NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers | Chemistry Class 12 PDF Download
2025
Q1: The total number of possible isomers (both structural as well as stereoisomers) of cyclic ethers of molecular formula C4H8O is: (NEET 2025)
(a) 10
(b) 11
(c) 6
(d) 8
 View Answer
View Answer 
Possible structures include:
- Four-membered rings (oxetanes) with different substitution patterns.
- Three-membered rings (epoxides) with different substitution patterns.
Epoxides can have cis and trans stereoisomers due to the planar nature of the three-membered ring. Oxetanes with different substitutions can also exhibit stereoisomerism.
Upon counting all possible structural and stereoisomers:
- Three-membered ring (epoxides): 6 isomers (including stereoisomers).
- Four-membered ring (oxetanes): 4 isomers (including stereoisomers).
- Total number of isomers = 6 (epoxides) + 4 (oxetanes) = 10.
2024
Q1: Identify the correct reagents that would bring about the following transformation. (NEET 2024)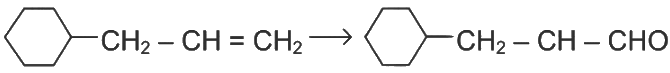
(a) 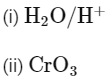
(b) 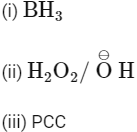
(c) 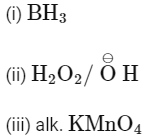
(d) 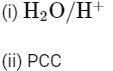
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)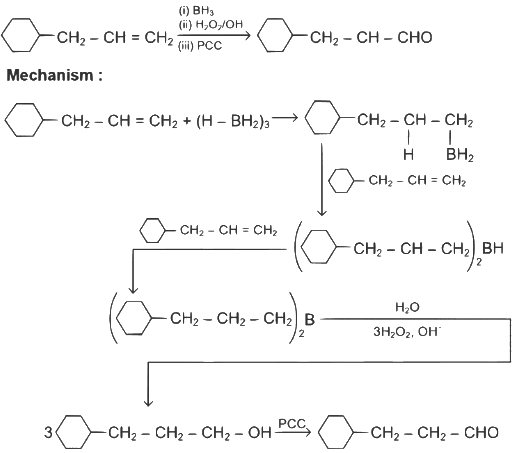
Q2: Which one of the following alcohols reacts instantaneously with Lucas reagent? (NEET 2024)
(a) 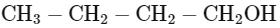
(b) 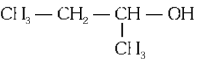
(c) 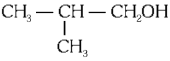
(d) 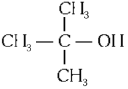
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Tertiary alcohols react instantaneously with Lucas reagent and gives immediate turbidity. In case of tertiary alcohols, they form halides easily with Lucas reagent (conc. HCl and ZnCl2)
Q3: Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is present in (NEET 2024)
(a) 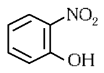
(b) 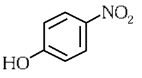
(c) 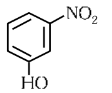
(d) HF
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
In o-nitrophenol intramolecular H-bonding is present.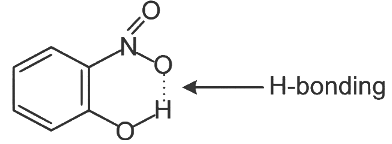
Q4: Major products A and B formed in the following reaction sequence, are (NEET 2024)
(a) 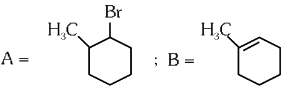
(b) 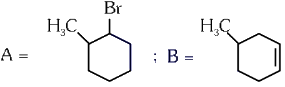
(c) 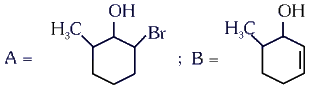
(d) 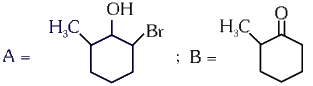
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)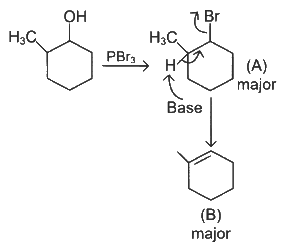
Q5: The major product D formed in the following reaction sequence is: (NEET 2024)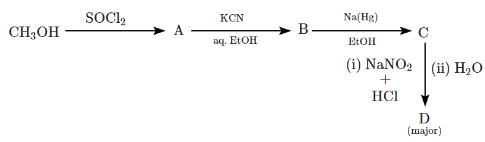 (a)
(a) 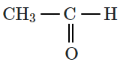
(b) 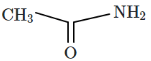
(c) CH3CH2OH
(d) CH3CH2Cl
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Step 1: Methanol (CH₃OH) reacts with SOCl₂
- SOCl₂ (thionyl chloride) is a reagent that is used to convert alcohols to alkyl chlorides.
- CH₃OH + SOCl₂ → CH₃Cl (methyl chloride) + SO₂ + HCl
This reaction replaces the hydroxyl group (-OH) with a chlorine atom (-Cl), forming CH₃Cl (methyl chloride).
Step 2: Reaction of CH₃Cl with KCN in ethanol
- KCN (potassium cyanide) reacts with CH₃Cl (methyl chloride) to replace the chlorine atom with a cyano group (-CN), forming CH₃CN (acetonitrile).
- CH₃Cl + KCN → CH₃CN + KCl
This reaction results in the formation of acetonitrile (CH₃CN).
Step 3: Reduction of acetonitrile (CH₃CN) with Na/H₂
- Na/H₂ (sodium in hydrogen) is a strong reducing agent that reduces nitriles to primary amines.
- CH₃CN + Na/H₂ → CH₃CH₂NH₂ (ethylamine).
This step reduces acetonitrile to ethylamine (CH₃CH₂NH₂).
Step 4: Reaction of ethylamine with NaNO₂ and HCl
- NaNO₂ (sodium nitrite) reacts with ethylamine (CH₃CH₂NH₂) in the presence of HCl (hydrochloric acid) to form a diazonium salt.
- The reaction proceeds as follows:
CH₃CH₂NH₂ + NaNO₂ + HCl → CH₃CH₂N₂⁺Cl⁻ (ethyl diazonium chloride) - However, ethyl diazonium chloride is unstable and undergoes hydrolysis when treated with water.
Step 5: Hydrolysis of the diazonium salt
- The diazonium salt formed in the previous step undergoes hydrolysis to form ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH).
- CH₃CH₂N₂⁺Cl⁻ + H₂O → CH₃CH₂OH + N₂ (nitrogen gas).
- The major product of the reaction is ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH).
Thus, the correct answer is (c) CH₃CH₂OH (ethanol).
Q6: Identify D in the following sequence of reactions: (NEET 2024)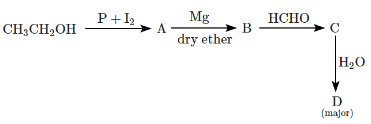 (a) n-Propyl alcohol
(a) n-Propyl alcohol
(b) Isopropyl alcohol
(c) Propanal
(d) Propionic acid
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Step 1: Reaction of Ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) with Phosphorus (P) and Iodine (I₂)
- When ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH) reacts with phosphorus (P) and iodine (I₂), it undergoes dehydrogenation and iodination to form 1-iodoethane (CH₃CH₂I).
- The reaction proceeds as follows:
CH₃CH₂OH + I₂ + P → CH₃CH₂I (1-iodoethane).
Step 2: Reaction of 1-Iodoethane (CH₃CH₂I) with Magnesium (Mg) in dry ether
- Magnesium in dry ether reacts with 1-iodoethane to form an ethyl magnesium halide (Grignard reagent). This Grignard reagent is CH₃CH₂MgI.
- CH₃CH₂I + Mg → CH₃CH₂MgI (ethyl magnesium iodide).
Step 3: Reaction of Ethyl Magnesium Iodide with Formaldehyde (HCHO)
- The Grignard reagent (CH₃CH₂MgI) reacts with formaldehyde (HCHO) to form an intermediate alcohol, specifically propan-2-ol (secondary alcohol).
- CH₃CH₂MgI + HCHO → CH₃CH₂CH(OH)CH₃ (propan-2-ol).
Step 4: Hydrolysis of the Intermediate (Propan-2-ol)
- The final product D is obtained after hydrolysis of the intermediate. Hydrolysis converts the alcohol to a carboxylic acid. This will give propionic acid (C₂H₅COOH), which is the major product of this reaction.
- CH₃CH₂CH(OH)CH₃ + H₂O → C₂H₅COOH (propionic acid).
So, the correct answer is (d) Propionic acid, which is formed after the Grignard reaction and hydrolysis of the intermediate.
2023
Q1: Consider the following reaction and identify the product (P).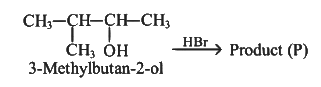
(a) 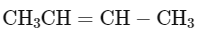
(b) 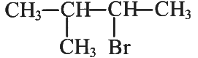
(c) 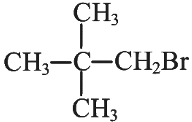
(d) 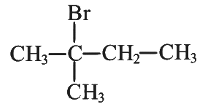
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
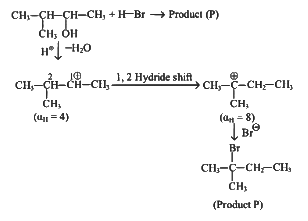
Q2: Consider the following reaction (NEET 2023)
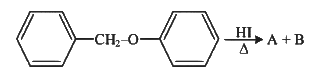
Identify products A and B :-
(a) 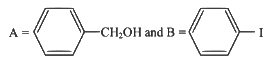
(b) 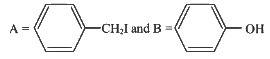
(c) 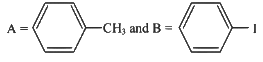
(d) 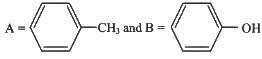
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Q3: Which amongst the following will be most readily dehydrated under acidic conditions? (NEET 2023)
(a) 
(b) 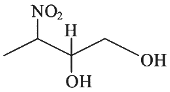
(c) 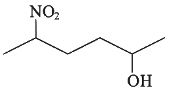
(d) 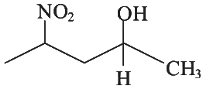
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Due to presence of conjugation in product.
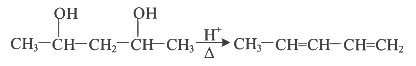
Q4: Reagents that can be used to convert alcohols to carboxylic acids are: (NEET 2023)
(a) CrO₃ - H₂SO₄
(b) K₂Cr₂O₇ + H₂SO₄
(c) KMnO₄ + KOH/H₃O⁺
(d) Cu, 573 K
(e) CrO₃ + (CH₃CO)₂O
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) (b), (c) and (d) only
(b) (b), (d) and (e) only
(c) (a), (b) and (c) only
(d) (a), (b) and (e) only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- (A) CrO₃ - H₂SO₄: This is a strong oxidizing agent, known as Jones reagent, which can oxidize alcohols (primary alcohols specifically) to carboxylic acids.
- (B) K₂Cr₂O₇ + H₂SO₄: This is another powerful oxidizing agent (chromic acid), which can also oxidize alcohols to carboxylic acids.
- (C) KMnO₄ + KOH/H₃O⁺: Potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) is a strong oxidizing agent that can oxidize alcohols to carboxylic acids.
- (D) Cu, 573 K: This reagent is used for the dehydrogenation of alcohols, typically producing aldehydes or ketones, not carboxylic acids.
- (E) CrO₃ + (CH₃CO)₂O: This is an esterification reaction (formation of esters), not related to the conversion of alcohols to carboxylic acids.
Hence, (A), (B), and (C) are the correct reagents for converting alcohols to carboxylic acids.
Q5: Consider the following reactions: (NEET 2023)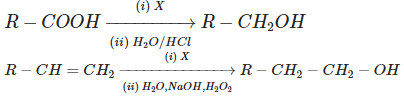 Identify 'X' in above reactions:
Identify 'X' in above reactions:
(a) B2H6
(b) LiAlH4
(c) NaBH4
(d) H2/Pd
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
In the given reactions, we have two steps, and the task is to identify the reagent "X" that converts the carboxylic acid (R-COOH) to the alcohol (R-CH₂OH) and also participates in the transformation of the alkene (R-CH=CH₂) into an alcohol (R-CH₂-CH₂-OH).
Let's break down the reactions:
First reaction:
R-COOH → X → R-CH₂OH
In this reaction, R-COOH (a carboxylic acid) is converted into R-CH₂OH (an alcohol). The most common reagent to reduce a carboxylic acid to an alcohol is borane (B₂H₆) or LiAlH₄.
Second reaction:
R-CH=CH₂ → X → R-CH₂-CH₂-OH
Here, R-CH=CH₂ (an alkene) is reduced to R-CH₂-CH₂-OH (an alcohol). The typical reagent that reduces alkenes to alcohols is hydrogen (H₂) in the presence of Pd (palladium), which is a well-known catalyst for hydrogenation reactions.
Conclusion:
- In the first reaction, B₂H₆ (diborane) is the reagent that reduces carboxylic acids to alcohols.
- In the second reaction, H₂/Pd is the reagent that reduces alkenes to alcohols.
Thus, 'X' is B₂H₆.
Answer: (a) B₂H₆
Q6: The major product formed in the following conversion is: (NEET 2023)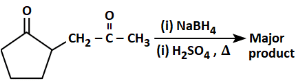 (a)
(a) 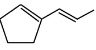
(b) 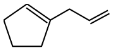
(c) 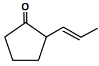
(d) 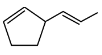
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Starting compound: The starting compound is a β-keto ester (a compound containing both a carbonyl group and an ester group).
The structure has a ketone (C=O) group attached to the second carbon and an ester (C=O) group attached to the first carbon.
First step (NaBH₄):
Sodium borohydride (NaBH₄) is a mild reducing agent. It selectively reduces ketones but does not affect esters.
NaBH₄ will reduce the ketone group to a secondary alcohol, resulting in the intermediate product where the carbonyl group is replaced by an -OH group.
Second step (H₂SO₄, Δ):
The ester group undergoes decarboxylation under acidic conditions (using sulfuric acid, H₂SO₄, and heat).
This reaction removes the CO₂ group, leading to the formation of a cyclohexene structure with a double bond between two adjacent carbons.
Major product:
The major product is the cyclic alkene formed after the decarboxylation step, which is the 1-cyclohexene structure.
Thus, the correct answer is Option 1, which shows the major product as 1-cyclohexene.
2022
Q1: Match the reagents (List-I) with the product (List-II) obtained from phenol. (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
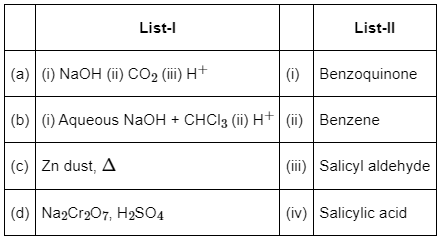
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (a) - (iv), (b) - (ii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii)
(b) (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (ii)
(c) (a) - (ii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (iii)
(d) (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (I)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
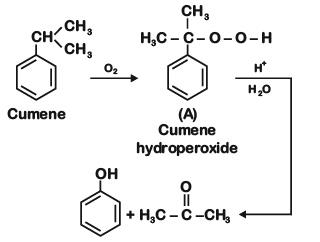
Q2: Which one of the following reaction sequence is incorrect method to prepare phenol? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) 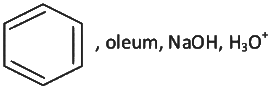
(b) Aniline, NaNO2 + HCl, H2O, heating
(c) Cumene, O2, H3O+
(d) 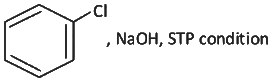
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
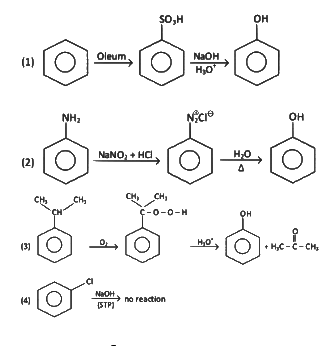
At STP condition substitution at sp2 carbon atom is not feasible.
Q2: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The acidic strength of monosubstituted nitrophenol is higher than phenol because of the electron-withdrawing into the group.
Statement II: o-nitrophenol, m-nitrophenol, and p-nitrophenol will have same acidic strength as they have one nitro group attached to the phenolic ring.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)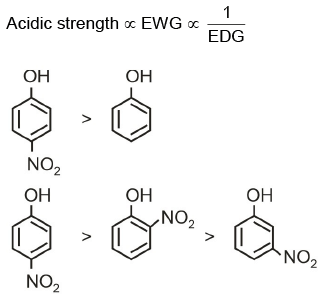
Statement I is correct, Statement II incorrect.
Q4: Given below are two statements:
Statement -I: In Lucas test, primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are distinguished on the basis of their reactivity with conc. HCl + ZnCl2, known as Lucas Reagent.
Statement -II: Primary alcohols are most reactive and immediately produce turbidity at room temperature on reaction with Lucas Reagent.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(c) Both statement I and Statement II are correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols can be differentiated by their reaction with (HCl + anhy ZnCl2) Lucas reagent
2020
Q1: Anisole on cleavage with HI gives : (NEET 2020)
(a)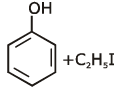
(b)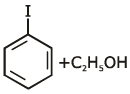
(c)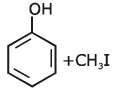
(d)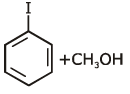
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)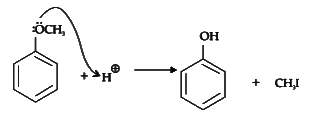
2019
Q1: The structure of intermediate A in the following reaction, is (NEET 2019)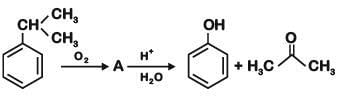
(a)
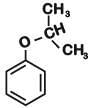
(b)
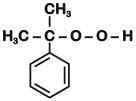
(c)
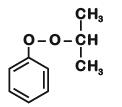
(d)
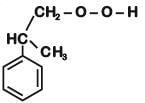
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: B
2018
Q1: In the reaction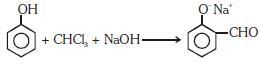 the electrophile involved is (NEET 2018)
the electrophile involved is (NEET 2018)
(a) dichloromethyl cation 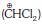
(b) formyl cation 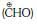
(c) dichloromethyl anion 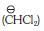
(d) dichlorocarbene 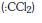
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
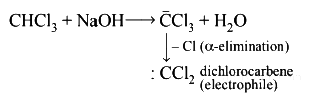
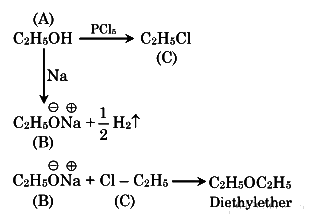
Q2: The compound A on treatment with Na gives B, and with PCl5 gives C. B and C react together to give diethyl ether. A, B and C are in the order (NEET 2018)
(a) C2H5OH, C2H6, C2H5Cl
(b) C2H5OH, C2H5Cl, C2H5ONa
(c) C2H5Cl,C2H6,C2H5OH
(d) C2H5OH,C2H5ONa,C2H5Cl
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
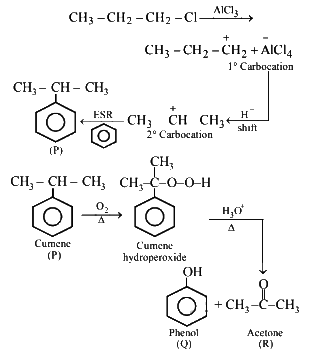
Q3: Identify the major products P, Q and R in the following sequence of reaction: (NEET 2018)
(a)
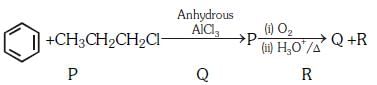
(b)
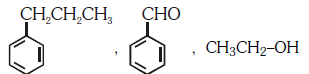
(c)
(d)
 View Answer
View Answer 
2017
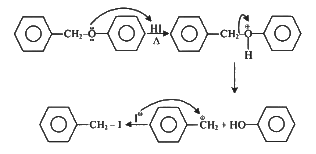
Q1: The heating of phenylmethyl ethers with HI produces (NEET 2017)
(a) iodobenzene
(b) phenol
(c) benzene
(d) ethyl chlorides
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
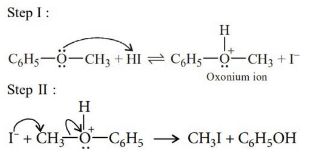
In case of phenyl methyl ether, methyl phenyl oxonium ion
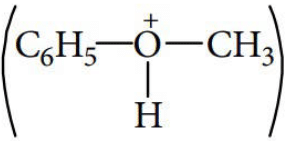 is formed by protonation of ether. The O—CH3 bond is weaker than O—C6H5 bond as O—C6H5 has partial double bond character. Therefore, the attack by I– ion breaks O—CH3 bond to form CH3I.
is formed by protonation of ether. The O—CH3 bond is weaker than O—C6H5 bond as O—C6H5 has partial double bond character. Therefore, the attack by I– ion breaks O—CH3 bond to form CH3I.
Q2: Which one is the most acidic compound? (NEET 2017)
(a) 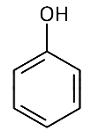
(b) 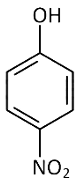
(c) 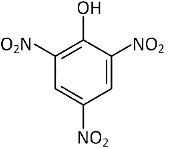
(d) 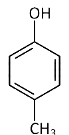
 View Answer
View Answer 
Electron withdrawing group at o and p-position w.r.t. OH group of phenol, increase the acidic strength.
Picric acid (2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol) is extremely more acidic among the given compounds due to the presence of three strong electron withdrawing groups ( NO2 group) at ortho and para-positions.
2016
Q1: The reaction:
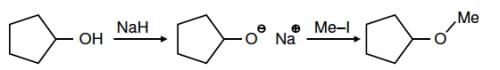
can be classified as: (NEET 2016)
(a) Williamson alcohol synthesis reaction
(b) Williamson ether synthesis reaction
(c) Alcohol formation reaction
(d) Dehydration reaction
 View Answer
View Answer 
The treatment of sodium alkoxide with a suitable alkyl halide to form an ether is called as Williamson ether synthesis reaction.
2015
Q1: Reaction of phenol with chloroform in the presence of dilute sodium hydroxide finally introduces which one of the following functional groups? (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
(a) −COOH
(b) −CHCl2
(c) −CHO
(d) −CH2Cl
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
This is Reimer–Tiemann reaction.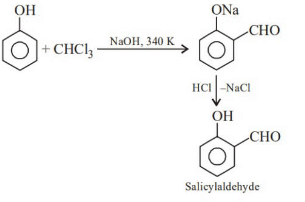
Q2: Which of the following reaction(s) can be used for the preparation of alkyl halides? (NEET / AIPMT 2015)
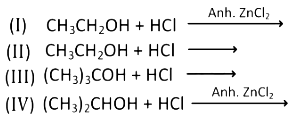
(a) (I) and (II) only
(b) (IV) only
(c) (III) and (IV) only
(d) (I), (III), and (IV) only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Lucas reagent [HCl + ZnCl2] can be used for
1° / 2° / 3° alcohol but if ZnCl2 is absent then only 3° alcohol can be used because it is most reactive due to 3° carbocation.
Q3: The reaction 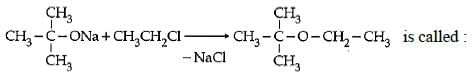 (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) Gatterman – Koch reaction
(b) Williamson Synthesis
(c) Williamson's continuous etherification process
(d) Etard reaction
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)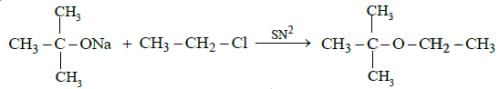 The reaction is called Williamson synthesis
The reaction is called Williamson synthesis
2014
Q1: Which of the following will not be soluble sodium hydrogen carbonate? (NEET 2014)
(a) o−Nitrophenol
(b) Benzenesulphonic acid
(c) 2, 4, 6 − trinitrophenol
(d) Benzoic acid
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate as follows :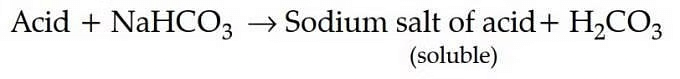 Among all the given options ortho-nitrophenol is weaker acid than HCO3 hence, it does not react with NaHCO3.
Among all the given options ortho-nitrophenol is weaker acid than HCO3 hence, it does not react with NaHCO3.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers - Chemistry Class 12
| 1. What are the general properties of alcohols, phenols, and ethers ? |  |
| 2. How do the boiling points of alcohols compare to those of ethers and phenols ? |  |
| 3. What is the mechanism of the dehydration of alcohols to form alkenes ? |  |
| 4. What are the common methods for the synthesis of ethers ? |  |
| 5. What are the uses of alcohols, phenols, and ethers in daily life ? |  |

















