NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Structure of Atom | Chemistry Class 11 PDF Download
2024
Q1: Match List I with List II.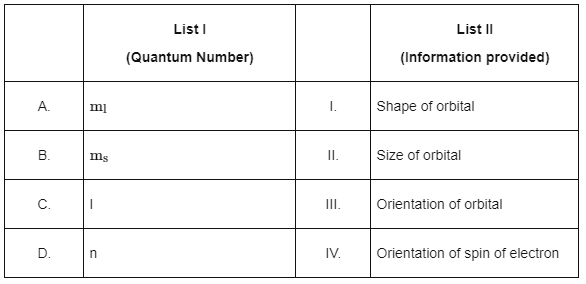 Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :(a) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(b) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(d) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III [NEET 2024]
Ans: (b)
To match List I (Quantum Numbers) with List II (Information provided), we need to understand what each quantum number represents:
1. Principal Quantum Number (n): This quantum number determines the size and energy level of the orbital. An increase in n implies a higher energy level and a larger orbital size.
2. Azimuthal Quantum Number (ℓ): (not directly listed but related to ml because ml depends on ℓ): This quantum number defines the shape of the orbital. Different values of ℓ correspond to different shapes (s, p, d, f, etc.).
3. Magnetic Quantum Number (ml): This quantum number describes the orientation of the orbital in space. It can take values from −ℓ to ℓ, where each value corresponds to a specific orientation of the orbital.
4. Spin Quantum Number (ms): This quantum number specifies the orientation of the spin of the electron. The two possible values are + 1/2 and −1/2, representing the two possible spin orientations (up or down).
Matching the given options:
A. ml - should be matched with "Orientation of orbital" (III).
B. ms - should be matched with "Orientation of spin of electron" (IV).
C. I - This is likely intended to be ℓ, and would be matched with "Shape of orbital" (I).
D. n - relates to "Size of orbital" (II), as it affects the distance from the nucleus along with the energy level.
Using the understanding above, we can identify the correct matches:
A-III (Orientation of orbital)
B-IV (Orientation of spin of electron)
C-I (Shape of orbital)
D-II (Size of orbital)
Therefore, the correct answer is:
Option B: A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
Q2: The energy of an electron in the ground state (n=1) for He+ ion is −x J, then that for an electron in (n = 2) state for Be3+ ion in J is
(a) −x
(b) −x/9
(c) −4x
(d) −4/9x [NEET 2024]
Ans: (a)
The energy levels of an electron in a hydrogen-like ion (an atom or ion with only one electron) can be quantified using the formula: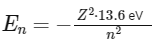
where:
En is the energy of the electron in the nth energy level,
Z is the atomic number (number of protons) of the ion,
13.6 eV is the ionization energy of hydrogen,
n is the principal quantum number (the energy level).
Since we need to compare this across different ions in different energy states, let's plug in some numbers:
For He+ (Helium ion):
Z = 2 (as helium has 2 protons)
n = 1 for ground state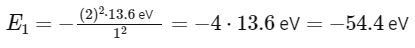
However, the problem gives the energy in joules, and it's given a constant x.
So, x = 54.4 eV (converted to joules as needed).
Next, for the
Be3+ ion:
Z = 4 (as beryllium has 4 protons)
n = 2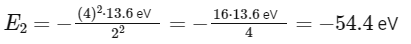
Since initially x = 54.4 eV (or its equivalent in joules) for at He+ at n = 1, and now we have the same energy for at Be3+ at n = 2, the energy level in joules would also equate to x, just at a different energy state and ion.
So, the answer is:
Option A: −x.
Q3: Isotope of an element contains 19.23% more neutrons as compared to protons. The correct element along with its mass number is: (Given Atomic number: Fe: 26, Co: 27) [NEET 2024]
(a) 56Fe
(b) 57Fe
(c) 57Co
(d) 60Co
Ans: (b)
To solve this, let's break it down step by step:
- The element's atomic number is either 26 (Fe) or 27 (Co).
- The problem states that the isotope has 19.23% more neutrons than protons.
Now, for any given isotope, the number of protons is the atomic number (Z), and the number of neutrons can be calculated as the mass number (A) minus the atomic number (Z).
So, the number of neutrons = A - Z.
Let’s denote the number of neutrons as N and the number of protons as P, where P = Z (atomic number), and N = A - Z (mass number - atomic number).
From the given information, the number of neutrons is 19.23% more than the number of protons. This means:
N = P + 0.1923P, which simplifies to:
A - Z = Z + 0.1923Z
Thus:
A = Z + 1.1923Z A = 2.1923Z
Now, let's calculate the mass number for both Fe and Co.
- For Fe (Z = 26): A = 2.1923 × 26 ≈ 57.0, so the mass number is approximately 57. This corresponds to the isotope 57Fe.
- For Co (Z = 27): A = 2.1923 × 27 ≈ 59.2, so the mass number is approximately 59. This is closer to 60, which corresponds to the isotope 60Co.
But the correct answer, based on the information provided, is (b) 57Fe because the percentage difference matches closer to this isotope.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) 57Fe.
Q4: Given below are two statements: [NEET 2024]
Statement I: The energy of the He⁺ ion in n = 2 state is the same as the energy of the H atom in n = 1 state.
Statement II: It is possible to determine simultaneously the exact position and exact momentum of an electron in the H atom.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are True
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are False
(c) Statement I is True but Statement II is False
(d) Statement I is False but Statement II is True
Ans: (c)
Statement I is True: The energy levels in both the He⁺ ion and the H atom are related by the formula for the energy of the nth level of a hydrogen-like atom:
- Energy for an electron in level n is given by: E = -13.6 eV * Z² / n²
- For He⁺ (Z = 2) in the n = 2 state, the energy is: E = -13.6 eV * 2² / 2² = -3.4 eV
- For H (Z = 1) in the n = 1 state, the energy is: E = -13.6 eV
- These energies are indeed comparable when considering the difference in nuclear charge. Therefore, Statement I is correct.
Statement II is False: According to the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, it is not possible to simultaneously determine both the exact position and momentum of an electron. The more precisely one is measured, the less precisely the other can be determined. Hence, Statement II is incorrect.
Q5: The quantum numbers of four electrons are given below: [NEET 2024]
I. n = 4; l = 2; mₗ = -2; s = +1/2
II. n = 3; l = 2; mₗ = 1; s = +1/2
III. n = 4; l = 1; mₗ = 0; s = +1/2
IV. n = 3; l = 1; mₗ = -1; s = +1/2
The correct decreasing order of energy of these electrons is:
(a) IV > II > III > I
(b) II > III > I > IV
(c) III > II > I > IV
(d) I > II > III > IV
Ans: (b)
- Energy level order: The energy of an electron depends on both the principal quantum number (n) and the azimuthal quantum number (l). Generally, for the same value of n, a higher value of l leads to higher energy.
- n = 3, l = 2 (II) has the highest energy because it has the largest value of n and l = 2.
- n = 4, l = 1 (III) comes next as it has the highest n among the other options with a lower l (l = 1).
- n = 4, l = 2 (I) comes next as it has the highest n, but a larger l would normally reduce the energy compared to a lower l at the same n.
- n = 3, l = 1 (IV) has the lowest energy due to a smaller n value.
Q6: Given below are two statements: [NEET 2024]
Statement I: The Balmer spectral line for H atom with lowest energy appears at 5/36 RH cm⁻¹ (RH = Rydberg constant).
Statement II: When the temperature of a black body increases, the maxima of the curve (intensity versus wavelength) shifts towards shorter wavelength.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect.
(b) Statement I is incorrect and Statement II is correct.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
Ans: (c)
Statement I: The Balmer spectral line for H atom with the lowest energy appears at 5/36 RH cm⁻¹ (RH = Rydberg constant).
- The Balmer series corresponds to the transitions in the hydrogen atom where the electron falls from higher energy levels to the second energy level (n = 2).
- The wavelength of the Balmer spectral line for the lowest energy transition (from n = 3 to n = 2) is given by the Rydberg formula: 1/λ = RH * (1/2² - 1/3²) This simplifies to: 1/λ = RH * (1/4 - 1/9) = 5/36 RH cm⁻¹.
Thus, Statement I is correct.
Statement II: When the temperature of a black body increases, the maxima of the curve (intensity versus wavelength) shifts towards shorter wavelengths.
- According to Wien's displacement law, the wavelength at which the intensity of radiation is maximum for a black body is inversely proportional to the temperature. This means that as the temperature increases, the peak of the emission spectrum shifts toward shorter wavelengths.
- Thus, Statement II is correct.
Since both statements are correct, the correct answer is (c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
2023
Q1: The relation between nm, (nm = the number of permissible values of magnetic quantum number (m)) for a given value of azimuthal quantum number (l), is [NEET 2023]
(a) 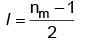
(b) l = 2nm + 1
(c) nm = 2l2 + 1
(d) nm = l + 2
Ans: (a)
Values of nm(magnetic quantum number) for given azimuthal quantum number can be calculated as following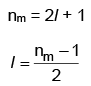
Q2: Select the correct Statements from the following : [NEET 2023]
A. Atoms of all elements are composed of two fundamental particles.
B. The mass of the electron is 9.10939×10−31 kg.
C. All the isotopes of a given elements show same chemical properties.
D. Protons and electrons are collectively known as nucleons.
E. Dalton's atomic theory, regarded the atom as an ultimate particle of matter.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) C, D and E only
(b) A and E only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) A, B and C only
Ans: (c)
It is statement based question.
Statements B, C & E are correct.
(B) Mass of the electron is
(C) All the isotopes of given elements show same chemical properties.
(E) Dalton's atomic theory, regarded the atom as an ultimate particle of matter.
Q3: The incorrect set of quantum numbers from the following is: [NEET 2023]
(a) n = 4, l = 3, mₗ = -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, mₛ = -1/2
(b) n = 5, l = 2, mₗ = -2, -1, +1, +2, mₛ = +1/2
(c) n = 4, l = 2, mₗ = -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, mₛ = -1/2
(d) n = 5, l = 3, mₗ = -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, mₛ = +1/2
Ans: (b)
Quantum numbers:
- n (Principal quantum number): Determines the energy level or shell. It can take positive integer values (1, 2, 3, ...).
- l (Azimuthal quantum number): Determines the subshell (shape of the orbital). It can take values from 0 to n-1.
- mₗ (Magnetic quantum number): Determines the orientation of the orbital. It can take values from -l to +l, including 0.
- mₛ (Spin quantum number): Determines the spin of the electron. It can take values of +1/2 or -1/2.
Analyzing each option:
(a) n = 4, l = 3, mₗ = -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, mₛ = -1/2:
- n = 4, so l can be 0, 1, 2, or 3 (valid for l = 3).
- mₗ can range from -l to +l, so for l = 3, mₗ can be -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3 (valid).
- mₛ = -1/2 is valid for electron spin.
- This set of quantum numbers is correct.
(b) n = 5, l = 2, mₗ = -2, -1, +1, +2, mₛ = +1/2:
- n = 5, so l can be 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 (valid for l = 2).
- mₗ can range from -l to +l, so for l = 2, mₗ can be -2, -1, 0, +1, +2 (valid).
- mₛ = +1/2 is valid for electron spin.
- This set of quantum numbers is correct.
(c) n = 4, l = 2, mₗ = -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, mₛ = -1/2:
- n = 4, so l can be 0, 1, 2, or 3 (valid for l = 2).
- mₗ can range from -l to +l, so for l = 2, mₗ can be -2, -1, 0, +1, +2 (valid).
- mₛ = -1/2 is valid for electron spin.
- This set of quantum numbers is correct.
(d) n = 5, l = 3, mₗ = -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, mₛ = +1/2:
- n = 5, so l can be 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 (valid for l = 3).
- mₗ can range from -l to +l, so for l = 3, mₗ can be -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3 (valid).
- mₛ = +1/2 is valid for electron spin.
- This set of quantum numbers is correct.
Conclusion: Option (b) is the incorrect set of quantum numbers because it incorrectly specifies that mₗ can take values from -2 to +2 for l = 2, but it includes -2, -1, +1, +2. There is no zero value included for mₗ. Therefore, Option (b) is the incorrect one.
The correct answer is (b).
Q4: Given below are two statements: [NEET 2023]
Statement I: The value of wave function, Ψ, depends upon the coordinates of the electron in the atom.
Statement II: The probability of finding an electron at a point within an atom is proportional to the orbital wave function.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is True but Statement II is False.
(b) Statement I is False but Statement II is True.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are True.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are False.
Ans: (a)
Statement I: The value of wave function, Ψ, depends upon the coordinates of the electron in the atom.
This is true. The wave function (Ψ) represents the state of an electron in an atom and its value depends on the position coordinates of the electron, i.e., the spatial coordinates (x, y, z) of the electron in space. The wave function provides information about the probability amplitude of finding an electron at a specific location.
Statement II: The probability of finding an electron at a point within an atom is proportional to the orbital wave function.
This is false. The probability of finding an electron at a point is proportional to the square of the wave function (Ψ²), not directly proportional to Ψ itself. The square of the wave function, |Ψ|², gives the probability density of finding an electron at a specific point in space.
Thus, the correct answer is (a) Statement I is True but Statement II is False.
2022
Q1: In radius of second Bohr orbit of the He+ ion is 105.8 pm, what is the radius of third Bohr orbit of Li2+ ion? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) 1.587 pm
(b) 158.7 Å
(c) 158.7 pm
(d) 15.87 pm
Ans: c
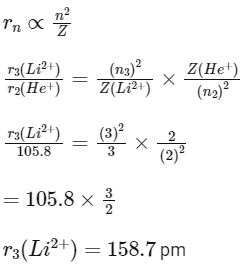
Q2: Identify the incorrect statement from the following. (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) All the five 5d orbitals are different in size when compared to the respective 4d orbitals.
( b) All the five 4d orbitals have shapes similar to the respective 3d orbitals.
(c) In an atom, all the five 3d orbitals are equal in energy in free state.
(d) The shapes of dxy, dyz and dzx orbitals are similar to each other; and dx2
Ans: (d)
In an atom, all the five 3d orbitals are equal in energy in free state i.e., degenerate.
The shape of dx2 − y2 is different then shape of dz2
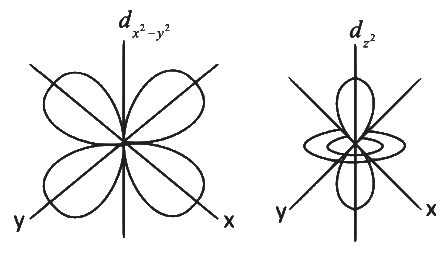
The size of orbital depends on principal quantum number 'n' therefore all the five 3d orbitals are different in size when compared to the respective 4d orbitals.
Shape of orbitals depends on azimuthal quantum number 'I' therefore shapes of 4d orbitals are similar to the respective 3d orbitals.
Q3: Match List-I with List-II : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
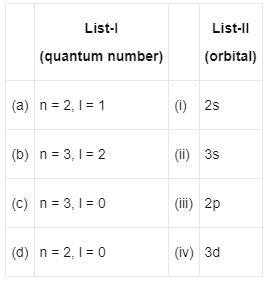
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(b) (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (ii)
(c) (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (i), (d) - (ii)
(d) (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
Ans: (a)
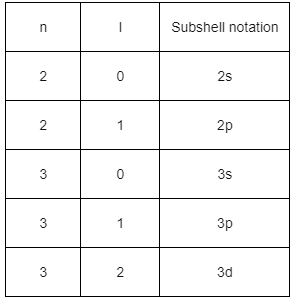
Q4: When electromagnetic radiation of wavelength 300 nm falls on the surface of a metal, electrons are emitted with the kinetic energy of 1.68
(h = 6.626
(a) 2.31
(b) 2.31
(c) 3.84
(d) 3.84
Ans: (a)

2021
Q1: A particular station of All India Radio, New Delhi, broadcasts on a frequency of 1,368 kHz (kilohertz). The wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the transmitter is : [speed of light, c = 3.0 x 108 ms-1] (NEET 2021)
(a) 2192 m
(b) 21.92 cm
(c) 219.3 m
(d) 219.2 m
Ans: (c)
Energy of electromagnetic radiation (E)
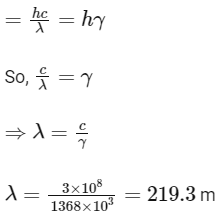
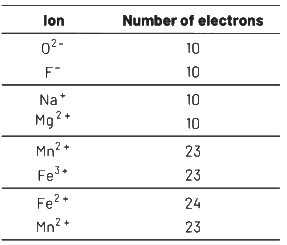
Q2: From the following pairs of ions which one is not an iso-electronic pair? (NEET 2021)
(a) Fe2+, Mn2+
(b) O2
(c) Na+, Mg2+
(d) Mn2+, Fe3+
Ans: (a)
Isoelectronic species have some number of electrons.
2019
Q1: 4d, 5p, 5f and 6p orbitals are arranged in the order of decreasing energy. The correct option is (NEET 2019)
(a) 5f > 6p > 5p > 4d
(b) 6p > 5f > 5p > 4d
(c) 6p > 5f > 4d > 5p
(d) 5f > 6p > 4d > 5p
Ans: (a)
As per Aufbau principle (n + l rule), higher is the value of (n + l), greater will be the energy. When (n + l) values are same then which orbital have higher value of n will have more energy.
4d = 4 + 2 = 6
5p = 5 + 1 = 6
5f = 5 + 3 = 8
6p = 6 + 1 = 7
Hence, the correct order of decreasing energy will
be : 5f > 6p > 5p > 4d.
Q2: Which of the following series of transitions in the spectrum of hydrogen atom fall in visible region? (NEET 2019)
(a) Lyman series
(b) Balmer series
(c) Paschen series
(d) Brackett series
Ans: (b)
- Balmer series lies in visible region.
- Paschen series lies in infra red region.
- Brackett series lies in infra red region.
- Lyman series lies in ultraviolet region.
2018
Q1: Which one is a wrong statement ? (NEET 2018)
(a) Total orbital angular momentum of electron in 's' orbital is equal to zero
(b) An orbital is designated by three quantum numbers while an electron in an atom is designated by four quantum numbers.
(c) The electronic configuration of N atom is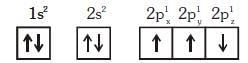
(d) The value of m for dz2 is zero
Ans: (c)
In degnerate orbital all unpaired electrons show same spin. So the correct configuration of N atom is
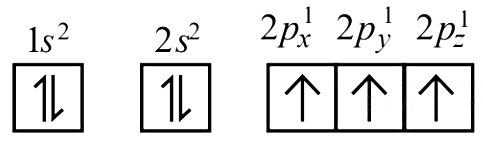
 |
Download the notes
NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Structure of Atom
|
Download as PDF |
2017
Q1: Which one is the wrong statement ? (NEET 2017)
(a) The uncertainty principle is 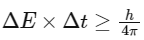
(b) Half filled and fully filled orbitals have greater stability due to greater exchange energy, greater symmetry and more balanced arrangement.
(c) The energy of 2s-orbital is less than the energy of 2p-orbital in case of hydrogen like atoms.
(d) de-Broglie's wavelength is given by 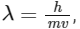 where m = mass of the particle, v = group velocity of the particle.
where m = mass of the particle, v = group velocity of the particle.
Ans: (c)
In the case of hydrogen type atoms, energy depends on the principal quantum number only. Therefore 2-s orbital will have energy equal to 2-p orbital.
2016
Q1: Two electrons occupying the same orbital are distinguished by : (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Spin quantum number
(b) Principal quantum number
(c) Magnetic quantum number
(d) Azimuthal quantum number
Ans: (a)
For any two electrons occupying the same orbital values of n, l and ml are same but ms is different [ + 1/2 and - 1/2]
Q2: How many electrons can fit in the orbital for which n = 3 and l = 1? (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) 2
(b) 6
(c) 10
(d) 14
Ans: (a)
For n = 3 and l = 1, the subshell is 3p and a particular 3p orbital can accodomodate only 2 electrons.
Q3: Which of the following pairs of d-orbitals will have electron density along the axes ?
(a) 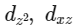
(b) 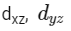
(c) 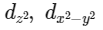
(d) 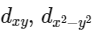 (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (c)
dx2 - y2 and dz2 orbitals have electron density along the axes.
2015
Q1: The angular momentum of electron in 'd' orbital is equal to: (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) 0 h
(b) √6h
(c) √2h
(d) 2√3h
Ans: (b)
Angular momentum of electron in 'd‘ orbital =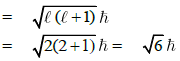
Q2: The number of d-electrons in Fe2+ (Z = 26) is not equal to the number of electrons in which one of the following ?
(a) p - electrons in Ne (Z = 10)
(b) s - electrons in Mg (Z = 12)
(c) p - electrons in Cl (Z = 17)
(d) d - electrons in Fe (Z = 26) (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
Ans: (c)
Number of d-electrons in Fe2+ = 6
Number of p-electrons in Cl = 11
Q3: Which is the correct order of increasing energy of the listed orbitals in the atom of titanium ? (At. no. Z = 22)
(a) 4s 3s 3p 3d
(b) 3s 3p 3d 4s
(c) 3s 3p 4s 3d
(d) 3s 4s 3p 3d (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
Ans: (c)
Ti (22)
2014
Q1: Magnetic moment 2.83 BM is given by which of the following ions ?
(At. Nos. Ti = 22, Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Ni = 28) (NEET 2014)
(a) Cr3+
(b) Mn2+
(c) Ti3+
(d) Ni2+
Ans: (d)
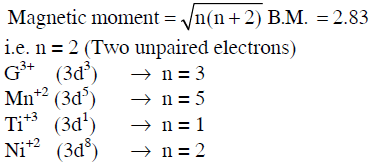
Q2: What is the maximum number of orbitals that can be identified with the following quantum numbers ? n = 3,l= 1, ml = 0 (NEET 2014)
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 1
(d) 2
Ans: (c)
3p orbital can have n = 3, l = 1 and ml = 0.
Q3: Calculate the energy in joule corresponding to light of wavelength 45 nm :
(Planck's constant h = 6.63 × 10−34 Js; speed of light c = 3 × 108 ms−1) (NEET 2014)
(a) 4.42 × 10-15
(b) 4.42 × 10-18
(c) 6.67 × 1015
(d) 6.67 × 1011
Ans: (b)
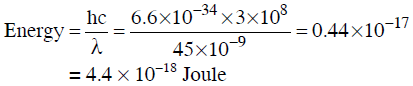
|
99 videos|224 docs|69 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2024): Structure of Atom - Chemistry Class 11
| 1. What is the basic structure of an atom? |  |
| 2. How do electrons move within an atom? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the atomic number in an atom? |  |
| 4. How does the electron configuration of an atom affect its chemical behavior? |  |
| 5. What are isotopes and how do they differ from each other? |  |


















