Past Year Questions: Levelling & Contouring | Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: Differential levelling is carried out from point P (B N + 200.000 m) to point R. The reading taken are given in the table.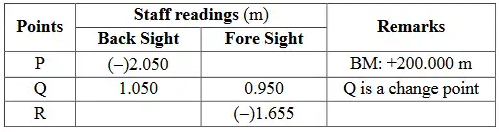
Reduced level (in meters) of the point R is ______(rounded off to 3 decimal places) [2024, Set-II]
Ans: 199.704 to 199.706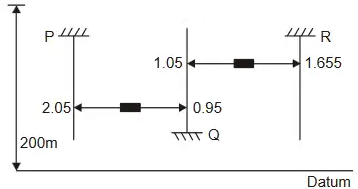 Using go through line (starting from P)
Using go through line (starting from P)
− 2.05 + 0.1 + 1.655 = − 0.295
(means R R is 0.295 lower than P)
∴ RL of R = 200 − 0.295
= 199.705
Q2: A map is prepared with a scale of 1: 1000 and a contour interval of 1 m. If the distance between two adjacent contours on the map is 10 mm, the slope of the ground between the adjacent contours is [2024, Set-I]
(a) 30 % 30%
(b) 10 % 10%
(c) 35 % 35%
(d) 40 % 40%
Ans: (b)
Given, contour Interval = 1 m
Distance between contour in map =10 mm
Map scale = 1/1000
∴ Distance between contour = 10 × 1000 = 10 × 1000 mm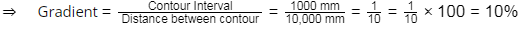
Q3: Trigonometric levelling was carried out from two stations P and Q to find the reduced level (R.L.) of the top of hillock, as shown in the table. The distance between stations P and Q is 55 m. Assume stations P and Q, and the hillock are in the same vertical plane. The R. L. of the top of the hillock (in m m ) is _____ (round off to three decimal places) [2023, Set-I]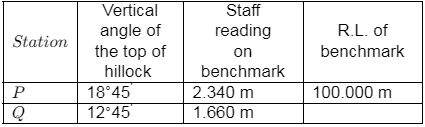 Ans: 137.5 to 137.73
Ans: 137.5 to 137.73
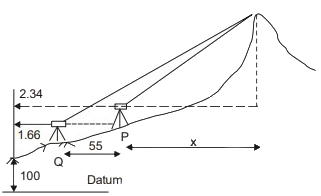 While taking reading from P,
While taking reading from P,
RL of hillock = HIP + x tan18∘ 45 ′
= 100 + 2.34 + x tan 18∘45 ′
While taking reading from Q.
RL of hillock = HIQ + (x + 55) tan 12∘ 45′
= 100 + 1.66 + (x + 55) tan 12∘ 45′
Equating both,
100 + 2.34 + x tan 18∘45′ = 100 + 1.66 + (x + 55) tan 12∘45′
2.34 + 0.339x = 1.66 + 12.445 + 0.226
∴ x = 104.115
∴ RL of hillock
= 100 + 2.34 + 104.115 tan 18∘45′
= 137.682
Q4: Which of the following is NOT a correct statement? [2021, Set-I]
(a) The first reading from a level station is a 'Fore Sight'
(b) Basic principle of surveying is to work from whole to parts
(c) Contours of different elevations may intersect each other in case of an overhanging cliff
(d) Planimeter is used for measuring 'area'
Ans: (a)
First reading from level station is called BS.
Q5: A series of perpendicular offsets taken from a curved boundary wall to a straight survey line at an interval of 6 m are 1.22,1.67, 2.04, 2.34, 2.14, 1.87, and 1.15 m. The area (in m2, round off to 2 decimal places) bounded by the survey line, curved boundary wall, the first and the last offsets, determined using Simpson's rule, is__________. [2019: 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans:
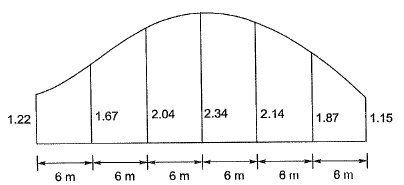
Area by Simpson’s rule
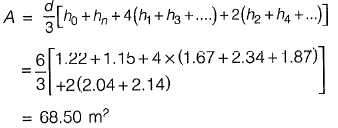
Q6: A staff is placed on a benchmark (BM) of reduced level (RL) 100.000 m and a theodolite is placed at a horizontal distance of 50 m from the BM to measure the vertical angles. The measured vertical angles from the horizontal at the staff readings of 0.400 m and 2.400 m are found to be the same. Taking the height of the instrument as 1.400 m, the RL (in m) of the theodolite station is_______. [2019 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
Ans:
HI = RL of BM + BS
= 100 + (0.4 + 1)
= 101.4
RL of Theodolite station
= Hl-height
= 101.4 - 1.4
= 100 m
Q7: A level instrument at a height of 1.320 m has been placed at a station having a Reduced Level (RL) of 112.565 m. The instrument reads -2.835 m on a levelling staff held at the bottom of a bridge deck. The RL (in m) of the bottom of the bridge deck is [2018 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
(a) 116.720
(b) 116.080
(c) 114.080
(d) 111.050
Ans: (a)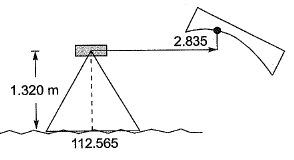 RL of bottom of bridge deck
RL of bottom of bridge deck
= 112.565 + 1.320 + (2.835)
= 116.720 m
Q8: An observer standing on the deck of a ship just sees the top of a lighthouse. The top of the lighthouse is 40 m above the sea level and the height of the observer’s eye is 5 m above the sea level. The distance (in km, up to one decimal place) of the observer from the lighthouse is _____. [2017 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans: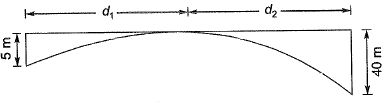 Distance of observer from the lighthouse,
Distance of observer from the lighthouse,
Q9: The vertical angles subtended by the top of a tower T at two instrument stations set up at P and Q, are shown in the figure. The two stations are in line with the tower and spaced at a distance of 60 m. Readings taken from these two stations on a leveling staff placed at the benchmark (BM = 450.000 m) are also shown in the figure. The reduced level of the top of the tower T (expressed in m) is__________ [2016 : 2 Marks, Set-I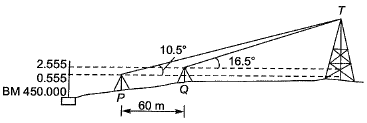 Ans:
Ans: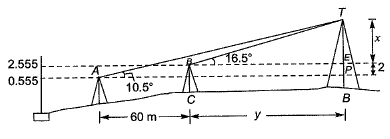 In ΔBET,
In ΔBET,
tan 16.5° = x/y
⇒ y = 3.3759x .....(i)
In ΔAOT,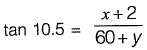 ......(ii)
......(ii)
Put value of y in eg. (ii)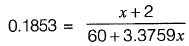
11.1203 + 0.6255x = x + 2
x = 24.3568 m
So, the reduced level of tower,
T = 450.000 + 2.555 + 24.356
= 476.911 m
Q10: The staff reading taken on a workshop floor using a level is 0.645 m. The inverted staff reading taken to the bottom of a beam is 2.960 m. The reduced level of the floor is 40.500 m. The reduced level (expressed in m) of the bottom of the beam is [2016 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
(a) 44.105
(b) 43.460
(c) 42.815
(d) 41.145
Ans: (a)
Height of instrument, HI
= R.L. of floor + staff reading from floor
= 40.500 + 0.645
= 41.145 m
R.L. of bottom of beam
= HI + inverted staff reading taken from bottom of beam
= 41.145 + 2.960
= 44.105 m
Q11: Two pegs A and B were fixed on opposite banks of a 50 m wide river. The level was set up at A and the staff readings on Pegs A and B were observed as 1.350 m and 1.550 m, respectively. Thereafter the instrument was shifted and set up at B. The staff readings on Pegs B and A were observed as 0.750 m and 0.550 m, respectively. If the R.L. of Peg A is 100.200 m, the R.L. (in m) of Peg B is _____. [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans: Staff readings shows that station B is below station A.
a1 = 1.350
a2 = 0.550
b3 = 1.550
b2 = 0.750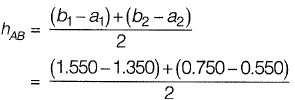
= 0.200
RL of B = RL of A - 0.200
= 100.200-0.200
= 100.000 m
Q12: The combined correction due to curvature and refraction (in m) for distance of 1 km on the surface of Earth is [2015 : 1 Mark, Set-II]
(a) 0.0673
(b) 0.673
(c) 7.63
(d) 0.763
Ans: (a)
Correction due to curvature,
Cc = -0.0785 d2
Correction due to refraction,
Cr = +0.0112 d2
Composite correction,
C = -0.0785d2 + 0.0112 d2
= -0.0673 d2
where d is in km, C is in m,
⇒ 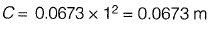
Q13: In a leveling work, sum of the Back Sight (B.S.) and Fore Sight (F.S.) have boon found to be 3.085 m and 5.645 m respectively. If the Reduced Level (R.l.) of the starting station is 100.000 m, the R.L. (in m) of the last station is [2015 : 1 Mark, Set-II]
Ans: Using Rise and Fall method,
∑F.S. > ∑B.S.
∴ Fall = ∑F.S. - ∑B.S. = R.L. of first station - R.L. of last station = 5.645-3.085 = 2.56 m
R.L. (last station) = R.L. (first station) - Fall
= 100 - 2.56 = 97.44 m
Q14: Which of the following statements is FALSE? [2015 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
(a) Plumb line is along the direction of gravity
(b) Mean Sea Level (MSL) is used as a reference surface for establishing the horizontal control
(c) Mean Sea Level (MSL) is a simplification of the Geoid
(d) Geoid is an equi-potential surface of gravity
Ans: (b)
Mean sea level (MSL) is used as a reference surface for establishing the vertical control.
Q15: A levelling is carried out to establish the Reduced Levels (RL) of point R with respect to the Bench Mark (BM) at P. The staff readings taken are given below: [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-I]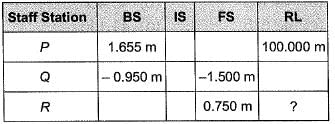 If RL of P is +100.000 m, then RL (in m) of R is
If RL of P is +100.000 m, then RL (in m) of R is
(a) 103.355
(b) 103.155
(c) 101.455
(d) 100.355
Ans: (c)
HI = RL + BS
and RL = HI - FS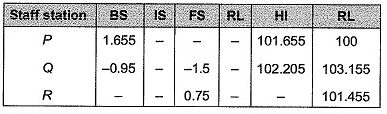
∴ RL of R = 101.455 m
Q16: The Reduced Levels (RLs) of the points Pand Q are +49.600 m and +51.870 m respectively. Distance PQ is 20 m. The distance (in m from P) at which the +51.000 m contour cuts the line PQ is [2014 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
(a) 15.00
(b) 12.33
(c) 3.52
(d) 2.27
Ans: (b)
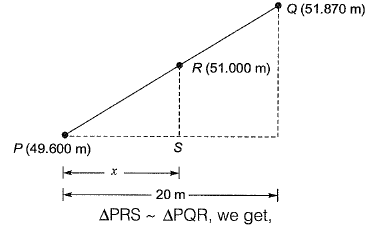
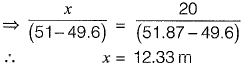
Q17: The horizontal distance between two stations P and Q is 100 m. The vertical angles from P and Q to the top of a vertical tower at T are 3° and 5° above horizontal, respectively. The vertical angles from P and Q to the base of the tower are 0.1° and 0.5° below horizontal, respectively. Stations P, Q and the tower are in the same vertical plane with P and Q being on the same side of T. Neglecting earth's curvature and atmospheric refraction, the height (in m) of the tower is [2012 : 2 Marks]
(a) 6.972
(b) 12.387
(c) 12.540
(d) 128.745
Ans: (b)
x (tan 3 + tan 0.1) = (x - 100) (tan5° + tan0.5°)
⇒ x = 228.758
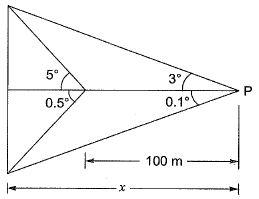 Height of tower= 228.758 (tan 3° + tan0.1°)
Height of tower= 228.758 (tan 3° + tan0.1°)
= 12.387 m
Note: Question has erroreous data, hence many other answers are also possible.
Q18: Which of the following errors can be eliminated by reciprocal measurements in differential leveling? [2012 : 1 Mark]
I. Error due to earth’s curvature
II. Error due to atmospheric refraction
(a) Both I and II
(b) I only
(c) II only
(d) Neither I nor II
Ans: (a)
Reciprocal levelling eliminates the errors due to
(i) Error in instrument adjustment.
(ii) Combined effect of earth’s curvature and the refraction of the atmosphere.
(iii) Variation in the average refraction.
Q19: Curvature correction to a staff reading in a differential leveling survey is [2011 : 1 Mark]
(a) always subtractive
(b) always zero
(c) always additive
(d) dependent on latitude
Ans: (a)
Q20: A bench mark has been established at the soffit of an ornamental arch at the known elevation of 100.0 m above mean sea level. The back sight used to establish height of instrument is an inverted staff reading of 2.105 m. A forward sight reading with normally held staff of 1.105 m is taken on a recently constructed plinth. The elevation of the plinth is [2010 : 2 Marks]
(a) 103.210 m
(b) 101.000 m
(c) 99.000 m
(d) 96.790 m
Ans: (d)
Height of instrument = BM + Back sight
Since the staff is inverted, the back sight will be negative.
∴ Height of instrument
= 100 + (- 2.105) = 97.897 m
Elevation of plinth = Height of instrument- Fore sight
= 97.895-1.105 = 96.790 m
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Levelling & Contouring - Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is the purpose of leveling and contouring in land surveying? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of leveling techniques used in surveying? |  |
| 3. How do contour lines indicate the steepness of terrain? |  |
| 4. What equipment is commonly used for leveling in surveying? |  |
| 5. What are the common mistakes to avoid while performing leveling and contouring? |  |
















