Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Previous Year Questions - Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: How did the process of liberalisation initiated in India in the 1990s promote globalisation? Explain. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Liberalisation in the 1990s removed many restrictions on foreign trade and foreign investment, allowing imports/exports to flow more freely and enabling foreign companies to set up factories and offices in India.
This increased foreign investment and trade, brought MNCs into India, raised competition and helped integrate Indian production and markets with the world — thereby promoting globalisation.
Q2: Two statements are given below. Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option: (1 Mark)
Statement I: Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor to stimulate the globalisation process.
Statement II: This has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs.
(a) Both statements I and II are correct and statement II is the correct explanation of statement I.
(b) Both statements I and II are correct, but statement II is not the correct explanation of statement I.
(c) Statement I is correct, but statement II is incorrect.
(d) Statement I is incorrect, but statement II is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Both statements I and II are correct and statement II is the correct explanation of statement I.
Both statements are correct, and statement II correctly explains statement I — rapid improvements in technology, especially in transportation, have enabled faster and cheaper delivery of goods across long distances, which has stimulated the process of globalisation.
Q3: Two statements are given below. Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option: (1 Mark)
Statement I: Information and communication technology stimulate the process of globalisation.
Statement II: It is used to contact each other, receive information instantly and communicate with remote areas.
(a) Both statements I and II are correct and statement II is the correct explanation of statement I.
(b) Both statements I and II are correct, but statement II is not the correct explanation of statement I.
(c) Statement I is correct, but statement II is incorrect.
(d) Statement I is incorrect, but statement II is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Both statements I and II are correct and statement II is the correct explanation of statement I.
Both statements are correct, and statement II correctly explains statement I — information and communication technology (like telecommunication, computers, and the Internet) enables instant contact and information exchange worldwide, which helps in spreading globalisation.
Q4: "Globalisation is the process of rapid integration and interconnection between countries." Explain the statement with examples. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Globalisation means growing interconnection and integration among countries through trade, investment, and information exchange.
- Goods and services produced in one country are now sold in many others, linking national economies.
- For example, Indian garments are exported to the USA, and foreign companies like Ford Motors and Coca-Cola operate in India, showing how production and markets are connected across the world.
Thus, globalisation has created a world where countries are economically and technologically interdependent.
Q5: Choose the correct option to fill in the blank:
The process of removing barriers on foreign trade and investment by the government is known as ____________ (1 Mark)
(a) Import Tax,
(b) Export Tax,
(c) Liberalisation,
(d) Industrialisation.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Liberalisation.
Liberalisation refers to the process of removing or reducing government-imposed restrictions or barriers on foreign trade and investment, allowing goods and services to move more freely between countries.
Q6: What changes did the Government of India make in its economic policies in the beginning of 1991? Explain. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In 1991, the Government of India introduced major economic reforms by removing barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment.
This meant that goods could be imported and exported more freely, and foreign companies were allowed to set up factories and offices in India.
These policy changes — known as liberalisation — aimed to make Indian producers more competitive globally and improve efficiency and quality through increased competition.
Q7: Explain any two benefits of globalisation. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two benefits of globalisation are:
- Increased Choice for Consumers:
Globalisation has brought many foreign goods and brands into Indian markets, giving consumers a wider range of products with better quality at competitive prices. - Growth of Investment and Employment:
Many multinational companies (MNCs) have invested in India, creating new industries and job opportunities, especially in sectors like IT, automobiles, and services.
Q8: The growth of digital technology has greatly influenced globalization. Which of the following is its main benefit? (1 Mark)
(a) Increased Communication Cost,
(b) Limited Access to Information,
(c) Enhanced Connectivity,
(d) Slower Transaction Speed.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Enhanced Connectivity.
Digital technology — including the Internet, mobile phones, and computers — has greatly enhanced global connectivity, allowing instant communication, faster exchange of information, and smoother coordination of production and trade across countries, thus boosting globalisation.
Q9: How did the trade policy implemented in 1991 stimulate the globalization in India? Explain with example. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The trade policy of 1991 stimulated globalisation in India by introducing liberalisation — removing barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment.
- Removal of Trade Barriers:
The government reduced import taxes and allowed easier export and import of goods. This encouraged competition and integration with the world market. - Attracting Foreign Investment:
Foreign companies were allowed to set up factories and offices in India, leading to an increase in foreign investment and technology inflow. - Example:
Companies like Ford Motors and Cargill Foods invested in India — Ford set up a large automobile plant near Chennai, while Cargill took over Parakh Foods — showing how foreign investment linked Indian production with global markets.
Thus, the 1991 trade reforms made India an active participant in the global economy.
Q10: Two Statements are given below. Read both the statements and choose the correct option: (1 Mark)
Statement I: In recent times technology in the areas of computer and internet has been changing rapidly.
Statement II: Internet allows us to send instant electronic mail (e-mail) and talk (voice-mail) across the world at negligible costs.
(a) Only I is false but II is true.
(b) Only I is true but II is false.
(c) Both I and II are true but II is not the correct explanation of I.
(d) Both I and II are true and II is the correct explanation of I.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Both I and II are true and II is the correct explanation of I.
Both statements are correct — technology in computers and the Internet has advanced rapidly, and this has enabled instant, low-cost global communication through e-mail and voice-mail, which explains how such technological progress supports globalisation.
Q11: Explain the contribution of foreign trade as an important factor of globalization. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Foreign trade plays a key role in promoting globalisation by connecting markets across countries.
- It allows producers to sell their goods not only in their own country but also in markets abroad, expanding business opportunities.
- It provides consumers with a wider variety of goods from different countries at competitive prices.
For example, the entry of Chinese toys into Indian markets gave buyers more choices at lower prices, showing how foreign trade integrates markets and promotes globalisation.
Q12: Read the following statements for stimulating the process of globalization and choose the correct options: (1 Mark)
I. Government reduces trade barriers.
II. Government reduces competition among producers.
III. Government reduces import and export taxes.
IV. Government removes restrictions on foreign investment.
(a) Only I, II, and III are correct.
(b) Only II, III, and IV are correct.
(c) Only I, III, and IV are correct.
(d) Only I, II, and IV are correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (C) Only I, III, and IV are correct.
Globalisation is stimulated when the government reduces trade barriers, lowers import and export taxes, and removes restrictions on foreign investment — all of which encourage freer flow of goods, services, and capital. Reducing competition among producers, however, goes against globalisation.
Q13: How did information and communication technology promote the process of globalization? Explain. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has promoted globalisation by making communication and information exchange instant, efficient, and low-cost.
- Instant Communication: Telecommunication, computers, and the Internet allow companies to coordinate production and services across countries in real time.
- Example: A magazine designed in Delhi can be sent instantly to London for printing, or customer care services can be handled from India — showing how ICT connects businesses globally and supports globalisation.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Examine the transformations observed in India's trade since 1991. (CBSE 2024) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Indian markets have been transformed since 1991 in the following ways:
- Wider choice: Consumers now enjoy a greater variety of goods and services.
- Access to global brands: The latest models of digital cameras, mobile phones, and televisions from leading manufacturers are readily available. For example, new automobile models are frequently seen on Indian roads.
- Explosion of brands: There is a significant increase in brands across various products, including shirts, televisions, and processed fruit juices.
- Global trade: Producers from any country can sell their products globally, linking markets through trade. Examples include online shopping platforms like Amazon and Flipkart.
- Liberalisation: Enterprises now have the freedom to choose what goods to import or export, with the government imposing far fewer restrictions than before.
Q2: Examine the factors that have enabled globalization in India. (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The factors that have enabled globalisation in India include:
- Information Technology (IT): IT has significantly boosted service production.
- Technological Improvements: Over the past 50 years, advancements in technology, such as the use of containers for transportation, have reduced costs and increased market reach.
- Transportation Advances: Rapid improvements in transportation have made long-distance shipping cheaper and faster.
- Government Policies: The Indian government has removed previous trade barriers, facilitating easier import and export of goods and services.

Previous Year Questions 2023
Q3: Which one of the following is a major benefit to an MNC when it works on joint production with a local company? (2023)(a) MNC shares its latest technology with the local company.
(b) MNC decides all parameters and prices of the product.
(c) MNC shares its institutional policy with local company.
(d) MNC built good and familial relations with the local company
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
When a multinational corporation (MNC) works on joint production with a local company, a major benefit is that the MNC shares its latest technology with the local company. This helps improve the local company’s production processes and quality, making it more competitive. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer, while the other options do not highlight the key advantage of technology transfer.
Q4: Explain any five steps taken by the developing countries to attract Foreign investment. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Steps to Attract Foreign Investment:
- The government has established Special Economic Zones (SEZs) that provide excellent facilities such as electricity, water, and transport.
- Companies operating in SEZs benefit from tax exemptions for the first five years.
- Labour laws have been made more flexible, allowing companies to hire workers without long-term job security during busy periods.
- Various legal concessions are offered to encourage foreign companies to invest.
- Efforts are made to improve infrastructure and services to create a more attractive investment environment.
Q5: Why did the Indian government liberalize trade regulations in 1991? (CBSE 2023)
(a) Government wanted foreign exchange equivalent to Indian Currency.
(b) Government wanted maintain good relations with Western Countries.
(c) Government wanted Indian producers to compete in the World Market.
(d) Government wanted to provide socio-economic justice to all.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The Indian government liberalized trade regulations in 1991 to help Indian producers compete in the global market. By reducing restrictions on imports and exports, it aimed to enhance the efficiency and competitiveness of Indian industries, enabling them to thrive in international trade. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer, while the other options do not directly address the main goal of liberalization.
Q6: How is information technology connected with globalization? (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Information technology has significantly accelerated the process of globalisation. It has transformed how people interact and communicate worldwide.
Key points include:
- People can connect instantly with anyone, anywhere in the world.
- Most transactions, except for the physical movement of goods, can be conducted online.
- Without information technology, globalisation would have progressed much more slowly.
- Communication of essential information would have taken longer, delaying integration among countries.
Q7: 'Liberalization of foreign trade involves policy framework at National and International level’. Explain the statement. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Liberalisation of foreign trade refers to the removal of government restrictions on trade. This process involves a policy framework at both national and international levels.
Key points include:
- Policy Changes in India: In 1991, India made significant policy changes to enhance competition among domestic producers, aiming to improve quality.
- Removal of Barriers: Restrictions on foreign trade and investment were largely lifted, supported by influential international organisations.
- Ease of Trade: This liberalisation allowed for easier import and export of goods, enabling foreign companies to establish factories and offices in India.
- Reduced Restrictions: The government now imposes fewer restrictions compared to the past, indicating a more liberal trade environment.
Q8: Explain the rapid transformation in the communication sector in modern times. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In recent times, technology in the telecommunications, computer, and internet fields has been changing rapidly. Telecommunication facilities such as telegraph, telephone (including mobile phones), etc., are used to contact one another around the world, access information instantly, and communicate from remote areas. Information and communication technology has played a major role in spreading out the production of services across countries. For example, a news magazine published for London readers can be designed and printed in Delhi, with the text of the magazine sent through the internet to the Delhi office.
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q9: Examine the steps taken by the Central and State governments to attract foreign companies to invest in India. (Term-II, 2021-22) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Central and State governments have taken several measures to attract foreign companies to invest in India. Some of these steps include:
- Simplification of rules and regulations: The government has simplified the procedures and regulations related to foreign direct investment (FDI) in order to create a more business-friendly environment. This includes streamlining the approval process and reducing bureaucratic red tape.
- Incentives and benefits: The government offers various incentives and benefits to foreign companies, such as tax exemptions, subsidies, and financial assistance. These incentives are aimed at attracting investment and promoting economic growth.
- Infrastructure development: The government has focused on developing world-class infrastructure, including transportation, communication, and industrial facilities. This infrastructure development provides a conducive environment for foreign companies to set up their operations.
- Skill development and training: The government has prioritized skill development and training programs to enhance the employability of the workforce. This ensures that foreign companies have access to a skilled and qualified pool of talent.
- Sector-specific policies: The government has formulated sector-specific policies to attract foreign investment in key industries such as manufacturing, services, and technology. These policies provide clarity and guidance to foreign companies interested in investing in these sectors.
Overall, the Central and State governments have been proactive in creating a favorable investment climate to attract foreign companies to invest in India.
Q10: “Technology is the vital force in the modern form of globalisation". Explain the statement with suitable examples.
(Term-II,2021-22)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Globalisation and technology are closely linked. The movement of people, goods, and ideas is accelerated by advancements in transport and communication. In turn, technological development benefits from the diversity of ideas and the larger scale that globalisation provides.
Key points about the role of technology in globalisation include:
- Revolutionised economy: Technology has transformed the global economy and is now a critical competitive strategy.
- New markets: Globalisation has opened up new markets, while information technologies support these emerging opportunities.
- Overcoming barriers: Technology helps address major challenges in globalisation, such as trade barriers, ethical standards, transportation costs, and delays in information exchange.
- Collaboration: It enables software experts to collaborate over networks with companies worldwide.
- Transport advancements: Improvements in transportation technology allow for faster and cheaper delivery of goods over long distances.
For example, the use of containers has significantly reduced port handling costs and increased the speed of exports. Additionally, the falling costs of air transport have enabled greater volumes of goods to be shipped by airlines.
Q11: "Globalisation is the process of rapid integration between countries”. Examine the statements. (Term-ll, 2021-22 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Globalisation refers to the integration of a country's economy with those of other nations, allowing for the free flow of trade, capital, and movement of people across borders. Historically, foreign trade has been a key channel connecting countries. This integration occurs when goods from one country are traded in another, thereby linking their markets.
Key points include:
- Trade routes, established in ancient times, connected regions like Asia to the rest of the world.
- These routes facilitated not just the movement of goods, but also the exchange of ideas and cultures.
- Trading companies, such as the East India Company, were drawn to regions like India due to trading interests.
- Foreign trade allows producers to expand beyond domestic markets, increasing competition.
- Consumers benefit from a wider variety of goods, leading to more choices.
As trade opens up, the prices of similar goods in different markets tend to equalise. Producers in different countries compete with each other, regardless of the distance between them. Thus, foreign trade leads to:
- Market integration across countries.
- Increased competition among producers.
- A greater selection of goods for consumers.
In summary, foreign trade plays a crucial role in connecting and integrating markets globally.
Q12: Examine the debate that took place in the World Trade Organisation for the developing countries. (Term-11,2021-22)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: All WTO agreements include special provisions for developing countries, such as:
- Extended timeframes to implement agreements and commitments.
- Measures to enhance their trading opportunities.
- Support for building infrastructure related to WTO activities.
- Assistance in handling disputes and implementing technical standards.
These provisions aim to ensure that developing countries can participate effectively in global trade.

Q13: "The impact of globalisation has not been uniform”. Explain the statement with suitable examples. (Term-ll, 2021-22,2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The impact of globalisation has varied significantly across different groups.
Here are some key points:
- Beneficiaries: Wealthy consumers and skilled producers have gained from globalisation, enjoying greater choice, improved quality, and lower prices.
- Challenges for Small Producers: Many small producers and workers have faced difficulties due to increased competition.
- Job Security: Globalisation has led to less job security for workers, as employers prefer flexible hiring practices.
- Resource Exploitation: Developed countries often source cheap materials from underdeveloped nations, then sell expensive finished goods back to them.
- MNC Investments: Multinational corporations (MNCs) have invested heavily in India, particularly in sectors like electronics and services, creating new jobs.
In summary, while globalisation has created opportunities for some, it has also resulted in significant challenges for others, highlighting the uneven nature of its impact.
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q14: Choose the correct statement about factors regarding globalisation in India:(I) Improvement in transportation technology.
(II) Liberalisation of foreign trade and foreign investment.
(III) Favourable rules of WTO towards India in comparison to developed countries.
Choose the correct options from the codes given below: (2020)
(a) I and II only
(b) I and III only
(c) II and III only
(d) III only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The correct answer is (a) I and II only. Factors contributing to globalization in India include improvements in transportation technology, which make it easier to move goods, and the liberalization of foreign trade and investment, which allows more foreign businesses to operate in India. However, the rules of the WTO do not necessarily favor India over developed countries, so option III is not correct.
Q15: Read the sources given below and answer the questions that follow: (2020)
Source A : Production across countries Until the middle of the twentieth century, production was largely organised within countries. What crossed the boundaries of these countries were raw material, food stuff and finished products. Colonies such as India exported raw materials and food stuff and imported finished goods. Trade was the main channel connecting distant countries. This was before large companies called multinational corporations (MNCs) emerged on the scene.
Source B : Foreign trade and integration of markets Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets, i.e., markets of their own countries. Producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country but can also compete in markets located in other countries of the world. Similarly, for the buyers, import of goods produced in another country is one way of expanding the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced.
Source C : Impact of globalisation in India Globalisation and greater competition among producers - both local and foreign producers - has been of advantage to consumers, particularly the well-off sections in the urban areas. There is greater choice before these consumers v/ho now enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products. As a result, these people today, enjoy much higher standards of living than v/as possible earlier.
Source A : Production across countries
(i) How are MNCs a major force in connecting the countries of the world?
Source B : Foreign trade and integration of markets
(ii) How does foreign trade become a main channel in connecting countries?
Source C : Impact of globalisation in India
(iii) How is globalisation beneficial for consumers?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Countries like India exports raw material, food stuff and finished products through multinational companies to the other countries. Hence, MNCs a major force in connecting the countries of the world.
(ii) Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets, i.e., foreign countries.
(iii) For consumers there is a greater choice than before who enjoy improved quality and lower priced for several product
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q16: State any one example of 'Trade Barrier'. (AI 2019) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Tax on imports is a common example of a trade barrier.
- It raises the price of imported goods.
- This can protect local industries from foreign competition.
- Governments use such barriers to control the amount and type of goods entering the country.
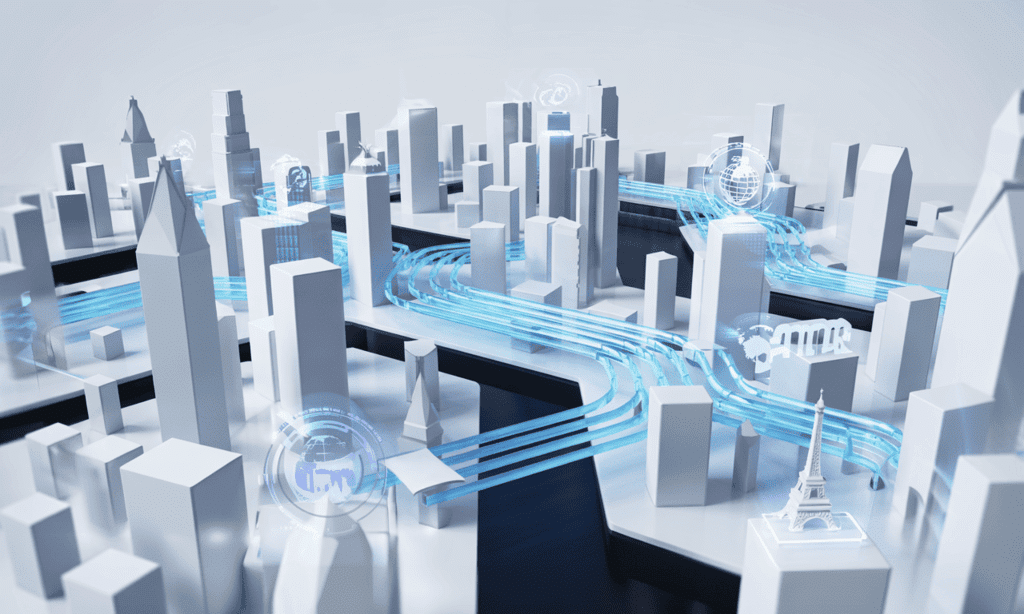
Q17: Analyse any three factors that make globalisation more fair. (AI 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Globalisation refers to the increasing interaction between people and companies worldwide, driven by advancements in transportation and communication technology.
To ensure that globalisation is fair, it is essential to focus on the following factors:
- Proper implementation of labour laws to protect workers' rights.
- Support for small businesses to help them compete against larger corporations.
- Application of trade barriers when necessary to protect emerging sectors.
- Collaboration with other countries to challenge the dominance of developed nations and negotiate fair rules with the WTO.
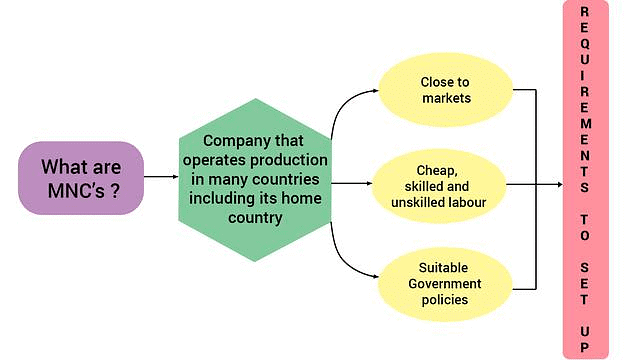
Q18: Analyse the impact of globalisation on Multi-national Corporations (MNCs) in India. (AI 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Globalisation has had a significant positive impact on Multi-National Corporations (MNCs) in India.
The benefits include:
- Proximity to Markets: MNCs can establish production facilities near their target markets, utilising both skilled and unskilled labour at lower costs.
- Favourable Government Policies: MNCs often choose locations based on supportive government policies that align with their interests.
- Joint Ventures: Globalisation allows MNCs to collaborate with local companies, providing them access to capital and advanced technology.
- Improved Products: MNCs have introduced better and safer products to consumers at competitive prices due to globalisation.
Q19: How has technology stimulated the globalisation process? Explain with examples. (CBSE 2019, 12)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Technology has significantly stimulated the globalisation process through various advancements:
- Transport technology: Improvements have enabled faster and cheaper delivery of goods over long distances.
- Containerisation: Goods are transported in containers, reducing port handling costs and speeding up exports.
- Air transport: The cost of air freight has decreased, allowing for larger volumes of goods to be transported quickly.
- Information and communication technology: Innovations in this area, such as the Internet and mobile communication, facilitate instant contact and transactions.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q20: How have our markets been transformed in recent years? Explain with examples.Or
What changes have taken place in the markets during the last twenty years or so? (CBSE 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Our markets have undergone significant transformations in recent years, leading to a remarkable shift in consumer choices.
- Wider selection: Consumers now enjoy a broader range of goods and services.
- Access to latest technology: The newest models of digital cameras, mobile phones, and cars from leading global manufacturers are readily available.
- Brand explosion: There is a vast increase in the number of brands across various products, from shirts to televisions.
These changes reflect a recent phenomenon, enhancing the shopping experience in our markets.
Q21: “Foreign trade integrates the markets in different countries.” Support the statement with arguments. (CBSE 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Foreign trade integrates the markets in different countries:
- Opportunities for Producers: Producers can expand their reach beyond domestic markets.
- Global Sales: They can sell products not only in their own country but also in various international markets.
- Competition: Producers face competition from other countries, enhancing their efficiency.
- Consumer Choice: Buyers gain access to a wider variety of goods from around the world, allowing them to choose according to their needs.
- Increased Collaboration: Producers from different countries may form joint ventures, such as AIG's partnership in India's insurance sector.
- Market Integration: Producers in different countries compete closely, even if separated by vast distances.
Thus, foreign trade effectively connects and integrates markets across nations.
Q22: The impact of globalisation has not been uniform.” Discuss with the help of examples.
Or
Discuss the impact of globalisation on India. (CBSE 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Positive impact:
(i) It has resulted in more choices for consumers to get various products of better quality and at lower prices.
(ii) It has improved the standard of living.
(iii) With the investments by the MNCs new jobs have been created in the developing countries.
(iv) New technology has been introduced.
(v) Large companies have become multi-national companies such as Infosys.
(b) Negative impact:
(i) Creation of special economic zones has disrupted the lives of the people who have been displaced.
(ii) Flexibility in labour laws has worsened the condition of workers who may be appointed temporarily.
(iii) Small producers are unable to compete with MNCs. Thus, several units have been shut down rendering many workers jobless.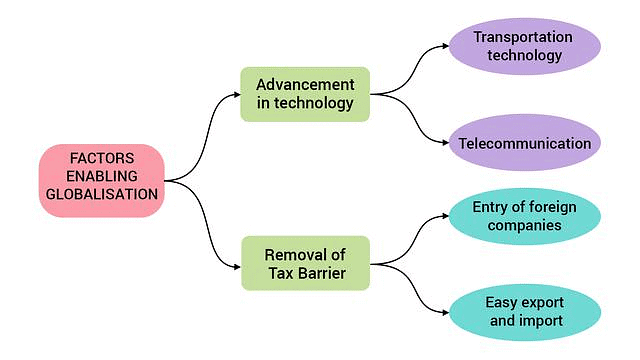
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q23: Why do MNCs set up their offices and factories in those regions where they get cheap labour and other resources? (AI 2016) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Multinational companies (MNCs) often establish their offices and factories in regions where they can access resources at lower costs.
This strategy helps them to:
- Acquire land, labour, and raw materials at cheaper rates.
- Enhance their competitiveness in the global market.
- Increase their profitability by minimising production costs.
Q24: Differentiate between investment and foreign investment. (AI 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Investment by any person or entity is the money spent for buying building, land or other assets with a motive to earn a profit in future by selling it or in any other fashion. Foreign investment is any investment made by a foreign business entity such as a MNC, or an individual or a foreign government in India for buying assets with the motive to earn a profit from it.
Q25: Due to which reason the latest models of different items are available within our reach? (Foreign 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Globalisation has made the latest models of various items easily accessible to consumers. Key reasons include:
- Improved technology: Advances in technology allow for quicker production and distribution.
- Liberalisation: Relaxation of trade restrictions has increased the variety of products available.
- Global markets: Consumers can now access goods from around the world.
As a result, we now enjoy a wider selection of products than ever before.
Q26: Barriers on foreign trade and investment were removed to a large extent in India since 1991.” Justify the statement. (CBSE 2016)
Or
Why had the Indian government put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investments after independence? (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) (i) The government had put restrictions on the import of goods to protect domestic producers from foreign competition.
(ii) The government allowed imports of only essential items such as machinery, fertilisers and petroleum. These restrictions helped to attain technological capability within the country.
(B) (i) Starting around 1991, the government wished to remove the barriers because India had attained technological capability.
(ii) The government decided that the time had come for Indian producers to compete with producers around the globe.
(iii) It felt that competition would improve the performance of producers within the country.
(iv) There would be an unrestricted exchange of capital, technology and experience between India and other countries of the world.
Q27: “Information and communication technology has played a major role in spreading out production of services across countries.” Justify the statement with examples. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Telecommunication facilities - telegraph, mobile phones, fax - are used to contact one another around the world and to communicate from remote areas.
(ii) This has been facilitated by satellite communication devices.
(iii) Computers have now entered almost every field of activity.
(iv) Internet allows us to send instant electronic mail (e-mail) and talk (voice mail) across the world at negligible costs.
(v) IT has played a major role in spreading out the production of services across countries. For example, for a magazine published for London readers different work is done as follows:
(a) Designing in Delhi.
(b) Orders how to design from London.
(c) Designing done on the computer.
(d) After printing sent to London by air.
(e) Payment through e-banking.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q28: How are MNCs controlling and spreading their productions across the world? Explain. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) MNCs set up production jointly with local companies.
(ii) MNCs buy up local companies to expand production.
(iii) MNCs in developed countries place orders for production with small producers of developing countries for various products such as garments, footwear etc. The MNCs sell these products under their brand name. MNCs determine price, quality, delivery and other conditions for these producers.
Q29: Explain the role of technology in stimulating globalisation process. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Technology plays a crucial role in stimulating the globalisation process:
- Transport advancements: Recent improvements in transport technology have enabled faster and cheaper delivery of goods worldwide.
- Containerisation: The use of containers has significantly reduced port handling costs and increased the speed of exports.
- Air transport: Lower costs in air transport have allowed for larger volumes of goods to be transported quickly.
- Information technology: Developments in IT, especially in telecommunications like the internet, have transformed global connectivity.
- Access to information: Tools such as telegraphs, mobile phones, and faxes have made information accessible anytime, anywhere.
- Cost reduction: These technological advancements have lowered operational costs, benefiting consumers globally.
- Research and development: Technology has opened new avenues for further advancements and innovation.
Q30: Why did the Indian government remove barriers to a large extent on foreign trade and foreign investment after 1991? (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Indian government removed barriers on foreign trade and investment after 1991 to:
- Encourage competition among local industries.
- Improve the quality of domestic products.
- Facilitate easier imports and exports.
- Attract foreign investment by allowing companies to establish operations in India.
This process, known as liberalisation, aimed to create a more open market, enabling businesses to make their own decisions regarding trade.
Previous Year Questions 2014
Q31: Explain any four ways by which MNCs exercise control on production. (CBSE 2014) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Multinational Corporations (MNCs) control production in several ways:
- Factory Location: They establish factories near markets to access skilled and unskilled labour at lower costs, along with other necessary resources.
- Local Partnerships: MNCs collaborate with local companies to enhance production capabilities.
- Acquisition: They often buy local firms, allowing them to expand and modernise production using advanced technology and capital.
- Outsourcing: Large MNCs place orders with small producers, selling these products under their own brand names globally.
Previous Year Questions 2012
Q32: How are MNCs spreading their production across countries? Explain with an example.Multinational Corporations (MNCs) are spreading their production in different ways. Some of them are: (CBSE 2012)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Multinational Corporations (MNCs) are expanding their production across countries in several ways:
- By buying local companies and, then expanding production. For example, Cargill Foods, a very large American MNC, purchased small Indian company, Parakh foods. Cargill Foods is, now, the largest producer of edible oil in India with a capacity making 5 million pouches daily.
- By placing orders for production with small producers. Garments, footwears, sports items are examples where production is carried out by small producers for large MNCs around the world.
- By producing jointly with some of the local companies. It benefits the local company in two ways.
- A MNC can provide money for additional investments.
- A MNC can bring latest technology for production.
For example, Ford Motors set up a large plant near Chennai, in collaboration with Mahindra and Mahindra, a major Indian manufacturer of jeeps and trucks.
|
88 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Previous Year Questions - Globalisation and the Indian Economy
| 1. What is the impact of globalization on the Indian economy? |  |
| 2. How has globalization affected Indian agriculture? |  |
| 3. What role do multinational corporations play in India's economy due to globalization? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits and drawbacks of globalization for Indian consumers? |  |
| 5. How has globalization influenced India's trade policies? |  |

















