Past Year Questions: Sources of Water Supply, Distribution System & Well Hydraulics | Environmental Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: A 30 cm diameter well fully penetrates an unconfined aquifer of saturated thickness 20 m with hydraulic conductivity of 10 m day. Under the steady pumping rate for a long time, the drawdowns in two observation wells located at 10 m and 100 m from the pumping well are 5 m and 1 m. respectively. The corresponding pumping rate (in m3 day) from the well is (rounded off to 2 decimal places). (2024 SET-1)
Ans: 1852 to 1858
Sol: Thickness of aquifer, H = 20 m
r1 = 10 m
r2 = 100 m
h2 = H − Sw1 = 20 − 5 = 15 m
h1 = H − Sw2 = 20 − 1 = 19 m
Now discharge for unconfined aquifer is given as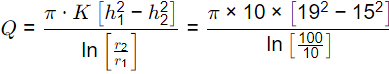
Q = 1855.55 m3/day.
Q1: The concentration s(x, t) of pollutants in a one-dimensional reservoir at position x and time t satisfies the diffusion equation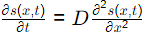 on the domain 0 ≤ x ≤L, where D is the diffusion coefficient of the pollutants. The initial condition s(x, 0) is defined by the step-function shown in the figure.
on the domain 0 ≤ x ≤L, where D is the diffusion coefficient of the pollutants. The initial condition s(x, 0) is defined by the step-function shown in the figure.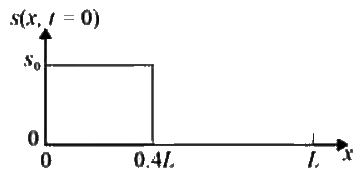
The boundary conditions of the problem are given by 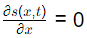 at the boundary points x = 0 and x = L at all times. Consider D = 0.1m2/s, s0 = 5μmol/m and L = 10m.
at the boundary points x = 0 and x = L at all times. Consider D = 0.1m2/s, s0 = 5μmol/m and L = 10m.
The steady-state concentration 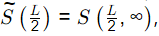 at the center x = L/2 of the reservoir (in μ mol/m) is ___________. (in integer) (2022 SET-2)
at the center x = L/2 of the reservoir (in μ mol/m) is ___________. (in integer) (2022 SET-2)
Ans: 2 to 2
Sol: From figure s(x, t)
at x = 0 ⇒ s(0, t) = s0 = 5
at x = 0.4L ⇒ s(0.4L, t) = s0 = 5
at x = L ⇒ s(L, t) = 0
From x = 0 to x = 0.4L
Concentration of pollutant 5μ mol/m × (0.4 × 10m) = 20μ mol
x = 0.4L to x = L
Concentration of pollutant = 0
Total concentration of pollutant in 10 m = 20 μmol
In infinite time this concentration will be diluted so concentration of pollutant per m
= (20/10)μ mol/m = 2μ mol/m
Under steady state condition, concentration of pollutant will be uniformly distributed.
Steady state concentration at x = L/2 = 2μ mol/m
Q1: A lake has a maximum depth of 60 m. If the mean atmospheric pressure in the lake region is 91 kPa and the unit weight of the lake water is 9790 N/m3, the absolute pressure (in kPa, round off to two decimal places) at the maximum depth of the lake is ___________ (2021 SET-2)
Ans: (677.5 to 679.5)
Sol: Absolute pressure at maximum depth of the lake = Patm + ρgh 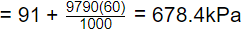
Q1: Dupuit’s assumptions are valid for [2018 : 1 Mark, Set-II]
(a) artesian aquifer
(b) confined aquifer
(c) leaky aquifer
(d) unconfined aquifer
Ans: (d)
Sol: Dupuit’s theory assumptions hold that groundwater flows horizontally in an unconfined aquifer and that ground water discharge is proportional to saturated aquifer thickness.
Q1: Water table of an aquifer drops by 100 cm over an area of 1000 km2. The porosity and specific retention of the aquifer material are 25% and 5%, respectively. The amount of water (expressed in km3 ) drained out from the area is__________.. [2016 : 1 Mark, Set-II]
Ans: 0.2km3
Sol: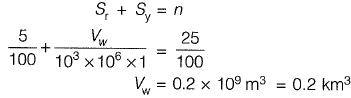
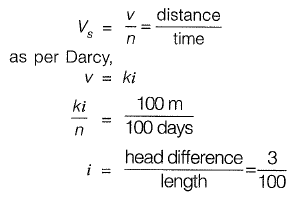
Q2: A tracer takes 100 days to travel from Well-1 to Well-2 which are 100 m apart. The elevation of water surface in Well-2 is 3 m below that in Well-1. Assuming porosity equal to 15%, the coefficient of permeability (expressed in m/day) is [2016 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
(a) 0.30
(b) 0.45
(c) 1.00
(d) 5.00
Ans: (d)
Sol: Seepage velocity
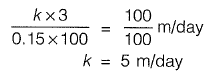
Q3: The hardness of a ground water sample was found to be 420 mg/L as CaC03. A softener containing ion exchange resins was installed to reduce the total hardness to 75 mg/L as CaC03 before supplying to 4 households. Each household gets treated water at a rate of 540L/day. If the efficiency of the softener is 100%, the bypass flow rate (expressed in L/day) is_______ [2016 :1 Mark, Set-II]
Ans: 385.7 l/day
Sol:
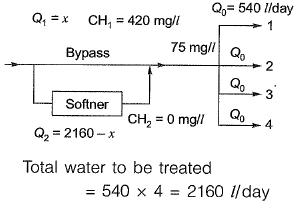
Total water to be treated
= 540 x 4 = 2160 l/day
Resultant hardness required = 75 mg/l.
Let bypass rate be x l/day having hardness of 420 mg/l
Resultant hardness required = 75 mg/l
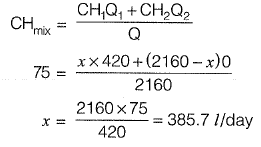
Q1: The relationship between porosity (η), specific yield (Sy) and specific retention (Sr) of an unconfined aquifer is [2015 : 1 Mark, Set-Il]
(a) Sy + Sr = η
(b) Sy + η = Sr
(c) Sr + η = Sy
(d) Sy + Sr + η = 1
Ans: (a)
Q1: In an aquifer extending over 150 hectare, the water table was 20m below ground level. Over a period of time the water table dropped to 23m below the ground level. If the porosity of aquifer is 0.40 and the specific retention is 0.15, what is the change in ground water storage of the aquifer? [2011 : 2 Marks]
(a) 67.5 ha-m
(b) 112.5ha-m
(c) 180.0 ha-m
(d) 450.0 ha-m
Ans: (b)
Sol: We know that,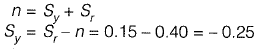
The negative sign signifies the decrease in storage.
Change in volume of aquifer
= 150 x ( 23 - 20 ) = 450 ha-m
Specific yield is nothing but the actual volume of water that can be extracted by force of gravity from a unit volume of aquifer.
∴ Change in water storage
= 450 x 0.25 = 112.5 ha-m
Q1: A well of diameter 20 cm fully penetrates a confined aquifer. After a long period of pumping at a rate of 2720 litres per minute, the observations of drawdown taken at 10m and 100m distances from the centre of the well are found to be 3m and 0.5 m respectively. The transmissivity of the aquifer is [2010 : 2 Marks]
(a) 676m2/day
(b) 576m2/day
(c) 526m2/day
(d) 249m2/day
Ans: 576 m2/day
Sol:
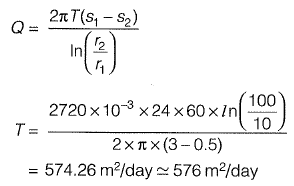
|
14 videos|120 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Sources of Water Supply, Distribution System & Well Hydraulics - Environmental Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the main sources of water supply for urban areas? |  |
| 2. How is water distributed within a municipal distribution system? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the hydraulics of a well? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of well hydraulics in groundwater management? |  |
| 5. How can water quality be maintained in a distribution system? |  |





















