NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Hydrocarbons | Chemistry Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Which one of the following reactions does not give benzene as the product? (NEET 2025)
(a) 
(b) 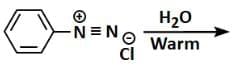
(c) 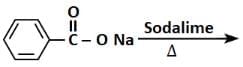
(d) 
Ans: (b)
Let's break down each reaction to determine whether it produces benzene or not:
- Reaction 1: C6H5COONa (Sodium Benzoate) + NaOH (Soda Lime) → C6H6 (Benzene)
This is a decarboxylation reaction known as the "Decarboxylation of Sodium Benzoate," which produces benzene as the product. When sodium benzoate reacts with soda lime (a mixture of NaOH and CaO), the carboxyl group is removed, and benzene is formed.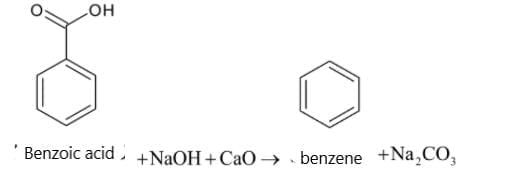
- Reaction 2: C6H12 (n-hexane) → Benzene (via MO3 at 773 K, 10–20 atm)
This reaction does produce benzene. The catalytic cracking of n-hexane under high pressure and temperature typically results in cyclisation and followed by aromatisation.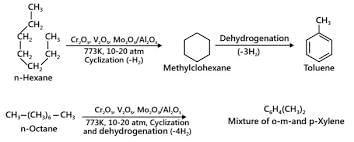
- Reaction 3: CH≡CH (Ethyne or Acetylene) → Benzene (via red-hot Iron Tube at 873 K)
This reaction is known as the "Pyrolysis of Acetylene." When acetylene is passed through a red-hot iron tube, it undergoes cyclotrimerization to form benzene as the product.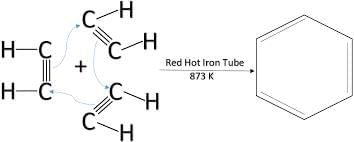
- Reaction 4: C6H5N2+Cl- (Benzenediazonium Chloride) → Phenol (via H2O warm)
This reaction involves the reduction of the benzenediazonium ion to form benzene via water as the reducing agent. This reaction also produces Phenol.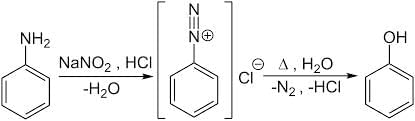
Conclusion: The correct answer is Option b.
Q2: Which one of the following compounds does not decolourize bromine water? (NEET 2025)
(a) 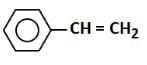
(b) 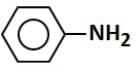
(c) 
(d) 
Ans: (c)
- Option 1: Cyclohexane (C6H12): Cyclohexane is a saturated hydrocarbon (alkane). Alkanes do not undergo addition reactions with bromine water because they do not have double or triple bonds. Therefore, it will not decolorize bromine water.
- Option 2: Phenol (C6H5OH): Phenol has a hydroxyl group attached to an aromatic ring. While phenol does not have double bonds like alkenes or alkynes, the hydroxyl group can act as an electron-donating group, but phenol can still decolorize bromine water by reacting with it, especially under certain conditions (e.g., electrophilic substitution).
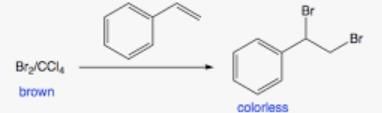
- Option 3: Styrene (C6H5CH=CH2): Styrene contains a C=C double bond (alkene), which can easily react with bromine water, decolorizing it by undergoing an addition reaction to form a dibromide.
- Option 4: Aniline (C6H5NH2): Aniline has an amine group (-NH2), which is electron-donating, and can participate in reactions with bromine, leading to the decolorization of bromine water by forming substitution products like brominated aniline.
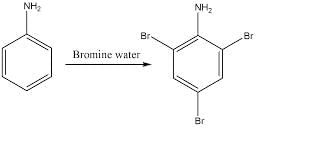
Therefore, the compound that does not decolorize bromine water is Cyclohexane (Option 1), as it is a saturated alkane and does not have any reactive sites like double bonds or groups that could react with bromine.
Q3: Predict the major product ′P′ in the following sequence of reactions - (NEET 2025)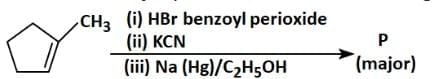
(a) 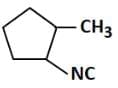
(b) 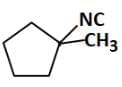
(c) 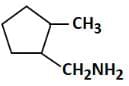
(d) 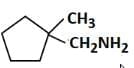
Ans: (c)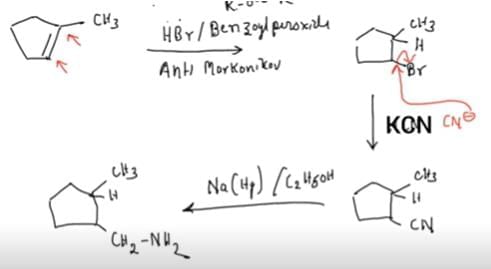
- In the first step, free radicals generated by benzoyl peroxide lead to the formation of a methyl bromide intermediate from CH₃ (methyl group) and HBr.
- In the second step, the cyanide ion (CN-) attacks the methyl bromide, displacing the bromine atom and forming a nitrile group (-CN) on the carbon chain.
- In the third step, sodium amalgam (Na(Hg)) in ethanol reduces the nitrile group (-CN) to a primary amine (-NH2), resulting in the final product, a primary amine.
Therefore, the major product 'P' is Option C.
Q4: Which one of the following compounds can exist as cis-trans isomers? (NEET 2025)
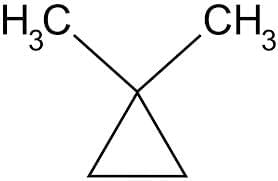
(a) 1, 1-Dimethycyclopropane
(b) 1, 2-Dimethylcyclohexane
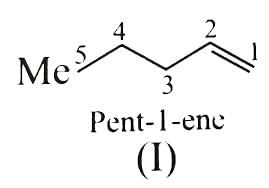
(c) Pent-1-ene
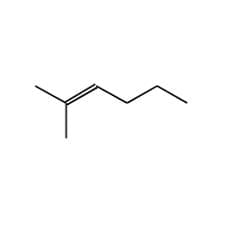
(d) 2-Methylhex-2-ene
Ans: (b)
- Pent-1-ene: Pent-1-ene has a terminal double bond (C1=C2), and one of the carbons in the double bond (C1) has two identical hydrogen atoms. Therefore, it cannot exhibit cis-trans isomerism.
- 2-Methylhex-2-ene: The double bond in 2-methylhex-2-ene (C2=C3) has two same groups attached to both C2. Therefore, it can not exhibit cis-trans isomerism.
- 1,1-Dimethylcyclopropane: In 1,1-dimethylcyclopropane, both methyl groups are attached to the same carbon atom in the ring. Since the substituents are not on different carbons, cis-trans isomerism is not possible.
- 1,2-Dimethylcyclohexane: In 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane, the methyl groups are attached to different carbons in the ring, and the ring restricts rotation. Therefore, it can exhibit cis-trans isomerism.
Therefore, the compounds that can exhibit cis-trans isomerism is 1,2-Dimethylcyclohexane
2024
Q1: Given below are two statements:Statement I : The boiling point of three isomeric pentanes follows the order
n-pentane > isopentane > neopentane
Statement II : When branching increases, the molecule attains a shape of sphere. This results in smaller surface area for contact, due to which the intermolecular forces between the spherical molecules are weak, thereby lowering the boiling point.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
The two statements provided deal with molecular structure and boiling points of isomers of pentane. Let's analyze both statements:
Statement I: This statement lists the boiling point order of the three isomers of pentane as n-pentane > isopentane > neopentane. To verify this statement, let's consider the molecular structure and boiling points of each isomer:
- n-pentane: It is a straight-chain alkane with the formula C5H12, and it has the highest boiling point among the isomers because of its larger surface area which allows for greater van der Waals forces (dispersion forces).
- isopentane (also known as methylbutane): It has one branch in its carbon chain. The branching reduces the surface area slightly, which slightly weakens the van der Waals forces compared to n-pentane.
- neopentane (also known as dimethylpropane): It has a highly branched structure making it almost spherical. This shape minimizes the surface area significantly, thereby reducing the van der Waals forces drastically compared to the other two isomers.
Thus, the boiling point order correctly reflects the influence of molecular structure and intermolecular forces. Hence, Statement I is correct.
Statement II: This statement elaborates on why branching leads to lower boiling points.
- The assertion is that increased branching gives the molecule a more spherical shape, which then results in a smaller surface area, and thus weaker intermolecular forces (primarily van der Waals forces).
- Weaker intermolecular forces correspond with a lower energy requirement for the liquid to gas phase transition, thereby lowering the boiling point.
- This explanation is coherent with concepts in physical chemistry regarding molecular interactions and phase change. Therefore, Statement II is also correct. In summary, both Statement I and Statement II are correct, reflecting the accurate relationship between molecular structure, intermolecular forces, and physical properties like boiling points. Therefore, the correct answer is:
Option A: Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
Q2: Identify the major product C formed in the following reaction sequence :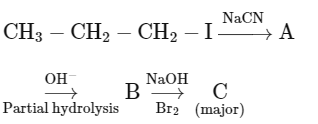
(a) propylamine
(b) butylamine
(c) butanamide
(d) α-bromobutanoic acid (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)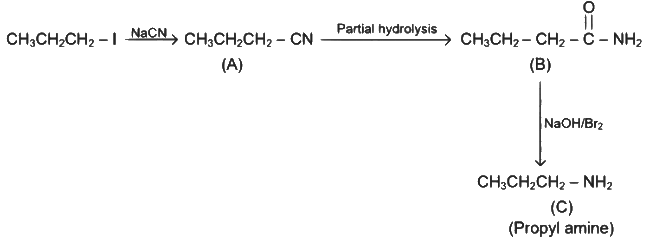
- Step-l is SN reaction with
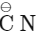 nucleophile.
nucleophile. - Step-II will give amide.
- Step-III is Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction.
Q3: For the given reaction: (NEET 2024)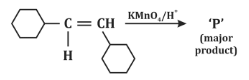
'P' is:
(a) 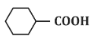
(b) 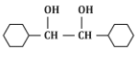
(c) 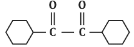
(d) 
Ans: (b)
In the given reaction, the compound is an alkene with a -CH=CH- group. When treated with KMnO₄ (potassium permanganate) under acidic conditions, the alkene undergoes oxidation, resulting in the formation of a diol (vicinal diol, where two hydroxyl groups are added across the double bond).
Therefore, the major product will be a diol, specifically option (b), where the two hydroxyl groups are added to the adjacent carbon atoms.
Thus, P is option (b).
Q4: Phenanthrene is an aromatic compound and follows Huckel's (4n+2)π electron rule. The value of n is: (NEET 2024)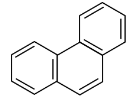
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Ans: (d)
In the given structure of phenanthrene, the compound is an aromatic hydrocarbon. To apply Huckel's rule, we need to determine the number of π-electrons involved in conjugation.
Huckel's rule states that for a compound to be aromatic, the number of π-electrons must fit the formula (4n + 2), where n is a non-negative integer.
Phenanthrene consists of three fused benzene rings, meaning the total number of π-electrons is 14 (6 from each benzene ring). We apply Huckel’s rule:
n = (π-electrons - 2) / 4
For phenanthrene, with 14 π-electrons:(4n + 2) = 14Solving this gives n = 3, which indicates the value of n is 3.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) 3.
Q5: Match List -I with List -II: (NEET 2024)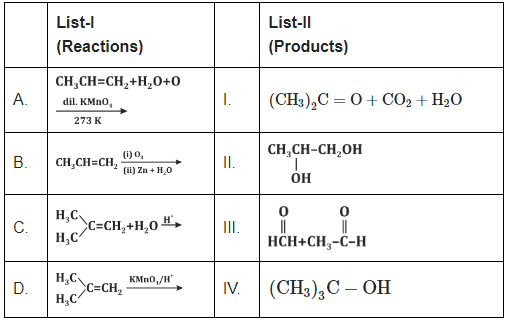 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
(b) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II
Ans: (b)
A. CH₃CH=CH₂ + H₂O + KMnO₄ (dil.) → This reaction is an oxidation reaction in which an alkene (propylene) is oxidized with potassium permanganate (diluted) and water. The product formed is acetone (CH₃₂C = O) as a result of the oxidative cleavage of the double bond.
B. CH₃CH=CH₂ + O₂ (air), (ii) Zn + H₂O → This reaction is an ozonolysis of propene followed by reduction with zinc and water, which gives propan-2-ol (CH₃CH(OH)CH₃) as a product.
C. CH₃CH=CH₂ + H₃O⁺ → This is an acid-catalyzed hydration of propene, which leads to the formation of propan-2-ol (CH₃CH(OH)CH₃), adding water to the double bond.
D. CH₃CH=CH₂ + KMnO₄ (conc.) → This reaction involves the oxidation of propene with concentrated potassium permanganate, which leads to acetic acid (CH₃COOH) due to cleavage of the double bond.
Now, matching with the correct products from List-II:
- A → I: CH₃₂C = O + CO₂ + H₂O (as propene undergoes oxidative cleavage)
- B → IV: CH₃CH(OH)CH₃ (propan-2-ol formed from ozonolysis)
- C → II: CH₃CH(OH)CH₃ (propan-2-ol formed from acid-catalyzed hydration)
- D → III: CH₃COOH (acetic acid formed from oxidation with KMnO₄)
Thus, the correct match is Option B.
Q6: The major product P formed in the following reaction sequence is: (NEET 2024)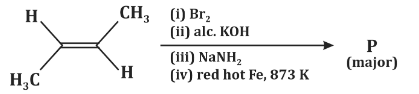 (a)
(a) 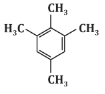
(b) 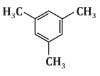
(c) 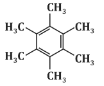
(d) 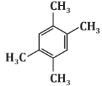
Ans: (c)
- Step (i) - Br₂: The first step involves the addition of bromine (Br₂) to the double bond of the starting compound, which will result in the formation of a dibromide.
- Step (ii) - Alcoholic KOH: Alcoholic KOH typically leads to the elimination of HBr (from the dibromide formed) and the formation of an alkene. This is an elimination reaction where the bromine atoms are removed, resulting in the formation of a new double bond.
- Step (iii) - NaNH₂: Sodium amide (NaNH₂) is a strong base and is often used in elimination reactions. It will further dehydrohalogenate (remove a hydrogen atom and a halogen) to form a new alkene.
- Step (iv) - Red hot Fe, 873 K: The final step involves heating the compound with red-hot iron (Fe) at a high temperature (873 K), which typically results in a coupling reaction. The final product is a substituted benzene ring.
Based on this sequence, the major product will be a disubstituted benzene ring with two methyl groups in a meta position. This matches the structure shown in option (c).
Therefore, the correct answer is (c).
Q7: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: Propene on treatment with diborane gives an addition product with the formula (CH₃)₂ - CH3) - B.
Statement II: Oxidation of (CH₃)₂ - CH3) - B with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of NaOH gives propan-2-ol.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Ans: (b)
Statement I: Propene on treatment with diborane gives an addition product with the formula (CH₃)₂ - CH3) - B.
Reaction of propene with diborane: Diborane (B₂H₆) reacts with alkenes (like propene) in a hydroboration reaction. This results in the addition of borane (BH₃) across the double bond, producing a trialkylborane. In the case of propene, this would result in B(CH₂CH₃)(CH₃)₂. The formula in the statement is not entirely accurate, as the actual structure would be (CH₃)₂CH-CH₂-B, with the B (boron) attached to the carbon of the propyl group. So, Statement I is incorrect.
Statement II: Oxidation of (CH₃)₂ - CH3) - B with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of NaOH gives propan-2-ol.
Oxidation of the trialkylborane: The oxidation of a trialkylborane (like the one formed in the reaction above) with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of NaOH leads to the formation of an alcohol. Specifically, in this case, the product of the oxidation would be propan-2-ol. So, Statement II is correct.
Conclusion: Statement I is incorrect, and Statement II is correct.
Thus, the correct answer is (b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Q8: Baeyer's reagent is: (NEET 2024)
(a) Acidic potassium permanganate solution
(b) Acidic potassium dichromate solution
(c) Cold, dilute, aqueous solution of potassium permanganate
(d) Hot, concentrated solution of potassium permanganate
Ans: (c)
Baeyer's reagent is a cold, dilute, aqueous solution of potassium permanganate (KMnO₄). It is commonly used in organic chemistry to test for the presence of double bonds, particularly alkenes. The reagent is a mild oxidizing agent that reacts with alkenes to form diols (vicinal diols) in a reaction known as Baeyer’s test.
- Option (a): Acidic potassium permanganate is a strong oxidizer, not Baeyer's reagent.
- Option (b): Acidic potassium dichromate is not Baeyer's reagent.
- Option (d): Hot, concentrated potassium permanganate is a stronger oxidizer and is used for different purposes, such as oxidizing alkyl side chains, but it is not Baeyer's reagent.
Q9: The major product X formed in the following reaction sequence is: (NEET 2024)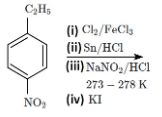
(a) 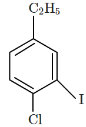
(b) 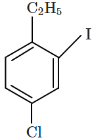
(c) 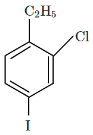
(d) 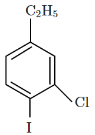
Ans: (c)
Step (i): Chlorination of nitrobenzene with chlorine (Cl₂) in the presence of FeCl₃.
Nitrobenzene undergoes electrophilic substitution where the chlorine attaches to the ortho or para position relative to the nitro group. However, due to the strong electron-withdrawing effect of the nitro group, chlorination primarily occurs at the para position to the nitro group. So, we would get para-chloro-nitrobenzene.
Step (ii): Reduction of para-chloro-nitrobenzene using Sn/HCl.
This reduction converts the nitro group (-NO₂) into an amino group (-NH₂), so the product becomes para-chloroaniline.
Step (iii): Reaction of para-chloroaniline with NaNO₂/HCl.
This step involves diazotization, where the amino group (-NH₂) is converted into a diazonium salt (-N₂⁺). The result is para-chlorobenzenediazonium chloride.
Step (iv): Reaction of para-chlorobenzenediazonium chloride with KI.
In this reaction, the diazonium ion undergoes nucleophilic substitution with the iodide ion (I⁻), replacing the diazonium group (-N₂⁺) with iodine (I). Thus, the product is para-chloro-iodobenzene.
So, the major product X formed in the given reaction sequence is option C, which is C₂H₅Cl with the chlorine at the para position to the ethyl group.
Thus, the correct answer is option C.
Q10: Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their solubilities in chloroform: (NEET 2024)
NaCl, CH₃OH, cyclohexane (C₆H₁₂), CH₃CN
(a) NaCl < CH₃CN < CH₃OH < cyclohexane
(b) CH₃OH < CH₃CN < NaCl < cyclohexane
(c) NaCl < CH₃OH < CH₃CN < cyclohexane
(d) cyclohexane < CH₃CN < CH₃OH < NaCl
Ans: (c)
- Solubility in chloroform is influenced by the polarity of the compounds. Chloroform (CHCl₃) is a relatively non-polar solvent, so compounds that are non-polar or weakly polar will generally be more soluble in it, while polar compounds will be less soluble.
- NaCl: Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an ionic compound and is highly polar. It is not soluble in chloroform, as chloroform does not provide the necessary interactions to break the ionic bonds.
- CH₃OH (Methanol): Methanol is a polar molecule, but it also has a non-polar methyl group (CH₃). While methanol is somewhat soluble in chloroform, its solubility is lower compared to non-polar substances.
- CH₃CN (Acetonitrile): Acetonitrile is a moderately polar molecule and is more soluble in chloroform than methanol, but still less soluble than non-polar molecules.
- Cyclohexane: Cyclohexane is non-polar and highly soluble in chloroform, which is also relatively non-polar.
Thus, the order of solubility in chloroform is: NaCl < CH₃OH < CH₃CN < cyclohexane
Q11: The alkane that can be oxidized to the corresponding alcohol by KMnO₄ as per the equation is, when: (NEET 2024)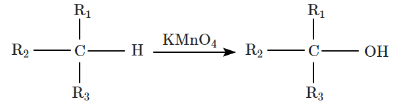 (a) R₁ = H, R₂ = H, R₃ = H
(a) R₁ = H, R₂ = H, R₃ = H
(b) R₁ = CH₃, R₂ = CH₃, R₃ = CH₃
(c) R₁ = CH₃, R₂ = H, R₃ = H
(d) R₁ = CH₃, R₂ = CH₃, R₃ = H
Ans: (c)
- KMnO₄ (potassium permanganate) is a strong oxidizing agent and is often used to oxidize alkanes to alcohols. However, KMnO₄ is most effective at oxidizing primary alkyl groups and secondary alkyl groups, where it can introduce hydroxyl groups.
- The equation typically represents oxidation of an alkane to a corresponding alcohol. When KMnO₄ is used, it will oxidize a primary carbon (C-H group) into a hydroxyl group (-OH), forming an alcohol.
- In option (c), R₁ = CH₃, R₂ = H, R₃ = H corresponds to ethyl (C₂H₅) as part of the alkane chain. This structure is appropriate for oxidation by KMnO₄, resulting in the corresponding alcohol.
Thus, R₁ = CH₃, R₂ = H, R₃ = H is the alkane that will be oxidized to the corresponding alcohol.
2023
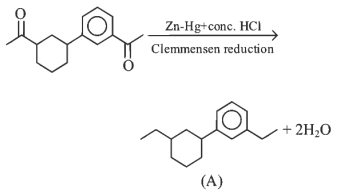
Q1: Identify product (A) is the following reaction: (NEET 2023)
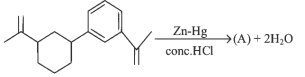
(a) 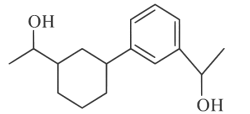
(b) 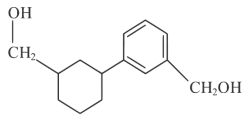
(c) 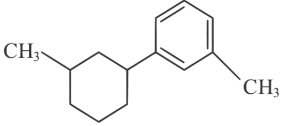
(d) 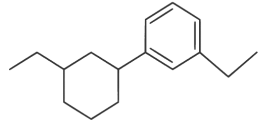
Ans: (d)
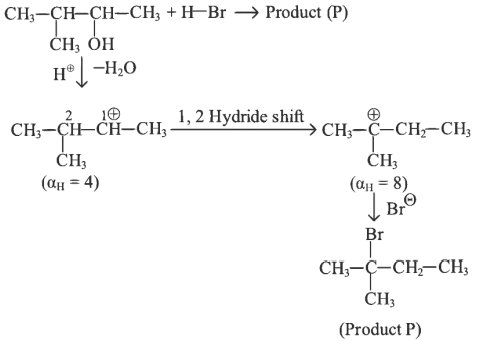
Q2: Consider the following reaction and identify the product (P). (NEET 2023)
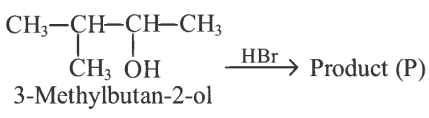
(a) 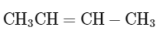
(b) 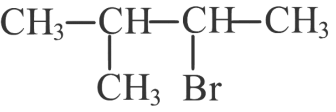
(c) 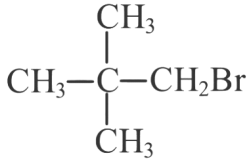
(d) 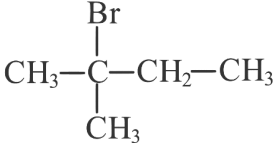
Ans: (d)
Q3: Consider the following compounds/species: (NEET 2023)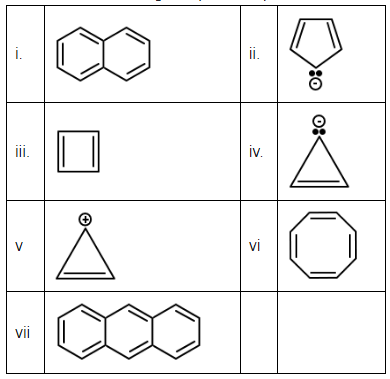 (a) 5
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 2
Ans: (b)
- i. The first compound is naphthalene, which consists of two fused benzene rings. This is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and it follows Hückel's rule (4n + 2 π-electrons), which makes it aromatic.
- ii. The second compound is pyridine, which consists of a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom replacing one of the carbon atoms. It is aromatic because it satisfies Hückel’s rule with 6 π-electrons (which makes it a 4n + 2 system, where n = 1).
- iii. The third compound appears to be a square structure, which is not aromatic. Aromatic compounds need to have a cyclic structure with conjugated double bonds (alternating single and double bonds) or a ring with π-electrons that follow Hückel's rule. This structure does not meet those criteria.
- iv. The fourth compound is pyrrole, which has a five-membered ring with one nitrogen atom and conjugated double bonds. It is aromatic because it has 6 π-electrons (following Hückel’s rule, 4n + 2).
- v. The fifth compound is a three-membered ring with one positive charge. This is not aromatic because the electron delocalization doesn't follow the necessary criteria for aromaticity (it doesn't have the required π-electrons for aromatic stabilization).
- vi. The sixth compound is benzene, which is a six-membered ring with alternating single and double bonds. It is aromatic because it follows Hückel’s rule with 6 π-electrons (n = 1).
- vii. The seventh compound is phenanthrene, which is another polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with fused benzene rings. It is aromatic because it satisfies the necessary criteria for aromaticity.
The aromatic compounds in the list are:
- i. Naphthalene (aromatic)
- ii. Pyridine (aromatic)
- iv. Pyrrole (aromatic)
- vi. Benzene (aromatic)
- vii. Phenanthrene (aromatic)
So, the correct answer is (b) 4, as only four out of the seven compounds are aromatic.
Q4: Which amongst the following compounds will show geometrical isomerism? (NEET 2023)
(a) Pent-1-ene
(b) 2,3-Dimethylbut-2-ene
(c) 2-Methylprop-1-ene
(d) 3,4-Dimethylhex-3-ene
Ans: (d)
The compound that will show geometrical isomerism is 3,4-Dimethylhex-3-ene.
Geometrical isomerism (also called cis-trans isomerism) occurs when a compound has a double bond (C=C) and each carbon of the double bond has two different groups attached to it, which allows for the existence of isomers where the positions of these groups relative to the double bond can differ (either on the same side or opposite sides).
Let's break down each compound:
- Pent-1-ene: This is an alkene (with a C=C bond), but there are no different groups attached to the same carbon of the double bond (both have hydrogen atoms). Hence, no geometrical isomerism is possible.
- 2,3-Dimethylbut-2-ene: This compound has a double bond between C2 and C3. However, on both sides of the double bond, the two carbons are attached to identical groups (hydrogen and methyl). So, this compound does not exhibit geometrical isomerism.
- 2-Methylprop-1-ene: This compound has a double bond between C1 and C2, but C1 and C2 are each attached to two hydrogens and there are no two different groups on each side of the double bond. Therefore, no geometrical isomerism is possible.
- 3,4-Dimethylhex-3-ene: This compound has a double bond between C3 and C4, and each carbon of the double bond is attached to two different groups (a methyl group and a hydrogen). This satisfies the condition for geometrical isomerism, so cis-trans isomerism is possible here.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) 3,4-Dimethylhex-3-ene, as it will show geometrical isomerism.
2022
Q1: The decreasing order of boiling points of the following alkanes is : (NEET 2022)
(a) heptane
(b) butane
(c) 2-methylbutane
(d) 2-methylpropane
(e) hexane
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (a) > (e) > (c) > (b) > (d)
(b) (a) > (c) > (e) > (d) > (b)
(c) (c) > (d) > (a) > (e) > (b)
(d) (a) > (e) > (b) > (c) > (d)
Ans: (a)
- With increase in number of carbons in alkane, boiling point increases
- In case of isomeric alkanes, greater is the number of branches, lesser is the boiling point.
Boiling point order :

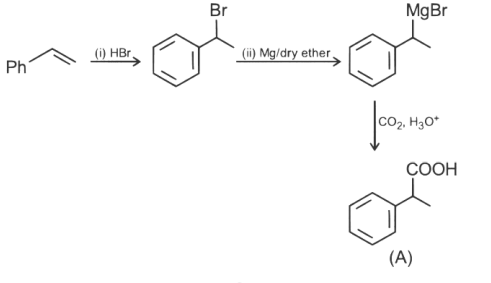
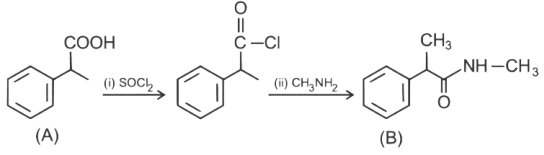
Q2: The products A and B in the following reaction sequence are : (NEET 2022)
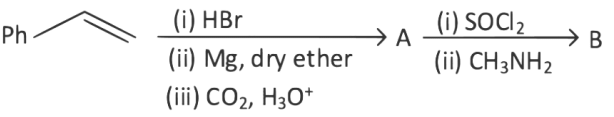
(a) 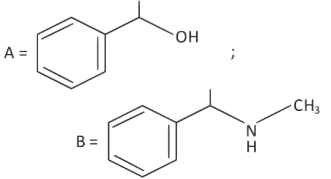
(b) 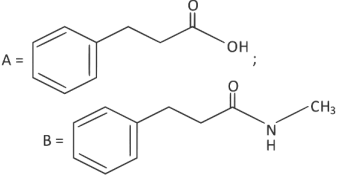
(c) 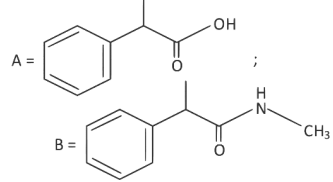
(d) 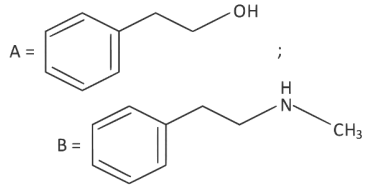
Ans: (c)
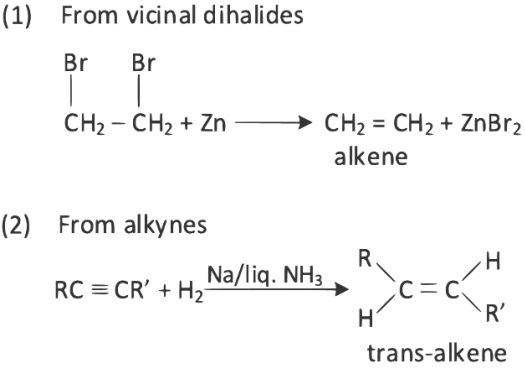
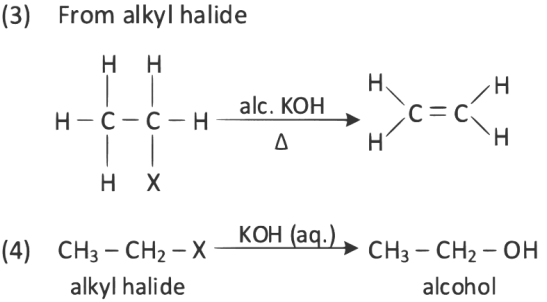
Q3: The incorrect method for the synthesis of alkenes is (NEET 2022)
(a) Treating vicinal dihalides with Zn metal
(b) Treating of alkynes with Na in liquid NH3
(c) Heating alkyl halides with alcoholic KOH
(d) Treating alkyl halides in aqueous KOH solution
Ans: (d)
Alkenes can be prepared
2021
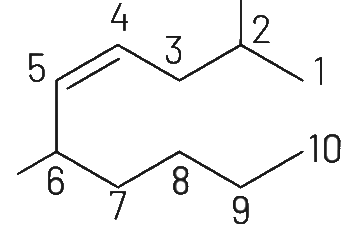
Q1: The correct structure of 2, 6-dimethyl-dec-4-ene is (NEET 2021)
(a) 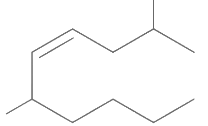
(b) 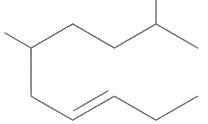
(c) 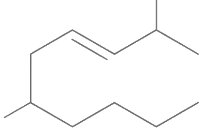
(d) 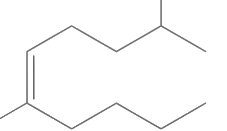
Ans: (a)
2020
Q1: An alkene on ozonolysis gives methanal as one of the product. Its structure is: (NEET 2020)
A: 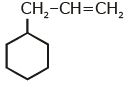
B: 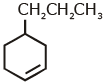
C: 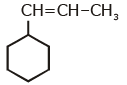
D: 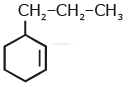
Ans: (a)
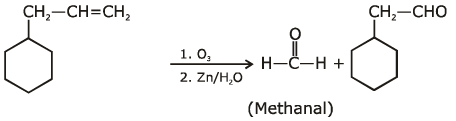
2019
Q1: The most suitable reagent for the following conversion, is : (NEET 2019)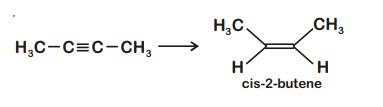
A: Na/liquid NH3
B: H2, Pd/C, quinoline
C: Zn/HCl
D: Hg2+/H+, H2O
Ans: (b)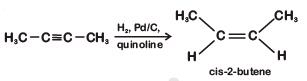
Q2: An alkene "A" on reaction with O3 and Zn–H2O gives propanone and ethanal in equimolar ratio. Addition of HCl to alkene "A" gives "B" as the major product. The structure of product "B" is: (NEET 2019)
A: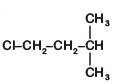
B: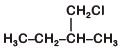
C: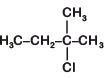
D: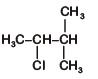
Ans: (c)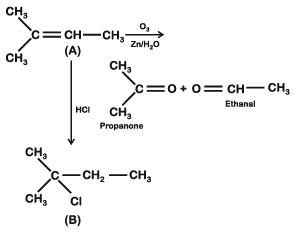
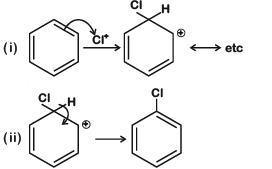
Q3: Among the following, the reaction that proceeds through an electrophilic substitution, is: (NEET 2019)
A: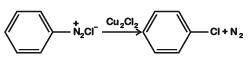
B: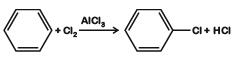
C: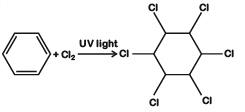
D: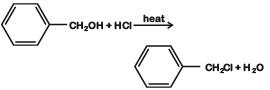
Ans: (b)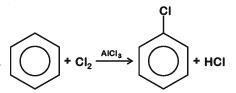
Generation of electrophile: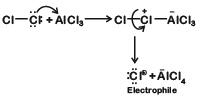
2018
Q1: Hydrocarbon (A) reacts with bromine by substitution to form an alkyl bromide which by Wurtz reaction is converted to gaseous hydrocarbon containing less than four carbon atoms. (A) is (NEET 2018)
A: CH
B: CH2 = CH2
C: CH3 - CH3
D: CH4
Ans: (d)
2017
Q1: Which one is the correct order of acidity ? (NEET 2017)
A: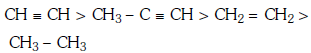
B: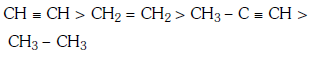
C: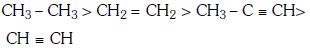
D: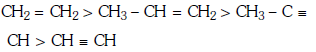
Ans: (a)
Greater the character of C-atom in hydrocarbons, greater the electronegativity of that carbon and thus greater the acidic nature of the H attached to electronegative carbon.
Thus CH
Q2: Predict the correct intermediate and product in the following reaction : (NEET 2017)
A: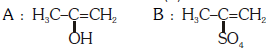
B: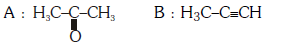
C: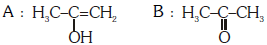
D: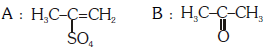
Ans: (c)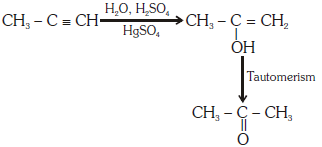
Q3: With respect to the conformers of ethane, which of the following statements is true? (NEET 2017)
(a) Bond angle changes but bond length remains same.
(b) Both bond angle and bond length change.
(c) Both bond angle and bond length remain same.
(d) Bond angle remains same but bond length changes.
Ans: (c)
Conformers are the isomers which are formed by rotation about single bonds without any cleavage of any bond. These conformers have same bond angle between them and have same bond length while their dihedral angle changes.
2016
Q1: The pair of electron in the given carbanion, 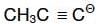 is present in which of the following orbitals? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
is present in which of the following orbitals? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
A: sp
B: 2p
C: sp3
D: sp2
Ans: (a)
Q2: In the reaction (NEET 2016 Phase 1)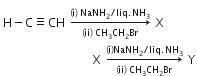
A: X=2-butyne; Y= 3-hexyne
B: X=1-butyne; Y =3-hexyne
C: X=1-butyne ;Y = 2-hexyne
D: X=2-butyne;Y=2-hexyne
Ans: (b)
NaNH2/liq.NH3 behaves as a base, so it abstracts a proton from acetylene to form acetylide anion followed by alkylation to give compound (X) i.e 1-butyne (X) further reacts with NaNH2/Liq NH3 followed by alkylation with ethyl bromide yields 3-hexyne (Y).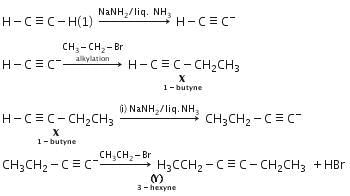
Q3: Consider the nitration of benzene using mixed conc. H2SO4 and HNO3 . If a larger amount of KHSO4 is added to the mixture the rate of nitration will be : (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
A: Doubled
B: Faster
C: Slower
D: Unchanged
Ans: (c)
In the nitration of benzene in the presence of conc. H2SO4 and HNO3, benzene is formed.
HNO3 +H2SO4 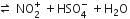
If a large amount of KHSO4 is added to this mixture more HSO4- ion furnishes and hence the concentration of electrophile decreases, rate of electrophilic aromatic reaction slows down.
Q4: For the following reactions : (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
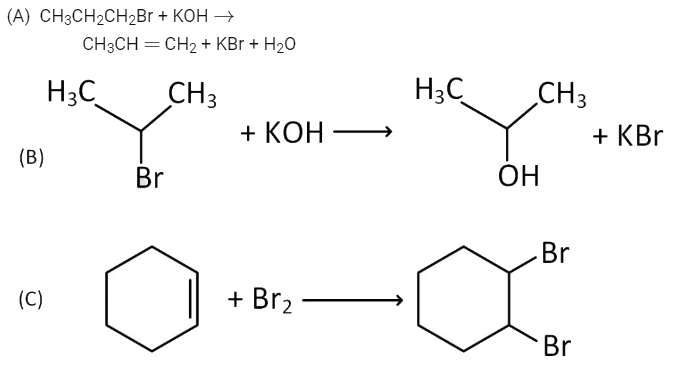
Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) (A) is elimination, (B) and (C) are substitution reactions.
(b) (A) is substitution, (B) and (C) are addition reactions.
(c) (A) and (B) are elimination reactions and (C) is addition reaction.
(d) (A) is elimination, (B) is substitution and (C) is addition reaction.
Ans: (d)
- (A) Saturated compound is converted into unsaturated compound by removal of group of atoms hence, it is an elimination reaction.
- (B) —Br group is replaced by —OH group hence, it is a substitution reaction.
- (C) Addition of Br2 converts an unsaturated compound into a saturated compound hence, it is an addition reaction.
Q5: Which of the following can be used as the halide component for Friedel-Crafts reaction?
(a) Chlorobenzene
(b) Bromobenzene
(c) Chloroethene
(d) Isopropyl chloride (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (d)
Friedel–Crafts reaction :
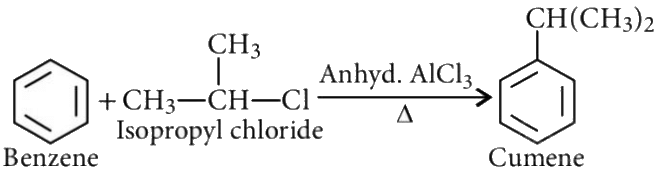
Chlorobenzene, bromobenzene and chloroethene are not suitable halide components as lone pair of electrons of halogen are delocalized with π-bonds to attain double bond (C = X) character.
Q6: In pyrrole the electron density is maximum on (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
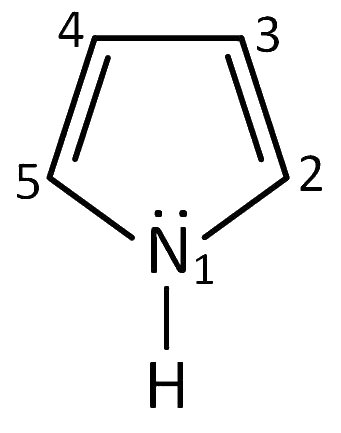
(a) 2 and 3
(b) 3 and 4
(c) 2 and 4
(d) 2 and 5
Ans: (d)
Pyrrole has maximum electron density on 2 and 5. It generally reacts with electrophiles at the C-2 or C-5 due to the highest degree of stability of the protonated intermediate.
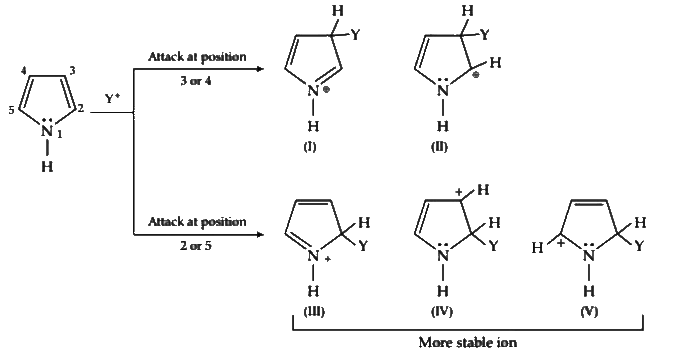
Attack at position 3 or 4 yields a carbocation that is a hybrid of structures (I) and (II). Attack at position 2 or 5 yields a carbocation that is a hybrid not only of structures (III) and (IV) (analogous to I and II) but also of structure (V). The extra stabilization conferred by (V) makes this ion the more stable one.
Also, attack at position 2 or 5 is faster because the developing positive charge is accommodated by three atoms of the ring instead of by only two.
Q7: In which of the following molecules, all atoms are coplanar? (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) 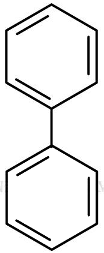
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 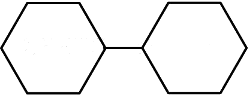
Ans: (a)
Biphenyl is coplanar as all carbon atoms are sp2 hybridised.
Q8: In the given reaction,
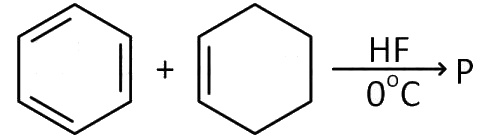
the product P is (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) 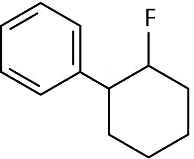
(b) 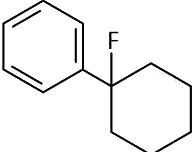
(c) 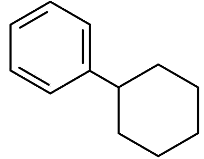
(d) 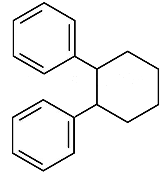
Ans: (c)
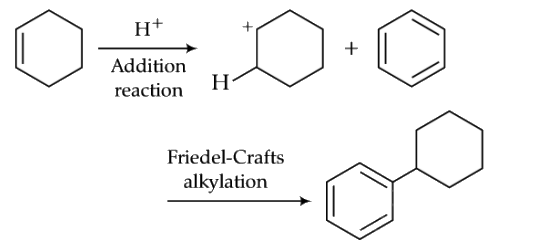
Q9: The compound that will react most readily with gaseous bromine has the formula (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) C3H6
(b) C2H2
(c) C4H10
(d) C2H4
Ans: (a)
Propene is most reactive towards Br2 (gaseous) than CH2 = CH2, HC
2015
Q1: Given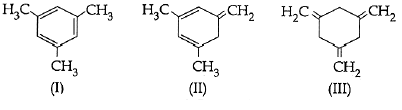
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of these compounds will be in the order as : (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
A: II > I > III
B: I > II > III
C: III > II > I
D: II > III > I
Ans: (c)
Higher is the stability, lower is the enthalpy of hydrogenation.
(I) is most stable due to aromatic character. Hence it has lowest enthalpy of hydrogenation.
(III) is least stable as no resonance is present. Hence, it has highest enthalpy of hydrogenation.
Thus, the decreasing order of the enthalpy of hydrogenation is III > II > I.
Q2: A single compound of the structure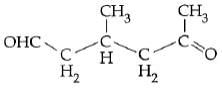
is obtainable from ozonolysis of which of the following cyclic compounds ? (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
A: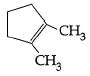
B: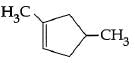
C: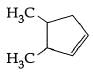
D: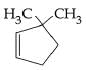
Ans: (b)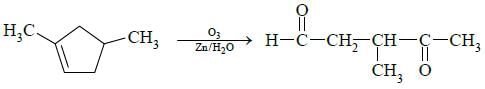
Q3: Which of the following is not the product of dehydration of (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
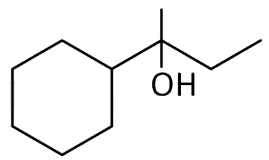
(a) 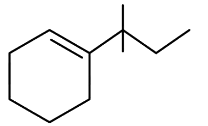
(b) 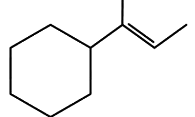
(c) 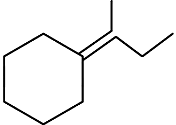
(d) 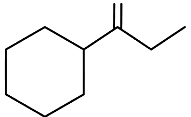
Ans: (a)
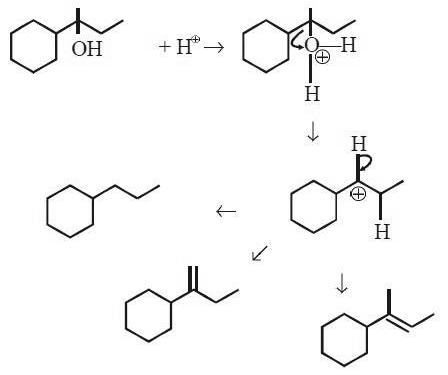
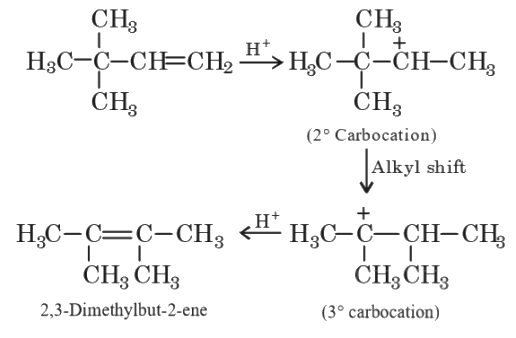
Q4: 2,3-Dimethyl-2-butene can be prepared by heating which of the following compounds with a strong acid?
(a) (CH3)3CCH
(b) (CH3)2C
(c) (CH3)2CHCH2CH
(d) 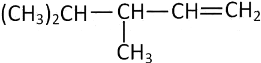 (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
(NEET / AIPMT 2015)
Ans: (a)
Q5: The reaction of C6H5CH = CHCH3 with HBr produces : (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
A: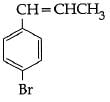
B: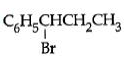
C: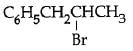
D: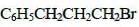
Ans: (b)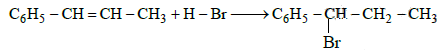
2014
Q1: Identity Z in the sequence of reactions (NEET 2014)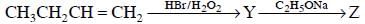
A: CH3 (CH2)4 −O−CH3
B: CH3CH2 −CH(CH3) −O−CH2CH3
C: CH3 − (CH2)3 −O−CH2CH3
D:(CH3)2CH2 −O−CH2CH3
Ans: C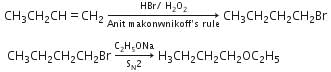
Q2: Which of the following organic compounds has same hybridization as its combustion product (CO2)? (NEET 2014)
A: Ethene
B: Ethanol
C: Ethane
D: Ethyne
Ans: D
HC ≡ CH and O = C = O both have sp−hybridised carbon
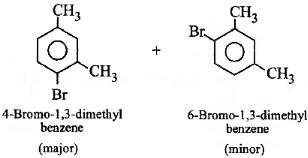
Q3: What products are formed when the following compound is treated with Br2 in the presence of FeBr3? (NEET 2014)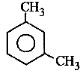
A: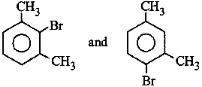
B: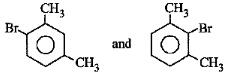
C: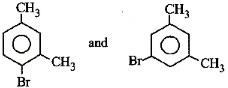
D: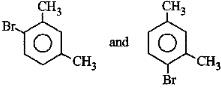
Ans: (d)
-CH3 group is o,p-directing. Because of crowding, no substitution occurs at the carbon atom between the two -CH3 groups in m-Xylene, even though two -CH3 groups activate that position.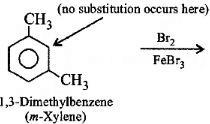
|
119 videos|346 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Hydrocarbons - Chemistry Class 11
| 1. What are hydrocarbons and why are they important in chemistry? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of hydrocarbons? |  |
| 3. How do you identify the structure of a hydrocarbon from its molecular formula? |  |
| 4. What are some common reactions involving hydrocarbons? |  |
| 5. How are hydrocarbons relevant to NEET exam preparation? |  |






















