Class 10 Social Science Previous Year Questions - Water Resources
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Match Column I with Column II and choose the correct option: (1 Mark)
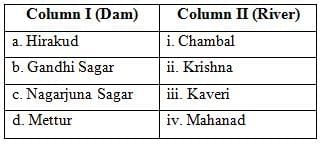
(a) a-iv, b-i, c-iii, d-ii
(b) a-i, b-ii, c-iv, d-iii
(c) a-iv, b-i, c-ii, d-iii
(d) a-i, b-ii, c-iii, d-iv
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) a-iv, b-i, c-ii, d-iii
The table below shows the correct matching of dams with their respective rivers:
Correct Matches:
a-iv (Hirakud - Mahanadi)
b-i (Gandhi Sagar - Chambal)
c-ii (Nagarjuna Sagar - Krishna)
d-iii (Mettur - Kaveri)
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Q2: Choose the correct option regarding major states involved in the Krishna-Godavari issue: (1 Mark)
(a) Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu
(b) Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh
(c) Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh
(d) Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, and Odisha
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh
The Krishna–Godavari dispute arose because Maharashtra diverted more water at Koyna for a multipurpose project, to which Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh raised objections.
Q3: Match Column I with Column II and choose the correct option: (1 Mark)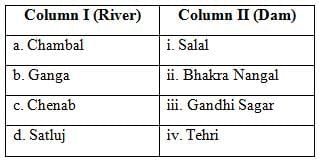
(a) a-ii, b-iii, c-i, d-iv
(b) a-ii, b-iii, c-iv, d-i
(c) a-iii, b-iv, c-i, d-ii
(d) a-iii, b-iv, c-ii, d-i
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) a-iii, b-iv, c-i, d-ii
The table below shows the correct matching of rivers with their respective dams:
Correct Matches:
- a-iii (Chambal - Gandhi Sagar)
- b-iv (Ganga - Tehri)
- c-i (Chenab - Salal)
- d-ii (Satluj - Bhakra Nangal)
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Q4: Choose the correct option of the states that have been majorly benefitted by the Sardar Sarovar Dam. (1 Mark)
Options:
(a) Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab, and Haryana
(b) Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Rajasthan
(c) Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh
(d) Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Karnataka, and Chhattisgarh
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Rajasthan
The Sardar Sarovar Dam is built on the Narmada River in Gujarat. It covers four states — Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Rajasthan — providing irrigation facilities, drinking water, and drought-proofing especially in arid regions like Barmer and Jalore in Rajasthan.
Q5: How has the overuse of underground water created a serious crisis in many parts of India? Explain with examples in the context of sustainable development. (5 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
The overuse of underground water has created a serious problem in many parts of India:
- Declining Water Table – Farmers use their own wells and tube-wells to irrigate crops. This has caused the groundwater level to fall rapidly.
- Food Security at Risk – Over-exploitation of water for irrigation reduces availability in the future and may threaten food production.
- Urban Areas – In many cities, housing societies depend on private pumps. This leads to depletion of fragile water resources.
- Industrialisation – Industries use huge amounts of water and also pollute it, further reducing usable freshwater.
- Need for Sustainable Use – Government programmes like Jal Jeevan Mission and Atal Bhujal Yojana promote conservation and smart management to protect this resource.
Hence, overuse of groundwater has caused a serious water crisis and can only be solved through conservation and sustainable development.
Q6: How have industrialization and urbanization impacted water supply? Explain. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Industrialisation and urbanisation have put immense pressure on water supply in India:
- Industrial Use – Industries are heavy users of water and also need large amounts of power, much of which comes from hydroelectric sources.
- Pollution of Water – Many industries discharge wastes, chemicals, and effluents, making freshwater hazardous for use.
- Urban Overuse – Rapid growth of cities with dense populations has increased demand. Most colonies have their own pumps, leading to over-exploitation and depletion of fragile groundwater resources.
Thus, industrialisation and urbanisation have worsened the problem of water scarcity.
Q7: Explain any three aims of Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM). (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) was started by the Government of India with the goal of providing safe water in rural areas. Its aims are:
- Assured Water Supply – To provide every rural household with a regular supply of potable piped water.
- Service Level – To ensure at least 55 litres per person per day is available.
- Long-term Functionality – To make sure tap connections remain functional on a long-term basis.
Thus, JJM focuses on improving the quality of life and ensuring safe drinking water for all rural households.
Q8: Choose the correct option to fill the blank.
An artificial lake built in the 11th century for water conservation is: (1 Mark)
(a) Sambhar Lake
(b) Wular Lake
(c) Bhopal Lake
(d) Chilka Lake
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Bhopal Lake
The Bhopal Lake, built in the 11th century, was one of the largest artificial lakes of its time for water conservation.
Q9: Match Column I with Column II and choose the correct option: (1 Mark)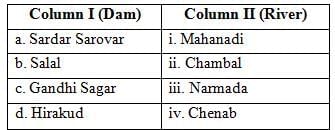
(a) a-ii, b-i, c-iv, d-iii
(b) a-iii, b-iv, c-i, d-ii
(c) a-iii, b-iv, c-ii, d-i
(d) a-i, b-iii, c-iv, d-ii
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) a-iii, b-iv, c-ii, d-i
The table below shows the correct matching of dams with their respective rivers: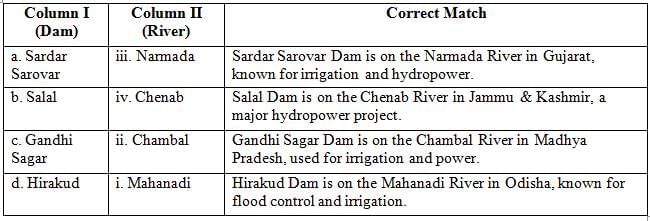
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Which one of the following is the irrigation system in Meghalaya? (CBSE 2024)(a) To irrigate land only during rainy season.
(b) To use large volumes of water for irrigation.
(c) To remove water from soil.
(d) To use bamboo drip irrigation system.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
In Meghalaya, farmers use a unique method called bamboo drip irrigation, which involves directing water through bamboo tubes to irrigate their fields. This traditional system is efficient and well-suited to the hilly terrain of the region, allowing for sustainable agriculture even in areas with limited water resources.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q2: In which of the following States Tungabhadra Dam is located? (2023)
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Kerala
(c) Andhra Pradesh
(d) Karnataka
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The Tungabhadra Dam is located in the state of Karnataka. Therefore, the correct answer is (d) Karnataka.
Q3: Read the given source and answer the questions that follow: (2023)
RAINWATER HARVESTING
Many thought that, given the disadvantages and rising resistance against the multi-purpose projects, the water harvesting system was a viable alternative, both socio-economically and environmentally. In ancient India, along with the sophisticated hydraulic structures, there existed an extraordinary tradition of water harvesting systems. People had in-depth knowledge of rainfall regimes and soil types and developed wide-ranging techniques to harvest rainwater, groundwater, river water and flood water in keeping with the local ecological conditions and their water needs. In hill and mountainous regions, people built diversion channels like the 'guls' or 'kuls' of the Western Himalayas for agriculture. 'Rooftop rainwater harvesting' was commonly practised to store drinking water, particularly in Rajasthan. In the floodplains of Bengal, people developed inundation channels to irrigate their fields. In arid and semi-arid regions, agricultural fields were converted into rain-fed storage structures that allowed the water to stand and moisten the soil like the 'khadins' in Jaisalmer and 'Johads' in other parts of Rajasthan.
(i) Why is water harvesting system a viable alternative?
(ii) Describe the process of 'rooftop rainwater harvesting.'
(iii) Mention any two methods adopted by ancient India for water conservation.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) The water harvesting system emerges as a viable alternative due to its dual benefits—socio-economic and environmental friendliness.
(ii) 'Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting' involves capturing rainwater from the roof, storing it in reservoirs, and providing a sustainable source of drinking water, especially notable in Rajasthan.
(iii) Ancient India employed diverse water conservation methods, such as building diversion channels like 'guls' or 'kuls' in the Western Himalayas for agriculture and creating rainfed storage structures like 'Khadins' in Jaisalmer and 'Johads' in Rajasthan's other regions.
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q4: Which one of the following factors is mainly responsible for declining water level in India? (2022)(a) Irrigation
(b) Industrialisation
(c) Urbanisation
(d) Over-utilisation
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Over-utilisation is mainly responsible for declining water level in India. A s the population increases, the consumption of water also increases.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q5: How are traditional rainwater harvesting methods being carried out to conserve water resources in different regions? Explain with examples. (2019 C) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) In hilly regions, people engineered diversion channels like ‘guls’ or ‘kuls’ in the Western Himalayas to support agriculture.
(ii) 'Rooftop rainwater harvesting' was a common practice in Rajasthan for storing drinking water.
(iii) In Bengal's floodplains, people ingeniously developed inundation channels for field irrigation.
(iv) Arid and semi-arid regions transformed agricultural fields into rainfed storage structures like 'Khadins' in Jaisalmer and 'Johads' in Rajasthan, while regions like Bikaner, Phalodi, and Barmer adopted underground tanks for drinking water.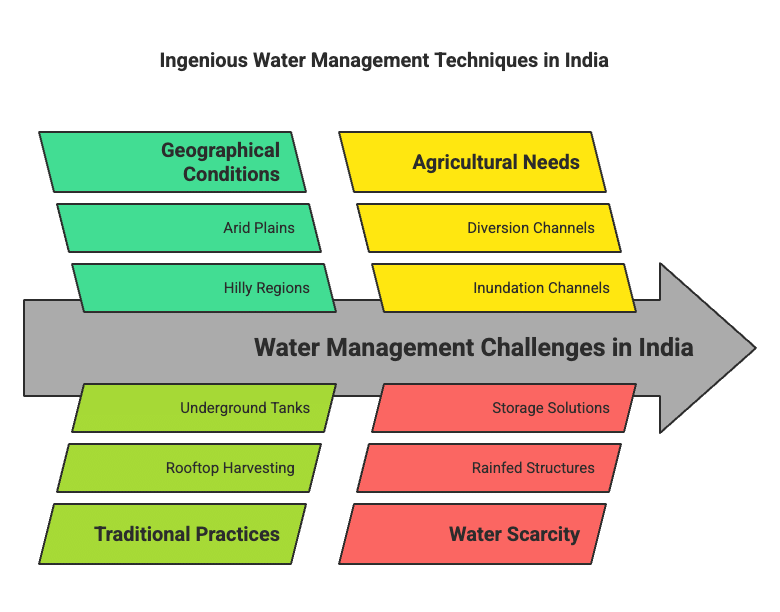
Q6: "Archaeological and historical records show that from ancient times we have been constructing sophisticated hydraulic structures in India.” Substantiate the statement by giving three pieces of evidence. (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Archaeological and historical records reveal India's rich tradition of sophisticated hydraulic structures:
- In the 1st century B.C., Sringaverapura near Allahabad showcased advanced water harvesting, channeling Ganga's floodwaters.
- During Chandragupta Maurya's rule, extensive construction of dams, lakes, and irrigation systems occurred.
- Evidence of sophisticated irrigation works is found in places like Kalinga, Nagarjunakonda, Bennur, and Kolhapur. In the 11th century, the construction of Bhopal Lake and the 14th-century tank in Hauz Khas, Delhi, further demonstrates India's historical prowess in hydraulic engineering.
Q7: "Water scarcity may be an outcome of large and growing population in India." Analyse the statement. (Delhi 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Water scarcity in India is exacerbated by its large and growing population:
- Greater demands for water arise not only from domestic use but also from increased food production.
- Densely populated areas experience groundwater over-exploitation, significantly lowering water tables.
- Industrial demands and associated pollution further strain freshwater resources, contributing to water scarcity in many Indian cities.
Q8: "Multi-purpose projects and large dams have been the cause of many new social movements." Highlight the concerns related to such movements. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Resistance to these projects (Narmada Bachao Andolan and Tehri Dam Andolan) has primarily been due to the large-scale displacement of local communities. So, if the local people are not benefiting from such projects then who is benefited? With abundance of water many farmers shifting to water intensive and commercial crops. This has great ecological consequences like salinization of the soil. It has transformed the social landscape i.e. increasing the social gap between the richer landowners and the landless poor.
Q9: "Urbanisation has added to water scarcity." Support the statement with arguments. (Al 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Urbanization exacerbates water scarcity in India due to:
- Increased water demand for personal use in densely populated urban centers.
- Over-exploitation of groundwater by housing societies and colonies.
- Industries in urban areas contribute to water stress through high consumption and pollution.
Q10: "The dams that were constructed to control floods have triggered floods.” Analyze the statement. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Damming of rivers affects their natural flow causing poor sediment flow and excessive sedimentation at the bottom of the reservoir, and poorer habitat for the rivers’ aquatic life. Dams also fragment rivers making it difficult for aquatic fauna to migrate, especially for spawning. Reservoirs created on the floodplains also submerge the existing vegetation and soil leading to its decomposition.
Q11: "Water harvesting system is an effective measure to reduce the problem of water scarcity.” Justify the statement. (Al 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A large amount of this precious water just drains away. The only way to save this water from wastage is by rainwater harvesting. In its simplest form it involves storing the rainwater in tanks, or by making embankments etc. The different methods of rainwater harvesting used in India have been as follows:
(a) Guls or Kuls in the Western Himalayas.
(b) Rooftop rainwater harvesting in Rajasthan associated with tankas. Khadins in Jaisalmer and Johads in other parts of Rajasthan were also popular.
(c) Inundation channels in West Bengal
(d) In Meghalaya which gets copious rain, rainwater harvesting is commonly practiced.
(e) In modern civil construction and housing societies provision for rainwater harvesting.
Q12: How has Shillong solved the problem of acute shortage of water ? (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In Meghalaya, a system of tapping stream and spring water by using bamboo pipes is prevalent. This system solved the problem of acute shortage of water, to some extent.
Q13: How has Tamil Nadu solved the problem of acute shortage of water ? (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Tamil Nadu has made roof top rainwater harvesting structure compulsory to all the houses across the state. This provision helped the state Tamil Nadu to solve the problem of acute shortage of water.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q14: Explain any three reasons for which the multi-purpose projects and large dams have come under great scrutiny and opposition in the recent years. (CBSE 2018) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Regulating and damming of rivers affect their natural flow causing poor sediment flow and excessive sedimentation at the bottom of the reservoir, resulting in rockier stream beds and poorer habitats for the rivers’ aquatic life.
(b) Dams also fragment rivers making it difficult for aquatic fauna to migrate, especially for spawning.
(c) The reservoirs that are created on the floodplains also submerge the existing vegetation and soil leading to its decomposition over a period of time.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q15: Water scarcity in most cases is caused by over-exploitation, excessive use and unequal access to water among different social groups.” Explain the meaning of statement with the help of examples. (CBSE 2016-17) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Water scarcity in most cases results from over-exploitation, excessive use, and unequal access among social groups:
- Over-exploitation is evident through extensive tubewell use for irrigation and industrial purposes.
- Excessive use is seen in urban areas where water is wasted due to inadequate recycling.
- Unequal access is apparent with affluent individuals having ample water while the poor face limited supply.
Q16: What is rainwater harvesting ?
Or
How is rainwater harvesting carried out in semi-arid regions of Rajasthan ? Explain. (CBSE 2016-17)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Rainwater harvesting is a technique of increasing the recharge of groundwater by capturing and storing rainwater by constructing structures, such as dugwells, percolation pits, checkdams.
(b) (i) In arid and semi-arid regions, agricultural fields were converted into rain fed storage structures that allowed the water to stand and moisten the soil like the ‘Khadins’ in Jaisalmer and ‘Johads’ in other parts of Rajasthan.
(ii) In Bikaner, Phalodi and Banner, almost all the houses had underground tanks for storing drinking water.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q17: “India has a monsoon type of climate, even then it faces water scarcity in many parts of the country”. Elucidate the given sentence by providing some examples.OR
What is water scarcity? Write the main reasons for water scarcity. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Water scarcity means shortage of water. It is usually associated with regions having low ground water but it can also be about inferior quality of the water available. There are many other reasons which can cause scarcity of water.
India has a monsoon type of climate which guarantees appropriate rainfall, yet it has water scarcity because:
(1) The availability of water resources varies over space and time, mainly due to the variations in seasonal and annual precipitation.
(2) Over-exploitation, excessive use and unequal access to water among different social groups of citizens also causes scarcity.
(3) Water scarcity may be an outcome of a large and growing population and consequent greater demand for water.
(4) Most farmers have their personal wells and tubewells in their farms for irrigation to increase their production. Excessive exploitation of groundwater can cause water scarcity.
(5) Water scarcity can also be caused due to availability of inferior quality of water. This happens because industrial and domestic waste are released into water bodies making them unfit for use.
Previous Year Questions 2012
Q18: How has intensive industrialisation and urbanisation posed a great pressure on existing fresh water resources in India? Explain with two examples for each. (CBSE 2012) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Intensive industrialisation and urbanisation has put greater pressure on existing fresh water resources as:
(1) With the rising number of industries, the demand for water, as a consequence, has grown tremendously.
(2) Industries are heavy users of fresh water as water is required for cooling the machines and processing of goods.
(3) The untreated industrial effluents which are discharged into water bodies pollute the water making it hazardous for human consumption causing qualitative scarcity.
(4) Urban lifestyles have further aggravated the problem. Urban population overdraws the groundwater by using their own groundwater pumping devices.
(5) Large populations have greater demand of water for consumption and domestic purposes which in turn has increased the stress on water bodies in regions surrounding them.
|
95 videos|815 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Social Science Previous Year Questions - Water Resources
| 1. What are the different sources of water resources? |  |
| 2. How do human activities impact water resources? |  |
| 3. What measures can be taken to conserve water resources? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of groundwater in water resources management? |  |
| 5. How does climate change affect water resources? |  |

















