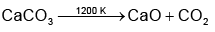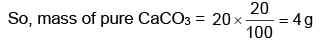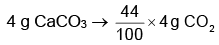NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Chemistry Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Among the following, choose the ones with equal number of atoms (NEET 2025)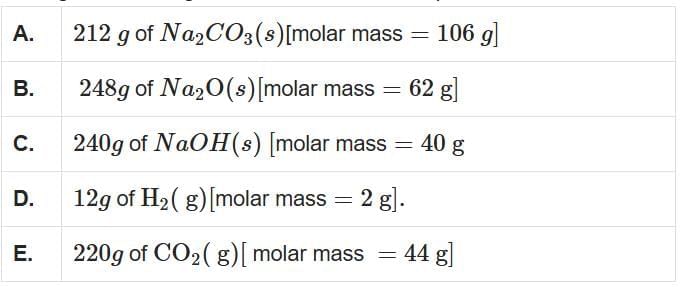
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, and D only
(b) B, D, and E only
(c) A, B, and C only
(d) A, B and D only
Ans: (d)
Equal Number of Atoms
- The number of atoms in a given sample depends on the number of moles of molecules present, as well as the number of atoms in each molecule.
- The number of moles can be calculated using the formula:
- Moles = Mass / Molar Mass
- Once the moles are determined, the number of molecules can be calculated using Avogadro's number:
- Number of molecules = Moles × 6.022 × 1023
- To calculate the total number of atoms, multiply the number of molecules by the number of atoms in the molecular formula.
For each option, calculate the number of moles and the total number of atoms:
A. 212 g of Na₂CO₃:
- Moles = 212 / 106 = 2 moles
- Na₂CO₃ contains 6 atoms per molecule (2 Na, 1 C, 3 O).
- Total atoms = 2 × 6 × 6.022 × 1023 = 72.264 × 1023 atoms
B. 248 g of Na₂O:
- Moles = 248 / 62 = 4 moles
- Na₂O contains 3 atoms per molecule (2 Na, 1 O).
- Total atoms = 4 × 3 × 6.022 × 1023 = 72.264 × 1023 atoms
C. 240 g of NaOH:
- Moles = 240 / 40 = 6 moles
- NaOH contains 3 atoms per molecule (1 Na, 1 O, 1 H).
- Total atoms = 6 × 3 × 6.022 × 1023 = 108.396 × 1023 atoms
D. 12 g of H₂:
- Moles = 12 / 2 = 6 moles
- H₂ contains 2 atoms per molecule (2 H).
- Total atoms = 6 × 2 × 6.022 × 1023 = 72.264 × 1023 atoms
E. 220 g of CO₂:
- Moles = 220 / 44 = 5 moles
- CO₂ contains 3 atoms per molecule (1 C, 2 O).
- Total atoms = 5 × 3 × 6.022 × 1023 = 90.33 × 1023 atoms
Comparing the total atoms A, B, and D have equal total atoms (72.264 × 1023).
Therefore, the correct answer is Option 2: A, B, and D only.
Q2: Dalton's Atomic theory could not explain which of the following? (NEET 2025)
(a) Law of multiple proportion
(b) Law of gaseous volume
(c) Law of conservation of mass
(d) Law of constant proportion
Ans: (b)
The Law of Gaseous Volume involves the concept of molecules and their behavior in the gaseous state.
For example:
- When hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas to form water vapor:
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g) - The volume ratio of hydrogen, oxygen, and water vapor is 2:1:2 under the same conditions.
Dalton's Atomic Theory assumed atoms as indivisible and did not account for the existence of molecules or the behavior of gases in terms of volume. Thus, it could not explain Gay-Lussac's Law of Gaseous Volume.
Therefore, Dalton's Atomic Theory could not explain the Law of Gaseous Volume.
2024
Q1: The highest number of helium atoms is in (NEET 2024)
(a) 4 mol of helium
(b) 4 u of helium
(c) 4 g of helium
(d) 2.271098L of helium at STP
Ans: (a)
To determine which option contains the highest number of helium atoms, we need to analyze each option based on the amount of helium it represents and apply Avogadro's number (6.022 × 10²³ atoms/mol).
Option A: 4 mol of helium
Number of atoms = 4 mol × 6.022 × 10²³ atoms/mol = 24.088 × 10²³ = 2.4088 × 10²⁴ atoms.
Option B: 4 u of helium
The atomic mass of helium is approximately 4 u (atomic mass units). Since 1 u is defined as 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom, 4 u corresponds to the mass of a single helium atom. Therefore, 4 u of helium represents exactly 1 helium atom.
Number of atoms = 1 atom.
Option C: 4 g of helium
The molar mass of helium is 4 g/mol. Moles = 4 g / 4 g/mol = 1 mol.
Number of atoms = 1 mol × 6.022 × 10²³ atoms/mol = 6.022 × 10²³ atoms.
Option D: 2.271098 L of helium at STP
At STP, 1 mole of an ideal gas occupies 22.4 L. Moles = 2.271098 L / 22.4 L/mol ≈ 0.10139 mol.
Number of atoms = 0.10139 mol × 6.022 × 10²³ atoms/mol ≈ 6.103 × 10²² atoms.
Conclusion:
Comparing the numbers:
Option A: 2.4088 × 10²⁴ atoms
Option B: 1 atom
Option C: 6.022 × 10²³ atoms
Option D: 6.103 × 10²² atoms
Option A clearly contains the highest number of helium atoms, which is 2.4088 × 10²⁴ atoms.
Q2: 1 gram of sodium hydroxide was treated with 25mL of 0.75M HCl solution, the mass of sodium hydroxide left unreacted is equal to
(a) 750 mg
(b) 250 mg
(c) Zero mg
(d) 200 mg (NEET 2024)
Ans: (b)
To find the mass of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) left unreacted, we first need to determine the moles of NaOH and HCl originally present and compare them to see which one is in excess.
The molar mass of NaOH is approximately 40 g/mol, so the number of moles of NaOH in 1 gram can be calculated as follows: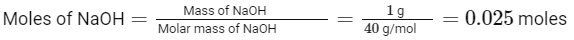 Next, we calculate the number of moles of HCl using its concentration and the volume of the solution. Recall that concentration (Molarity, M) is defined as moles of solute per liter of solution. Given that the concentration of HCl is 0.75 M and the volume of the solution is 25 mL or 0.025L, we can find the moles of HCl:
Next, we calculate the number of moles of HCl using its concentration and the volume of the solution. Recall that concentration (Molarity, M) is defined as moles of solute per liter of solution. Given that the concentration of HCl is 0.75 M and the volume of the solution is 25 mL or 0.025L, we can find the moles of HCl:
Moles of HCl = Concentration × Volume in liters = 0.75 M × 0.025 L = 0.01875 moles
Now, we compare the moles of NaOH and HCl. The stoichiometry of the reaction between NaOH and HCl is:
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
Each mole of NaOH reacts with one mole of HCl. Given that there are more moles of NaOH (0.025 moles) than HCl (0.01875 moles), HCl is the limiting reactant and will be completely consumed. The excess NaOH can be calculated:
Excess moles of NaOH = Moles of NaOH − Moles of HCl = 0.025 moles − 0.01875 moles = 0.00625 moles
To find the mass of the unreacted NaOH:
Mass of unreacted NaOH = Moles of unreacted NaOH × Molar mass of NaOH = 0.00625 moles × 40 g/mol = 0.25 g = 250 mg
Therefore, the mass of sodium hydroxide left unreacted is 250 mg, which corresponds to Option B.
Q3: A compound X contains 32% of A, 20% of B and remaining percentage of C. Then, the empirical formula of X is :
(Given atomic masses of A = 64 ; B=40 ; C = 32 u)
(a) A2BC2
(b) ABC3
(c) AB2C2
(d) DABC4 (NEET 2024)
Ans: (b)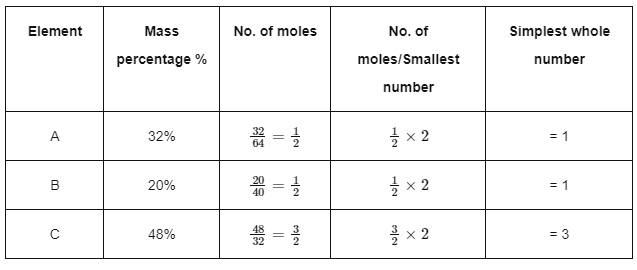 So, empirical formula of
So, empirical formula of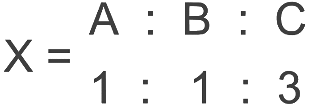
∴ The correct empirical formula of compound X is ABC3
Q4: A compound with a molecular formula of C6H14 has two tertiary carbons. Its IUPAC name is :
(a) n-hexane
(b) 2-methylpentane
(c) 2,3-dimethylbutane
(d) 2,2-dimethylbutane (NEET 2024)
Ans: (c)
Q5: 4.74 g of an inorganic compound contains 0.39g of K, 0.27 g of Al, 1.92 g of SO₄ radicals, and 2.16 g of water. If the molar mass of the compound is 948 g mol⁻¹, the molecular formula of the inorganic compound is: (NEET 2024)
(a) KAl(SO₄)₂ · 12H₂O
(b) K₂Al₂(SO₄)₆ · 12H₂O
(c) K₂SO₄ · Al₂(SO₄)₃ · 24H₂O
(d) K₂SO₆ · Al₂(SO₄)₃ · 12H₂O
Ans: (c)
Given:
- Total mass of the compound = 4.74 g
- Mass of K = 0.39 g
- Mass of Al = 0.27 g
- Mass of SO₄ = 1.92 g
- Mass of water (H₂O) = 2.16 g
- Molar mass of the compound = 948 g/mol
Step 1: Calculate moles of each component
- Moles of K (Potassium):
Molar mass of K = 39.1 g/mol
Moles of K = 0.39 g / 39.1 g/mol ≈ 0.00997 mol - Moles of Al (Aluminum):
Molar mass of Al = 26.98 g/mol
Moles of Al = 0.27 g / 26.98 g/mol ≈ 0.00999 mol - Moles of SO₄ (Sulfate radicals):
Molar mass of SO₄ = 32 + 4×16 = 96.06 g/mol
Moles of SO₄ = 1.92 g / 96.06 g/mol ≈ 0.0200 mol - Moles of H₂O (Water):
Molar mass of H₂O = 18.02 g/mol
Moles of H₂O = 2.16 g / 18.02 g/mol ≈ 0.1199 mol
Step 2: Find the simplest ratio of elements
Divide the moles by the smallest value (0.00997):
- K: 0.00997 / 0.00997 ≈ 1
- Al: 0.00999 / 0.00997 ≈ 1
- SO₄: 0.0200 / 0.00997 ≈ 2
- H₂O: 0.1199 / 0.00997 ≈ 12
The empirical formula is KAl(SO₄)₂·12H₂O.
Step 3: Verify the molar mass
Molar mass of KAl(SO₄)₂·12H₂O:
- K: 39.1
- Al: 26.98
- SO₄: 2 × 96.06 = 192.12
- H₂O: 12 × 18.02 = 216.24
- Total ≈ 39.1 + 26.98 + 192.12 + 216.24 ≈ 474.44 g/mol
The given molar mass is 948 g/mol, approximately twice 474.44 g/mol. Thus, the molecular formula is:
K₂Al₂(SO₄)₄·24H₂O, which can be written as K₂SO₄·Al₂(SO₄)₃·24H₂O.
Step 4: Confirm the molecular formula
Molar mass of K₂SO₄·Al₂(SO₄)₃·24H₂O:
- K₂SO₄: 2×39.1 + 32 + 4×16 = 174.2
- Al₂(SO₄)₃: 2×26.98 + 3×(32 + 4×16) = 53.96 + 288.18 = 342.14
- 24H₂O: 24 × 18.02 = 432.48
- Total = 174.2 + 342.14 + 432.48 = 948.82 g/mol, which matches 948 g/mol.
Thus, the correct molecular formula is K₂SO₄·Al₂(SO₄)₃·24H₂O.
Final Answer: (c)
Q6: Molar mass of a compound (X) whose 2.6 mol weighs 312 g is: (NEET 2024)
(a) 312 g mol⁻¹
(b) 120 g mol⁻¹
(c) 60 g mol⁻¹
(d) 811.2 g mol⁻¹
Ans: (b)
Molar mass is calculated using the formula:
Molar mass = Mass / Moles
Here, the mass of the compound is 312 g, and the number of moles is 2.6 mol.
Molar mass = 312 g / 2.6 mol = 120 g mol⁻¹
Thus, the molar mass of the compound is 120 g mol⁻¹.
Q7: How much glucose is needed to prepare 250 mL of a 1/20 M (M/20) glucose solution? (NEET 2024)
(Molar mass of glucose: 180 g/mol)
(a) 2.25 g
(b) 4.5 g
(c) 0.44 g
(d) 1.125 g
Ans: (a)
To solve this, we can use the formula for molarity:
Molarity (M) = moles of solute / volume of solution in liters.
Given:
- Molarity of the solution = 1/20 M
- Volume of the solution = 250 mL = 0.25 L
- Molar mass of glucose = 180 g/mol
moles of glucose = Molarity × Volume of solution
moles of glucose = (1/20) × 0.25 = 0.0125 moles
mass of glucose = moles of glucose × molar mass
mass of glucose = 0.0125 × 180 = 2.25 g
So, the correct answer is 2.25 g.
Q8: 1.0 g of H₂O₂ has the same number of molecules as in: (NEET 2024)
(a) 0.823 of N₂
(b) 18 g of H₂O
(c) 16 g of CO
(d) 28 g of N₂
Ans: (a)
To solve this, we calculate the number of molecules in 1.0 g of H₂O₂ and find the option with the same number of molecules.
Step 1: Number of molecules in 1.0 g of H₂O₂
Molar mass of H₂O₂ = 2×1 + 2×16 = 34 g/mol
Moles of H₂O₂ = 1.0 g / 34 g/mol ≈ 0.02941 mol
Number of molecules = 0.02941 mol × 6.022 × 10²³ molecules/mol ≈ 1.771 × 10²² molecules
Step 2: Compare with the options
We need a mass of a substance that contains 1.771 × 10²² molecules.
- Option (a): 0.823 g of N₂
Molar mass of N₂ = 28 g/mol
Moles of N₂ = 0.823 g / 28 g/mol ≈ 0.02939 mol
Number of molecules = 0.02939 × 6.022 × 10²³ ≈ 1.770 × 10²² molecules
This is very close to 1.771 × 10²² molecules, suggesting option (a) is correct. - Option (b): 18 g of H₂O
Molar mass of H₂O = 18 g/mol
Moles = 18 g / 18 g/mol = 1 mol
Molecules = 1 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 6.022 × 10²³ molecules (much higher). - Option (c): 16 g of CO
Molar mass of CO = 12 + 16 = 28 g/mol
Moles = 16 g / 28 g/mol ≈ 0.5714 mol
Molecules = 0.5714 × 6.022 × 10²³ ≈ 3.441 × 10²³ molecules (too high). - Option (d): 28 g of N₂
Molar mass of N₂ = 28 g/mol
Moles = 28 g / 28 g/mol = 1 mol
Molecules = 1 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 6.022 × 10²³ molecules (too high).
Conclusion:
Option (a) 0.823 g of N₂ has approximately 1.770 × 10²² molecules, matching the 1.771 × 10²² molecules in 1.0 g of H₂O₂.
2023
Q1: Select the correct statements from the following (2023)
A. Atoms of all elements are composed of two fundamental particles.
B. The mass of the electron is 9.10939 × 10–31 kg.
C. All the isotopes of a given element show same chemical properties.
D. Protons and electrons are collectively known as nucleons.
E. Dalton’s atomic theory, regarded the atom as an ultimate particle of matter.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) A, B and C only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A and E only
(d) B, C and E only
Ans: d
- Atoms consist of three fundamental particles: Electrons, protons and neutrons
- The mass of the electron is 9.10939 × 10–31 kg
- All the isotopes of a given element show same chemical properties.
- Protons and neutrons present in the nucleus are collectively called as nucleons.
- Dalton’s atomic theory, regarded the atom as the ultimate particle of matter.
So, the correct statements are B, C, E only
Q2: The mass of CO2 produced by heating 20 g of 20% pure limestone as per the equation given below is: (NEET 2023)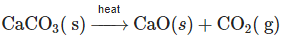 (a) 1.32 g
(a) 1.32 g
(b) 1.12 g
(c) 1.76 g
(d) 2.64 g
Ans: (c)
Given:
- The reaction: CaCO₃ (s) → CaO (s) + CO₂ (g)
- You are heating 20 g of 20% pure limestone.
Step 1: Find the amount of pure limestone in the sample.
The sample is 20% pure limestone, so the actual mass of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) in the sample is:
20% of 20 g = 4 g of CaCO₃.
Step 2: Calculate moles of CaCO₃ in the sample.
The molar mass of CaCO₃ is:
Molar mass of CaCO₃ = 40 (Ca) + 12 (C) + 48 (3O) = 100 g/mol.
Now, calculate the moles of CaCO₃:
Moles of CaCO₃ = 4 g / 100 g/mol = 0.04 mol.
Step 3: Use the stoichiometry of the reaction.
From the balanced equation, we can see that 1 mole of CaCO₃ produces 1 mole of CO₂. Therefore, 0.04 mol of CaCO₃ will produce 0.04 mol of CO₂.
Step 4: Calculate the mass of CO₂ produced.
The molar mass of CO₂ is:
Molar mass of CO₂ = 12 (C) + 32 (O₂) = 44 g/mol.
Now, calculate the mass of CO₂:
Mass of CO₂ = 0.04 mol × 44 g/mol = 1.76 g.
Conclusion: The mass of CO₂ produced is 1.76 g. Therefore, the correct answer is Option C (1.76 g).
Q3: A 1 M solution of a compound 'X' has a density of 1.25 g/mL. If the molar mass of compound X is 85 g, what is the molality (m) of the solution? (NEET 2023)
(a) 0.705 m
(b) 1.208 m
(c) 1.165 m
(d) 0.858 m
Ans: (d)
To calculate the molality of the solution, we use the formula:
Molality (m) = moles of solute / mass of solvent (in kg)
Given:
- Molarity (M) = 1 M
- Density of solution = 1.25 g/mL
- Molar mass of compound X = 85 g/mol
- Volume of solution = 1 L = 1000 mL
Step 1: Calculate the mass of the solution.
Mass of solution = density × volume = 1.25 g/mL × 1000 mL = 1250 g.
Step 2: Calculate the mass of the solute (X).
- Moles of X = 1 mole
- Mass of solute = moles × molar mass = 1 mole × 85 g/mol = 85 g.
Step 3: Calculate the mass of the solvent (water).
Mass of solvent = Mass of solution - Mass of solute = 1250 g - 85 g = 1165 g = 1.165 kg.
Step 4: Calculate the molality.
Molality (m) = moles of solute / mass of solvent in kg = 1 mole / 1.165 kg = 0.858 m.
Conclusion: The molality of the solution is 0.858 m, so the correct answer is (d).
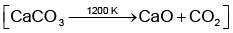
2022
Q1: What mass of 95% pure CaCO3 will be required to neutralise 50 mL of 0.5 M HCl solution according to the following reactions?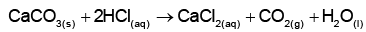
[Calculate upto second place of decimal point] (NEET 2022)
(a) 3.65 g
(b) 9.50 g
(c) 1.25 g
(d) 1.32 g
Ans: d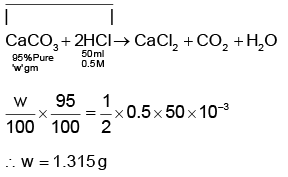
2021
Q1: An organic compound contains 80% (by wt.) carbon and the remaining percentage of hydrogen. The right option for the empirical formula of this compound is: [Atomic wt. of C is 12, H is 1] (NEET 2021)
(a) CH3
(b) CH4
(c) CH
(d) CH2
Ans: a
An empirical formula represents the simplest whole number ratio of various atoms present in a compound, whereas, the molecular formula shows the exact number of different types of atoms present in a molecule of a compound.
2020
Q1: Which one of the followings has maximum number of atoms? (NEET 2020)
(a) 1g of O2(g) (Atomic mass of O = 16)
(b) 1g of Li(s) (Atomic mass of Li = 7)
(c) 1g of Ag(s) (Atomic mass of Ag = 108)
(d) 1g of Mg(s) (Atomic mass of Mg = 24)
Ans: b
(a) no. of atoms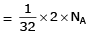
(b) no. of atoms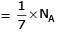
(c) no. of atoms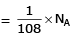
(d) no. of atoms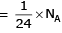
∴ 1 gm of Li is having maximum no. of atoms.
2019
Q1: The number of moles of hydrogen molecules required to produce 20 moles of ammonia through Haber's process is : (2019)
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 30
(d) 40
Ans: c
Haber's process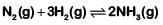
20 moles need to be produced
2 moles of NH3 → 3 moles of H2
Hence 20 moles of 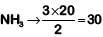 moles of H2
moles of H2
2018
Q1: In which case is the number of molecules of water maximum? (2018)
(a) 18 mL of water
(b) 0.18 g of water
(c) 0.00224 L of water vapours at 1 atm and 273 K
(d) 10-3 mol of water
Ans: a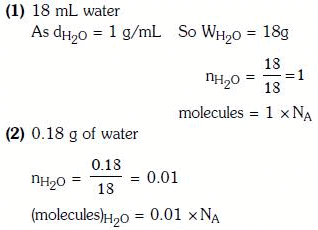
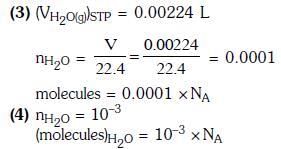
2015
Q1: A mixture of gases contains H2 and O2 gases in the ratio of 1 : 4 (w/w). What is the molar ratio of the two gases in the mixture ? (NEET 2015)
(a) 2:1
(b) 1:4
(c) 4:1
(d) 16:1
Ans: c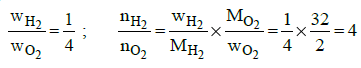
(At. wt. Mg = 24; O = 16)
2014
Q1: When 22.4 litres of H2 (g) is mixed with 11.2 litres of Cl2 (g) , each at S.T.P., the moles of HCl (g) formed is equal to : (2014)
(a) 0.5 mol of HCl (g)
(b) 1.5 mol of HCl (g)
(c) 1 mol of HCl (g)
(d) 2 mol of HCl (g)
Ans: c
1 mole = 22.4 liters at S.T.P.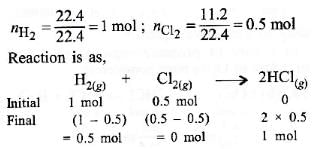
Here, Cl2 is limiting reagent. So, 1 mole of HCI(g) is formed.
|
119 videos|346 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry - Chemistry Class 11
| 1. What are the basic concepts of chemistry? |  |
| 2. How are elements and compounds different in chemistry? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of understanding atoms and molecules in chemistry? |  |
| 4. How does the periodic table help in organizing elements in chemistry? |  |
| 5. What role do chemical reactions play in chemistry? |  |