NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): The d & f-Block Elements | Chemistry Class 12 PDF Download
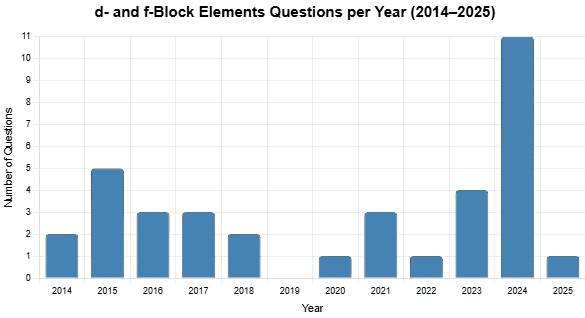
From 2014 to 2025, 36 questions were asked on d- and f-block elements. Typically, one to five questions appeared in the exam (2014–2018, 2020–2023, 2025), with a peak of 11 in 2024 and none in 2019. The questions focused on magnetic properties (paramagnetism, diamagnetism), oxidation states, lanthanoid contraction, and redox reactions, with no specific difficulty distribution provided in the data.
2025
Q1: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Ferromagnetism is considered as an extreme form of paramagnetism.
Statement II: The number of unpaired electrons in a Cr2+ ion (Z=24) is the same as that of a Nd3+ ion (Z = 60)
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is True but Statement II is False.
(b) Statement I is False but Statement II is True.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are True.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are False.
Ans: (a)
Statement I: "Ferromagnetism is considered as an extreme form of paramagnetism."
- This statement is true because ferromagnetic materials exhibit a stronger and more ordered alignment of magnetic moments compared to paramagnetic materials. Ferromagnetism can be considered as an extreme or special case of paramagnetism.
Statement II: "The number of unpaired electrons in a Cr2+ ion (Z = 24) is the same as that of a Nd3+ ion (Z = 60)."
This statement is false because:
- Cr2+ has 4 unpaired electrons (from its 3d4 configuration).
- Nd3+ has 3 unpaired electrons (from its 4f3 configuration).
Hence, the number of unpaired electrons is not the same for Cr2+ and Nd3+.
Therefore, the correct answer is: Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
2024
Q1: 'Spin only' magnetic moment is same for which of the following ions?
A. Ti3+
B. Cr2+
C. Mn2+
D. Fe2+
E. Sc3+
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) B and D only
(b) A and E only
(c) B and C only
(d) A and D only (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)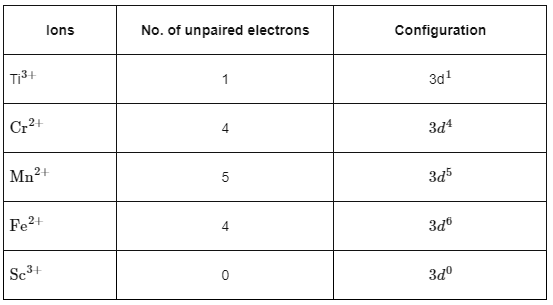 Spin only magnetic moment is given by
Spin only magnetic moment is given by 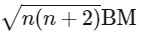
∴ Cr2+ and Fe2+ will have same spin only magnetic moment.
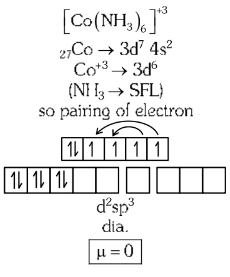
Q2: Given below are two statements :
Statement I: Both [Co(NH3)6]3+ and [CoF6]3− complexes are octahedral but differ in their magnetic behaviour.
Statement II: [Co(NH3)6]3+ is diamagnetic whereas [CoF6]3− is paramagnetic.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
Statement I: Both [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺ and [CoF₆]³⁻ complexes are octahedral but differ in their magnetic behaviour.
- Both are octahedral coordination complexes.
- But they differ in magnetic behavior due to the nature of ligands (NH₃ is a strong field ligand; F⁻ is a weak field ligand).
- So, this statement is correct.
Statement II: [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺ is diamagnetic whereas [CoF₆]³⁻ is paramagnetic.
- Oxidation state of Co in both: +3
- Electronic configuration of Co³⁺ = [Ar] 3d⁶
- In [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺:
- NH₃ is a strong field ligand → causes pairing of electrons → low-spin complex → diamagnetic
- In [CoF₆]³⁻:
- F⁻ is a weak field ligand → no pairing → high-spin complex → paramagnetic
Q3: The E∘ value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is more positive than that of Cr3+/Cr2+ or Fe3+/Fe2+ due to change of
(a) d5 to d4 configuration
(b) d5 to d2 configuration
(c) d4 to d5 configuration
(d) d3 to d5 configuration (NEET 2024)
Ans: (c)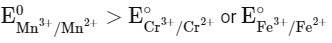
Electronic configuration of 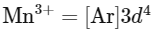
Electronic configuration of 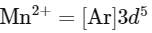
Electronic configuration of 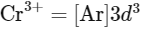
Electronic configuration of 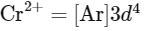
As Mn3+ from d4 configuration goes to more stable d5 configuration (Half filled), due to more exchange energy in d5 configuration.
Q4: The pair of lanthanoid ions which are diamagnetic is
(a) Ce4+ and Yb2+
(b) Ce3+ and Eu2+
(c) Gd3+ and Eu3+
(d) Pm3+ and Sm3+ (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
Magnetic moment 
n ↣ number of unpaired electrons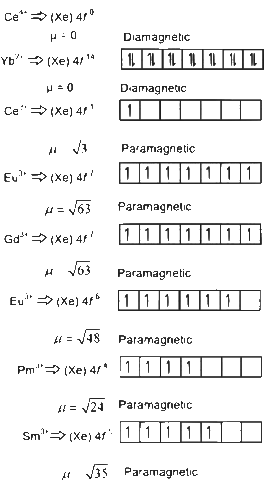
Hence Ce4+ and Yb2+ are only diamagnetic.
Q5: During the preparation of Mohr's salt solution (Ferrous ammonium sulphate), which of the following acid is added to prevent hydrolysis of Fe2+ ion?
(a) dilute hydrochloric acid
(b) concentrated sulphuric acid
(c) dilute nitric acid
(d) dilute sulphuric acid (NEET 2024)
Ans: (d)
Mohr's salt is the ammonium iron(II) sulfate, with the chemical formula (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2⋅6H2O. It is known for its stability compared to the other iron(II) salts which tend to readily oxidize to iron(III) salts when exposed to the air. To prevent the oxidation and hydrolysis of the Fe2+ ion during the preparation of Mohr's salt, an acid is added. This acid serves several purposes: it maintains the acidic environment necessary to prevent hydrolysis, aids in the solubilization of iron(II) sulfate, and minimizes the oxidation of Fe2+ ions to Fe3+.
The options provided give four different types of acids, from which one needs to be selected for the preparation of this salt. We can evaluate them based on their appropriateness:
- Dilute Hydrochloric Acid: While capable of maintaining a low pH to prevent oxidation, HCl can potentially introduce chloride ions (Cl−), which can form complexes with iron, changing the composition of the solution.
- Concentrated Sulphuric Acid: This choice is too strong and can lead to excessive acidity as well as potential safety issues during handling and dilution. It is unnecessary for this application.
- Dilute Nitric Acid: Nitric acid is an oxidizing agent and can promote the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+, which is undesirable in the preparation of Mohr's salt.
- Dilute Sulphuric Acid: This is a very common choice since it helps maintain the stability of the Fe2+ ion without contributing extraneous ions that could form undesired complexes or products. Moreover, it keeps the solution acidic, helping prevent oxidation and hydrolysis, while not introducing any oxidizing characteristics.
Given these considerations, the best choice for preventing hydrolysis of the Fe2+ ion during the preparation of Mohr's salt is Dilute Sulphuric Acid (Option D). This is because it maintains the suitable acidic conditions needed for stabilizing the ferrous ion and does not interfere with the redox stability of the iron by providing an oxidative chemical environment.
Q6: The behaviour of samarium (Z = 62) is very much like europium (Z = 63), since both elements: (NEET 2024)
(a) exhibit +2 and +3 oxidation states.
(b) have 4f⁶6s² and 4f⁶6s² electronic configurations, respectively.
(c) have 4f⁷6s² and 4f⁸6s² electronic configurations, respectively.
(d) have the same atomic radii.
Ans: (a)
Samarium (Z = 62) and Europium (Z = 63) both belong to the lanthanoid series and show similar chemical behavior, especially in their oxidation states.
- Samarium (Sm) usually exists in +3 oxidation state, but can also form +2 oxidation state under certain conditions, especially in solid compounds.
- Europium (Eu) also commonly exists in the +3 oxidation state, but is particularly stable in the +2 oxidation state due to its half-filled 4f⁷ configuration, which offers extra stability.
This similarity in exhibiting both +2 and +3 oxidation states makes their behavior very much alike.
Let’s look at the other options:
- (b) is incorrect: Samarium has configuration [Xe] 4f⁶6s², but europium has [Xe] 4f⁷6s² — so not the same.
- (c) is incorrect: Their configurations are 4f⁶ and 4f⁷ respectively, not 4f⁷ and 4f⁸.
- (d) is incorrect: They do not have the same atomic radii, although both are similar in size due to lanthanoid contraction, the radii are slightly different.
Hence, option (a) is the most accurate reason for their similar behavior.
Q7: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2024)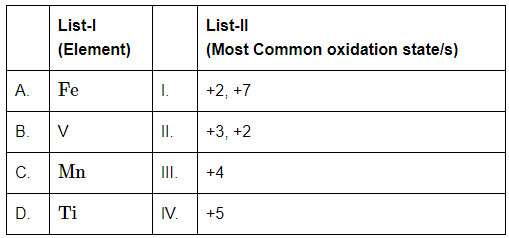 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(b) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
(c) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(d) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
Ans: (a)
A. Fe (Iron) → +2, +3
- Iron most commonly exhibits +2 (ferrous) and +3 (ferric) oxidation states.
- These are well-known in compounds like FeSO₄ (+2) and FeCl₃ (+3).
Matches with II
B. V (Vanadium) → +5
- Vanadium has multiple oxidation states: +2, +3, +4, and +5.
- However, +5 is the most stable and common in compounds like vanadium pentoxide (V₂O₅).
Matches with IV
C. Mn (Manganese) → +2, +7
- Manganese exhibits a wide range of oxidation states: +2 to +7.
- The most common ones are +2 (e.g., MnSO₄) and +7 (e.g., KMnO₄).
Matches with I
D. Ti (Titanium) → +4
Titanium generally shows +4 oxidation state, as in TiO₂ or TiCl₄.
Matches with III
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q8: The number of moles of MnO₄⁻ being reduced to Mn²⁺ under acidic conditions by 4.517 × 10²⁴ electrons is: (NEET 2024)
(a) 1.5 moles
(b) 7.5 moles
(c) 2.5 moles
(d) 5.0 moles
Ans: (a)
In acidic conditions, MnO₄⁻ is reduced to Mn²⁺ by gaining 5 electrons per ion.
So, to find moles of MnO₄⁻:
Total moles of electrons = (4.517 × 10²⁴) / (6.022 × 10²³) = 7.5 moles
Since 5 electrons are required per MnO₄⁻ ion:
Moles of MnO₄⁻ = 7.5 /5 = 1.5 moles
Q9: Which of the following pairs of ions will have the same spin-only magnetic moment values within the pair? (NEET 2024)
(a) Zn²⁺, Ti²⁺
(b) Cr²⁺, Fe²⁺
(c) Ti³⁺, Cu²⁺
(d) V²⁺, Cu⁺
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C and D only
(b) A and D only
(c) A and B only
(d) B and C only
Ans: (d)
Magnetic moment depends on the number of unpaired electrons:
Cr²⁺ = 3d⁴ → 4 unpaired electrons
Fe²⁺ = 3d⁶ → 4 unpaired electrons
→ Both have same spin-only moment → Pair B is correct
Ti³⁺ = 3d¹ → 1 unpaired electron
Cu²⁺ = 3d⁹ → 1 unpaired electron
→ Both have 1 unpaired electron → Pair C is correct
So, B and C only is the correct answer.
Q10: Which of the following set of ions act as oxidizing agents? (NEET 2024)
(a) Ce⁴⁺ and Tb⁴⁺
(b) La³⁺ and Lu³⁺
(c) Eu²⁺ and Yb²⁺
(d) Eu²⁺ and Tb⁴⁺
Ans: (a)
Oxidizing agents gain electrons to get reduced.
Ce⁴⁺ easily gets reduced to Ce³⁺ → strong oxidizer
Tb⁴⁺ also gets reduced to Tb³⁺ → good oxidizer
In contrast:
Eu²⁺ and Yb²⁺ prefer to lose electrons (reducing agents)
La³⁺ and Lu³⁺ are already stable and don't act as oxidizers
Hence, Ce⁴⁺ and Tb⁴⁺ are the correct oxidizing agents.
Q11: The UV-visible absorption bands in the spectra of lanthanoid ions are 'X', probably because of the excitation of electrons involving 'Y'. The 'X' and 'Y', respectively, are: (NEET 2024)
(a) Broad and f orbitals
(b) Narrow and f orbitals
(c) Broad and d and f orbitals
(d) Narrow and d and f orbitals
Ans: (b)
- The f-electrons in lanthanoids are shielded and not much affected by their surroundings.
- So the transitions between f-orbitals (called f-f transitions) lead to narrow and sharp absorption bands.
- These transitions happen within f orbitals, not d-orbitals.
Therefore, the correct combination is: Narrow and f orbitals
2023
Q1: The stability of Cu2+ is more than Cu+ salts in aqueous solution due to (NEET 2023)(a) First ionisation enthalpy
(b) Enthalpy of atomization
(c) Hydration energy
(d) Second ionisation enthalpy
Ans: (c)
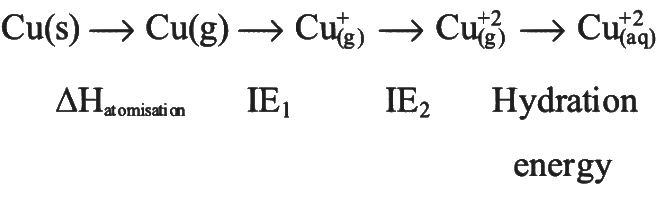
The stability of Cu²⁺ is higher than Cu⁺ in aqueous solutions primarily due to the hydration energy.
Hydration energy refers to the energy released when an ion is surrounded by water molecules. Since Cu²⁺ is a highly charged ion, it attracts water molecules more strongly compared to Cu⁺, which results in more hydration energy being released when Cu²⁺ is hydrated.
The increased hydration energy stabilizes the Cu²⁺ ion, making it more stable than Cu⁺ in aqueous solutions.
Q2: Which of the following statements is INCORRECT? (NEET 2023)
A. All the transition metals except scandium form MO oxides which are ionic.
B. The highest oxidation number corresponding to the group number in transition metal oxides is attained in Sc2O3 to Mn2O7.
C. Basic character increases from V2O3 to V2O4 to V2O5.
D. V2O4 dissolves in acids to give VO₄³⁻ salts.
E. CrO is basic but Cr2O3 is amphoteric.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and E only
(b) B and D only
(c) C and D only
(d) B and C only
Ans: (c)
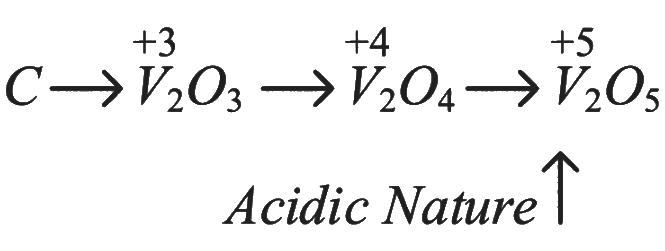
Statement A: "All the transition metals except scandium form MO oxides which are ionic."
Correct: Most transition metals form ionic oxides, except scandium, which forms a covalent oxide (Sc₂O₃).
Statement B: "The highest oxidation number corresponding to the group number in transition metal oxides is attained in Sc₂O₃ to Mn₂O₇."
Correct: The highest oxidation states of transition metals generally correspond to their group numbers, as seen in Sc₂O₃ to Mn₂O₇.
Statement C: "Basic character increases from V₂O₃ to V₂O₄ to V₂O₅."
Incorrect: As the oxidation state increases from +3 in V₂O₃ to +5 in V₂O₅, the acidic character increases and basic character decreases.
Statement D: "V₂O₄ dissolves in acids to give VO₃⁻ salts."
Incorrect: V₂O₄ does not dissolve in acids to form VO₃⁻ salts; V₂O₅ does.
Statement E: "CrO is basic but Cr₂O₃ is amphoteric."
Correct: CrO is basic, while Cr₂O₃ is amphoteric, reacting with both acids and bases.
The incorrect statements are C and D
Q3: Assertion (A): Ionization enthalpy increases along each series of transition elements from left to right. However, small variations occur. (NEET 2023)
Reason (R): There is a corresponding increase in nuclear charge which accompanies the filling of electrons in the inner d-orbitals.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
(b) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(d) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Ans: (c)
As we move across a period in the transition series (from left to right), the nuclear charge increases due to the addition of protons. Although d-electrons are being added, they do not effectively shield each other from the nucleus. As a result, the effective nuclear attraction on the valence electrons increases, leading to a gradual increase in ionization enthalpy. The small variations are due to extra stability of half-filled and fully filled d-orbitals. Since the increase in nuclear charge is the reason for the increase in ionization energy, (R) correctly explains (A).
Q4: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)
Assertion (A): Ionisation enthalpies of early actinoids are lower than for early lanthanoids.
Reason (R): Electrons are entering 5f orbitals in actinoids which experience greater shielding from nuclear charge.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is True but (R) is False.
(d) (A) is False but (R) is True.
Ans: (c)
The early actinoids have lower ionization enthalpies than the early lanthanoids because the 5f orbitals in actinoids are more diffused and extend further from the nucleus compared to the more contracted 4f orbitals in lanthanoids. This makes the outer electrons in actinoids easier to remove.
However, the 5f orbitals do not experience greater shielding; in fact, they shield poorly, which increases electron–electron repulsions. Therefore, (R) is not a correct reason — while both phenomena are true separately, the stated reason does not explain the assertion correctly.
2022
Q1: Given below are two statements : (NEET 2022)
Statement I : Cr2+ is oxidising and Mn3+ is reducing in nature.
Statement II : Sc3+ compounds are repelled by the applied magnetic field.
In the light of the above statements,
choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
(a) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(d) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Ans: (a)
Statement I: Cr²⁺ is oxidizing and Mn³⁺ is reducing in nature.
- Cr²⁺ is reducing, not oxidizing, as it can easily lose an electron to become Cr³⁺.
- Mn³⁺ is oxidizing, not reducing, because it can gain an electron to become Mn²⁺.
- Conclusion: Statement I is incorrect.
Statement II: Sc³⁺ compounds are repelled by the applied magnetic field.
- Sc³⁺ has no unpaired electrons, so it is diamagnetic and will be repelled by a magnetic field.
- Conclusion: Statement II is correct.
The correct answer is (a) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
2021
Q1: Zr (Z=40) and Hf (Z=72) have similar atomic and ionic radii because of: (NEET 2021)
(a) lanthanoid contraction
(b) having similar chemical properties
(c) belonging to same group
(d) diagonal relationship
Ans: (a)
- Hf is a post lanthanoid element. Due to presence of 4f-orbitals which have poor shielding effect, the effective nuclear charge on valence shell electrons is more which result in the decrease of the size of Hf. This effect is known as lanthanoid contraction.
- The almost identical radii of Zr (160 pm) and Hf (159 pm) is a consequence of the lanthanoid contraction.
Q2: The incorrect statement among the following is : (NEET 2021)
(a) Lanthanoids are good conductors of heat and electricity.
(b) Actinoids are highly reactive metals, especially when finely divided.
(c) Actinoid contraction is greater for element-to-element than Lanthanoid contraction.
(d) Most of the trivalent Lanthanoid ions are colourless in the solid state.
Ans: (d)
- Most trivalent lanthanoid ions are colored in both the solid state and in solution due to the presence of partially filled f-orbitals, which allow for electronic transitions that absorb visible light. For example, Ce³⁺ and Pr³⁺ ions are colorful. Therefore, the statement that they are colorless in the solid state is incorrect.
Q3: Which of the following reactions is the metal displacement reaction? Choose the right option. (NEET 2021)
(a) 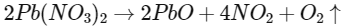
(b) 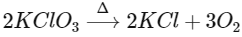
(c) 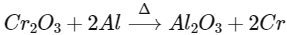
(d) 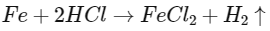
Ans: (c)
- Both reactions (a) and (b) are examples of decomposition reactions.
- Reactions (c) and (d), both are examples of displacement reactions, while reaction (c) is an example of metal displacement reaction n in which a more reactive metal displaces/replaces the less reactive metal.
2020
Q1: Identify the incorrect statement. ( NEET 2020)
(a) Interstitial compounds are those that are formed when small atoms like H, C or N are trapped inside the crystal lattices of metals.
(b) The oxidation states of chromium in CrO24- and Cr2O72- are not the same.
(c) Cr2+(d4) is a stronger reducing agent than Fe2+(d6) in water.
(d) The transition metals and their compounds are known for their catalytic activity due to their ability to adopt multiple oxidation states and to form complexes.
Ans: (b)
Oxidation state of Cr in CrO42- and Cr2O72- is + 6.
2018
Q1: Which one of the following ions exhibits d-d transition and paramagnetism as well?
(a) CrO42-
(b) Cr2O72–
(c) MnO4-
(d) MnO42- (NEET 2018)
Ans: (d)
In CrO42- Cr+6 (n = 0) diamagnetic
In Cr2O72– Cr+6 (n = 0) diamagnetic
In MnO4- Mn+7 (n = 0) diamagnetic
In MnO42- Mn+6 (n = 1) paramagnetic
In MnO42-, one unpaired electron(n) is present in d-orbital so, d-d transition is possible.
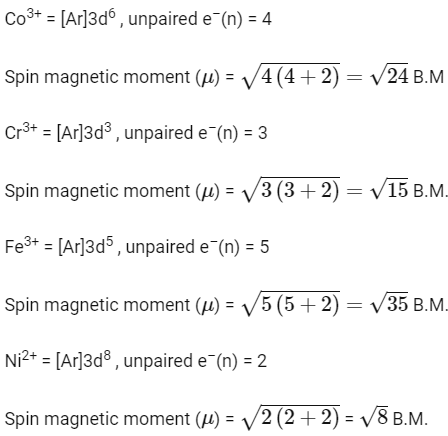
Q2: Match the metal ions given in Column I with the spin magnetic moments of the ions given in Column II and assign the correct code :
(NEET 2018)

(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Ans: (a)
2017
Q1: Name the gas that can readily decolourise acidified KMnO4 solution : (NEET 2017)
(a) SO2
(b) NO2
(c) P2O5
(d) CO2
Ans: (a)
Acidified KMnO4 is a strong oxidizing agent thus, among the given options which readily undergoes oxidation with KMnO4 will decolourise it. CO2, NO2 and P2O5 are already in their highest oxidation state while SO2 can further oxidize with KMnO4 to give sulphate ions.
2MnO4– + 5SO2 + 2H2O
Q2: HgCl2 and I2 both when dissolved in water containing I– ions the pair of species formed is : (NEET 2017)
(a) HgI2, I–
(b) HgI42-, I3-
(c) Hg2I2, I–
(d) HgI2, I¯3
Ans: (b)
HgCl2 + 4I– (aq)
I2(s) + I– (aq)
Q3: The reason for greater range of oxidation states in actinoids is attributed to :- (NEET 2017)
(a) actinoid contraction
(b) 5f, 6d and 7s levels having comparable energies
(c) 4f and 5d levels being close in energies
(d) the radioactive nature of actinoids
Ans: (b)
Minimum or comparable energy gap between 5f, 6d and 7s subshell makes electron excitation easier, hence there is a greater range of oxidation states in actinoids.
2016
Q1: Which one of the following statements is correct when SO2 is passed through acidified K2Cr2O7 solution? (NEET 2016)
(a) Green Cr2(SO4)3 is formed.
(b) The solution turns blue
(c) The solution is decolourized.
(d) SO2 is reduced.
Ans: (a)
K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4 + 3SO2 → K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 (Green) + H2O
Q2: The electronic configurations of Eu (Atomic No. 63) Gd (Atomic No. 64) and Tb (Atomic No. 65) are : (NEET 2016)
(a) [Xe]4f7 6s2, [Xe]4f75d16s2 and [Xe]4f96s2
(b) [Xe]4f7 6s2, [Xe]4f8 6s2 and [Xe]4f8 5d16s2
(c) [Xe]4f6 5d16s2, [Xe]4f7 5d16s2 and [Xe]4f9 5d16s2
(d) [Xe]4f6 5d16s2, [Xe]4f7 5d16s2 and [Xe]4f8 5d16s2
Ans: (a)
Eu (63) = [Xe] 4f7 6s2
Gd (64) = [Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2
Tb (65) = [Xe] 4f9 6s2
Q3: Which one of the following statements related to lanthanoids is incorrect.
(a) Europium shows + 2 oxidation state.
(b) The basicity decreases as the ionic radius decreases from Pr to Lu.
(c) All the lanthanides are much more reactive than aluminium.
(d) Ce(+4) solutions are widely used as oxidizing agent in volumetric analysis. (NEET 2016)
Ans: (c)
The first few members of the lanthanoid series are quite reactive, almost like calcium. However, with increasing atomic number, their behavior becomes similar to that of aluminium.
2015
Q1: Which of the following processes does not involve oxidation of iron ? (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper )
(a) Liberation of H2 from steam by iron at high temperature
(b) Rusting of iron sheets
(c) Decolourization of blue CuSO4 solution by iron
(d) Formation of Fe(CO)5 from Fe
Ans: (d)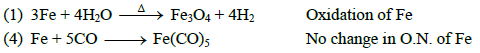
Q2: Because of lanthanoid contraction, which of the following pairs of elements have nearly same atomic radii ? (Numbers in the parenthesis are atomic numbers). (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper )
(a) Zr (40) and Ta (73)
(b) Ti (22) and Zr (40)
(c) Zr (40) and Nb (41)
(d) Zr (40) and Hf (72)
Ans: (d)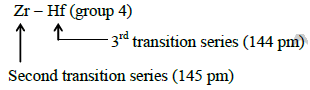
Q3: Magnetic moment 2.84 B.M. is given by (At. nos. Ni = 28, Ti = 22, Cr = 24, Co = 27)
(a) Cr2+
(b) Co2+
(c) Ni2+
(d) Ti3+ (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper )
Ans: (c)
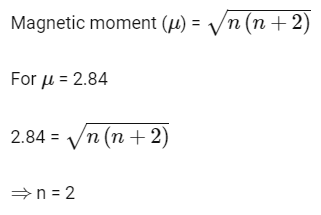
Cr2+ – [Ar]3d44s0 , 4 unpaired electrons
Co2+ – [Ar]3d74s0 , 3 unpaired electrons
Ni2+ – [Ar]3d8 4s0 , 2 unpaired electrons
Ti3+ – [Ar]3d14s0 , 1 unpaired electron
Q4: Gadolinium belongs to 4f series. Its atomic number is 64. Which of the following is the correct electronic configuration of gadolinium
(a) [Xe]4f95s1
(b) [Xe]4f75d16s2
(c) [Xe]4f65d26s2
(d) [Xe]4f86d2 (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
Ans: (b)
Gd(64) = [Xe]4f75d16s2
Q5: Assuming complete ionisation, same moles of which of the following compounds will require the least amount of acidified KMnO4 for complete oxidation
(a) FeSO3
(b) FeC2O4
(c) Fe(NO2)2
(d) FeSO4 (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
Ans: (d)
FeSO4 will require the least amount of acidified KMnO4 for complete oxidation.
2014
Q1: Reason of lanthanoid contraction is : (NEET 2014)
(a) Decreasing nuclear charge
(b) Decreasing screening effect
(c) Negligible screening effect of 'f ' orbitals
(d) Increasing nuclear charge
Ans: (c)
The shape of f-orbitals is very much diffused and they have poor shielding effect. The effective nuclear charge increases which causes the contraction in the size of electron charge cloud. This contraction in size is quite regular and known as lanthanoid contraction.
Q2: The reaction of aqueous KMnO4 with H2O2 in acidic conditions gives : (NEET 2014)
(a) Mn2+ and O3
(b) Mn4+ and MnO2
(c) Mn4+ and O2
(d) Mn2+ and O2
Ans: (d)
Hydrogen peroxide is oxidised to H2O and O2.
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 + 5H2O2
Thus, Mn2+ and O2 are produced.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): The d & f-Block Elements - Chemistry Class 12
| 1. What are the key properties of d-block elements? |  |
| 2. How do d-block elements differ from f-block elements? |  |
| 3. Why are transition metals important in biological systems? |  |
| 4. What are some common oxidation states of transition metals? |  |
| 5. How do the properties of d-block elements affect their use in catalysts? |  |

















