Class 9 History Chapter 1 Previous Year Questions - The French Revolution
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. What was the Bastille?
Who had stormed the Bastille during the last years of the 18th century? [2024]
Ans. The Bastille was a fortress-prison in Paris, stormed by citizens on 14 July 1789. This event marked a significant moment in the French Revolution.
- It symbolised the tyranny of the king.
- The storming led to the release of a few prisoners.
- After its capture, the Bastille was demolished, and its stones were sold as souvenirs.
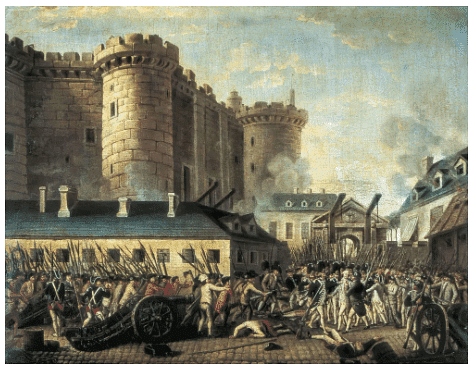 Storming of Bastille
Storming of Bastille
Q.2. Who wrote the Declaration of the Rights of woman and citizen? [2024]
Ans. Olympe de Gouges wrote the Declaration of the Rights of Woman and Citizen in 1791.
Key points from her declaration include:
- Women are born free and equal to men in rights.
- The aim of political associations is to preserve the natural rights of both women and men.
- All citizens should have a say in the law, which must apply equally to everyone.
- No woman is exempt from the law; she is subject to the same legal standards as men.
Q.3. What was the name give to newly-elected assembly of the Jacobins? [2023]
Ans. The newly elected assembly of the Jacobins was known as the Convention.
Key points include:
- It abolished the monarchy.
- France was declared a republic on 21 September 1792.
- In a republic, the government is elected by the people.
 Montesquieu
Montesquieu
Q.4. Who wrote The Spirit of the Laws? [2022]
Ans. The Spirit of the Laws was written by Montesquieu.
Q.5. Which ruler came to power in France in 1774? [2022]
Ans. Louis XVI of the Bourbon family ascended the throne of France in 1774.
Q.6. Which social group emerged in France in the 18th century? [2021]
Ans. The middle class emerged in France during the 18th century.
Q.7. What did John Locke write in his book Two Treaties of Government? [2020]
Ans. In his book, Two Treatises of Government, John Locke aimed to challenge the idea of the divine right of kings. His key points include:
- Rejecting the notion that monarchs have absolute power granted by God.
- Arguing that governments should be based on the consent of the governed.
- Emphasising the importance of individual rights and freedoms.
Q.8. What was the most revolutionary reform of the Jacobin regime? [2020]
Ans. The most revolutionary reform of the Jacobin regime was the abolition of slavery in the French colonies. This reform aimed to end the inhumane practice of slavery, particularly in the Caribbean colonies.
Q.9. Which principle was followed by Estate General for taking vote? [2019]
Ans. Voting in the Estates General was based on the principle that each estate had one vote.
This meant:
- Each of the three estates (clergy, nobility, and third estate) had equal voting power.
- This practice was upheld by King Louis XVI during the assembly.
- Members of the third estate argued for a change, proposing that each individual member should have one vote instead.
- This idea was inspired by democratic principles from philosophers like Rousseau.
- When the king rejected their proposal, the third estate members protested by walking out.
Q.10. What was Marseillaise? Who composed it? [2018]
Ans. Marseillaise was a patriotic song sung by volunteers from Marseilles as they marched into Paris. It was composed by Rouget de Lisle and has become the national anthem of France.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Explain the “Reign of Terror” in brief. [2019]
Ans. 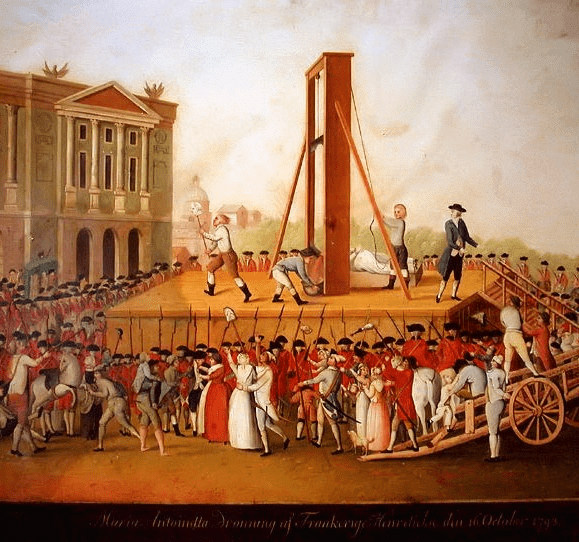 Guillotine
Guillotine
The Reign of Terror lasted from 1793 to 1794 and was marked by extreme measures taken by Robespierre's government.
Key points include:
- Severe Control: Robespierre enforced strict policies, leading to the arrest and execution of ex-nobles, clergy, and even members of his own party who opposed him.
- Economic Regulations: The government set maximum limits on wages and prices, rationing meat and bread. Peasants had to sell grain at government-fixed prices.
- Equality in Diet: The use of expensive white flour was banned, and all citizens were required to eat pain d'égalité (equality bread), made from whole wheat.
- Language Reform: To promote equality, traditional forms of address like Sir and Madam were replaced with Citizen for all.
- Closure of Churches: Many churches were shut down, and their buildings repurposed for military or administrative use.
- Robespierre's Downfall: His relentless policies led to his arrest and execution by guillotine in July 1794.
Q.2. Explain the features of the constitution of France drafted in 1791. [2018]
Ans. The Constitution of 1791was the first written constitution in France, established after the end of absolute monarchy. Its primary goals were:
- To limit the powers of the monarch.
- To separate powers among different institutions:
- Legislature
- Executive
- Judiciary
- To create a constitutional monarchy.
Key features included:
- The National Assembly was responsible for making laws and was indirectly elected.
- Only men aged 25 and older who paid certain taxes were considered active citizens and could vote.
- All other men and women were classified as passive citizens and had no voting rights.
This constitution marked a significant shift in French governance, establishing a framework for citizen participation while still maintaining a monarchy.
Q.3. How was the National Assembly recognised and how did it start exercising its powers? [2017]
Ans. Faced with the power of the revolting people, Louis XVI recognised the National Assembly and accepted that his powers would now be limited by a constitution.
The National Assembly began exercising its powers in several significant ways:
- On the night of 4 August 1789, the Assembly passed a decree to abolish the feudal system of obligations and taxes.
- Members of the clergy were compelled to relinquish their privileges.
- Tithes were abolished, and lands owned by the Church were confiscated, resulting in government assets worth at least 2 billion livres.
Q.4 How did philosophers influence the thinking of the people of France? [2016]
Ans.

The philosophers significantly shaped the thinking of the French people in several ways:
- John Locke and Jean Jacques Rousseau introduced ideas about a society founded on freedom and equal laws.
- In his work, Two Treatises of Government, Locke challenged the belief in the divine rights of kings.
- Rousseau expanded on Locke's ideas, advocating for a government based on a social contract between the people and their leaders.
- Montesquieu, in The Spirit of the Laws, proposed a separation of powers within government: legislative, executive, and judiciary.
- The ideas of these philosophers were widely discussed in salons and coffee-houses, and circulated through books and newspapers.
- Many who could not read benefited from these discussions, as readings were often done aloud.
Q.5 Describe the middle class in three points. [2016]
Ans. The following points describe the middle class in French society:
- The middle class emerged in France during the 18th century, gaining wealth through expanding overseas trade and manufacturing goods like woollen and silk textiles.
- This class included not only merchants and manufacturers but also professionals such as lawyers and administrative officials.
- Members of the middle class were educated and believed that social position should be based on merit rather than birthright.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 History Chapter 1 Previous Year Questions - The French Revolution
| 1. What were the main causes of the French Revolution? |  |
| 2. What were the key events during the French Revolution? |  |
| 3. How did the French Revolution impact the rest of the world? |  |
| 4. What role did the Enlightenment play in the French Revolution? |  |
| 5. What were the outcomes of the French Revolution? |  |






















