Losses in Transformers | Electrical Machines for Electrical Engg. - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
There are two types of losses occurs in a transformer:
- Iron loss or Core loss Pi
- Copper loss or I2R loss Pc
Iron loss or core loss (Pi)
Iron loss in transformers is the combination of hysteresis loss (Ph) and eddy current loss (Pe). This type of loss mainly occurs in the magnetic core of the transformer, and depends on magnetic properties of core material.
Pi = Ph + Pe
The formula for hysteresis and eddy current losses is as follows:
Ph = khf Bxm
Pe = kef2 B2m
Where,
kh = It is a constant which is proportional to the volume, quantity of the core material and the units used.
ke = It is a constant which is proportional to the volume, resistivity of the core material, thickness of laminations and the units used.
Bm = maximum flux density in the core.
f = frequency of the alternating flux.
The exponent 'x' is called Steinmetz constant. Depending upon the magnetic properties of the core material its value varies from 1.5 to 2.5.
Therefore the total core loss in the transformer is
Pi = Ph + Pe
Pi = khf Bxm + kef2 B2m
As we know that the voltage applied is approximately equal to the induced voltage in the transformer.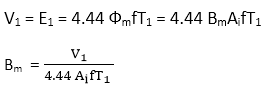
And 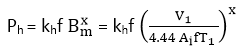
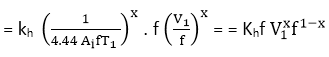
where 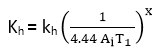
The above relation shows that the hysteresis loss depends upon both the applied voltage and frequency.
Pe = kef2 B2m
The above relation shows that the eddy current loss is proportional to the square of the applied voltage and is independent of frequency.
Since, V1 = 4.44 BmAifTi,
V1 ∝ Bmf
Which means for any voltage if f decreases, Bm increases. Similarly, if f increases, Bm decreases.
The total core loss can be written as
Pi = Kh Vx f1-x+Ke V2
Copper loss or I2R loss (Pc)
The loss which takes place in the primary and secondary winding of the transformer because of the winding resistance is called the Copper loss or I2R loss.
Total copper loss in the transformer = Primary winding copper loss + Secondary winding copper loss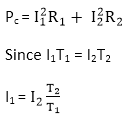
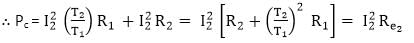
Therefore copper loss varies as the square of the load current.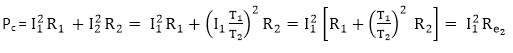
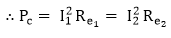
Stray Loss
Eddy current in the conductor, tank, etc., produced by the leakage flux in a transformer is known as stray losses. We can neglect these losses, as the percentage of these losses is very less as compared to iron and copper loss.
Dielectric loss
The losses that occur in insulating materials, i.e., in the transformer oil and the solid insulation of the transformer, are known as a dielectric loss. This loss occurs only in high voltage transformer, and is very small so that we can neglect these losses.
|
35 videos|95 docs|42 tests
|
FAQs on Losses in Transformers - Electrical Machines for Electrical Engg. - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What are the different types of losses in transformers? |  |
| 2. How do hysteresis losses occur in transformers? |  |
| 3. What are eddy current losses in transformers? |  |
| 4. How can core losses be reduced in transformers? |  |
| 5. How can copper losses be minimized in transformers? |  |
















