if an object dissolves in water? |  |
| 3. Why do some objects not dissolve in water? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of insoluble substances? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of understanding which substances dissolve in water? |  |






















