NCERT Exemplar: Tissues | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Epithelial tissue
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Parenchyma - Living tissues with thin cell wall with central vacuole and dense cytoplasm. Parenchyma cells are located in the soft parts of the plants such as pith and cortex.
Sclerenchyma - These are dead tissues which have thick cell wall due to deposition of lignin. They are generally located in the leaf veins, hard coverings of the seeds and can also be found surrounding the vascular bundle.
Collenchyma - Living tissues which have an elongated shape and thick cell wall in the corner. Collenchyma tissue can be located in the leaf stalks, below the epidermis, etc.
Epithelial tissues - Epithelial tissues are covering or protective tissues in the animal body. Almost all organs and cavities are covered by Epithelium.
Q.2. Find out incorrect sentence
(a) Parenchymatous tissues have intercellular spaces
(b) Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners
(c) Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues
(d) Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues because these are meristematic tissues, not permanent tissues. Meristematic tissues are actively dividing cells responsible for growth, while permanent tissues are mature, non-dividing cells.
Q.3. The girth of stem increases due to
(a) apical meristem
(b) lateral meristem
(c) intercalary meristem
(d) vertical meristem
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Lateral meristems (e.g., vascular cambium and cork cambium) are responsible for secondary growth, which increases the thickness (girth) of stems and roots in plants.
Q.4. Which cell does not have perforated cell wall?
(a) Tracheids
(b) Companion cells
(c) Sieve tubes
(d) Vessels
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Tracheids are elongated cells in the xylem that help in water conduction, but they lack perforated cell walls. Instead, they have pits for water movement. Companion cells, sieve tubes, and vessels have specialized structures, including perforations, to facilitate transport.
Q.5. Intestine absorbs the digested food materials. What type of epithelial cells are responsible for that?
(a) Stratified squamous epithelium
(b) Columnar epithelium
(c) Spindle fibres
(d) Cuboidal epithelium
Ans: (b)
Explanation: The columnar epithelium is pillar-like cells which have nuclei towards their base. Columnar epithelium forms the lining of the stomach, small intestine and colon, forming the mucous membrane. They facilitate movement across the epithelial barrier. Their main function is absorption and secretion.
Q.6. A person met with an accident in which two long bones of hand were dislocated. Which among the following may be the possible reason?
(a) Tendon break
(b) Break of skeletal muscle
(c) Ligament break
(d) Areolar tissue break
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Dislocation of bones occurs when joints held by ligaments get separated.
Tendons join skeletal muscle and they cause inflammation upon a break.
Break of skeletal muscle cannot be the reason for bone dislocation as bones are joined by ligaments.
Areolar tissues are found around muscles, nerves and blood vessels hence they are not connected with bone dislocation.
Q.7. While doing work and running, you move your organs like hands, legs etc. Which among the following is correct?
(a) Smooth muscles contract and pull the ligament to move the bones
(b) Smooth muscles contract and pull the tendons to move the bones
(c) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the ligament to move the bones
(d) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the tendon to move the bones
Ans: (d)
Explanation: While doing work and running, you move your organs like hands, legs etc, skeletal muscles contract and they pull the tendon, connecting muscles to bones. This will help bones to move and they do not pull the ligament as that will cause a sprain or stretch.
Q.8. Which muscles act involuntarily?
(i) Striated muscles
(ii) Smooth muscles
(iii) Cardiac muscles
(iv) Skeletal muscles
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles which are also striated muscles hence the answer should be cardiac muscles which are smooth muscles.
Q.9. Meristematic tissues in plants are
(a) localised and permanent
(b) not limited to certain regions
(c) localised and dividing cells
(d) growing in volume
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Meristematic tissues in plants are the dividing cells, which are responsible for plant growth in certain specific region. Meristematic tissues are classified as apical, lateral and intercalary based on their location.
Q.10. Which is not a function of epidermis?
(a) Protection from adverse condition
(b) Gaseous exchange
(c) Conduction of water
(d) Transpiration
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Conduction of water is a function of xylem tissue whereas protection, gaseous exchange and transpiration are the function of epidermis.
Q.11. Select the incorrect sentence
(a) Blood has matrix containing proteins, salts and hormones
(b) Two bones are connected with ligament
(c) Tendons are non-fibrous tissue and fragile
(d) Cartilage is a form of connective tissue
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Tendons are fibrous tissues which are highly elastic and strong.
12. Cartilage is not found in
(a) nose
(b) ear
(c) kidney
(d) larynx
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Cartilage is a connective tissue which provides support and flexibility to various parts of our body. Cartilage is found in nose, ear, larynx but not in kidney. Renal tubules and corpuscles in the kidney are formed by Cuboidal epithelium tissue.
Q.13. Fats are stored in human body as
(a) cuboidal epithelium
(b) adipose tissue
(c) bones
(d) cartilage
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Adipose tissue present below the skin and between internal organs stores fat. Cells in these tissues are filled with fat globules. Fat storage acts as an insulator.
Q.14. Bone matrix is rich in
(a) fluoride and calcium
(b) calcium and phosphorus
(c) calcium and potassium
(d) phosphorus and potassium
Ans: (b)
Explanation: The bone matrix is primarily composed of collagen fibers and minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus, in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals. These minerals provide bones with strength and rigidity. Fluoride and potassium are not major components of bone matrix.
Q.15. Contractile proteins are found in
(a) bones
(b) blood
(c) muscles
(d) cartilage
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Muscles cells have contractile proteins in them. These proteins are responsible for the contraction and relaxation of muscles.
Q.16. Voluntary muscles are found in
(a) alimentary canal
(b) limbs
(c) iris of the eye
(d) bronchi of lungs
Ans: (b)
Explanation: We can move some muscles on our own will. Muscles present in our limbs can move at our will and stop when we so decide. Such muscles are called voluntary muscles. On the other hand, alimentary canal, iris of the eye and bronchi of lungs has involuntary muscles.
Q.17. Nervous tissue is not found in
(a) brain
(b) spinal cord
(c) tendons
(d) nerves
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Connective tissue which connects muscles to bones is tendons. They are fibrous in nature and give strength and limited flexibility.
Q.18. Nerve cell does not contain
(a) axon
(b) nerve endings
(c) tendons
(d) dendrites
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Neurons do not contain tendons as they are connective tissues that join skeletal muscles to bones.
Q.19. Which of the following helps in repair of tissue and fills up the space inside the organ?
(a) Tendon
(b) Adipose tissue
(c) Areolar
(d) Cartilage
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Areolar connective tissue is found between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow. It fills the space inside the organs, supports internal organs and helps in the repair of tissues.
Areolar tissue located between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow. Areolar tissue fills the space inside the organs and supports internal organs and helps in the repair of tissue.
Q.20. The muscular tissue which functions throughout the life continuously without fatigue is
(a) skeletal muscle
(b) cardiac muscle
(c) smooth muscle
(d) voluntary muscle
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Heart muscles are cylindrical, branched and uninucleated which shows rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life. Skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and voluntary muscles work as and when required.
Q.21. Which of the following cells is found in the cartilaginous tissue of the body
(a) Mast cells
(b) Basophils
(c) Osteocytes
(d) Chondrocytes
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Mast cells are found in areolar tissue.
Basophils are found in blood
Osteocytes are found in bone.
Q.22. The dead element present in the phloem is
(a) companion cells
(b) phloem fibres
(c) phloem parenchyma
(d) sieve tubes
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Phloem fibres possess narrow lumen and they are thick-walled elongated spindle-shaped dead cells. They provide mechanical support to the tissue. Phloem parenchyma is thin-walled living cells of parenchyma. They have two functions, storage and lateral food conduction. Except for phloem fibres, other phloem cells are living cells.
Q.23. Which of the following does not lose their nucleus at maturity?
(a) Companion cells
(b) Red blood cells
(c) Vessel
(d) Sieve tube cells
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Companion cells retain their nucleus at maturity, unlike red blood cells, vessel elements, and sieve tube cells, which lose their nucleus.
Q.24. In desert plants, the rate of water loss gets reduced due to the presence of
(a) cuticle
(b) stomata
(c) lignin
(d) suberin
Ans: (a)
Explanation: The cuticle is a protective layer covering the epidermis of the leaf, young shoots and other aerial parts of a plant. It contains lipids and polymers impregnated with wax. This minimizes the effect of heat and reduces the loss of water.
Q.25. A long tree has several branches. The tissue that helps in the sideways conduction of water in the branches is
(a) collenchyma
(b) xylem parenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) xylem vessels
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Collenchyma is an active tissue which has no role in the conduction of water. Parenchyma is a supportive tissue. Xylem vessels which are also known as xylem trachea are responsible for conduction of water in plants.
Q.26. If the tip of sugarcane plant is removed from the field, even then it keeps on growing in length. It is due to the presence of
(a) cambium
(b) apical meristem
(c) lateral meristem
(d) intercalary meristem
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Stem located at the base of leaves or nodes and leads to the increase in the length of an organ such as leaves and internodes is intercalary meristem. They are responsible for the longitudinal growth of the plant, hence the length of the sugarcane keep on increasing.
Q.27. A nail is inserted in the trunk of a tree at a height of 1 metre from the ground level. After 3 years the nail will
(a) move downwards
(b) move upwards
(c) remain at the same position
(d) move sideways
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Longitudinal growth in the stem always takes place on the top hence apical meristem in the below region remains constant, hence there will be no change in position of nail inserted in the trunk of the tree.
Q.28. Parenchyma cells are
(a) relatively unspecified and thin-walled
(b) thick-walled and specialised
(c) lignified
(d) none of these
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Parenchyma is the most common simple permanent tissue. It consists of relatively unspecialised cells with thin cell walls. They are living cells. They are usually loosely arranged, thus large spaces between cells (intercellular spaces) are found in this tissue.
Q.29. Flexibility in plants is due to
(a) collenchyma
(b) sclerenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) chlorenchyma
Ans: (a)
Explanation: The flexibility in plants is due to collenchyma. Collenchyma allows bending of various parts of a plant-like tendrils and stems of climbers without breaking. It also provides mechanical support. Collenchyma is found in leaf stalks below the epidermis.
Q.30. Cork cells are made impervious to water and gases by the presence of
(a) cellulose
(b) lipids
(c) suberin
(d) lignin
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Cork cells have a thickened, waterproof cell wall due to the presence of suberin, a waxy substance. It makes cork impervious to water and gases, providing protection and preventing water loss.
Q.31. Survival of plants in the terrestrial environment has been made possible by the presence of
(a) intercalary meristem
(b) conducting tissue
(c) apical meristem
(d) parenchymatous tissue
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Conducting tissues xylem and phloem are responsible for the survival of plants in the terrestrial environment. Xylem conduct water from roots to all the parts of the plants and phloem transports food and other nutrients from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Q.32. Choose the wrong statement
(a) The nature of matrix differs according to the function of the tissue
(b) Fats are stored below the skin and in between the internal organs
(c) Epithelial tissues have intercellular spaces between them
(d) Cells of striated muscles are multinucleate and unbranched
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Epithelial tissues do not have intercellular spaces between them rather they are tightly bound together to make a continuous sheet.
Q.33. The water-conducting tissue generally present in gymnosperm is
(a) vessels
(b) sieve tube
(c) tracheids
(d) xylem fibres
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Vessels are generally absent in Gymnosperms.
Sieve tubes are present in phloem hence they have no role in conduction of water
Xylem fibres provide structural rigidity and they have no role in conduction of water.
Short Answer Questions
Q.34. Animals of colder regions and fishes of cold water have thicker layer of subcutaneous fat. Describe why?
Ans: Animals of colder regions and fishes of cold water have a thicker layer of subcutaneous fat because fats act as insulator and prevent the escape of heat from their body. This will help the animals in resisting low temperature in cold climates.
Q.35. Match the column (A) with the column (B)
(A) – (B)
(a) Fluid connective tissue – (i) Subcutaneous layer
(b) Filling of space inside the organs – (ii) Cartilage
(c) Striated muscle – (iii) Skeletal muscle
(d) Adipose tissue – (iv) Areolar tissue
(e) Surface of joints – (v) Blood
(f) Stratified squamous epithelium – (vi) Skin
Ans:
(A) – (B)
(a) Fluid connective tissue – (v) Blood
(b) Filling of space inside the organs – (iv) Areolar tissue
(c) Striated muscle – (iii) Skeletal muscle
(d) Adipose tissue – (i) Subcutaneous layer
(e) Surface of joints – (ii) Cartilage
(f) Stratified squamous epithelium – (vi) Skin
Q.36. Match the column (A) with the column (B)
(A) – (B)
(a) Parenchyma – (i) Thin-walled, packing cells
(b) Photosynthesis – (ii) Carbon fixation
(c) Aerenchyma – (iii) Localized thickenings
(d) Collenchyma – (iv) Buoyancy
(e) Permanent tissue – (v) Sclerenchyma
Ans:
(A) – (B)
(a) Parenchyma – (i) Thin-walled, packing cells
(b) Photosynthesis – (ii) Carbon fixation
(c) Aerenchyma – (iv) Buoyancy
(d) Collenchyma – (iii) Localized thickenings
(e) Permanent tissue – (v) Sclerenchyma
Q.37. If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapours appear on the wall of glass jar. Explain why?
Ans: Because of a process called transpiration, the water is released from the plants in the form of vapours. These vapours appear on the glass jar if a potted plant is covered with the glass jar.
Q.38. Name the different components of xylem and draw a living component?
Ans: Xylem comprises tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. The only living component of xylem is xylem parenchyma.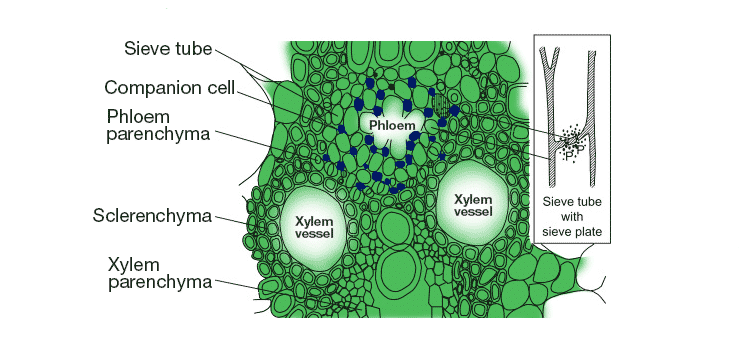
Q.39. Draw and identify different elements of phloem.
Ans: 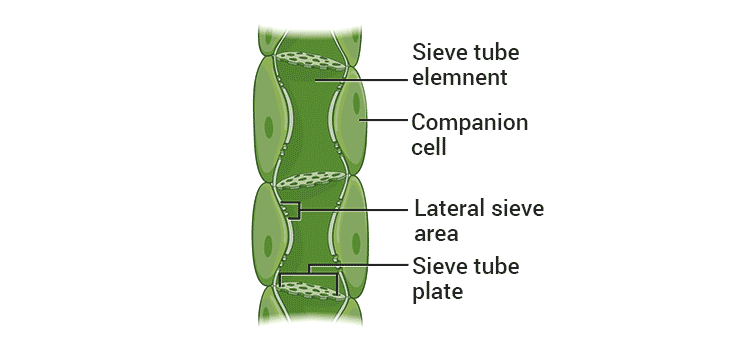
Q.40. Write true (T) or false (F)
(a) Epithelial tissue is protective tissue in animal body.
(b) The lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli and kidney tubules are all made up of epithelial tissue.
(c) Epithelial cells have a lot of intercellular spaces.
(d) Epithelial layer is permeable layer.
(e) Epithelial layer does not allow regulation of materials between body and external environment.
Ans:
(a) True
(b) True
(c) False
(d) True
(e) False
Q.41. Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Give one example of each type.
Ans: 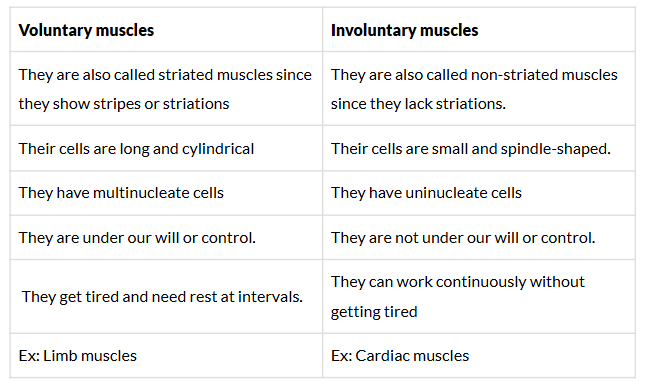
Q.42. Differentiate the following activities on the basis of voluntary (V) or involuntary (I V) muscles.
(a) Jumping of frog
(b) Pumping of the heart
(c) Writing with hand
(d) Movement of chocolate in your intestine
Ans:
a-v, b-iv, c-v, d-iv
(a) Jumping of frog – is an activity of voluntary muscles
(b) Pumping of the heart- is a function of involuntary muscles
(c) Writing with hand- is a function of voluntary muscles
(d) Movement of chocolate in your intestine- is a function of involuntary muscles
Q.43. Fill in the blanks
(a) Lining of blood vessels is made up of———.
(b) Lining of small intestine is made up of ———.
(c) Lining of kidney tubules is made up of———.
(d) Epithelial cells with cilia are found in———of our body
Ans:
(a) Lining of blood vessels is made up of squamous epithelium
(b) Lining of small intestine is made up of columnar epithelium
(c) Lining of kidney tubules is made up of cuboidal epithelium
(d) Epithelial cells with cilia are found in respiratory tract of our body
Q.44. Water hyacinth float on water surface. Explain.
Ans: Water hyacinth float on the water surface because of the presence of the air cavities present in the parenchyma tissue.
Q.45. Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites?
Ans: The epidermis is the structure that protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites. It has thick cuticle and dermal tissue which help in preventing the attack from parasites.
Q.46. Fill in the blanks
(a) Cork cells possesses———on their walls that makes it impervious to gases and water.
(b) ——— have tubular cells with perforated walls and are living in nature.
(c) Bone possesses a hard matrix composed of———and ———.
Ans:
(a) Cork cells possesses suberin on their walls that makes it impervious to gases and water.
(b) Sieve tubes have tubular cells with perforated walls and are living in nature.
(c) Bone possesses a hard matrix composed of calcium and Phosphorus.
Q.47. Why is epidermis important for the plants?
Ans: The epidermis is important for it gives protection against water loss. Epidermal cell present on the aerial parts of the plant often secretes a waxy, water-resistant layer on their outer surface. This provides protection against loss of water, mechanical injury and invasion by parasitic fungi. Epidermal tissue forms a continuous layer which helps to avoid mechanical stress.
Q.48. Fill in the blanks (a) ———are forms of complex tissue. (b) ———have guard cells. (c) Cells of cork contain a chemical called——— (d) Husk of coconut is made of ———tissue. (e) ———gives flexibility in plants. (f) ———and———are both conducting tissues. (g) Xylem transports———and———from soil. (h) Phloem transport———from———to other parts of the plant
Ans:
(a) Xylem and Phloem
(b) Stomata
(c) Suberin
(d) Sclenchyma
(e) Collenchyma
(f) Xylem;Phloem
(g) Water and minerals
(h) Food, leaf
Long Answer Questions
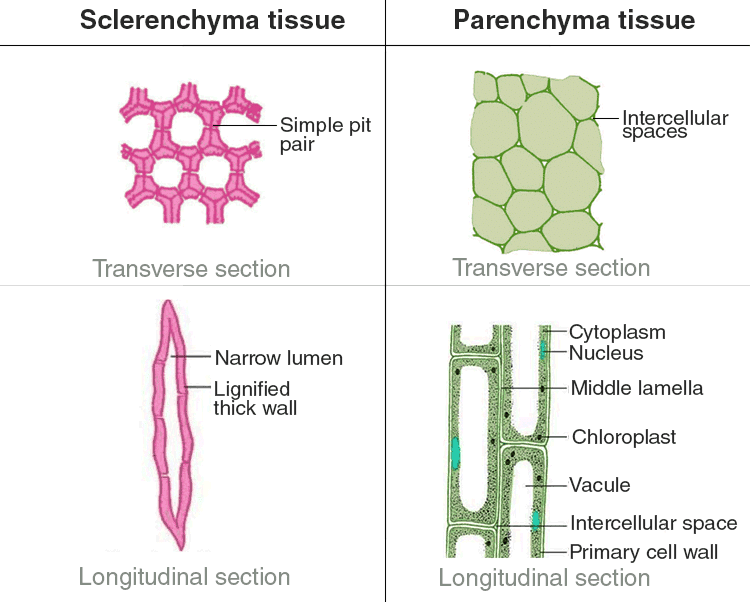
Q.49. Differentiate between sclerenchyma and parenchyma tissues. Draw well labelled diagram.
Ans: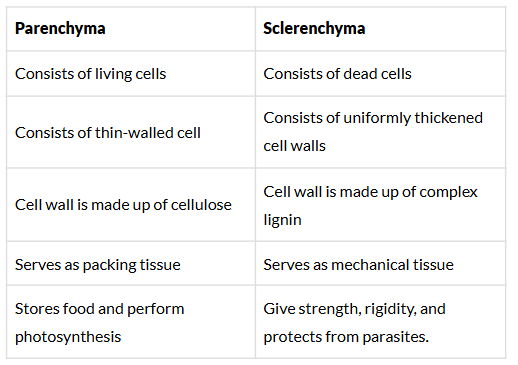
Q.50. Describe the structure and function of different types of epithelial tissues. Draw diagram of each type of epithelial tissue.
Ans: Epithelial cells are the thin protective coverings that line most organs and cavities within the body. It also forms a barrier to keep different body systems separate. The skin, the lining of the mouth, the lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli and kidney tubules are all made of epithelial tissue. Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet.
Depending on the shape and function, epithelial cells are classified into:
a) Squamous epithelial tissue: In cells lining blood vessels or lung alveoli transportation of substances occurs through a selectively permeable surface, this epithelium is a flat kind of epithelium. This is called the simple squamous epithelium. Simple squamous epithelial cells are extremely thin and flat and form a delicate lining. The oesophagus and the lining of the mouth are also covered with squamous epithelium.
b) Stratified squamous epithelium: Skin epithelial cells are arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear. Since they are arranged in a pattern of layers, the epithelium is called stratified squamous epithelium.
c) Columnar epithelium: Where absorption and secretion occur, as, in the inner lining of the intestine, these tall epithelial cells are present. This columnar epithelial facilitates movement across the epithelial barrier. In the respiratory tract, the columnar epithelial tissue also has cilia, which are hair-like projections on the outer surfaces of epithelial cells.
d) Cuboidal epithelium: These form the lining of the kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands where these provide mechanical support. Sometimes, a portion of the epithelial tissue folds inward and a multicellular gland is formed. This is the glandular epithelium.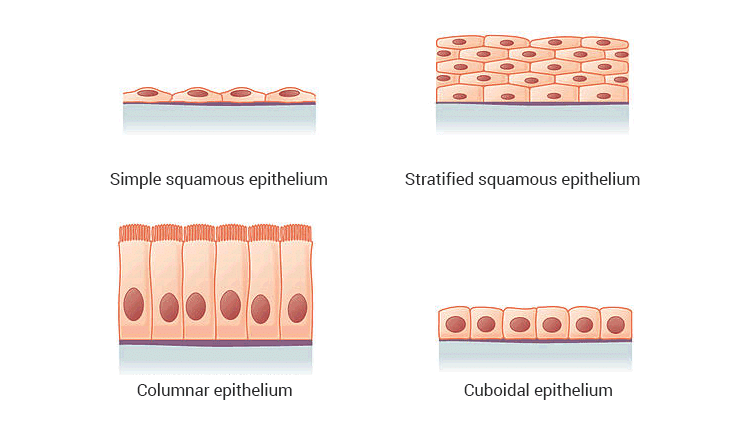
Q.51. Draw well labelled diagrams of various types of muscles found in human body.
Ans: 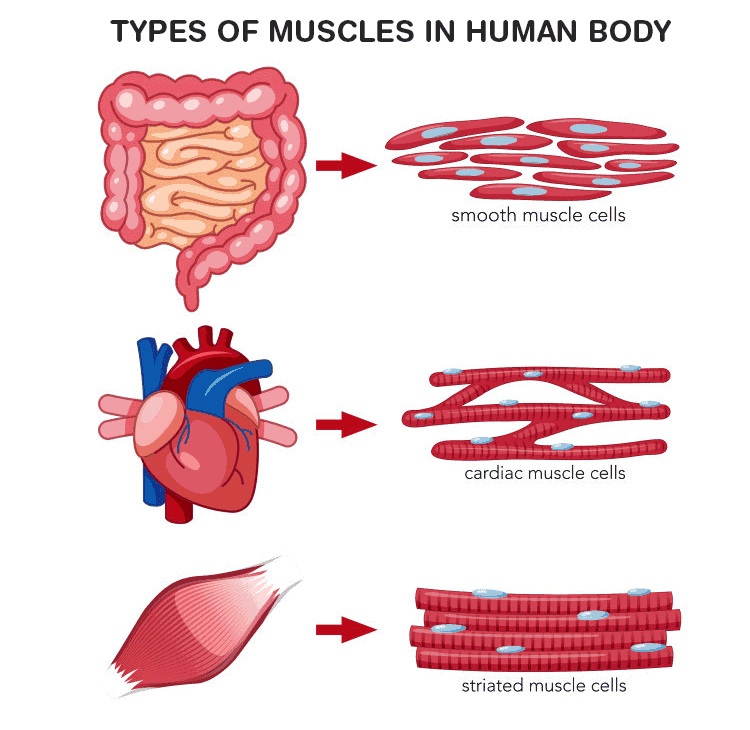
Q.52. Give reasons for
(a) Meristematic cells have a prominent nucleus and dense cytoplasm but they lack vacuole.
(b) Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissues.
(c) We get a crunchy and granular feeling, when we chew pear fruit.
(d) Branches of a tree move and bend freely in high wind velocity.
(e) It is difficult to pull out the husk of a coconut tree.
Ans:
a) Meristematic tissue cells are continuously dividing and they have a prominent nucleus and a dese cytoplasm. Since they are diving rigorously they need not store food or waste products hence they lack vacuoles.
b) Cellwall of sclerenchyma are lignified and are packed densely to protect the plant and to give mechanical strength hence intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissues.
c) In pear fruit sclerenchyma cells are called stone cells. They are small, thick and hard. Due to this, we get a crunchy and granular feeling, when we chew pear fruit.
d) Junction of the tree branch composed of collenchyma cells which provide rigidity and flexibility to the branches. Hence, branches of a tree move and bend freely in high wind velocity.
e) Husk of coconut tree is sclerenchyma which is hard. Hence it is difficult to pull out the husk of a coconut tree.
Q.53. List the characteristics of cork. How are they formed? Mention their role.
Ans: Characteristics of cork.
- Cork cells are mature and dead
- They are compactly arranged
- They do not have intercellular spaces
- They are thick and have several layers.
Outer protective tissue of the plant undergoes changes with age. The epidermis of the stem is replaced by a secondary meristem call phellogen or cork cambium .It is a simple tissue which consists of rectangular cells whose protoplasts are vacuolated. Cork cells contain tannins.
Cork cambium forms cork on the outer side and secondary cortex on the inner side by giving off new cells on both its sides. The layer of cells which is cut by cork cambium on the outer side ultimately becomes several layered thick cork (bark) of trees.
Cork cells are compactly arranged dead cells and they lack intercellular spaces. Walls of cork cells are thickened with suberin which is fat. Due to Suberin, these cells are impermeable to water and gases.
Role of cork
Cork provides protection to plant and it prevents loss of water from plant body. Cork protects the plants from infection and mechanical injury. Cork is light in weight and it cannot catch fire. Because of this property, it is used as insulators. Cork is hard in nature hence it is used to make sports goods.
Q.54. Why are xylem and phloem called complex tissues? How are they different from one other?
Ans: A complex tissue is the one which has more than one type of cells having a common origin which coordinates to perform a common function. Xylem and phloem are made of different types of cells hence they are called complex tissues.
Xylem is made up of four different types of cells (elements), namely
(i) tracheids- Tracheids are elongated cells in the xylem of vascular plants that serve in the transport of water and mineral salts.
(ii) vessels- A vessel element (trachea) is one of the cell types found in xylem, the water-conducting tissue of plants. Vessel elements are found in flowering plants
(iii) xylem parenchyma- xylem parenchyma. live plant cells that are short, lignified and generally thin-walled. They surround conducting elements and assist directly or indirectly in the conduction of water upwards through vessels and tracheids, and also serve for food storage.
(iv) xylem sclerenchyma (or fibre)- Xylem fibres are mainly supportive in function.
Phloem is also made of four different types of elements
(i) sieve tubes- Sieve tube, in flowering plants, elongated living cells (sieve-tube elements) of the phloem, the nuclei of which have fragmented and disappeared and the transverse end walls of which are pierced by sievelike groups of pores (sieve plates). They are the channels of food (mostly sugar) transport.
(ii) companion cells- companion cell A type of cell found within the phloem of flowering plants. Companion cell is usually closely associated with a sieve element. Its function is uncertain, though it appears to regulate the activity of the adjacent sieve element and to take part in loading and unloading sugar into the sieve element.
(iii) phloem parenchyma
(iv) phloem fibre
Q.55. (a) Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissues in plants
(b) Define the process of differentiation.
(c) Name any two simple and two complex permanent tissues in plants.
Ans:
The basic differences between meristematic and permanent tissues of plants are tabulated below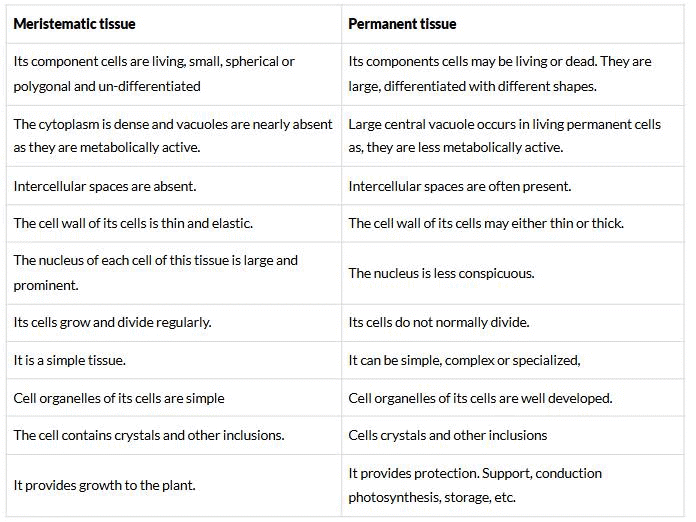
(b) Cells derived from the division of meristematic tissues take up specific roles and gradually lose their ability to divide. Thus, they form permanent tissue. Differentiation is a process by which the cells divide meristematically to take a permanent shape, size and function
(c) Parenchyma and collenchyma are two simple permanent tissues whereas xylem and phloem are two complex permanent tissues.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Tissues - Science Class 9
| 1. What are the main types of tissues found in plants? |  |
| 2. How are animal tissues classified? |  |
| 3. What is the function of xylem and phloem in plants? |  |
| 4. What role does epithelial tissue play in the human body? |  |
| 5. How do meristematic tissues contribute to plant growth? |  |






















