Past Year Questions: Properties of Soils | Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: A homogeneous earth dam has a maximum water head difference of 15 m between the upstream and downstream sides. A flownet was drawn with the number of potential drops as 10 and the average length of the element as 3 m. Specific gravity of the soil is 2.65. For a factor of safety of 2.0 against piping failure, void ratio of the soil is (rounded off to 2 decimal places). [2024, Set-2]
Ans: 0.63 to 0.67
Sol: (ΔH) total head loss = 15 m
(nd) number of equipotential drops = 10
(I) length of flow field = 3 m
(G) specific gravity = 2.65
(FOS) factor of safety = 2
(e) void ratio = ?
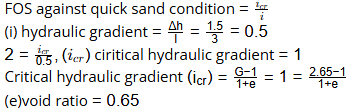
Q2: Which of the following statement(s) is/are CORRECT? [2024, Set-1]
(a) Swell potential of soil decreases with an increase in the shrinkage limit.
(b) Both loose and dense sands with different initial void ratios can attain similar void ratio at large strain during shearing.
(c) Among the several corrections to be applied to the SPT-N value, the dilatancy correction is applied before all other corrections.
(d) In electrical resistivity tomography, the depth of current penetration is half of the spacing between the electrodes.
Ans: (a), (b)
Sol: Shrinkage limit is defined as the maximum water content at which further reduction in water content of soil does not lead to reduction in the volume of soil as water is being just replaced by air.
Higher is the shrinkage limit lower is the compressibility (volume change).
Dilatancy correction is applied to the already corrected N-values for overburden pressure.
At large value of shearing strain, both the initially loose and initially dense sands approach a constant value of void ratio called critical void ratio.
Q1: A standard penetration test (SPT) was carried out at a location by using a manually operated hammer dropping system with 50% efficiency. The recorded SPT value at a particular depth is 28. If an automatic hammer dropping system with 70% efficiency is used at the same location, the recorded SPT value will be [2023, Set-2]
(a) 28
(b) 20
(c) 40
(d) 25
Ans: (b)
Sol: We know that,
Efficiency of blow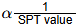
⇒ η1 N1 = η2 N2
Hence,
0.50 x 28 = 0.70 x N2
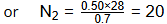
Option (B) is correct
Q2: A soil having the average properties, bulk unit weight = 19kN/m3; angle of internal friction = 25º and cohesion = 15kPa, is being formed on a rock slope existing at an inclination of 35º with the horizontal. The critical height (in m) of the soil formation up to which it would be stable without any failure is_______ (round off to one decimal place). [2023, Set-1]
Ans: 4.8 to 5.2
Sol: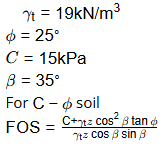
For critical height FOS = 1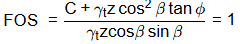
= 19 x Hc x cos 35º sin 35º
= 15 + 19 x Hc x cos2 35 tan 25
Hc = 5.03 m
Q1: Letψ represent soil suction head and K represent hydraulic conductivity of the soil. If the soil moisture content increases, which one of the following statements is TRUE? [2022, Set-1]
(a)ψ decreases and K increases.
(b)ψ increases and K decreases.
(c) Bothψ and K decrease.
(d) Bothψ and K increase.
Ans: (a)
Sol: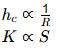
Water content ↑→ R ↑→ hc ↓→ ψ ↓
Water content ↑→ S ↑→ K ↑
Q1: In an aggregate mix, the proportions of coarse aggregate, fine aggregate and mineral filler are 55%, 40% and 5%, respectively. The values of bulk specific gravity of the coarse aggregate, fine aggregate and mineral filler are 2.55,2.65 and 2.70 , respectively. The bulk specific gravity of the aggregate mix (round off to two decimal places) is _______ [2021, Set-2]
Ans: 2.58 to 2.61
Sol:
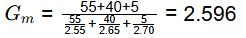
Q2: A partially-saturated soil sample has natural moisture content of 25% and bulk unit weight of 18.5kN/m3. The specific gravity of soil solids is 2.65 and unit weight of water is 9.81kN/m3. The unit weight of the soil sample on full saturation is [2021, Set-1]
(a) 21.12kN/m3
(b) 19.03kN/m3
(c) 20.12kN/m3
(d) 18.50kN/m3
Ans: (b)
Sol: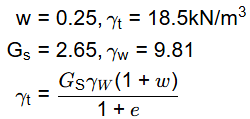
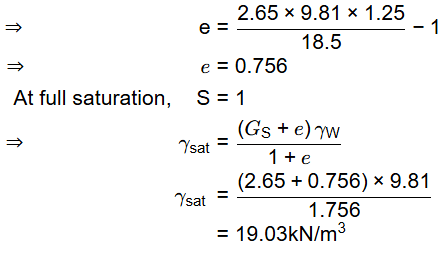
Q1: A soil has dry weight of 15.5kN/m3, specific gravity of 2.65 and degree of saturation of 72%. Considering the unit weight of water as 10kN/m3, the water content of the soil (in %, round off to two decimal places) is ________. [2020, Set-2]
Ans: 19 to 19.5
Sol: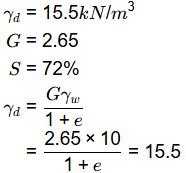
Q2: A sample of 500 g dry sand, when poured into a 2 litre capacity cylinder which is partially filled with water, displaces 188 cm3 of water. The density of water is 1 g/cm3. The specific gravity of the sand is [2020, Set-2]
(a) 2.72
(b) 2.66
(c) 2.55
(d) 2.52
Ans: (b)
Sol:
Ws = 500gm
Vs= 188cc
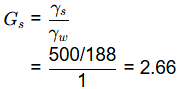
Q3: Soil deposit formed due to transportation by wind is termed as [2020, Set-2]
(a) aeolian deposit
(b) alluvial deposit
(c) estuarine deposit
(d) lacustrine deposit
Ans: (a)
Sol: Soil deposited by wind is Aeolian soil.
Q1: The dimensions of a soil sampler are given in the table. [2019, Set-2]
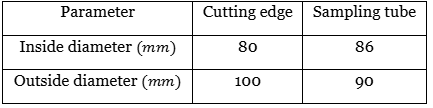 For this sampler, the outside clearance ratio (in percent, round off to 2 decimal places) is ______
For this sampler, the outside clearance ratio (in percent, round off to 2 decimal places) is ______
Ans: 11.1 to 11.12
Sol: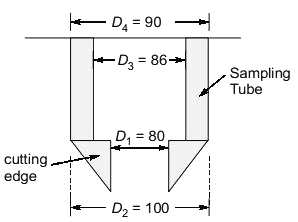
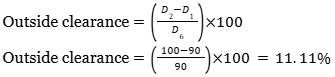
Q2: If the fineness modulus of a sample of fine aggregates is 4.3, the mean size of the particles in the sample is between [2019, St-2]
(a) 150μmand300μm
(b) 300μm and 600μm
(c) 1.18μm and 2.36μm
(d) 2.36μm and 4.75μm
Ans: (c)
Sol: F.M of mean size 2.36 = 5
F.M of mean size 1.18 = 4
Hence for F.M of 4.3, the mean size of aggregate will be between 1.18 mm and 2.36 mm.
Q3: The notation "SC" as per Indian Standard Soil Classification System refers to [2019, Set-2]
(a) Silty clay
(b) Clayey sand
(c) Sandy clay
(d) Clayey silt
Ans: (b)
Sol: SC → Clayey sand
Q4: A box measuring 50 cm × 50 cm × 50 cm is filled to the top with dry coarse aggregate of mass 187.5 kg. The water absorption and specific gravity of the aggregate are 0.596 and 2.5, respectively. The maximum quantity of water (in kg, round off to 2 decimal places) required to fill the box completely is _______ [2019, Set-1]
Ans: 50.5 to 51.2
Sol: Total volume of Box = 0.5 × 0.5 × 0.5 = 0.125 m3
wt of aggregates = 187.5 kg
sp. gravity = 2.5
Unit weight =2.5 × 9.81 = 24.525kN/m3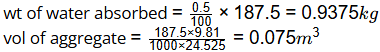
volume of voids = 0.125 - 0.075 = 0.05 m3
wt of water in voids = 0.05 × 1000 = 50 kg
wt of water required to fill the box = 50 + 0.9375 = 50.94 kg
Q5: A soil has specific gravity of its solids equal to 2.65. The mass density of water is 1000 kg/m3. Considering zero air voids and 10% moisture content of the soil sample, the dry density (in kg/m3, round off to 1 decimal place) would be _______. [2019, Set-1]
Ans: 2086.6 to 2095
Sol: Gs = 2.65
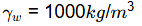
Degree of saturation, S = 100% (Zero air voids)
w = 10%
The dry density corresponding to zero air voids or 100% saturation,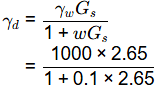
= 2094.9kg/m3
Q1: The clay mineral, whose structural units are held together by potassium bond is [2018, Set-2]
(a) Halloysite
(b) Illite
(c) Kaolinite
(d) Smectite
Ans: (b)
Sol:
Kaolinite → Hydrogen bond
lllite → Ionic Bond/Potassium Bond
Montmorillonite → Water Bond
Q2: A core cutter of 130 mm height has inner and outer diameters of 100 mm and 106 mm, respectively. The area ratio of the core cutter (in %, up to two decimal places) is ______ [2018, Set-1]
Ans: 12.36%
Sol:
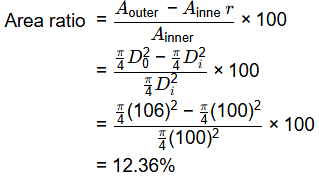
Q3: in a shrinkage limit test, the volume and mass of a dry soil pat are found to be 50 cm3 and 88 g. respectively. The specific gravity of the soil solids is 2.71 and the density of water is 1 g/cc. The shrinkage limit (in % up to two decimal places) is ________ . [2018, Set-1]
Ans: 0.1990
Sol:
Dry soil mass = 88 g
Volume of dry soil = 50 cc
Dry density of soil mass,
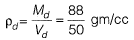
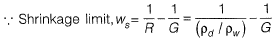
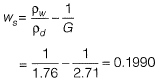
Q1: Let G be the specific gravity of soil solids, w is the water content in the soil sample, γw the unit weight of water, and γd the dry unit weight of the soil. The equation for the zero air voids line in a compaction test plot is [2017, Set-2]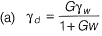
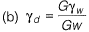
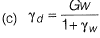
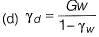
Ans: (a)
Sol: Percentage air void line is relation between dry unit weight and water content at constant air void. Hence equation of zero air void line is
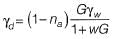 (na = 0)
(na = 0)
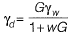
Q2: The laboratory tests on a soil sample yield the following results; natural moisture content = 18%, liquid limit = 60%, plastic limit = 25%, percentage of clay sized fraction = 25%. The liquidity index and activity (as per the expression proposed by Skempton) of the soil, respectively, are [2017, Set-1]
(a) -0.2 and 1,4
(b) 0.2 and 1.4
(c) -1.2 and 0.714
(d) 1.2 and 0.714
Ans. (A)
Solution:
Given data: wn = 18%, wL = 60%, wp = 25% % of clay size particle = 25%
Liquidity index,
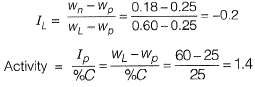
Q1: The porosity (n) and the degree of saturation (S) of a soil sample are 0.7 and 40%, respectively. In a 100 m3 volume of the soil, the volume (expressed in m3) of air is _____ [2016, Set-I]
Solution: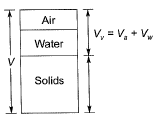
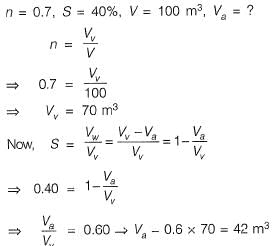
Q1: A 588 cm3 volume of moist sand weighs 1010 gm. its dry weight is 918 gm and specific gravity of solids, G is 2.67. Assuming density of water as 1 gm/cm3, the void ratio is _________ . [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Solution:
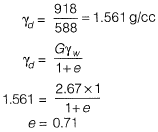
Q.9 If the water content of a fully saturated soil mass is 100%, the void ratio of the sample is
(a) less than specific gravity of soil
(b) equal to specific gravity of soil
(c) greater than specific gravity of soil
(d) independent of specific gravity of soil
Ans. (B)
Solution:
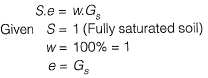
Q.10 An earth embankment is to be constructed with compacted cohesionless soil. The volume of the embankment is 5000 m3 and the target dry unit weight is 16.2 kN/m3. Three nearby sites (see figure below) have been identified from where the required soil can be transported to the construction site. The void ratios (e) of different sites are shown in the figure. Assume the specific gravity of soil to be 2.7 for ail three sites. If the cost of transportation per km is twice the cost of excavation per m3 of borrow pits, which site would you choose as the most economic solution? (Use unit weight of water = 10 kN/m3) [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-I]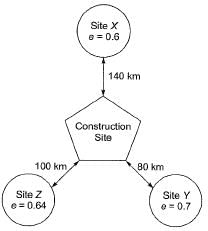
(a) Site X
(b) Site Y
(c) Site Z
(d) Any of the sites
Ans. (A)
Solution:
Volume of solids at embankment,
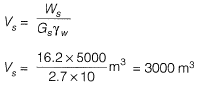
Volume of solids will remain constant,
also,
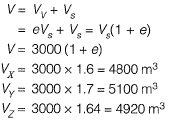
Let cost of excavation be α/m3,
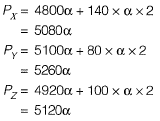
Hence Px is least.
∴ Hence total cost for site X is least.
Q.11 A fine-grained soil has 60% (by weight) silt content. The soil behaves as semi-solid when water content is between 15% and 28%. The soil behaves fluidlike when the water content is more than 40%.
The ‘Activity’ of the soil is [2015 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
(a) 3.33
(b) 0.42
(c) 0.30
(d) 0.20
Ans.(C)
Solution:
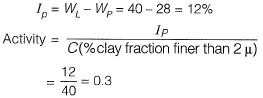
Q.12 A certain soil has the following properties: Gs = 2.71, n - 40% and w= 20%. The degree of saturation of the soil (rounded off to the nearest percent) is _________ . [2014 : 1 Mark, Set-II]
Solution:
Se = wG
and
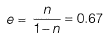
⇒ 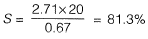
Q.13 A given cohesionless soil has emax = 0.85 and emin = 0.50. In the field, the soil is compacted to a mass density of 1800 kg/m3 at a water content of 8%. Take the mass density of water as 1000 kg/m3 and Gs as 2.7. The relative density (in %) of the soil is [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
(a) 56.43
(b) 60.25
(c) 62.87
(d) 65.71
Ans. (D)
Solution:
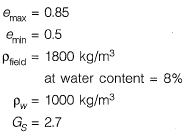
Relative density, ID = ?
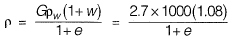
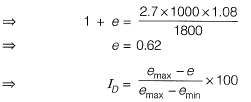
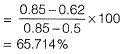
Q.14 In its natural condition a soil sample has a mass of 1.980 kg and a volume of 0.001 m3. After being completely dried in an oven; the mass of the sample is 1.800 kg. Specific gravity is 2.7. Unit weight of water is 10 kN/m3. The degree of saturation of soil is [2013 : 1 Mark]
(a) 0.65
(b) 0.7
(c) 0.54
(d) 0.61
Ans. (C)
Solution:
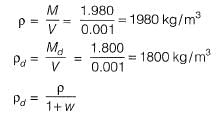
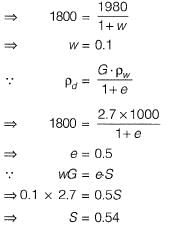
Q.15 A soil is composed of solid spherical grains of identical specific gravity and diameter between 0.075 mm and 0.0075 mm. If the terminal velocity of the largest particle falling through water without flocculation is 0.5 mm/s, that for the smallest particle would be [2011 : 1 Mark]
(a) 0.005 mm/s
(b) 0.05 mm/s
(c) 5 mm/s
(d) 50 mm/s
Ans.(A)
Solution:
According to Stake’s law,
V ∝ D2
|
30 videos|126 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Properties of Soils - Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the main physical properties of soils? |  |
| 2. How does soil pH affect plant growth? |  |
| 3. What is soil permeability and why is it important? |  |
| 4. How do organic materials influence soil properties? |  |
| 5. What are soil horizons and their significance? |  |
















