Past Year Questions: Prestressed Concrete | Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: An inverted T-shaped concrete beam (B1) in the figure, with centroidal axis X − X is subjected to an effective prestressing force of 1000kN acting at the bottom kern point of the beam cross-section. Also consider an identical concrete beam (B2) with the same grade of concrete but without any prestressing force.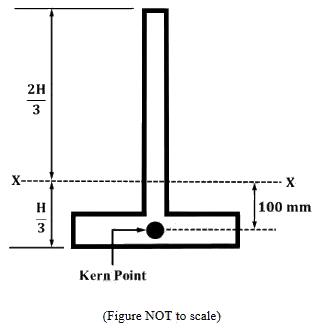
The additional cracking moment (in KNm ) that can be carried by beam B1 m comparison to beam B2 is ______ (rounded off to the nearest integer). [2024, Set-1]
Ans: 299 to 301
Sol: At bottom fibre,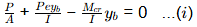
where
P = Prestressing force
e = Eccentricity of P-force
Mcr = cracking moment for beam B1
yt and ybare distance of top and bottom fibre from neutral axis respectively, At top fibre
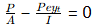
[P-force is at kern point]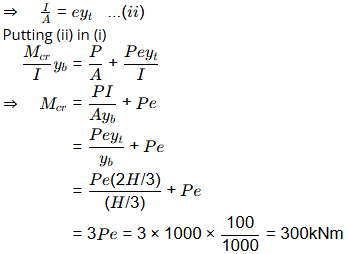
Q2: Consider a balanced doubly reinforced concrete section. If the material and other sectional properties remain unchanged, for which of the following cases will the section becomes under-reinforced? [2024, Set-1]
(a) Area of tension reinforcement is increased.
(b) Area of compression reinforcement is increased.
(c) Area of tension reinforcement is decreased.
(d) Area of compression reinforcement is decreased.
Ans: (b, c)
Sol: In a doubly reinforced balance section, the Ast and Aac are such that the depth of neutral axis is xu,lim or xbal.
To make the above section an under-reinforced section, the strength of compression side has to be increased compared to that of tension side.
This can be done by either increasing the amount of compression reinforcement or decreasing the amount of tension reinforcement.
Hence, the correct options are (B) and (C)
Q1: Consider a doubly reinforced RCC beam with the option of using either Fe250 plain bars or Fe500 deformed bars in the compression zone. The modulus of elasticity of steel is 2 x 105 N/mm2. As per 15456-2000, in which type(s) of the bars, the stress in the compression steel (fsc) can reach the design strength (0.87fy) at the limit state of collapse? [2023, Set-1]
(a) Fe250 plain bars only
(b) Fe500 deformed bars only
(c) Both Fe250 plain bars and Fe500 deformed bars
(d) Neither Fe250 plain bars nor Fe500 deformed bars
Ans: (a)
Sol: In a doubly reinforced beam, at the limit state of collapse. The strain in the extreme corrosion fibre will be 0.0035 . As the compression reinforcement will be below this, the strain in if will be 0.0035. As the compression reinforcement will be below this, the strain in if will be always less than 0.0035.
For Fe250, the yield strain
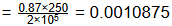
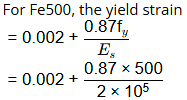
= 0.004175 > 0.0035
So, it is possible that Fe250 can reach upto its yield strain and hence can reach the design strength 0.87f y.
Q2: A singly reinforced concrete beam of balanced section is made of M20 grade concrete and Fe415 grade steel bars. The magnitudes of the maximum compressive strain in concrete and the tensile strain in the bars at ultimate state under flexure, as per IS 456 : 2000 are _______ respectively. (round off to four decimal places) [2023, Set-1]
(a) 0.0035 and 0.0038
(b) 0.0020 and 0.0018
(c) 0.0035 and 0.0041
(d) 0.0020 and 0.0031
Ans: (a)
Sol: Given data,
Grade of concrete M-20
Grade of steel Fe-415
Balanced section, singly reinforced beam.
As per Clause No. 38.1, 1S 456 : 2000,
Maximum strain in concrete at the outermost compression fibre = 0.0035
and strain in the tension reinforcement for balanced section at ultimate state under flexure
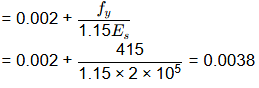
Hence, correct answer is (A).
Q1: A post-tensioned concrete member of span 15 m and cross-section of 450 mm×450 mm is prestressed with three steel tendons, each of cross-sectional area 200 mm2. The tendons are tensioned one after another to a stress of 1500MPa. All the tendons are straight and located at 125 mm from the bottom of the member. Assume the prestress to be the same in all tendons and the modular ratio to be 6 . The average loss of prestress, due to elastic deformation of concrete, considering all three tendons is [2022, Set-2]
(a) 14.16MPa
(c) 7.08MPa
(c) 28.32MPa
(d) 42.48MPa
Ans: (a)
Sol: This is a question of calculation of elastic shortening loss in post tensioned member.
Given data,
length = 15 m
b x D = 450 mm x 450 mm
Number of tendons = 3
Cross-section area of each tendon (As) = 200mm2.
Prestress = 1500 MPa
Modular ratio (m) = 6
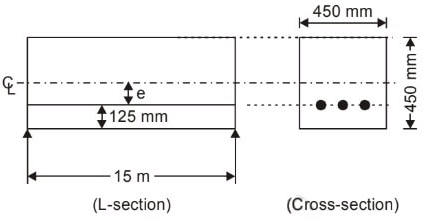
From the given data, eccentricity (e) = 450/2 - 125 = 100 mm
Force in each cable (P) = 1500 × 200 × 10-3 = 300kN
The tendons are tensioned one after another, and hence when tendon (1) is pulled no loss in tenson (1)
When tendon (2) is pulled, loss in tendon (1) but no loss in tendon (2).
When tendon (3) is pulled, loss in tendon (1) and (2), but no loss in tendon (3).
Hence, there will be 2 times losses in tendon (1), time loss in tendon (1) and no loss in tendon (3).
While calculating elastic shortening loss, self weight of the structure is neglected to be on the conservative side.
Consider tensioning of tendon-1
No loss in tendon (1)
Consider tensioning of tendon-2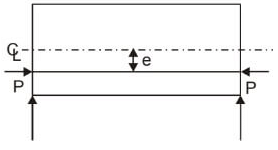 Stress in concrete at the level of prestressing tendon
Stress in concrete at the level of prestressing tendon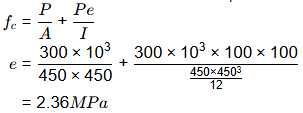
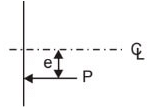 I = moment of inertial of the section about the centroidal axis.
I = moment of inertial of the section about the centroidal axis.
As the tendons are horizontal and at the same level fc,avg = fc.
Loss due to elastic deformation = mfc = 6 × 2.36 = 14.16MPa.
Considering tensioning of tendon 3
Loss due to elastic deformation in (1) = mfc = 6 × 2.36 = 14.16MPa.
Loss due to elastic deformation in (2) = mfc = 6 × 2.36 = 14.16MPa.
Total loss in tendon (1) = 2 x 14.16 = 28.32 MPa
In tendon (2) = 14.16 MPa
In tendon (3) = 0
Average loss of pre-stress, considering all three tendons is =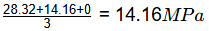
Q1: A prismatic cantilever prestressed concrete beam of span length, L = 1.5 m has one straight tendon placed in the cross-section as shown in the following figure (not to scale). The total prestressing force of 50kN in the tendon is applied at dc = 50 mm from the top in the cross-section of width, b = 200 mm and depth, d = 300 mm. [2021, Set-1]
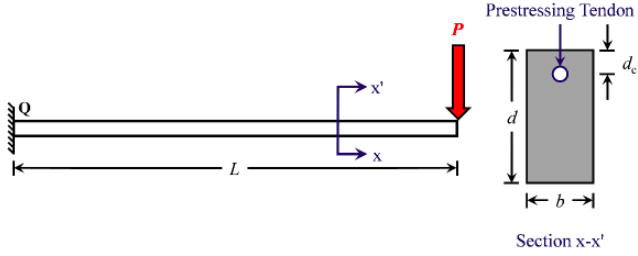
If the concentrated load, P = 5 kN, the resultant stress (in Mpa, in integer) experienced at point 'Q' will be _________
Ans: 0
Sol: 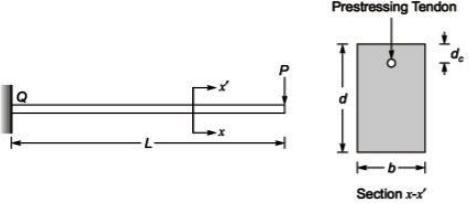
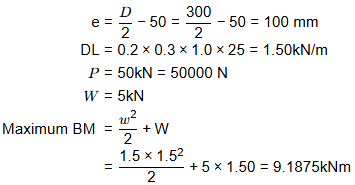
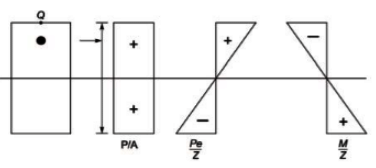
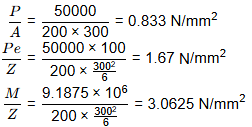
Stress at Q,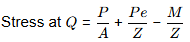
= 0.833 + 1.67 - 3.0625
= -0.56 N/mm2 (Tensile)
Q1: A concrete beam of span 15 m,150 mm wide and 350 mm deep is prestressed with a parabolic cable as shown in the figure (not drawn to the scale). Coefficient of friction for the cable is 0.35 , and coefficient of wave effect is 0.0015 per metre.
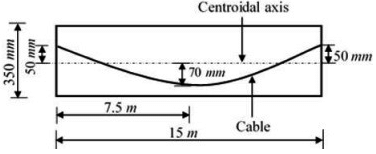 If the cable is tensioned from one end only, the percentage loss (round off to one decimal place) in the cable force due to friction, is ________. [2020, Set-2]
If the cable is tensioned from one end only, the percentage loss (round off to one decimal place) in the cable force due to friction, is ________. [2020, Set-2]
Ans: 3.8 to 4.7
Sol: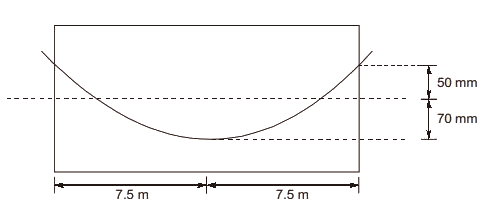 x = L = 15 m
x = L = 15 m
Wobble correction factor, K = 0.0015
Coefficient of friction = 0.35 = μ
P = Not given
p0 = Unknown
Change of gradient, α = tanα = 8h/L = 8x120 / 15000 = 0.064
% loss of stress in steel due to friction
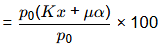
= (0.0015 × 15 + 0.35 × 0.064) × 100
= 4.49%
Q2: A simply supported prismatic concrete beam of rectangular cross-section, having a span of 8 m, is prestressed with an effective prestressing force of 600 kN. The eccentricity of the prestressing tendon is zero at supports and varies linearly to a value of e at the mid-span. In order to balance an external concentrated load of 12 kN applied at the mid-span, the required value of e (in mm, round off to the nearest integer) of the tendon, is _______. [2020, Set-1]
Ans: 39 to 41
Sol: 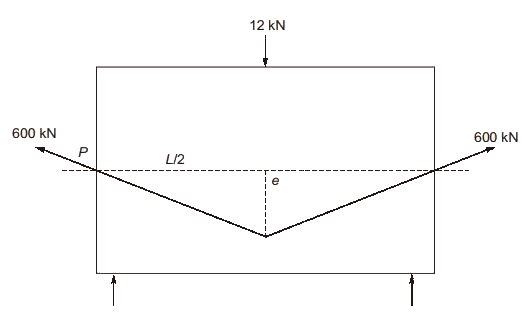 P = 600 kN
P = 600 kN
Simply supported span = L = 8 m
To support a point load applied at mid span (W) = 12 kN
Balancing load = Point load
Q1: A 3m × 3m square precast reinforced concrete segments to be installed by pushing them through an existing railway embankment for making an underpass as shown in the figure. A reaction arrangement using precast PCC blocks placed on the ground is to be made for the jacks.
At each stage, the jacks are required to apply a force of 1875kN to push the segment. The jacks will react against the rigid steel plate placed against the reaction arrangement. The footprint area of reaction arrangement on natural ground is 37.5 m2. The unit weight of PCC block is 24kN/m3. The properties of the natural ground are: c = 17kPa; ϕ = 25 and = 1 8kN/m3. Assuming that the reaction arrangement has rough interface and has the same properties that of soil, the factor of safety (round off to 1 decimal place) against shear failure is ______ [2019, Set-1]
Ans: 1.8 to 2.1
Sol: Weight of Precast PCC block,
W = volume x γc = 37.5 × 7.5 × 24 = 6750kN
Shear resistance below the Precast PCC block is,
S = C.A + W tan ϕ
F.O safety against shear failure,
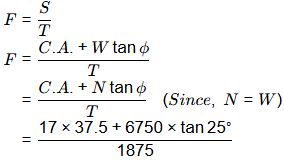
= 2.0187 ≈ 2.0
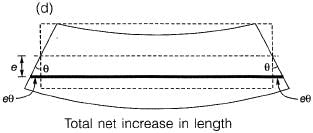
Q1: A 6 m long simply-supported beam is prestressed as shown in the figure.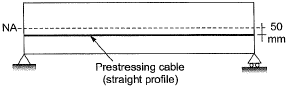
The beam carries a uniformly distributed load of 6 kN/m over its entire span. If the effective flexural rigidity EI = 2 x 104 kNm2 and the effective prestressing force is 200 kN, the net increase in length of the prestressing cable (in mm, up to two decimal places) is ________ . [2018, Set-2]
Ans: 0.1 to 0.12
Sol: Span of PSC beam = 6 m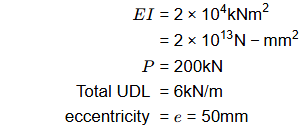
(a) Slope of beam due to P-force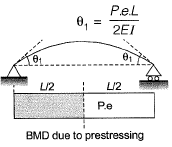
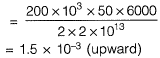
(b) Slope of beam due to UDL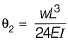
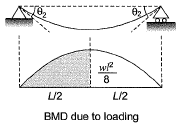
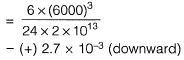
(c) Net slope of beam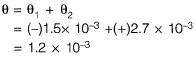
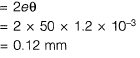
Q1: A simply supported rectangular concrete beam of span 8 m has to be prestressed with a force of 1600 kN. The tend on is of parabolic having zero eccentricity at the supports. The beam has to carry an external uniformly distributed load of intensity 30 kN/m. Neglecting the self-weight of the beam, the maximum dip (in meters, up to two decimal places) of the tendon at the mid-span to balan ce the external load should be _____ . [2017, Set-2]
Sol:
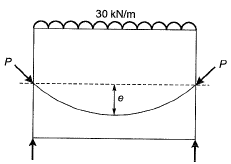
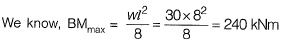
Note: Tendon profile shall follow the shape of bending moment diagram.
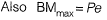
∴ 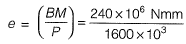
e = 150 mm
e =0.15 m
Q2: A pre-tensioned rectangular concrete beam 150 mm wide and 300 depth is prestressed with three straight tendons, each having a cross- sectional area of 50 mm2 , to an initial stress of 1200 N/mm2. The tendons are located at 100 mm from the soffit of the beam. If the modular ratio is 6, the loss of prestressing force (in kN, up to one decimal place) due to the elastic deformation of concrete only is _________. [2017 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
Solution:
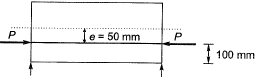
Prestressing force,
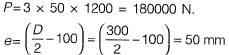
Stress in concrete at the location of steel
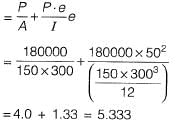
Loss of stress
= m x fc = 6 x 5.3333 = 32 N/mm2
Loss of prestressing force
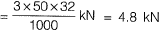
Q3: In a pre-stressed concrete beam section shown in the figure, the net loss is 10% and the final pre-stressing force applied at X is 750 kN. The initial fiber stresses (in N/mm2) at the top and bottom of the beam were: [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-II]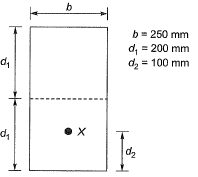
(a) 4.166 and 20.833
(b) -4.166 and -20.833
(c) 4.166 and -20.833
(d) -4.166 and 20.833
Ans: (D)
Solution:
Given, net loss = 10%
Final prestressing force after loss = 750 kN
Hence, initial prestressing force
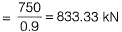
Initial stresses at top and bottom
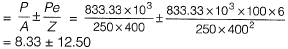
Stress at top = 8.33 - 12.50 = - 4.17 (tensile)
Stress at bottom = 8.33 + 12.50 = 20.83 (Comp.)
Q4; A rectangular concrete beam 250 mm wide and 600 mm deep is prestressed by means of 16 wire of high tensile steel wires, each of 7 mm dia. located at 200 mm from the bottom face of the beam at a given section. If the effective prestress in the wires is 700 MPa. What is the maximum sagging BM (in kN-m) due to live load which this section of the beam can withstand without causing tensile stresses at the bottom face of the beam. Neglect the self weight of the beam. [2013 : 2 Marks]
Solution:
Since the tensile stress at bottom face of the beam is zero.
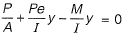
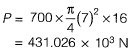
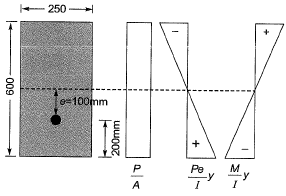
Since the prestressing force is located at 200 mm from the bottom face of the beam.
∴ Eccentricity = 300 - 200 = 100 mm
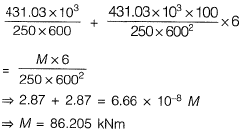
Q5: Which one of the following is categorised as a long-term loss of prestresss in a pre-stressed concrete member? [2012 : 1 Mark]
(a) Loss due to elastic shortening
(b) Loss due to friction
(c) Loss due to relaxation of strands
(d) Loss due to anchorage slip
Ans: (C)
Solution: Loss due to relaxation, shrinkage of concrete and due to creep are long term losses.
Q6: A concrete beam pre-stressed with a parabolic tendon is shown in the sketch. The eccentricity of the tendon is measured from the centroid of the cross-section. The applied pre-stressing force at service is 1620 kN. The uniformly distributed load of 45 kN/m includes the self-weight.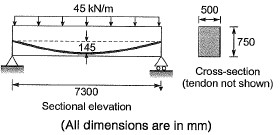
The stress (in N/mm2) in the bottom fibre at midspan is [2012 : 2 Marks]
(a) tensile 2.90
(b) compressive 2.90
(c) tensile 4.32
(d) compressive 4.32
Ans. (B)
Solution:
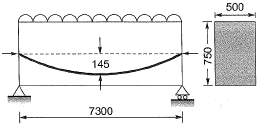
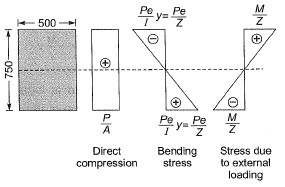
Total stress at Bottom = 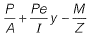

FAQs on Past Year Questions: Prestressed Concrete - Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is the basic principle of prestressed concrete? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of using prestressed concrete in construction? |  |
| 3. What are the common methods of prestressing concrete? |  |
| 4. How does the design process for prestressed concrete structures differ from conventional concrete? |  |
| 5. What are the typical applications of prestressed concrete in civil engineering? |  |






















