Class 10 Maths Previous Year Questions - Circles- 1
Previous Year Questions 2024
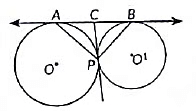
Q1: The maximum number of common tangents that can be drawn to two circles intersecting at two distinct points is: (CBSE 2024)(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 1
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)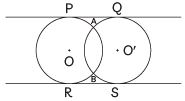 Here, circle with centre O and O' are intersecting at two distinct points A and B. So, in this situation PQ, RS are the tangents which can be drawn.
Here, circle with centre O and O' are intersecting at two distinct points A and B. So, in this situation PQ, RS are the tangents which can be drawn.
Q2: In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. MN is the chord and the tangent ML at point M makes an angle of 70° with MN. The measure of ∠MON is: (CBSE 2024)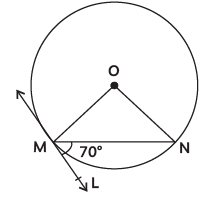
(a) 120º
(b) 140º
(c) 70º
(d) 90º
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
OM ⊥ ML [as tangent from centre is ⊥ at point of contact]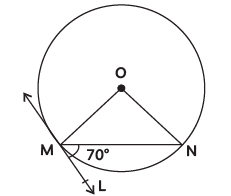
∠OML = 90º
and ∠NML = 70º
⇒ ∠OMN = 90º – 70º = 20º
∵ OM = ON = Radii of same circle
∴ ∠OMN = ∠ONM = 20º
In ∆MON,
∠OMN + ∠ONM + ∠MON = 180º
⇒ 20º + 20º + ∠MON = 180º
⇒ ∠MON = 140º
Q3: In the given figure, if PT is tangent to a circle with centre O and ∠TPO = 35º, then the measure of ∠x is (CBSE 2024)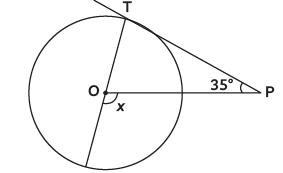 (a) 110º
(a) 110º
(b) 115º
(c) 120º
(d) 125º
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (d)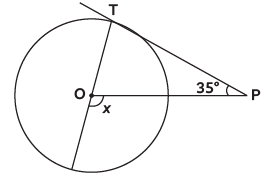 ∠OTP = 90º [Line from centre is ⊥ to tangent at point of contact]
∠OTP = 90º [Line from centre is ⊥ to tangent at point of contact]
∠x = ∠TPO + ∠OTP [Exterior Angle Prop.]
x = 35º + 90º = 125º
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q4: In the given figure, PT is a tangent at T to the circle with centre O. If ∠TPO = 25°, then x is equal to: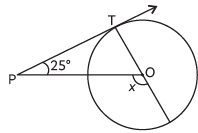 (a) 25°
(a) 25°
(b) 65°
(c) 90°
(d)115° (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (d)
Since tangent is perpendicular to radius at the point of contact.
∴ ∠PTO = 90°
Hence, by the exterior angle formula, in ΔOTP, we get x = 90° + 25°
= 115°
Q5: In the given figure, PQ is tangent to the circle centred at O. If ∠AOB = 95o, then the measure of ∠ABQ will be (2023)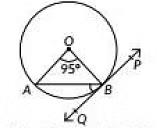 (a) 47.5°
(a) 47.5°
(b) 42.5°
(c) 85°
(d) 95°
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a)
We have ∠AOB = 95°
In ΔAOB, ∠OAB = ∠OBA
Now, ∠OAB + 95° + ∠OBA =180° (Angle sum property of a triangle)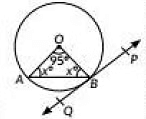
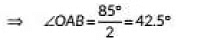
∴ ∠OAB = ∠OBA = 42.5° [From (i)]
Now, OB is perpendicular to the tangent line PQ
∠OBQ = 90°
OA = OB (Radius of circle)
So ∠OAB = ∠OBA
95 + 2x = 180 (Sum of angles of a triangle is 180)
2x = 85
=> x = 42.5
∠ABQ = 90 - 42.5
= 47.5
Q6: In the given figure. TA is a tangent to the circle with centre O such that OT = 4 cm, ∠OTA= 30o, then length of TA is (2023)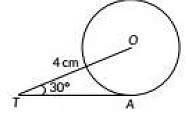 (a) 2√3 cm
(a) 2√3 cm
(b) 2cm
(c) 2√2 cm
(d) √3 cm
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a)
Draw OA ⊥ TA.
In ΔOTA ∠OAT = 90° [∵ Tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius passing through the point of contact]
and ∠OTA = 30°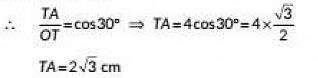
Q7: In figure, from an external point P, two tangents PQ and PR are drawn to a circle of radius 4 cm with centre O. If ∠QPR= 90°. then length of PQ is (2023)
(a) 3 cm
(b) 4 cm
(c) 2 cm
(d) 2√2 cm
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
Join OR.
We know that tangent to a circle is ⊥ to radius at the point of contact. So, QQ⊥PQ and QR ⊥ PR.
Also, ∠QPR = 90°
Now, in quadrilateral OQPR,
∠QQR - 360o - (90° + 90° + 90°)
= 90°
Also, PQ - PR [∵ Tangents drawn from an external point are equal)
∴ PQQR is a square.
Hence, PQ = OQ = 4 cm
Q8: The length of tangent drawn to a circle of radius 9 cm from a point 41 cm from the centre is (2023)
(a) 40 cm
(b) 9 cm
(c) 41 cm
(d) 50 cm
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a)
OB ⊥ AB [∵As tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of the contact]
In ΔOAB,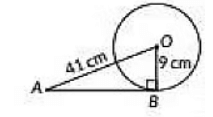
OA2 = OB2 + AB2 [By Pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (41)2 = 92 + AB2
⇒ AB2 = 412 – 92
= (41 - 9)(41 + 9)
= (32)(50)
= 1600
⇒ AB = 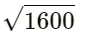
= 40 cm
Q9: In the given figure. O is the centre of the circle and PQ is the chord. If the tangent PR at P makes an angle of 50° with PQ, then the measure of ∠POQ is (2023)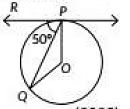 (a) 50°
(a) 50°
(b) 40°
(c) 100°
(d) 130°
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (c)
PR is tangent which touches circle at point P.
So, ∠OPR = 90°
∠OPQ = 90° - ∠RPQ = 90° - 50° = 40°
In, ΔPOQ,
OP = OQ (Radii of circle)
So, ∠OQP = ∠OPQ=40°
⇒ ∠POQ = 180° - 40° - 40° = 100°
Q10: Case Study: The discus throw is an event in which an athlete attempts to throw a discus. The athlete spins anti-clockwise around one and a half times through a circle, then releases the throw. When released, the discus travels along tangent to the circular spin orbit.
In the given figure, AB is one such tangent to a circle of radius 75cm. Point O is the centre of the circle and ∠ABO = 30°. PQ is parallel to OA.
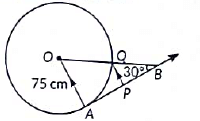
Based on above information
(a) Find the length of AB.
(b) Find the length of OB.
(c) Find the length of AP.
OR
Find the value of PQ. (2023)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns:
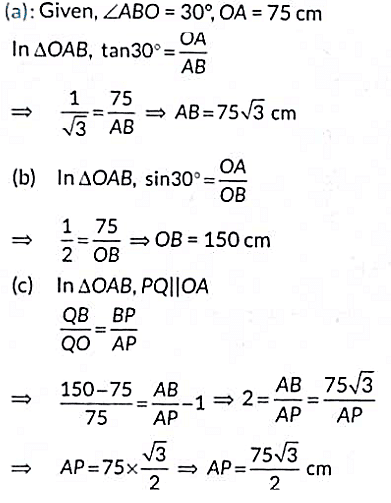
OR

Q11: Two tangents TP and TQ are drawn to a circle with centre O from an external point T. Prove that ∠PTQ = 2∠OPQ. (2023)
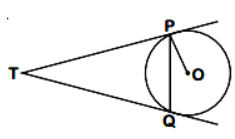
 View Answer
View AnswerAns:
We know that the lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
∴ TP = TQ ... (1)
∴ ∠TQP = ∠TPQ (angles of equal sides are equal) ... (2)
Now, PT is tangent, and OP is the radius.
∴ OP ⊥ TP (Tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact)
∴ ∠OPT = 90°
or, ∠OPQ + ∠TPQ = 90°
or, ∠TPQ = 90° - ∠OPQ ... (3)
In ∆TPQ,
∠TPQ + ∠PQT + ∠QTP = 180° (Sum of angles of a triangle is 180°)
or, 90° - ∠OPQ + ∠TPQ + ∠QTP = 180°
or, ∠(90° - ∠OPQ) + ∠TPQ + ∠QTP = 180° [from (2) and (3)]
or, 180° - 2∠OPQ + ∠TPQ = 180°
or, 2∠OPQ = ∠TPQ - proved
Q12: In the given figure, a circle is inscribed in a quadrilateral ABCD in which ∠B = 90°. If AD = 17 cm, AB = 20 cm and DS = 3 cm, then find the radius of the circle. (2023)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given, ∠B = 90°, AD = 17 cm, AB = 20cm, DS = 3 cm
Now, DS = DR and AR = AQ [∵ Tangents drawn from an externa! point to the circle are equal]
∴ DR = 3 cm
AR = AD - DR = 17 - 3 = 14 cm
∴ AQ = 14 cm
Now, BQ = AB - AQ = 20 - 14 = 6 cm
OQ ⊥ BQ, OP ⊥ BP (∵ Tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact)
∴ Quadrilateral BQOP is a square
∴ BQ = OQ = r = 6 cm
Hence, the radius of the circle = 6 cm.
Q13: From an external point, two tangents are drawn to a circle. Prove that the line joining the external point to the centre of the circle bisects the angle between the two tangents. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Let P lie an external point, O be the centre of the circle and PA and PB are two tangents to the circle as shown in figure.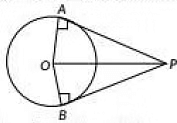
In ΔQAP and ΔOBP.
OA = OB [Radius of the circle]
OP = OP [common]
PA = PB
[∵ Tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal]
So, ΔOAP = ΔOPB
So, ∠APO = ∠BPO
Hence. OP bisects ∠APB
Q14: Two concentric circles are of radii 5 cm and 3 cm. Find the length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Let the centre of the two concentric circlet is O and AB be the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle at point P as shown in figure.
∴ AB is a tangent to the smaller circle at point P
⇒ OP ⊥ AB
By Pythagoras theorem, in ΔOPA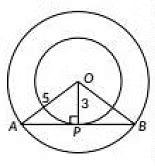
OA2 = AP2 + OP2
⇒ 52 = AP2 +32
⇒ AP2 =52 - 32 = 25 - 9
⇒ AP2 = 16 ⇒ AP = 4cm
∴ AB = 2AP = 8cm
In ΔOPB Since, OP ⊥ AB
AP = PB [∵ Perpendicular drawn from the centre of the circle bisects the chord]
∴ AS = 2AP = 2 x 4 = 8 cm
∴ The length of the chord of the larger circle is 8 cm.
Q15: Prove that the angle between the two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle is supplementary to the angle subtended by the line segment joining the points of contact at the centre. (2023)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Let PA and PB are two tangents on a circle from point P as shown in the figure.
Let is known that tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
∠OAP =∠OBP = 90°
In quadrilateral AOBP,
∠OAP + ∠APB + ∠PBO + ∠BOA = 360°
90° + ∠APB + 90° + ∠BOA = 360° [Using (i)]
∠APB + ∠BOA = 360° - 180°
∴ ∠APB + ∠BOA = 180°
Hence proved.
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q16: In Fig, AB is the diameter of a circle centered at O. BC is tangent to the circle at B. If OP bisects the chord AD and ∠AOP= 60°, then find m∠C. (2022)
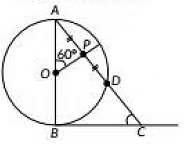
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Since, OP bisects the chord AD, therefore ∠OPA = 90° ....[∵ The line drawn through the centre of a circle to bisect a chord is perpendicular to the chord]
Now, In ΔAOP,
∠A = 180° – 60° – 90°
= 120° – 90°
= 30°
Also, we know that the tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact
∴ ∠ABC = 90°
Now, In ΔABC,
∠C = 180° – ∠A – ∠B
= 180° – 30° – 90°
= 150° – 90°
= 60°
Q17: In Fig. XAY is a tangent to the circle centred at 0. If ∠ABO = 40°. Then find ∠BAY and ∠AOB (2022)
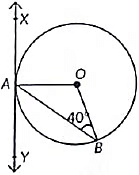
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: 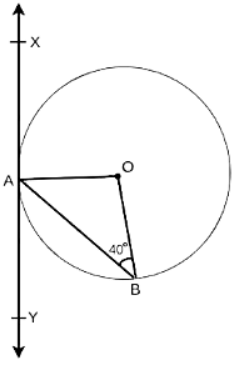
Given, ∠ABO = 40°
∠XAO = 90° ...(Angle between radius and tangent)
OA = OB ...(Radii of same circle)
⇒ ∠OAB = ∠OBA
∴ ∠OAB = 40°
Now, applying the linear pair of angles property,
we get
∠BAY + ∠OAB + ∠XAO = 180°
⇒ ∠BAY + 40° + 90° = 180°
⇒ ∠BAY + 130° = 180°
⇒ ∠BAY = 180° – 130°
⇒ ∠BAY = 50°
Now, In ΔAOB,
∠AOB + ∠OAB + ∠OBA = 180°
or, ∠AOB + 40° + 40° = 180°
or, ∠AOB = 180° – 80° = 100°
Hence proved.
Q18: In Figure, two circles with centres at O and O' of radii 2r and r, respectively, touch each other internally at A. A chord AB of the bigger circle meets the smaller circle at C. Show that C bisects AB. (2022)
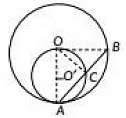
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given: Two circles with centres O and O' of radii 2r and r respectively, touch each other internally at A, AB is the chord of bigger circle touches the smaller circle at C.
To prove: C bisects AB i.e. AC = CB
Here, for smaller circle (O' r)
∠ACO = 90° (Angle in a semicircle is 90°)
∴ OC ⊥ AC
Now, in bigger circle (O, 2r)
Since. AB is a chord and OC ⊥ AB.
AB = CB
[∵ Perpendicular drawn from centre of the circle to a chord bisects the chord]
Hence, C bisects the chord AB.
Q19: In Figure, PQ and PR are tangents to the circle centred at O. If ∠OPR = 45°, then prove that ORPQ is a square. (2022)
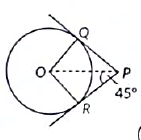
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: It is given that ∠QPR = 90°
We know that the lengths of the tangents drawn from the outer point to the circle are equal.
PQ = PR ... (1)
The radius is Perpendicular to the tangent line at the point of contact.
∴ ∠PQO = 90°
and
∠ORP = 90°
In quadrilateral OQPR:
∠QPR + ∠PQO + ∠QOR + ∠ORP = 360°
⇒ 90° + 90° + ∠QOR + 90° = 360°
⇒ ∠QOR = 360° - 270° = 90°
∴ QPR = ∠PQO = ∠QOR = ∠ORP = 90°
It can be concluded that PQOR is a square.
Q20: In Fig., there are two concentric circles with centre O. If ARC and AQB are tangents to the smaller circle from point A lying on the larger circle, find the length of AC if AO = 5 cm. (2022)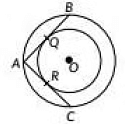
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given, AQ = 5 cm
AQ = AR = 5 cm {v Tangents drawn from an external point to the circle are equal)
Now, AC = AR + RC (∵ OR is a perpendicular bisector of AC AR = RC)
AC = 10 cm
Q21: In Figure, O is the centre of the circle. PQ and PR are tangent segments. Show that the quadrilateral PQOR is cyclic. (2022)
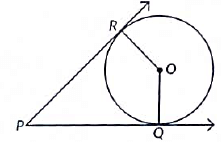
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given: PQ and PR are tangents from an external point P.
To prove: PQOR is a cyclic quadri lateral.
Proof OR and OQ are tlie radius of circle centred at O, and PR a ltd PQ are tangents.
∠ORP = 90° and ∠OQP = 90°
In quadrilateral PQOR, we have
∠OQP + ∠QOR + ∠ORP + ∠RPQ = 360°
90° + ∠QOR + 90° + ∠RPQ = 360°
180° + ∠QOR + ∠RPQ = 360°
∠QOR + ∠RPQ = 360° - 180°
So, ∠O + ∠P = 180°
∠P and ∠O are opposite angles of quadrilateraI which are supplementary.
∴ PQOR is a cyclic quadrilateral.
Q22: In Figure O is centre of a circle of radius 5 cm. PA and BC are tangents to the circle at A and B respectively. If OP = 13 cm. then find the length of tangents PA and BC. (2022)
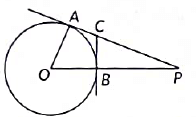
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: 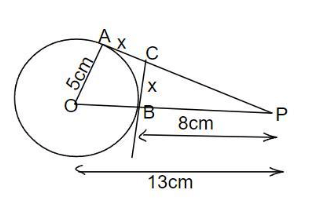
Given, radius of circle =5cm
PA and BC are two tangent at point A and B
OP = 13 cm
Step1: OA is perpendicular on tangent AP (OA is radius of the circle)
In right angle triangle AOAP
(OP)2 = (OA)2 + (AP)2
⇒ (AP)2 = (OP)2 – (0A)2
⇒ (AP)2 = (13)2 - (5)2 = 169 - 25 = 144
AP = √144 = 12
AP = PA = 12 cm
Step 2: Let length of BC be x
But AC = BC= x (tangent from an external point)
So length of PC = 12 - x and PB = OP - OB = 13 - 58cm
(OB is the radius and length of OP is given)
OB is perpendicular on tangent CB , so ∠OBC = ∠CBP = 90 °
In right angle triangle ΔCBP
(CP)2 = (BP)2 + (BC)2
⇒ (12 - x)2 = (8)2 + (x)2
⇒ 144 - 2x + x2 = 64 + x2
⇒ 144 - 24x - 64 = 0
⇒ 80 - 24x = 0 ⇒ x = 80/24 = 3.33cm
Hence, the length of BC is 3.33 cm and PA is 12 cm
Q23: In fig. PQ is a chord of length 8 cm of a circle of radius 5 cm. The tangents at P and Q meet at a point T. Find the length of TP. (2022)
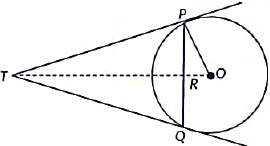
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: In the given figure,
PQ = 8 cm and OP = 5 cm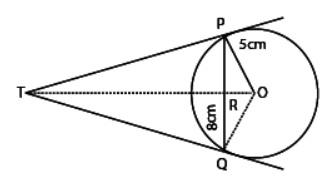
OR ⊥ PQ and so, OR bisects PQ. [ ∵ Perpendicular drawn from the center to the chord bisects the chord]
⇒ PR = RQ = 4 cm
In Δ POR ,
OP2 = OR2 + PR2
⇒ 52 = OR2 + 42
⇒ OR = 3 cm
In ΔTPO and ΔPRO,
∠ TOP = ∠ ROP [common]
and ∠ TPO = ∠ PRO [each 90º]
∴ Δ TPO and Δ PRO are similar. [by AAA Similarity]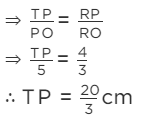
[∵Tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal in length]
Q24: Prove that a parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus. (2022)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given : A parallelogram ABCD circumscribing a circle with centre O.
To prove : ABCD is a rhombus.
Proof: We know that the tangents drawn to a circle from an external Doint are eaual in length.
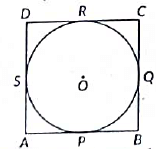
⇒ AP = AS [Tangents drawn from A] ...(i)
⇒ BP = BQ [Tangents drawn from B] ...(ii)
⇒ CR= CQ [Tangents drawn from C] ...(iii)
⇒ DR = DS [Tangents drawn from D] ...(iv)
Adding (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) we get
AP + BP + CR + DR = AS + BQ + CQ + DS
= (AP + BP) + (CR + DR) = (AS + DS) + (BQ + CQ)
⇒ AB + CD = AD + BC
⇒ 2AB = 2BC [Opposite sides of the given parallelogram are equal ∴ AB = DC and AD = BC)
AB = BC = DC = AD
Hence, ABCD is a rhombus.
Q25: In fig, if a circle touches the side QR of ΔPQR at S and extended sides PQ and PR at M and N, respectively, then
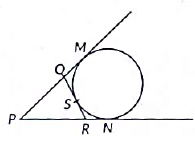
Prove that 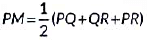 (2022)
(2022)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given: A circle is touching a side QR of ΔPQR at point S.
PQ and PR are produced at M and N respectively.
To prove: 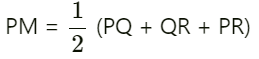
Proof: PM = PN ...(i) (Tangents drawn from an external point P to a circle are equal)
QM = QS ...(ii) (Tangents drawn from an external point Q to a circle are equal)
RS = RN ...(iii) (Tangents drawn from an external point R to a circle are equal)
Now, 2PM = PM + PM
= PM + PN ...[From equation (i)]
= (PQ + QM) + (PR + RN)
= PQ + QS + PR + RS ...[From equations (i) and (ii)]
= PQ + (QS + SR) + PR
= PQ + QR + PR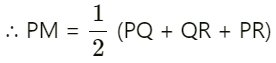
Hence proved.
Q26: In figure, a triangle ABC with ∠B = 90° is shown. Taking AB as diameter, a circle has been drawn intersecting AC at point P. Prove that the tangent drawn at point P bisects BC. (2022)
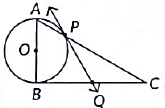
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: 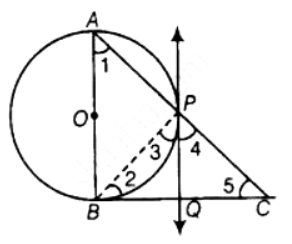
According to the question,
In a right angle ΔABC is which ∠B = 90°, a circle is drawn with AB as diameter intersecting the hypotenuse AC at P.
Also PQ is a tangent at P
To Prove: PQ bisects BC i.e. BQ = QC
Proof: ∠APB = 90° ...[Angle in a semicircle is a right-angle]
∠BPC = 90° ...[Linear Pair]
∠3 + ∠4 = 90° ...[1]
Now, ∠ABC = 90°
So in ΔABC
∠ABC + ∠BAC + ∠ACB = 180°
90° + ∠1 + ∠5 = 180°
∠1 + ∠5 = 90° ...[2]
Now, ∠1 = ∠3 ...[Angle between tangent and the chord equals angle made by the chord in alternate segment]
Using this in [2] we have
∠3 + ∠5 = 90° ...[3]
From [1] and [3] we have
∠3 + ∠4 = ∠3 + ∠5
∠4 = ∠5
QC = PQ ...[Sides opposite to equal angles are equal]
But also, PQ = BQ ...[Tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal]
So, BQ = QC
i.e. PQ bisects BC.
Q27: In the figure, two circles touch externally at P. A common tangent touches them at A and B, and another common tangent is at P, which meets the common tangent AB at C. Prove that ∠APB = 90°. (2022)
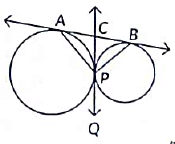
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Let common tangent at P meets the tangent AB at C. Since, tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal
∴ AC = CP
and BC = CP
⇒ ∠CAP = ∠CPA = x (say) ...(i)
and ∠CBP = ∠CPB = y (say) ...(ii)
Now, ∠ACP+ ∠BCP = 180° [Linear pair] ...(*)
In ΔACP, ∠ACP + ∠CPA + ∠CAP = 180° ...(iii)
and in ΔBCP, ∠BCP+ ∠CPB + ∠CBP = 180°...(iv)
Adding (iii) and (iv), we get
∠ACP + x + x + ∠BCP + y + y = 360°
∠ACP + ∠BCP + 2x + 2y = 360° [Using (i) & (ii)]
= 2(x + y) = 360° - 180° = 180°[Using ('))
⇒ x + y = 90°
i.e., ∠CPA + ∠CPB = 90° => ∠APB = 90°
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q28: In the given figure, PT and PS are tangents to a circle with centre O, from a point P such that PT = 4 cm and ∠TPS = 60°. Find the length of the chord TS. (2021)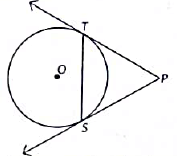
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given TP and SP are tangents from an external point P.
PT = PS = 4 cm (v Tangents drawn from an external point to the circle are equal)
∠PTS = ∠PST
(∵ Angles opposite to equal sides are equal) In A TPS, by angle sum property
∠TPS = ∠PTS =∠PST = 60°
⇒ ΔTPS is an equilateral triangle.
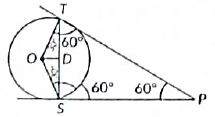
∴ TP = PS = TS = 4 cm
∠OSP = 90º and ∠TSP = 60º
∴ ∠OSD = 30º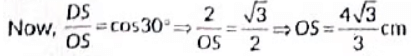
Previous Year Questions 2020
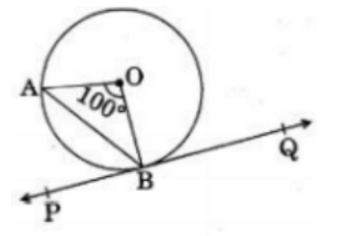
Q29: In figure, PQ is tangent to the circle with centre at O, at the point B. If ∠AOB = 100°, then ∠ABP is equal to (2020)
(a) 50°
(b) 40°
(c) 60°
(d) 80°
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a)
Given that
∠ AOB = 100°
Since OA = OB
So ∠ OAB = ∠ OBA = 40°
Since PQ is tangent on the circle. So OB is perpendicular to PQ.
So,
∠ OBP = 90°
∠ OBA + ∠ ABP = 90°
∠ ABP = 90 – ∠ OBA
∴ ∠ ABP = 90° – 40°
∴ ∠ ABP = 50°
Q30: In the given figure, PT is a tangent at T to the circle with centre O. If ∠TPO = 25°, then x is equal to (2020)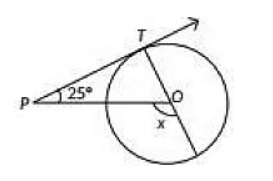 (a) 25°
(a) 25°
(b) 65°
(c) 90°
(d) 115°
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (d)
Since ∠TPO = 25° and ∠OTP = 90°
x = ∠OTP + ∠TPO
= 90° + 25° = 115°
[∵ Radius is perpendicular to the tangent T]
Q31: In the given figure, QR is a common tangent to the given circles, touching externally at the point T. The tangent at T meets QR at P If PT = 3.8 cm, then the length of QR(in cm] is (2020)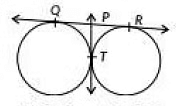 (a) 3.8
(a) 3.8
(b) 7.6
(c) 5.7
(d) 1.9
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (b)
It is known that the length of the tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
∴ QP = PT= 3.8 cm and PR = PT = 3.8 cm
Now, QR = QP + PR = 3.8cm + 3.8cm = 7.6 cm
Q32: In Figure, if tangents PA and PB from an external paint P to a circle with centre O are inclined to each other at an angle of 80° then ∠POA is equal to (2020)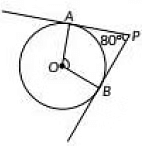 (a) 50°
(a) 50°
(b) 60°
(c) 80°
(d) 100°
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: (a)
A tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact.
In ΔOAP and in ΔOBP:
- OA = OB (radii of the circle are always equal)
- AP = BP (length of the tangents)
- OP = OP (common)
Therefore, by SSS congruency ΔOAP ≅ ΔOBP.
SSS congruence rule: If three sides of one triangle are equal to the three sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
If two triangles are congruent, then their corresponding parts are equal.
Hence:
- ∠POA = ∠POB
- ∠OPA = ∠OPB
Therefore, OP is the angle bisector of ∠APB and ∠AOB.
Hence, ∠OPA = ∠OPB = 1/2 (∠APB)
= 1/2 × 80°
= 40°
By the angle sum property of a triangle, in ΔOAP:
∠A + ∠POA + ∠OPA = 180°
OA ⊥ AP (Theorem 10.1: The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.)
Therefore, ∠A = 90°
90° + ∠POA + 40° = 180°
130° + ∠POA = 180°
∠POA = 180° - 130°
∠POA = 50°
Thus, option (A) 50° is the correct answer.
Q33: In figure, a quadrilateral ABCD is drawn to circumscribe a circle. Prove that AB + CD = BC + AD. (2020)
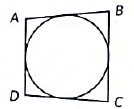
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Let the circle touches the sides AB, BC, CD and DA of quadrilateral ABCD at P, Q, R and S respectively Since, lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to the circle are equal.
AP = AS ...(1) (Tangents drawn from A)
BP = BQ ...(2) (Tangents drawn from B)
CR = CQ ...(3) (Tangents drawn from C)
DR = DS ...(4) (Tangents drawn from D)
Adding (1), (2), (3) and (4), we get
AP + BP + CR + DR = AS + BQ + CQ + DS
⇒ (AP + PB) + (CR + RD) = (AS + SD) + (BQ + QC)
⇒ AB + CD = AD + BC
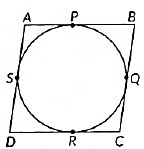
Q34: In figure, find the perimeter of ΔABC if AP =12 cm. (2020)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns:
Step 1: Identify the Tangents
From the problem, we know that AP and AQ are tangents to the circle from point A, and BC is also a tangent. According to the properties of tangents from an external point, the lengths of the tangents drawn from the same external point to a circle are equal.
Step 2: Set Up the Equations
Since AP = 12 cm, we can conclude that:
- AP = AQ = 12 cm (Equation 1)
Step 3: Identify Other Tangents
From point B, the tangents BD and BP are equal:
- BD = BP (Equation 2)
From point C, the tangents CD and CQ are equal:
- CD = CQ (Equation 3)
Step 4: Express Perimeter of Triangle ABC
The perimeter of triangle ABC can be expressed as:
Perimeter = AB + BC + AC
Step 5: Substitute for BC
Since BC is composed of the tangents from B and C:
BC = BD + CD
Thus, we can rewrite the perimeter as:
Perimeter = AB + (BD + CD) + AC
Step 6: Express AB and AC in Terms of Tangents
From the properties of tangents:
- AP = AB + BP
- AQ = AC + CQ
Substituting BP and CQ with BD and CD respectively, we have:
- AP = AB + BD (Equation 4)
AQ = AC + CD (Equation 5)
Step 8: Simplify the Expression
Since AP = AQ and both are equal to 12 cm:
Perimeter = (12 - BD) + (BD + CD) + (12 - CD)
This simplifies to:
Perimeter = 12 + 12 = 24 cm
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q35: In the given figure, a circle is inscribed in a ΔABC having sides BC = 6 cm, AB = 10 cm and AC = 12 cm. Find the lengths BL, CM and AN. (2019)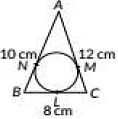
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Let BL = x, BN = x
[∵ Tangents drawn from an external point to to the circle are equal in length]
CL = CM = 8 - x [∵ BC = 8cm]
AN = AM = 10 - x [∵ AB = 10cm]
But AC= 12cm[Given]
∴ AM + MC = 12
10 - x + 8 - x = 12
⇒ 18 - 2x = 12
⇒ 6 = 2x
⇒ x = 3
Length of BL = 3cm
Length of CM = 8 - 3 = 5 cm
Length of AN = 10 - 3 = 7 cm
Q36: Prove that tangents drawn at the ends of a diameter of a circle are parallel. (2019)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns:
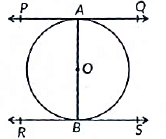
Given : A circle C(O, r)with diameter AB and let PQ and RS be the tangents drawn to the circle at point A and B.
To prove: PQ || RS
Proof: Since tangent at a point to a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
∴ AB ⊥ PQ and AB ⊥ R S
⇒ ∠PAB = 90° and ∠ABS = 90°
⇒ ∠PAB = ∠ABS
⇒ PQ || RS [∵ ∠PAB and ∠ABS are alternate interior angles]
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q37: The difference between the radii of the smaller circle and the larger circle is 7 cm and the difference between the areas of the two circles is 1078 sq. cm. Find the radius of the smaller circle. [CBSE Delhi 2017 (C)] View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given: r2 - r1 = 7 (r2 > r1) ...(i)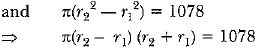
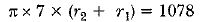 (From equation (i))
(From equation (i))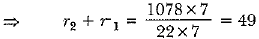 ..... (ii)
..... (ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), we get
2r2 = 56
⇒ r2 = 28 cm
Also, r1 = 21 cm (From equation (i))
∴ Radius of simaller circle = 21 cm.
Q38: Prove that the tangent drawn at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact. [AI (C) 2017]
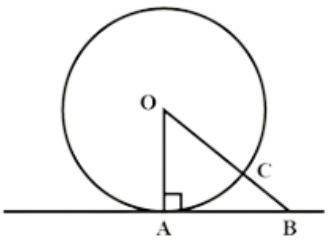
 View Answer
View AnswerAns:
Referring to the figure:
OA = OC (Radii of circle)
Now OB = OC + BC
∴ OB > OC (OC being radius and B any point on tangent)
⇒ OA < OB
B is an arbitrary point on the tangent.
Thus, OA is shorter than any other line segment joining O to any point on the tangent.
Shortest distance of a point from a given line is the perpendicular distance from that line.
Hence, the tangent at any point of the circle is perpendicular to the radius.
Q39: In Fig., PQ is a chord of length 8 cm of a circle of radius 5 cm. The tangents drawn at P and Q intersect at T. Find the length of TP. [AI (C) 2017, Foreign 2015]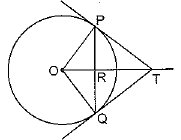
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given: PQ is a chord of length 8 cm
Radius OP = 5 cm. PT and QT are tangents to the circle.
To find: TP
OT is perpendicular bisector of PQ
∠ORP = 90°
(Line joining the centre of circle to the common point of two tangents drawn to circle is perpendicular bisector of line joining the point of contact of the tangents.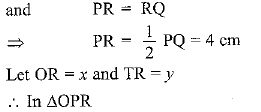
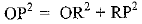
⇒ 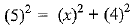
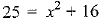
x2 = 16
⇒ x = 3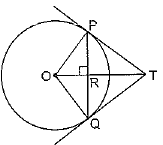
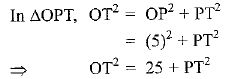
(OR + RT)2 = 25 + PT2
(3 + y)2 = 25 + PT2
9 + y2 + 6y = 25 + PT2 .......(i)
In ΔPRT, TP2 = PR2 + RT2
⇒ PT2 = (4)2 + (y)2 .......(ii)
Put value of PT2 in eq (i)
9 + y2 + 6y = 25 + 16 + y2
6y = 25 + 16 - 9
6y = 32
y = 32/6 = 16/3 cm
Putting y = 16/3 cm in eq (ii), we get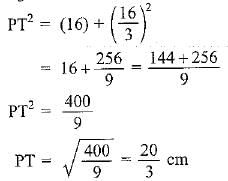
Q40: From an external point P, two tangents PA and PB are drawn to the circle with centre O. Prove that OP is the perpendicular bisector of chord AB. (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Join OA and OB.
In ΔOAP and ΔOBP.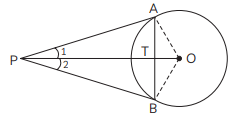
OA = OB [Radii of same circle]
PA = PB [Tangents from external point]
OP = OP [Common]
So ΔOAP ≅ ΔOBP (By SSS rule)
∠1 = ∠2 [By C.P.C.T.]
Now, In ΔATP and ΔBTP.
PA = PB [Tangents from external point]
AT = BT [By C.P.C.T.] ...(1)
∠ATP = ∠BTP [By CPCT] ...(2)
Since, ATB is a straight line.
∠ATP + ∠BTP = 180º
⇒ ∠ATP + ∠ATP = 180º [From (2) ]
⇒ 2∠ATP = 180º
⇒ ∠ATP = 90º ...(3)
From (1) and (3) we can say that OP is ⊥ bisector of AB
Q41: In the given figure, PQ is a tangent from an external point P and QOR is a diameter. If ∠POR = 130º and S is a point on the circle, find ∠1 + ∠2. (CBSE 2017)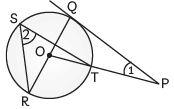
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given, PQ is a tangent to a circle, and QOR is a diameter of a circle.
Also, ∠POR = 130º
Now, ∠RST = 1/ 2 ∠TOR
∠2 = 1/ 2 × 130º = 65º ...(i) [∠TOR = ∠POR]
[Since, angle subtended by the arc at centre is twice the angle subtended by it on any remaining part of the circle]
Since, ROQ is the diameter of the circle
∴ ∠ROT + ∠QOT = 180º
∠QOT = 180º – 130º = 50º ...(ii)
and ∠PQR = 90º ...(iii) [tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact]
In ΔQOP
∠QOP + ∠PQO + ∠OPQ = 180º
⇒ 50º + 90º + ∠1 = 180º [from (ii) and (iii)]
∠1 = 180º – 140º = 40º ...(iv)
∴ ∠1 + ∠2 = 40º + 65º [From (i) and (iv)]
= 105º
Hence, the sum of ∠1 + ∠2 is 105º
Q42: In the figure, the radius of the circle of DABC of area 84 cm2 is 4 cm and the lengths of the segments AP and BP into which side AB is divided by the point of contact P are 6 cm and 8 cm. Find the lengths of the sides AC and BC. (CBSE 2017)
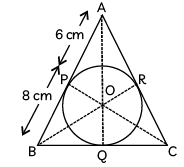
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given: area (∆ABC) = 84 cm2
Radius of circle, r = OP = OQ = OR = 4 cm AP = 6 cm and BP = 8 cm
Now AP = AR = 6 cm [Q two tangents from an external point to a circle are equal]
Similarly, BP = BQ = 8 cm
and QC = RC = x (say)
AC = 6 + x
and BC = 8 + x
Now, area (∆ABC) = area (∆AOB) + area (∆BOC) + area (∆AOC)
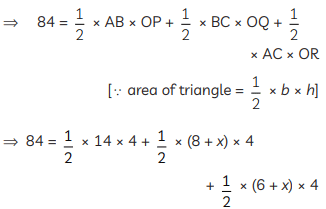
⇒ 84 = 28 + (16 + 2x) + (12 + 2x)
⇒ 84 = 56 + 4x
⇒ 4x = 84 – 56
⇒ 4x = 28
⇒ x = 7
Hence, AC = 6 + 7 = 13 cm
and BC = 8 + 7 = 15 cm.
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q43: If from an external point P of a circle with centre 0, two tangents PQ and PR are drawn such that QPR = 120°, prove that 2PQ = PO. [CBSE Delhi (F) 2016] View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given, ∠QPR = 120°
Radius is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact.
∠OQP = 90° ⇒ ∠QPO = 60°
(Tangents drawn to a circle from an external point are equally inclined to the segment, joining the centre to that point.)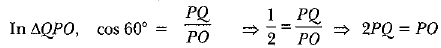
Q44: In Fig. 8.42, AP and BP are tangents to a circle with centre O, such that AP = 5 cm and ∠APS = 60°. Find the length of chord AB. [CBSE Delhi 2016]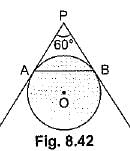
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: PA = PB (Tangents from an external point are equal)
and ∠APB = 60°
⇒ ∠PAB = ∠PBA = 60°
∴ ΔPAB is an equilateral triangle.
Hence AB = PA = 5 cm.
Q45: In Fig. 8.43 from an external point P, two tangents PT and PS are drawn to a circle with centre O and radius r. If OP = 2r, show that ∠OTS = ∠OST = 30°. [CBSE (AI) 2016]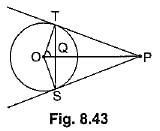
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Let ∠TOP = θ
∴ 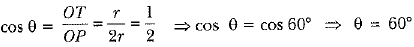
Hence, ∠TOS = 120°
In ∠OTS, OT = OS (Radii of circle)
⇒ 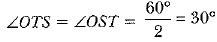
Q46: In Fig. 8.44, are two concentric circles of radii 6 cm and 4 cm with centre O. If AP is a tangent to the larger circle and BP to the smaller circle and length of AP is 8 cm, find the length of BP. [CBSE (F) 2016]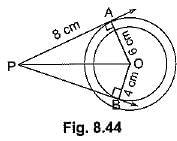
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: OA = 6 cm, OB = 4 cm, AP = 8 cm
OP2 = OA2 + AP2 = 36 + 64 = 100
⇒ OP = 10 cm
BP2 = OP2 - OB2 = 100 - 16 = 84
⇒ 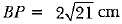
Q47: From an external point P, tangents PA and PR are drawn to a circle with centre O. If ∠PAB = 50°, then find ∠AOB. [CBSE Delhi 2016]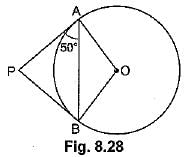
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: ∵ PA = PB ⇒ ∠BAP = ∠ABP = 50°
∴ ∠APB = 180° - 50° - 50° = 80°
and ∠AOB = 180° - 80° = 100°
Q48: In Fig. 8.29, PQ is a tangent at a point C to a circle with centre O. If AB is a diameter and ∠CAB = 30°, find ∠PCA. [CBSE (AI) 2016]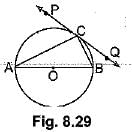
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: ∠ACB = 90° (Angle in the semicircle)
∠CAB = 30° (given)
In ΔABC,
90° + 30° + ∠ABC = 180°
⇒ ΔABC = 60°
Now, ∠PCA = ∠ABC (Angles in the alternate segment)
∴ ∠PCA = 60°
OR
Construction: Jo in 0 to C.
∠PCO = 90° (∵ Line joining centre to point of contact is perpendicular to PQ)
In ΔAOC, OA = OC (Radii of circle)
∴ ∠OAC = ∠OCA = 30° (Equal sides have equal opp. angles)
Now, ∠PCA = ∠PCO - ∠ACO
= 90° - 30° = 60°
Q49: Two tangents PA and PB are drawn to the circle with centre O, such that ∠APB = 120°. Prove that OP = 2AP. (Foreign 2016)
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given. A circle C(0, r). PA and PB are tangents to the circle from point P, outside the circle such that ∠APB = 120°. OP is joined.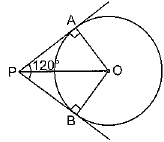
To Prove. OP = 2AP.
Construction. Join OA and OB.
Proof. Consider Δs PAO and PBO
PA = PB [Tangents to a circle, from a point outside it, are equal.]
OP = OP [Common]
∠OAP = ∠OBP = 90°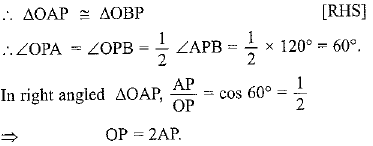
Q50: In Fig. 8.62, two equal circles, with centres O and O', touch each other at X.OO' produced meets the circle with centre O' at A. AC is tangent to the circle with centre O, at the point C. O'D is perpendicular to AC. Find the value of 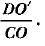 [CBSE (AI) 2016]
[CBSE (AI) 2016]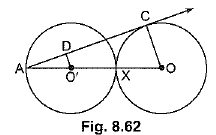
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: AC is tangent to circle with centre O.
Thus ∠ACO = 90°
In ΔAO'D and ΔAOC
∠ADO' = ∠ACO = 90º
∠A = ∠A (Common)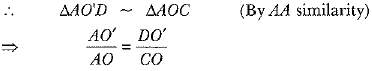
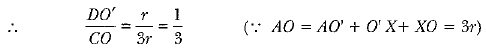
Q51: In Fig. 8.63, O is the centre of a circle of radius 5 cm. T is a point such that OT = 13 cm and OT intersects circle at E. If AB is a tangent to the circle at E, find the length of AB, where TP and TQ are two tangents to the circle. [CBSE Delhi 2016]
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: 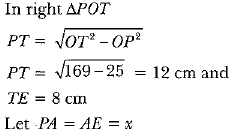
(Tangents from an external point to a circle are equal)
In right ΔAET.
TA2 = TE2 + EA2
⇒ (12 - x)2 = 64 + x2 ⇒ 144 + x2 - 24x = 64 + x2
⇒ x = 80/24 ⇒ x = 3.3 cm
Thus, AB = 6.6 cm
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q52: In figure, PQ is a chord of a circle with centre O and PT is a tangent. If ∠QPT = 60°, find ∠PRQ. (CBSE 2015)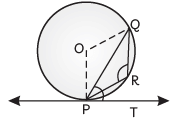
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given, ∠QPT = 60°
So, OP is the radius of the circle.
Now, ∠OPT = 90°
∠OPQ = ∠OPT – ∠QPT = 90° – 60° = 30°
In ΔOPQ, OP = OQ [radii of circle]
∠OQP = ∠OPQ = 30° [Q Angles opposite to equal sides are equal]
∠POQ = 180° – (30° + 30°) = 120°
Reflex ∠POQ = 360° – 120° = 240°
We know that, angle subtended by an arc at the centres double the angle subtended by it on the remaining part of the circle.
so, ∠PRQ = 1/ 2 Reflex ∠POQ
Therefore, 240 / 2 ° = 120°
Previous Year Questions 2014
Q53: Prove that the parallelogram circumscribing a circle is a rhombus. [CBSE Delhi 2014; CBSE 2019 (30/5/1)] View Answer
View AnswerAns: Let ABCD be a parallelogram such that its sides touch a circle with centre O.
We know that the tangents to a circle from an exterior point are equal in length.
Therefore, we have
AP = AS (Tangents from A) ... (i)
BP = BQ (Tangents from B) ... (ii)
CR = CQ (Tangents from C) ... (iii)
And DR = DS (Tangents from D) ... (iv)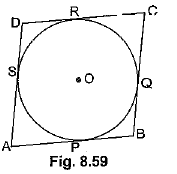
Adding (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv), we have
(AP + BP) + (CR + DR) = (AS + DS) + (BQ + CQ)
AB + CD = AD + BC
AB + AB = BC + BC (∵ ABCD is a parallelogram ∴ AB = CD, BC = DA)
2AB = 2BC ⇒ AB = BC
Thus, AB = BC = CD = AD
Hence, ABCD is a rhombus.
Q54: Prove that the lengths of two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal. [CBSE, Delhi 2014, (F) 2014, Delhi 2016, (AI) 2016, (F) 2016, CBSE Delhi 2017, (AI) 2017, (F) 2017, Delhi 2017 (C)]
 View Answer
View AnswerAns: Given: AP and AQ are two tangents from a pointed to a circle C (O, r).
To Prove: AP = AQ
Construction: Join OP, OQ and OA.
Proof: In order to prove that AP = AQ, we shall first prove that ΔOPA ≅ ΔOQA.
Since a tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
∴ OP ⊥ AP and OQ ⊥ AQ
⇒ ∠OPA = ∠OQA = 90° ........(i)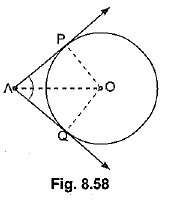
Now, in right triangles OPA and OQA, we have
OP = OQ (Radii of a circle)
∠OPA = ∠OQA (Each 90°)
and OA = OA (Common)
So, by RHS-criterion of congruence, we get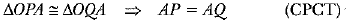
Hence, lengths of two tangents from an external point are equal.
|
126 videos|457 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Maths Previous Year Questions - Circles- 1
| 1. What are the properties of circles that are important for Class 10 exams? |  |
| 2. How do you find the area of a circle in Class 10? |  |
| 3. What is the formula for the circumference of a circle? |  |
| 4. How do you solve problems involving tangent lines to circles? |  |
| 5. What types of questions can be expected in exams regarding circles? |  |























