Overview: Metals & Non-metals - 2 | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 9 PDF Download
Physical Properties of Metals and Non-Metals
| Property | Metal | Non-Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Malleability | Can be hammered into thin sheets | Generally not malleable |
| Ductility | Can be drawn into wires | Not ductile |
| Conductivity | Good conductor of heat and electricity | Generally poor conductor |
| State at Room Temperature | Usually solid (except mercury) | Can be solid, liquid, or gas |
| Appearance | Shiny (lustrous) | Dull or shiny |
Chemical Properties of Metals
Reaction of metals with Air
Magnesium burns in the air easily to produce magnesium oxide. But not all metals combine with oxygen easily. Some metals require heating in combination with oxygen.

For example :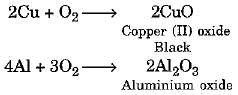
Reaction of metals with water
Different metals show different reactivity with water.
(i) Metals like Na, K and Ca react with cold water instantly. Na and K metals react so violently that hydrogen produced in the reaction catches fire.
2K (s) + 2H2O (l)→ 2KOH (aq) + H2 (g) + Energy
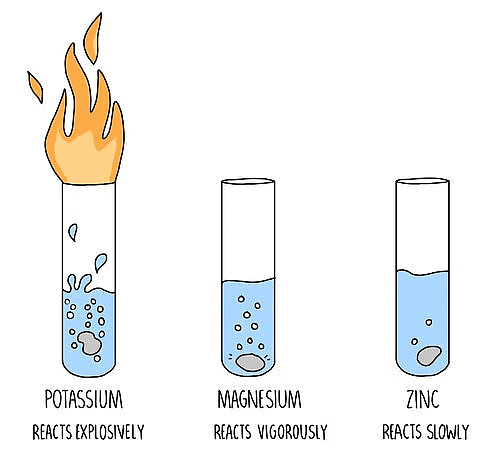
(ii) Reaction with Ca is less violent. Heat evolved is not sufficient for hydrogen to catch fire.
Ca (s) + 2H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2(g)
Calcium floats on water because bubbles of hydrogen formed sticks to the metal (hydrogen is lighter than air).
(iii) Magnesium does not react with cold water. It reacts with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen. It also starts floating like calcium.
Mg + 2H2O (hot) → Mg(OH)2 + H2
(iv) Metals like Al, Fe and Zn do not react either with cold or hot water. They react with steam to form metal oxide and hydrogen.
The reaction of metals with acids
Different metals react with acid with different rate of reaction. Some metals do not react at all.It is observed that different metals react with different speeds. It is found that rate of reaction is fastest with Mg. It decreases in the order : Mg > Al > Zn > Fe.
There is no reaction at all with copper.
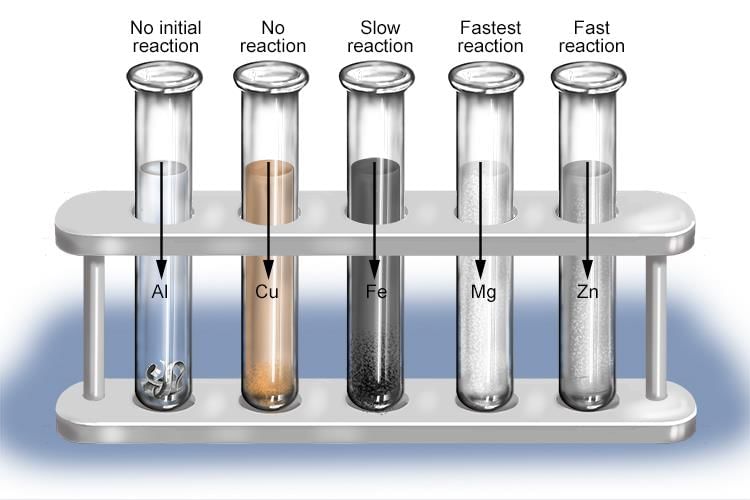

The reactions with metals can be written as:
Mg + 2HCl-----> MgCl2 + H2
2Al + 6HCl-----> 2AlCl3 + 3H2
Zn + 2HCl-----> ZnCl2 + H2
Fe + 2HCl----->FeCl2 + H2
Copper does not react at all with dilute hydrochloric acid.
How do Metals react with Solutions of other Metal Salts?
Metals can react with solutions of other metals through displacement reactions. A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its solution. For example, zinc can displace copper from copper sulfate solution, leading to the formation of zinc sulfate and copper.
Metal A + Salt solution of B → Salt solution of A + Metal B

The Reactivity Series
The reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in decreasing order of their reactivity. More reactive metals are placed higher in the series. Metals like potassium and sodium are highly reactive, while gold and platinum are less reactive. The series helps predict the displacement reactions between metals and their salts in chemical reactions.
how do metals and non-metals react ?
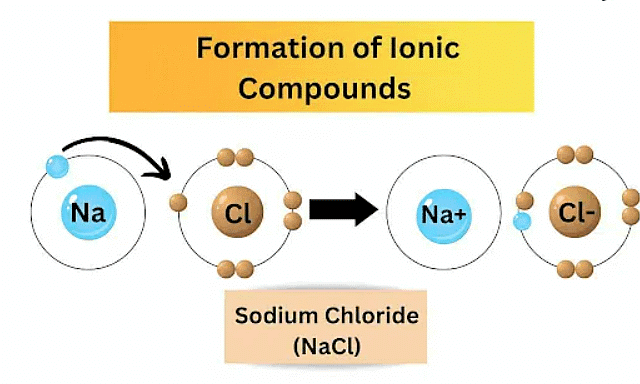
Metals react with non-metals to form ionic compounds through a transfer of electrons. In these reactions, metals tend to lose electrons, becoming positively charged ions (cations), while non-metals gain electrons to form negatively charged ions (anions).
Ionic compounds
The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions results in the formation of ionic compounds. For example, in the reaction between sodium (a metal) and chlorine (a non-metal), sodium loses an electron to become Na⁺, and chlorine gains an electron to become Cl⁻. The combination of Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions results in the formation of sodium chloride (NaCl), which is an ionic compound. Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces between ions.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
1. High Melting and Boiling Points: Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because they consist of a three-dimensional array of ions held together by strong electrostatic forces. Significant energy is required to break these bonds and change the state of the compound.
2. Solubility in Water: Most ionic compounds are soluble in water, as water molecules surround and separate the individual ions, facilitating their dispersal. However, there are exceptions, such as insoluble salts like silver chloride.
3. Electrical Conductivity: In the molten or dissolved state, ionic compounds can conduct electricity because their ions are free to move and carry an electric charge. In the solid state, they do not conduct electricity as the ions are held in a fixed position.
4. Brittleness: Ionic compounds are often brittle and tend to shatter when subjected to force. This is because applying pressure can cause the layers of ions to shift, resulting in repulsion between like charges and causing the crystal lattice to break.
|
12 videos|50 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Metals & Non-metals - 2 - Advance Learner Course: Science Class 9
| 1. What are the physical properties of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. What are the chemical properties of metals? |  |
| 3. How do metals and non-metals react? |  |
| 4. Can metals and non-metals react with each other? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of reactions between metals and non-metals? |  |