Class 9 Science - Structure of the Atom Previous Year Questions
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. (a) What are isotopes? Write two isotopes of carbon.
(b) Write two applications of isotopes.
Ans. (a) Atoms of the same elements containing the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes have similar chemical properties but different physical properties.
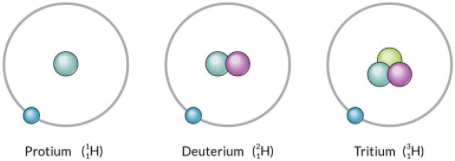 Isotopes of HydrogenIsotopes of carbon: Carbon has two isotopes, carbon-12 and carbon-14.
Isotopes of HydrogenIsotopes of carbon: Carbon has two isotopes, carbon-12 and carbon-14.
Carbon-12 (126C)
No. of protons = 6
No. of neutrons = 6
Carbon-14 (146C)
No. of protons = 6
No. of neutrons = 8
(b) Applications:
1. An isotope of uranium is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors.
2. An isotope of cobalt is used in the treatment of cancer.
Q.2. Two elements X and Y have atomic number 16 and 19 respectively. Compare their valency, number of protons in their ions and number of electrons in their ions.
Ans. Element X is sulphur.
Element Y is potassium.
Valency 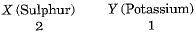
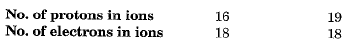
Q.3. An element X forms the following compounds with hydrogen, carbon and phosphorous: 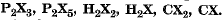 Find the valencies of X and another element present in the compound.
Find the valencies of X and another element present in the compound.
Ans.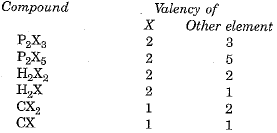
Q.4. Write the electronic configuration and valency of the following:
(i) Chlorine
(ii) Sodium and
(iii) Silicon.
Ans.
Q.5. (a) Both helium and beryllium have two electrons in the valence shells. Helium is a noble gas where as Beryllium is a metal, justify.
(b) Hydrogen exists in three isotopic forms. Why are the isotopes of hydrogen chemically a like?
Ans. (a) Maximum capacity of the first orbit is 2 electrons. Therefore, helium having two electrons in the valence shell is stable and hence has no tendency to react.
Beryllium has two shells K and L. The maximum capacity of the L-shell is 8 whereas beryllium has only 2 electrons in the L-shell. It will therefore react with other beryllium atoms to form Be-Be bonds. It is therefore a metal.
(b) The three isotopes of hydrogen are 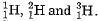 The chemical property of an element depends upon the number of protons. Since the number of protons in the isotopes is the same, the isotopes are chemically alike.
The chemical property of an element depends upon the number of protons. Since the number of protons in the isotopes is the same, the isotopes are chemically alike.
Q.6. An element is represented as 168X. Find
(а) the number of electrons in elements X.
(b) a mass number of the element X.
(c) the number of neutrons in element X.
Ans. The notation 168X illustrates that the element has atomic number as 8 and mass number as 16. This means
Number of protons (or electrons) = 8
Number of protons + Number of neutrons = 16
or
8 + Number of neutrons = 16
or
Number of neutrons = 16 - 8 = 8
Hence,
(a) Number of electrons in the element X = 8
(b) Mass number of element X = 16
(c) Number of neutrons in the element X = 8
Q.7. What was the drawback of Rutherford’s model of the atom?
Ans. It could not explain the stability of atom.
Q.8. According to Bohr and Bury scheme what is the maximum number of electrons present in M-shell of an atom?
Ans. The maximum number of electrons in M-shell = 2 x 32 = 2 x 9 = 18.
Q.9. (a) How do we know the presence of atoms if they do not exist independently for most of the elements?
(b) Write full form of IUPAC.
Ans. (a) Atoms do not exist independently for most of the elements. But they combine with other elements through a chemical bond and form compounds. Through the study of compounds, we come to know about the presence of atoms.
(b) International union of pure and applied chemists.
Q.10. If chlorine atom is available in the form of two isotopes 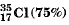 and
and 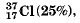 calculate the average atomic mass of chlorine atom.
calculate the average atomic mass of chlorine atom.
Ans. This is calculated as under: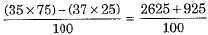
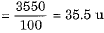
Q.11. Define the term isobar with one example.
Ans. Isobars are atoms of different elements having the same mass number but different atomic numbers.
Q.12. (a) Calculate the average atomic mass of chlorine if it exists commonly in two isotopes.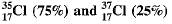
(b) Write the main drawback of Rutherford’s model of an atom.
Ans. (a) Average atomic mass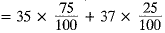
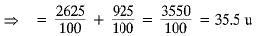
(b) Draw backs of Rutherford’s Model of an Atom: Any charged particle when accelerated is expected to radiate energy. To remain in a circular orbit, the electron would need to undergo acceleration. Therefore, it would radiate energy.
The loss of energy would lead to shrinking of the orbit in size. In short time, it would hit the nucleus. Therefore, an atom cannot be expected to be stable.
Q.13. In the following table, the mass number and the atomic number of certain elements are given: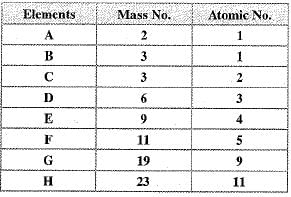
(a) How many neutrons are present in ‘F'?
(b) Which atoms are isotopes of the same element?
(c) Which atom will form singly positively charged ion?
(d) Which is the atom of an inert gas?
(e) Which will form singly negatively charged ion?
(f) Which of these has 11 electrons?
Ans. (a) Number of neutrons in 'F’ is equal to 11 - 5 = 6
(b) A and B are isotopes of the same element.
(с) 'D’ and ‘H’ can form singly +ve ions.
(d) Element 'C’ is inert gas.
(e) 'G’ will form singly negatively charged ion.
(f) 'H’ has 11 electrons.
Q.14. Give reasons:
(a) Mass number of an atom excludes the mass of an electron.
(b) Nucleus of an atom is charged.
(c) Alpha particle scattering experiment was possible by using gold foil only and not by foil of any other metal.
Ans. (a) It is because mass of electron is negligible.
(b) Nucleus of an atom consists of positively charged protons and neutrons which do not have charge.
(c) It is because gold metal is highly malleable and very thin foil of gold foil was taken.
Q.15. What is a proton? Who discovered it?
Ans. Proton is positively charged particle present in nucleus.
It was discovered by Goldstein.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. (i) Define Isotopes and Isobars with examples.
(ii) Give electronic configuration of any one pair of isotopes and isobars.
Ans. (i) Isotopes: Isotopes are defined as the atoms of the same element having the same atomic number but different mass numbers. For example, protium 11H and deuterium 21H.
Isobars: Atoms of different elements having same mass number but with different atomic numbers are called isobars. For example 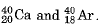

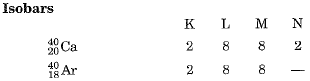
Q.2. Give reasons for the following:
(а) Isotopes of an element are chemically similar.
(b) An atom is electrically neutral.
(c) Noble gases show least reactivity.
(d) Ions are more stable than atoms.
(e) Na+ has completely filled K and L shells.
Ans. (a) Chemical properties of an element depend upon the atomic number. All the isotopes of an element have the same atomic number and therefore are chemically similar.
(b) An atom has the equal number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons. Therefore atom is electrically neutral.
(c) Noble gases contain 8 electrons in the outermost shell (2 in case of helium). This is the maximum capacity of the outermost shell. Hence they show least reactivity.
(d) Ions are more stable than atoms because the former have an octet structure.
(e) Electronic configuration of Na is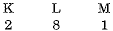
Na+ is formed from Na by removing the electron from the M shell. Therefore it has the completely filled K and L shells.
Q.3. (a) Define Valency. What conclusions can be drawn about the reactivity of an atom from its valency?
(b) Why does an atom of Argon have zero valency? Explain using the electronic configuration of Argon.
Ans. (a) Valency is defined as the number of electrons lost or gained or shared to attain the nearest noble gas (stable) configuration. If valency is equal to 1 or 2, the element is highly reactive. If valency is equal to zero, it is not reactive. If valency equal to 3 or 4 it is less reactive.
(b) Argon has its octet complete (2, 8, 8), therefore, it cannot gain or lose or share electrons. So, its valency is equal to zero.
Q.4. (a) The average atomic mass of a sample of an element X is 16.2 u. What are the percentage of isotope 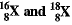 in the sample.
in the sample.
(b) On the basis of Thomson’s model of an atom explain how the atom is neutral as a whole.
Ans. (a) Percentage of Isotopes 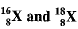
Let percentage of 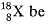 'x', therefore, percentage of
'x', therefore, percentage of 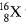 will be 100 - x
will be 100 - x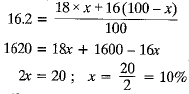
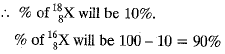
(b) Positively charged particles and negative charged particles are equal, therefore, an atom is neutral on the basis of Thomson model.
Q.5. (a) A helium atom has an atomic mass of 4 u and two protons in its nucleus. How many neutrons does it have?
(b) Write down the electronic configuration of oxygen. [At. No. = 8]
(c) The atomic mass of an element S is 16.2 u. What are the percentages of isotopes of X having atomic number 8 and mass numbers 16 and 18.
Ans. (a) The atomic mass of helium = 4 u
∴ No. of protons of + No. of neutrons = 4
or 2 + No. of neutrons = 4
or No. of neutrons = 4 - 2 = 2
(b) Electronic configuration of oxygen is 2, 6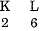
(c) Let the percentage of isotope with mass no 16 = x
Then percentage of isotope with mass no. 18 = 100 - x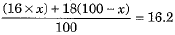
or 16x + 1800 - 18x = 1620 or - 2x = 1620 - 1800
or - 2x = - 180 or x = 90
The percentage of isotope with mass number 16 = 90
Percentage of isotope with mass number 18 = 100 - 90 = 10
|
84 videos|544 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science - Structure of the Atom Previous Year Questions
| 1. What are the basic components of an atom? |  |
| 2. How do isotopes differ from each other? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the atomic number? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of electron shells? |  |
| 5. What is the role of neutrons in an atom? |  |

















