Past Year Questions: Classification of Soils & Clay Minerals | Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: Consider the statements P and Q.
P: Soil particles formed by mechanical weathering, and close to their origin are generally sub rounded.
Q: Activity of the clay physically signifies its swell potential.
Which one of the following options is CORRECT? [2024, Set-1]
(a) Both P and Q are TRUE
(b) P is TRUE and Q is FALSE
(c) Both P and Q are FALSE
(d) P is FALSE and Q is TRUE
Ans: (d)
Sol: Bulky particles are formed mostly by mechanical weathering of rocks and minerals. Geologists use such terms as angular, subangular, subrounded and rounded to describe the shape of bulky particles. Small sand particles located close to their origin are generally very angular sand particles carried by wind and water for a long distance can be subangular to rounded in shape.
Activity number of clay is used to study the swelling behaviour.
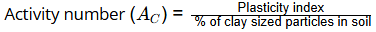
AC < 0.75 → normal active
0.75 < AC < 1.25 → inactive
AC > 1.25 → active
Active means more prone to volume change.
Q1: The correct match between the physical states of the soils given in Group I and the governing conditions given in Group II is [2022, Set-1]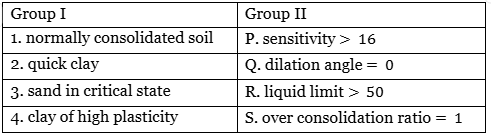
(a) 1-S, 2-P, 3-Q, 4-R
(b) 1-Q, 2-S, 3-P, 4-R
(c) 1-Q, 2-P, 3-R, 4-S
(d) 1-S, 2-Q, 3-P, 4-R
Ans: (a)
Q2: Four different soils are classified as CH, ML, SP, and SW, as per the Unified Soil Classification System. Which one of the following options correctly represents their arrangement in the decreasing order of hydraulic conductivity? [2022, Set-1]
(a) SW, SP, ML, CH
(b) CH, ML, SP, SW
(c) SP, SW, CH, ML
(d) ML, SP, CH, SW
Ans: (a)
Sol: Hydraulic conductivity Order.
Gravel > Sand > silt > lay
Q1: From laboratory investigations, the liquid limit, plastic limit, natural moisture content and flow index of a soil specimen are obtained as 60%, 27%, 32% and 27%, respectively. The corresponding toughness index and liquidity index of the soil specimen, respectively, are [2021, Set-2]
(a) 0.15 and 1.22
(b) 0.19 and 6.60
(c) 1.22 and 0.15
(d) 6.60 and 0.19
Ans: (c)
Sol: Flow index = 27
Plasticity index, IP = WL - WP = 33
Toughness index, IT = IP/If = 33/27 = 1.22
Liquidity index,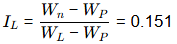
Q2: As per the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS), the type of soil represented by 'MH' is [2021, Set-2]
(a) Inorganic silts of high plasticity with liquid limit more than 50%
(b) Inorganic silts of low plasticity with liquid limit less than 5096
(c) Inorganic clays of high plasticity with liquid limit less than 50%
(d) Inorganic clays of low plasticity with liquid limit more than 50%
Ans: (a)
Sol: 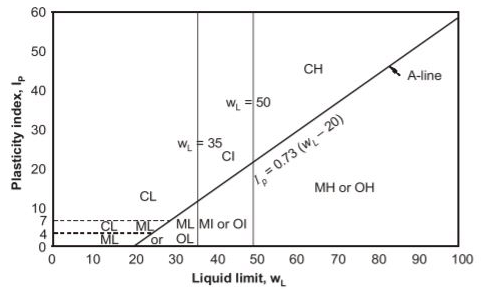
Q1: A staff is placed on a benchmark (BM) of reduced level (RL) 100.000 m and a theodolite is placed at a horizontal distance of 50 m from the BM to measure the vertical angles. The measured vertical angles from the horizontal at the staff readings of 0.400 m and 2.400 m are found to be the same. Taking the height of the instrument as 1.400 m, the RL (in m ) of the theodolite station is [2019, Set-1]
Ans: 100
Sol: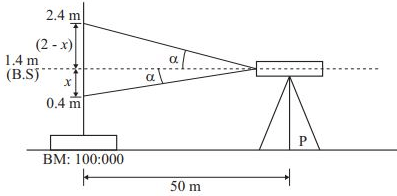 x = 50tan α
x = 50tan α
2 - x = 50tan α
∴ x = 2 - x
2x = 2
x = 1m
R.L of theodolite station (P): 100 + 1.4 - 0.1 - 0.4 = 100 m
Q2: A survey line was measured to be 285.5 m with a tape having a nominal length of 30 m. On checking, the true length of the tape was found to be 0.05 m too short. If the line lay on a slope of 1 in 10 , the reduced length (horizontal length) of the line for plotting of survey work would be [2019, Set-1]
(a) 283.6 m
(b) 284.5 m
(c) 285 m
(d) 285.6 m
Ans: (a)
Sol: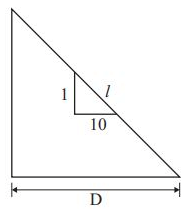 L = 30m, L' = 30 - 0.05 = 29.95m
L = 30m, L' = 30 - 0.05 = 29.95m
∴ Correct Length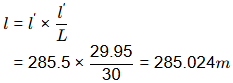
D = l cos θ
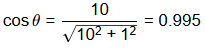
∴ D = correct Horizontal length
= l cos θ
= 285.024 × 0.9950
= 283.6m
Q1: A fine-grained soil is found to be plastic in the water content range of 26-48%. As per Indian Standard Classification System, the soil is classified as [2016, Set-1]
(a) CL
(b) CH
(c) CL-ML
(d) CI
Ans: (d)
Sol: Soil is plastic in the range of 26-48%.
Hence, Plastic limit = 26% and liquid limit = 48%.
Because the liquid limit is in the range of 35% to 50%. Hence intermediate compressible soil.
Q.4. As per the Indian Standard soil classification system, a sample of silty clay with a liquid limit of 40% and plasticity index of 28% is classified as [2012: 1 Mark]
(a) CH
(b) CI
(c) CL
(d) CL-ML
Ans. (b)
Solution: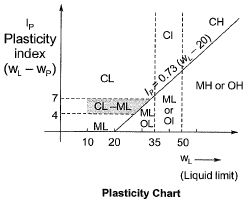 Ip of soil = 28%
Ip of soil = 28%
Ip of A-line = 0.73(WL - 20) = 0.73 (40 - 20) = 14.6
∵ Ip of soil > Ip of A-line
∴ It will lie above Aline and also 35 < WL < 50
So it is CI.
Q.5. The results for sieve analysis carried out for three types of sand, P, Q, and R, are given in the adjoining figure. If the fineness modulus values of the three sands are given as FMP, FMQ, and FMR, it can be stated that [2011: 1 Mark]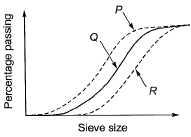
(a) FMQ = √( FMP x FMR )
(b) FMQ = 0.5 ( FMP + FMR )
(c) FMP > FMQ > FMR
(d) FMP < FMQ < FMR
Ans. (a)
Solution: The term fineness modulus is used to indicate an index number roughly proportional to the average size of a particle in the entire quantity of aggregate.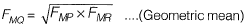
|
30 videos|77 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Classification of Soils & Clay Minerals - Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the main classifications of soils based on grain size? |  |
| 2. How are clay minerals classified in terms of their structure? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of Atterberg limits in soil classification? |  |
| 4. How does soil texture affect its classification and properties? |  |
| 5. What role do clay minerals play in soil fertility? |  |