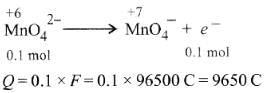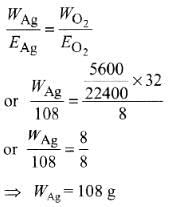2025
Q1: If the molar conductivity (Λm) of a 0.050 mol L-1 solution of a monobasic weak acid is 90 S Cm2 mol-1, its extent (degree) of dissociation will be [Assume Λo+ = 349.6 S Cm2 mol-1 and Λo - = 50.4 S cm2 mol-1.] (NEET 2025)
(a) 0.225
(b) 0.215
(c) 0.115
(d) 0.125
Ans: (a)
Calculate Λm0:
- Λm0 = Λ+0 + Λ-0
- = 349.6 S cm2 mol-1 + 50.4 S cm2 mol-1
- = 400 S cm2 mol-1
Calculate α:
- α = Λm / Λm0
- = 90 S cm2 mol-1 / 400 S cm2 mol-1
- = 0.225
Therefore, the degree of dissociation (α) is 0.225, and the correct answer is Option A.
2024
Q1: Match List I with List II.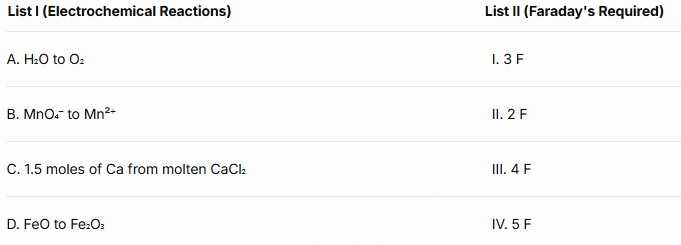
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(b) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(c) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I (NEET 2024)
Ans: (b)
Corrected Explanation:
A. H₂O to O₂: The reaction is 2H₂O → O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻, requiring 4 F per mole of O₂. Matches III (4 F).
B. MnO₄⁻ to Mn²⁺: MnO₄⁻ + 8H⁺ + 5e⁻ → Mn²⁺ + 4H₂O, requiring 5 F. Matches IV (5 F).
C. 1.5 moles Ca from CaCl₂: Ca²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Ca, 2 F per mole, so 1.5 × 2 = 3 F. Matches I (3 F).
D. FeO to Fe₂O₃: 2FeO + ½O₂ → Fe₂O₃, Fe²⁺ to Fe³⁺ requires 1 electron per Fe, so 2 F total. Matches II (2 F).
Note: The original List II had two 2 F entries (II and III), which was a typo. Corrected List II replaces one 2 F with 4 F to reflect standard electrochemistry problems.
Conclusion: The correct answer is (b) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II.
Q2: Mass in grams of copper deposited by passing 9.6487 A current through a voltmeter containing copper sulphate solution for 100 seconds is (Given : Molar mass of Cu : 63 g mol−1,1 F = 96487C)
(a) 3.15 g
(b) 0.315 g
(c) 31.5 g
(d) 0.0315 g (NEET 2024)
Ans: (b)
The mass of copper deposited when passing an electric current through a copper sulphate solution can be calculated using Faraday's laws of electrolysis. The first law states that the amount of a substance deposited or liberated at an electrode during electrolysis is proportional to the amount of electricity (charge) passed through the electrolyte.
To find the mass of copper deposited, we use the formula:
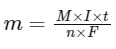
Where:
m is the mass of the substance deposited (in grams),
M is the molar mass of the substance (in g/mol),
I is the current (in amperes, A),
t is the time electricity is passed through the solution (in seconds),
n is the number of moles of electrons required to deposit or dissolve 1 mole of the substance (valence number, which is 2 for copper in copper sulphate solution as copper ions are Cu2+),F is the Faraday constant, approximately 96487C/mol of electrons.
Given:
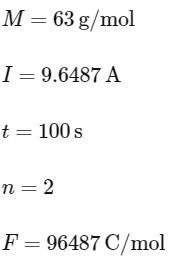
Substitute these values into the formula:

Hence, the mass of copper deposited is approximately 0.315 g, making Option B the correct answer.
Q3: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: 2 F electricity is required for the oxidation of 1 mole H₂O to O₂.
Statement II: To get 40.0 g of Aluminium from molten Al₂O₃, the required electricity is 4.44 F.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: (d)
Statement I: False. The oxidation reaction is 2H₂O → O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻, requiring 4 F per mole of O₂ (2 moles H₂O). For 1 mole H₂O, the stoichiometry doesn’t produce 1 mole O₂, so 2 F is incorrect.
Statement II: True. Molar mass of Al = 27 g/mol, 40.0 g = 40/27 ≈ 1.4815 mol. Al³⁺ + 3e⁻ → Al requires 3 F per mole, so 1.4815 × 3 ≈ 4.44 F.
Conclusion: The correct answer is (d) Statement I is false, Statement II is true.
Q4: Select the one which is not an example of corrosion: (NEET 2024)
(a) Rusting of an iron object
(b) Production of hydrogen by electrolysis of water
(c) Tarnishing of silver
(d) Development of green coating on copper and bronze ornaments
Ans: (b)
- Corrosion is a chemical or electrochemical process in which a material, usually a metal, deteriorates due to reactions with environmental factors like oxygen, water, and pollutants.
- Rusting of an iron object (Option 1) is a classic example of corrosion, where iron reacts with oxygen and water to form iron oxide (rust).
- Tarnishing of silver (Option 3) is also an example of corrosion, where silver reacts with sulfur compounds in the air to form silver sulfide, leading to a tarnished appearance.
- Development of green coating on copper and bronze ornaments (Option 4) is another example of corrosion, where copper reacts with oxygen and moisture to form copper carbonate, which appears as a green patina (often seen on old copper roofs or coins).
However, the production of hydrogen by electrolysis of water (Option 2) is not an example of corrosion. Electrolysis is a process where electrical energy is used to break down water (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂), which is a controlled process, not a degradation or deterioration of a material due to environmental factors.
Therefore, Option B is the correct answer.
Q5: The standard cell potential of the following cell: Zn | Zn²⁺ (aq) || Fe²⁺ (aq) | Fe is 0.32 V. (NEET 2024)
Calculate the standard Gibbs energy change for the reaction:
Zn (s) + Fe²⁺ (aq) → Zn²⁺ (aq) + Fe (s)
(Given: 1 F = 96487 C mol⁻¹)
(a) -61.75 kJ mol⁻¹
(b) +5.006 kJ mol⁻¹
(c) -5.006 kJ mol⁻¹
(d) +61.75 kJ mol⁻¹
Ans: (a)
The standard Gibbs free energy change (ΔG°) for the reaction can be calculated using the following equation:
ΔG° = -nFΔE°
Where:
- n = number of moles of electrons exchanged,
- F = Faraday's constant (96487 C/mol),
- ΔE° = standard cell potential.
Step 1: Identify the values
- ΔE° (standard cell potential) = 0.32 V (given).
- n = 2 (since the reaction involves the exchange of 2 electrons — Zn is oxidized from Zn to Zn²⁺ and Fe²⁺ is reduced to Fe).
- F = 96487 C/mol (given).
Step 2: Calculate ΔG°
Substitute the values into the equation:
ΔG° = -nFΔE°
ΔG° = -2 × 96487 C/mol × 0.32 V
Since 1 V = 1 J/C, the unit of V is equivalent to J/C, so the result will be in J/mol.
ΔG° = -2 × 96487 × 0.32
ΔG° = -61675.2 J/mol = -61.75 kJ/mol
Final Answer: The standard Gibbs energy change for the reaction is -61.75 kJ/mol, so the correct answer is: (a) -61.75 kJ mol⁻¹.
2023
Q.1. The conductivity of centimolar solution of KCl at 25°C is 0.0210 ohm–1 cm–1 and the resistance of the cell containing the solution at 25°C is 60 ohm. The value of cell constant is (NEET 2023)
(a) 1.34 cm–1
(b) 3.28 cm–1
(c) 1.26 cm–1
(d) 3.34 cm–1
Ans: (c)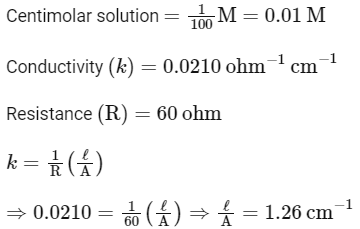
Q.2. Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R (NEET 2023)
Assertion A : In equation △rG = –nFEcell’ value of △rG depends on n.
Reasons R: Ecell is an intensive property and △rG is an extensive property.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: (b)
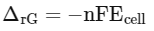
ΔEcell is an intensive property and ΔrG is an extensive property as it depends on number of eΘ transferred in cell reaction.
Q3: The molar conductance of an electrolyte increases with dilution according to the equation: (NEET 2023)
Λₘ = Λₘ⁰ − A√c
Consider the following four statements:
(A) This equation applies to both strong and weak electrolytes.
(B) The value of the constant A depends upon the nature of the solvent.
(C) The value of constant A is the same for both BaCl₂ and MgSO₄.
(D) The value of constant A is the same for both BaCl₂ and Mg(OH)₂.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) (A) and (B) only
(b) (A), (B), and (C) only
(c) (B) and (C) only
(d) (B) and (D) only
Ans: (a)
(A): True. The equation Λₘ = Λₘ⁰ − A√c (Debye-Hückel-Onsager) applies primarily to strong electrolytes but can approximate weak electrolytes under certain conditions, especially at low concentrations.
(B): True. The constant A depends on the solvent’s dielectric constant and viscosity.
(C): False. A depends on the electrolyte’s ion charges and mobilities. BaCl₂ (2:1) and MgSO₄ (2:2) have different ionic interactions, so A differs.
(D): False. BaCl₂ (2:1) and Mg(OH)₂ (2:1) have different ion mobilities, and Mg(OH)₂’s low solubility affects its behavior, so A differs.
Conclusion: The correct answer is (a) A, B.
Q4: The correct value of cell potential in volts for the reaction that occurs when the following two half-cells are connected is:
Fe²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Fe(s), E° = -0.44 V
Cr₂O₇²⁻(aq) + 14H⁺ + 6e⁻ → 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O, E° = +1.33 V
(a) +1.77 V
(b) +2.65 V
(c) +0.01 V`
(d) +0.89 V (NEET 2023)
Ans: (a)
To calculate the cell potential, we use the formula:
E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode
- The cathode is where reduction occurs (gain of electrons), and the anode is where oxidation occurs (loss of electrons).
Given half-reactions:
- Fe²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Fe(s), E° = -0.44 V (This is the oxidation half-reaction, because the potential is negative, and we need to reverse it when using it as the anode).
- Cr₂O₇²⁻(aq) + 14H⁺ + 6e⁻ → 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O, E° = +1.33 V (This is the reduction half-reaction, so it is the cathode).
Step 1: Identify the cathode and anode:
- Cr₂O₇²⁻ is reduced to Cr³⁺, so this is the cathode (reduction).
- Fe²⁺ is oxidized to Fe, so this is the anode (oxidation).
Step 2: Reverse the anode half-reaction: The anode reaction for Fe will be the reverse of the given reduction half-reaction, so the potential for the anode is +0.44 V (since we reverse the sign when oxidation occurs).
Step 3: Calculate the cell potential:
Now, use the formula:
E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode
E°cell = 1.33 V - (-0.44 V)
E°cell = 1.33 V + 0.44 V = 1.77 V
Thus, the correct cell potential is +1.77 V, and the answer is (a) +1.77 V.
Q5: The molar conductance of a solution, given its conductivity (0.248 S m⁻¹) and concentration (0.2 mol m⁻³), is: (NEET 2023)
(a) 0.124 S cm² mol⁻¹
(b) 1.24 S m² mol⁻¹
(c) 124 S cm² mol⁻¹
(d) 124 S m² mol⁻¹
Ans: (b)
To calculate the molar conductance (Λₘ), use the formula:
Λₘ = κ / c
Where:
- κ is the conductivity (0.248 S/m),
- c is the concentration (0.2 mol/m³).
Substitute the values:
Λₘ = 0.248 / 0.2 = 1.24 S·m²/mol.
Thus, the molar conductance is 1.24 S·m²/mol, and the correct answer is (b).
2022
Q1: Two half cell reactions are given below. (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
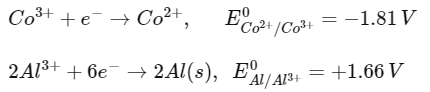
The standard EMF of a cell with feasible redox reaction will be :
(a) −3.47 V
(b) +7.09 V
(c) +0.15 V
(d) +3.47 V
Ans: (d)
Since E0OP of Al is more than Co2+, so at anode Al will oxidise and at cathode Co3+ will reduce.
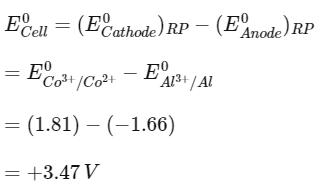
Q2: Standard electrode potential for the cell with cell reaction (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
is 1.1 V. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy change for the cell reaction. (Given F = 96487 C mol−1)
(a) −200.27 J mol−1
(b) −200.27 kJ mol−1
(c) −212.27 kJ mol−1
(d) −212.27 J mol−1
Ans: (c)
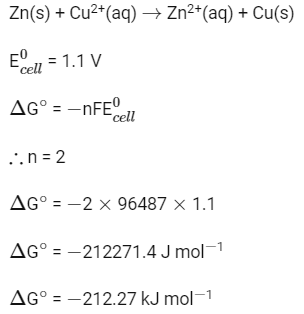
Q3: At 298 K, the standard electrode potentials of Cu2+ / Cu, Zn2+/Zn, Fe2+/Fe and Ag+/Ag are 0.34 V, – 0.76 V, – 0.44 V and 0.80 V, respectively. On the basis of standard electrode potential, predict which of the following reaction can not occur?
(a) FeSO4(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + Fe(s)
(b) 2CuSO4(aq) + 2Ag(s) → 2Cu(s) + Ag2SO4(aq)
(c) CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
(d) CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Ans: (b)
(a)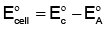
= 0.44 ( 0.76)
= + 0.32 V ( will occurs)
(b)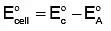
= 0.34 (0.80)
= -0.46 V ( will not occurs)
(c) 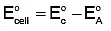
= 0.34 ( 0.76 )
= + 1.10 V ( will occurs)
(d) 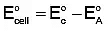
= 0.34 ( 0.44 )
= + 0.78 V ( will occurs)
Q4: Given below are half-cell reactions: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
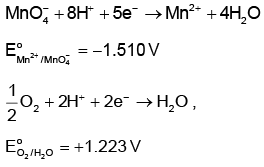
Will the permanganate ion,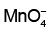 liberate O2 from water in the presence of an acid?
liberate O2 from water in the presence of an acid?
(a) Yes, because E°cell = + 2.733 V
(b) No, because E°cell = – 2.733 V
(c) Yes, because E°cell = + 0.287 V
(d) No, because E°cell = – 0.287 V
Ans: (c)
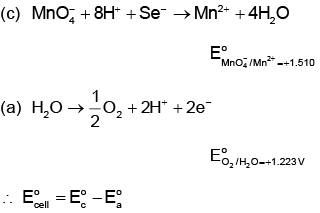
= 1.51 - 1.223
= +0.287 V
Since E°cell is positive, O2 will be released.
Q5: Find the emf of the cell in which the following reaction takes place at 298 K
Ni(s) + 2Ag+ (0.001 M) → Ni2+(0.001 M) + 2Ag(s)
(Given that 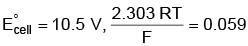 at 298 K)
at 298 K)
(a) 0.9615 V
(b) 1.05 V
(c) 1.0385 V
(d) 1.385 V (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Ans: (a)
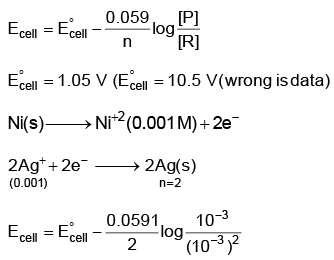
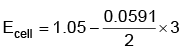
= 1.05 – 0.0885
= 0.9615 V
2021
Q1: The molar conductance of NaCl, HCI, and CH3COONa at infinite dilution are 126.45, 426.16, and 91.0 S cm mol-1 respectively. The molar conductance of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is. Choose the right option for your answer. (NEET 2021)
(a) 698.28 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1
(b) 540.48 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1
(c) 201.28 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1
(d) 390.71 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1
Ans: (d)
According to Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions.
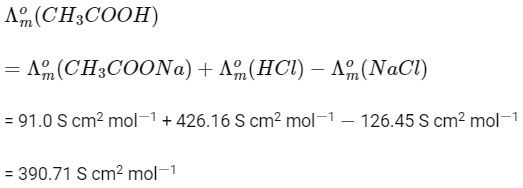
Q2: The molar conductivity of 0.007 M acetic acid is 20 S cm2 mol-1. What is the dissociation constant of acetic acid? Choose the correct option. (2021)
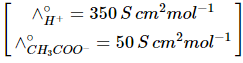
(a) 1.75 × 10–5 mol L–1
(b) 2.50 × 10–5 mol L–1
(c) 1.75 × 10–4 mol L–1
(d) 2.50 × 10–4 mol L–1
Ans: (a)
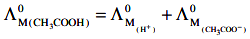
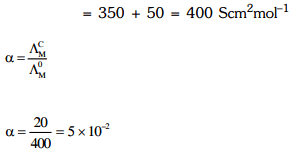
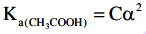
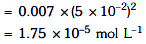
2020
Q1: On electrolysis of dil. sulphuric acid using platinum (Pt) electrode, the product obtained at the anode will be: (NEET 2020)
(a) H2S gas
(b) SO2 gas
(c) Hydrogen gas
(d) Oxygen gas
Ans: (d)
During the electrolysis of dil. sulphuric acid using Pt electrodes following reaction will take place.
At cathode :
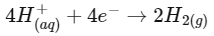
At anode :
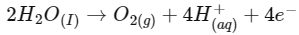
At the anode oxygen gas will be released.
Q2: The number of Faradays (F) required to produce 20g of calcium from molten CaCl2 (Atomic mass of Ca = 40 g mol-1) is:
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 1
(d) 2 (NEET 2020)
Ans: (c)
1 equivalent of any substance is deposited by 1F of charge.
We have 20g calcium.
No. of equivalent = given mass / equivalent mass
Ca2+ + 2e- → Ca(s)
v.f. = 2
According to Faraday's 1st law
Charge passed in Faradey = g. equivalent of product
= 20/40 x 2 = 1 F
So, 1 F of charge is required.
2019
Q1: For a cell involving one electron E°cell = 0.59 V at 298 K, the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction is :
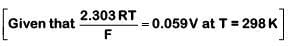 (NEET 2019)
(NEET 2019)
(a) 1.0 × 102
(b) 1.0 × 105
(c) 1.0 × 1010
(d) 1.0 × 1030
Ans: (c)
We know,
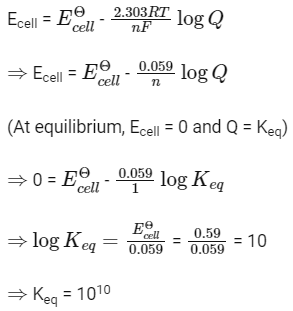
Q2: For the cell reaction
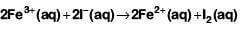
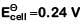 at 298 K. The standard Gibbs energy
at 298 K. The standard Gibbs energy 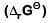 of the cell reaction is :[Given that Faraday constant F = 96500 C mol–1] (NEET 2019)
of the cell reaction is :[Given that Faraday constant F = 96500 C mol–1] (NEET 2019)
(a) – 46.32 kJ mol–1
(b) – 23.16 kJ mol–1
(c) 46.32 kJ mol–1
(d) 23.16 kJ mol–1
Ans: (a)
Here, n = 2
ΔGo = -nFEo
= – 2 × 96500 × 0.24
= – 46320 J mol–1
= – 46.32 KJ mol–1
2018
Q1: Consider the change in the oxidation state of Bromine corresponding to different emf values as shown in the diagram below:
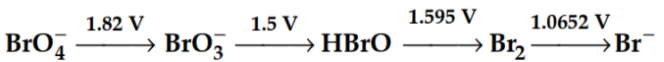 Then the species undergoing disproportionation is:- (NEET 2018)
Then the species undergoing disproportionation is:- (NEET 2018)
(a) BrO3-
(b) BrO4-
(c) Br2
(d) HBrO
Ans: (d)
Calculate Eocell corresponding to each compound undergoing disproportionation reaction. The reaction for which Eocell comes out + ve is spontaneous.
HBrO → Br2, EoHBrO/Br2 = 1.595 V
HBrO → BrO3–, EoBrO3-/HBrO = 1.595 V
Eocell for the disproportionation of HBrO,
Eocell = EoHBrO/Br2 - EoBrO3-/HBrO
= 1.595 - 1.5
= 0.095 V = + ve
So, Eocell > 0
So, ΔGo < 0 (Spontaneous)
2017
Q1: In the electrochemical cell : 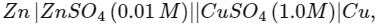 the emf of this Daniell cell is E1. When the concentration of ZnSO4 is changed to 1.0 M and that of CuSO4 changed to 0.01 M, the emf changes to E2. From the followings, which one is the relationship between E1 and E2? (Given, RT/F = 0.059) (NEET 2017)
the emf of this Daniell cell is E1. When the concentration of ZnSO4 is changed to 1.0 M and that of CuSO4 changed to 0.01 M, the emf changes to E2. From the followings, which one is the relationship between E1 and E2? (Given, RT/F = 0.059) (NEET 2017)
(a) E1 < E2
(b) E1 > E2
(c) E2 = 0 ≠ E1
(d) E1 = E2
Ans: (b)
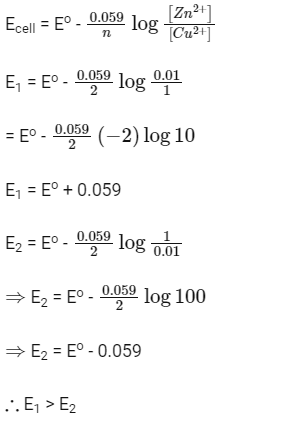
2016
Q1: The molar conductivity of a 0.5 mol/dm3 solution of AgNO3 with electrolytic conductivity of 5.76 x 103 S cm1 at 298 K is
(a) 2.88 S cm2/mol
(b) 11.52 S cm2/mol
(c) 0.086 S cm2/mol
(d) 28.8 S cm2/mol (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (b)
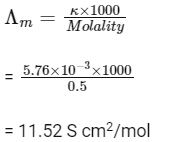
Q2: If the Eocell for a given reaction has a negative value, which of the following gives the correct relationships for the values of ΔGo and Keq ?
(a) ΔGo > 0; Keq < 1
(b) ΔGo > 0; Keq > 1
(c) ΔGo < 0; Keq > 1
(d) ΔGo < 0; Keq < 1 (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (a)
We know that
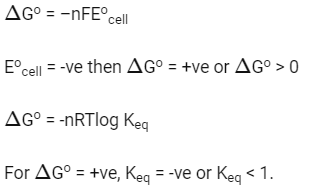
Q3: During the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, the time required to produce 0.10 mol of chlorine gas using a current of 3 amperes is (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) 55 minutes
(b) 110 minutes
(c) 220 minutes
(d) 330 minutes
Ans: (b)
At cathode : 2Na+ + 2e– 2Na
At anode : 2Cl– Cl2 + 2e–
----------------------------------------------
Net reaction: 2Na+ + 2Cl– 2Na + Cl2
From Faraday’s first law of electrolysis,
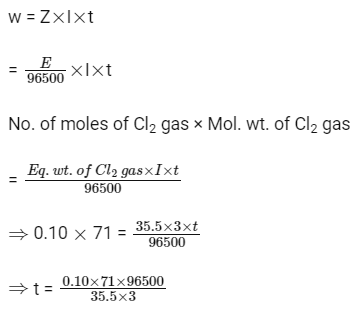
= 6433.33 sec
= 107.22 min ≃ 110 min
Q4: Zinc can be coated on iron to produce galvanized iron but the reverse is not possible. It is because
(a) zinc is lighter than iron
(b) zinc has lower melting point than iron
(c) zinc has lower negative electrode potential than iron
(d) zinc has higher negative electrode potential than iron (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (d)
The reduction potential values are
E°Zn2+/Zn = – 0.76 V
E°Fe2+/Fe = – 0.44 V
Thus, due to higher negative electro potential value of zinc than iron, iron cannot be coated on zinc.
Q5: The number of electrons delivered at the cathode during electrolysis by a current of 1 ampere in 60 seconds is (charge on electron = 1.60 × 10−19C)
(a) 6 × 1023
(b) 6 × 1020
(c) 3.75 × 1020
(d) 7.48 × 1023 (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (c)
Q = I × t
Q = 1 × 60 = 60 C
Now, 1.60 × 10–19 C ≡ 1 electron
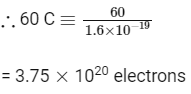
Q6: The pressure of H2 required to make the potential of H2-electrode zero in pure water at 298 K is : (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) 10-4 atm
(b) 10-14 atm
(c) 10-12 atm
(d) 10-10 atm
Ans: (b)
pH = 7 for water.
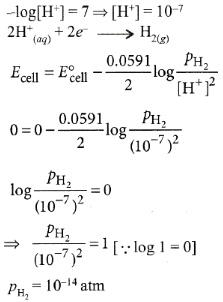
2015
Q1: Aqueous solution of which of the following compounds is the best conductor of electric current ?
(a) Hydrochloric acid, HCl
(b) Ammonia, NH3
(c) Fructose, C6H12O6
(d) Acetic acid, C2H4O2 (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
Ans: (a)
HCl completely dissociates to give H+ and Cl- ions, hence act as very good electrolyte. While others are non- electrolytes.
Q2: A device that converts the energy of combustion of fuels like hydrogen and methane, directly into electrical energy is known as (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) Ni-Cd cell
(b) Fuel Cell
(c) Electrolytic Cell
(d) Dynamo
Ans: (b)
A device that converts energy of combustion of fuels, directly into electrical energy is known as fuel cell.
2014
Q1: When 0.1 mol 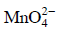 is oxidised the quantity of electricity required to completely oxidise
is oxidised the quantity of electricity required to completely oxidise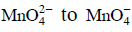 is :
is :
(a) 9650 C
(b) 96.50 C
(c) 96500 C
(d) 2 × 96500 C (NEET / AIPMT 2014)
Ans: (a)
The oxidation reaction is
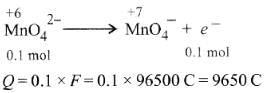
Q2: The weight of silver (at. wt. = 108) displaced by a quantity of electricity that displaces 5600 mL of O2 at STP will be :
(a) 54.0 g
(b) 108.0 g
(c) 5.4 g
(d) 10.8 g (NEET / AIPMT 2014)
Ans: (b)
According to Faraday's second law,
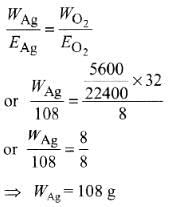



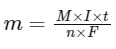

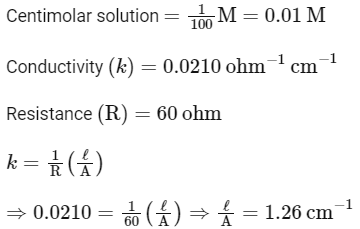
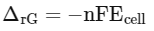
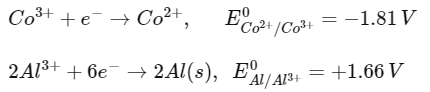
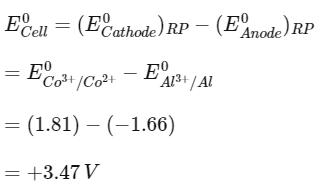
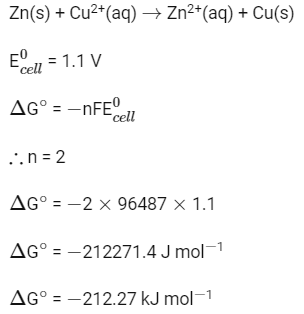
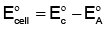
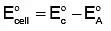
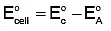
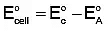
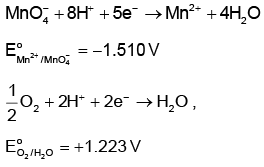
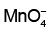 liberate O2 from water in the presence of an acid?
liberate O2 from water in the presence of an acid?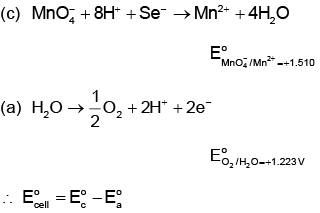
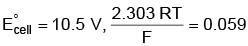 at 298 K)
at 298 K)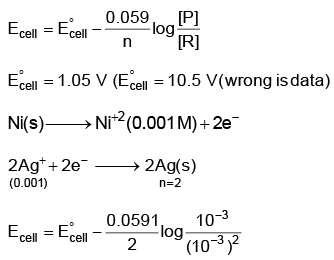
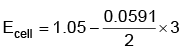
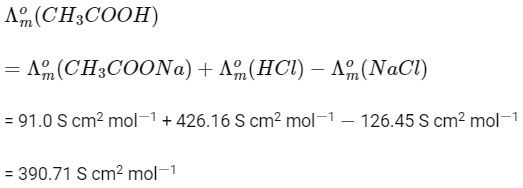
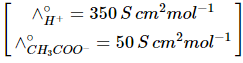
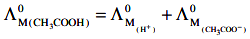
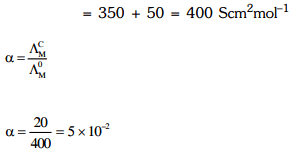
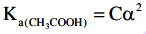
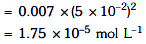
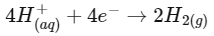
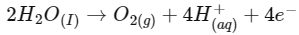
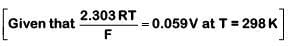 (NEET 2019)
(NEET 2019)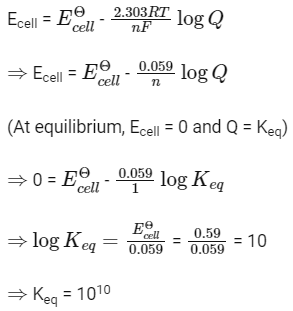
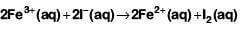
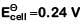 at 298 K. The standard Gibbs energy
at 298 K. The standard Gibbs energy  of the cell reaction is :[Given that Faraday constant F = 96500 C mol–1] (NEET 2019)
of the cell reaction is :[Given that Faraday constant F = 96500 C mol–1] (NEET 2019)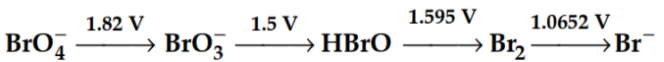 Then the species undergoing disproportionation is:- (NEET 2018)
Then the species undergoing disproportionation is:- (NEET 2018)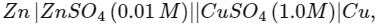 the emf of this Daniell cell is E1. When the concentration of ZnSO4 is changed to 1.0 M and that of CuSO4 changed to 0.01 M, the emf changes to E2. From the followings, which one is the relationship between E1 and E2? (Given, RT/F = 0.059) (NEET 2017)
the emf of this Daniell cell is E1. When the concentration of ZnSO4 is changed to 1.0 M and that of CuSO4 changed to 0.01 M, the emf changes to E2. From the followings, which one is the relationship between E1 and E2? (Given, RT/F = 0.059) (NEET 2017)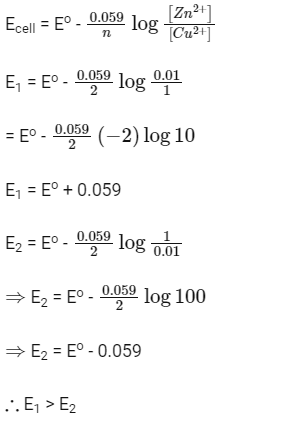
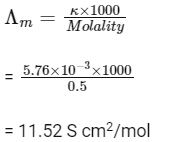
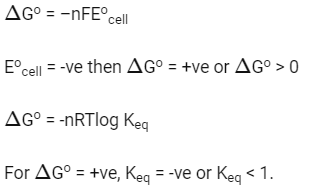
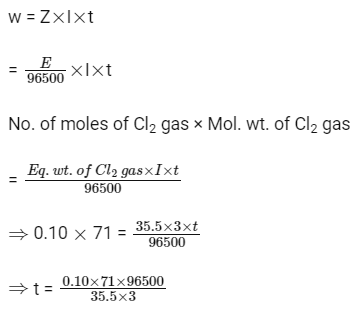
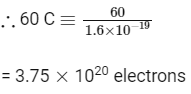
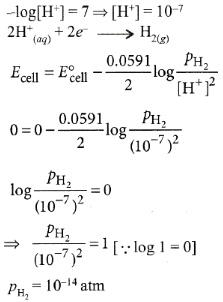
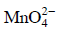 is oxidised the quantity of electricity required to completely oxidise
is oxidised the quantity of electricity required to completely oxidise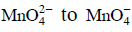 is :
is :