Cell - The Unit of Life Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 8
1. Cytology: (G.k. kyios = cell ; logas = study) is the branch of biology that comprises the study of cell structure and function.
2. Cell is the structural and functional unit of all living beings.
3. There are two types of cells:
- Plant Cell
- Animal Cell
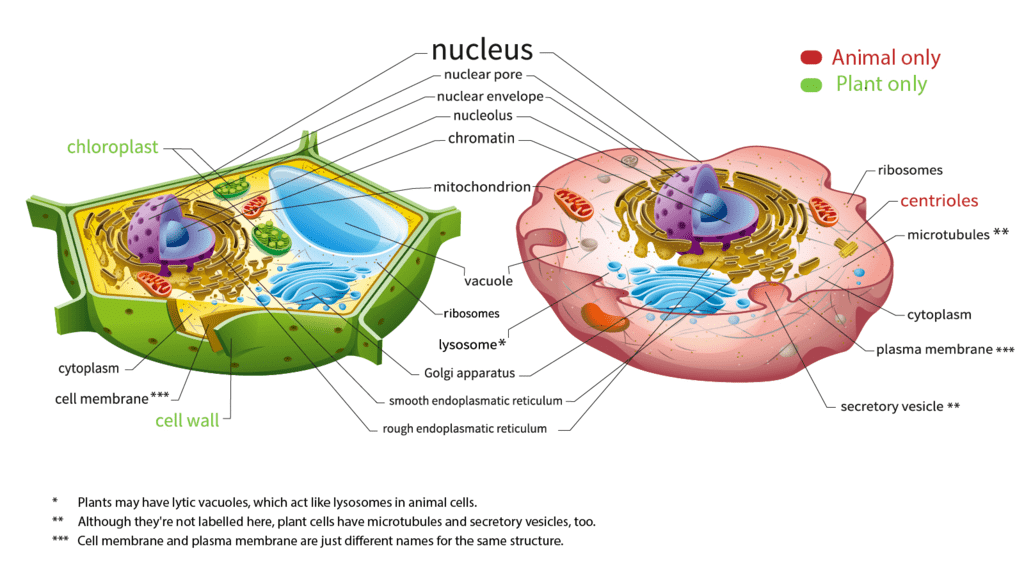 Animal and Plant CellDifference between Plant Cell and Animal Cell:
Animal and Plant CellDifference between Plant Cell and Animal Cell:
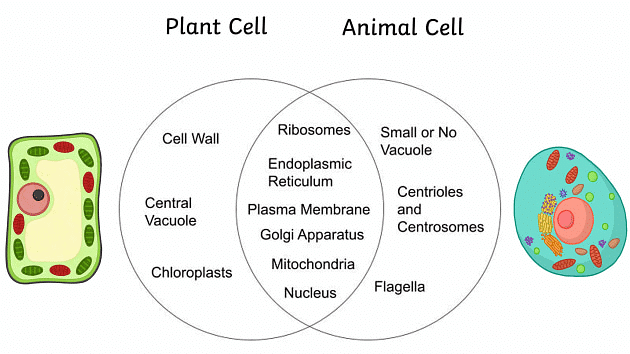
Important Points
- Jan Swammerdam: First to see red blood cells of frog.
- Marcello Malpighi: Observed small utricles in slice of plant and animal tissue.
- N. Grew: Initiated cell concept
- Lamarck: All living beings are formed of cells.
- Corti: First to point out living substance filled inside the cell. It was called “Sarcode” by Dujardin.
- In vivo (in life) study: Study of cells in their natural environment within the intact organism.
- In vitro (cultural condition) study: Study of isolated life system in laboratory and cultural condition.
- Max Shultze proposed protoplasm theory.
- Sachs proposed organismic theory.
- Crystallo: colloidal theory (Fischer), substances dispersed and dissolved in water forming both true solution as well as colloidal solution
4. Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
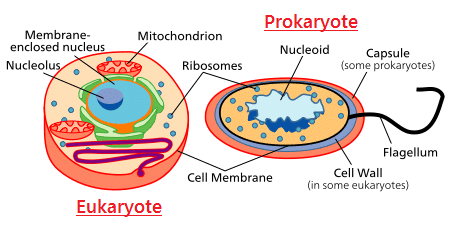
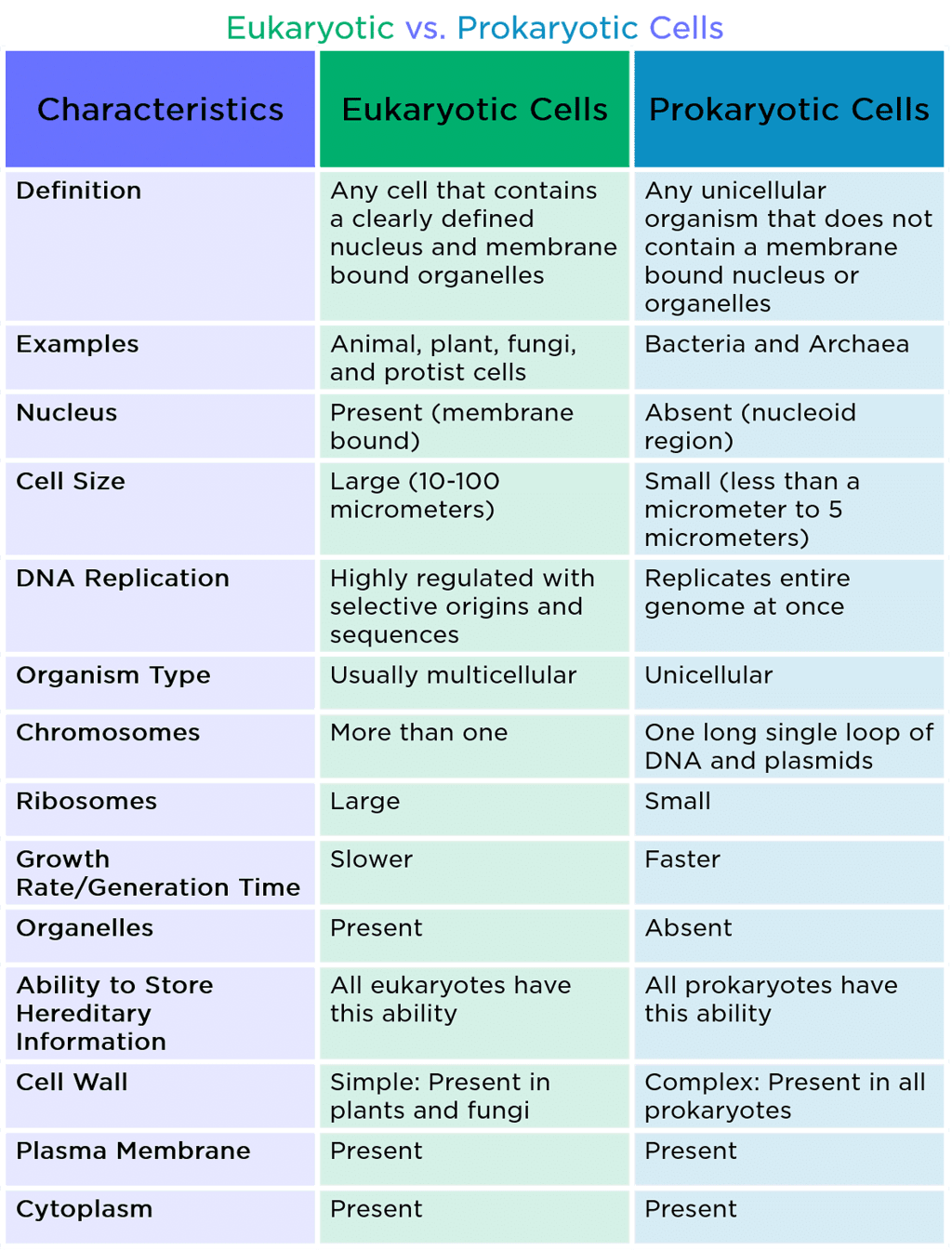
5. Difference between Primary Cell Wall and Secondary Cell Wall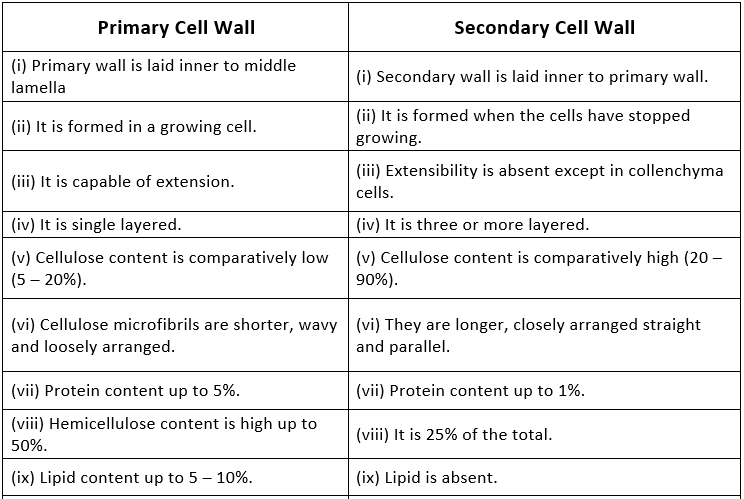
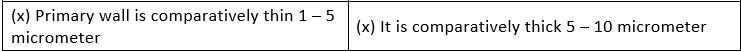
6. Difference between Extrinsic Protein and Intrinsic Protein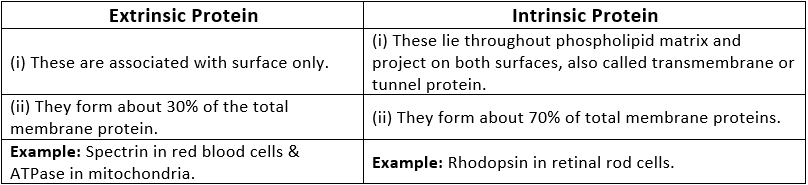
7. Cell Wall
- Discovery: It was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665.
- Cell wall is the outer most, rigid, protective, non living and supportive layer found in all the plant cells, bacteria, cyanobacteria and some protists.
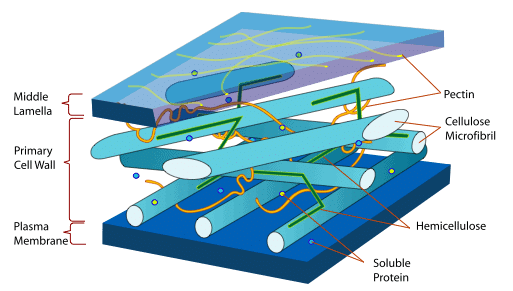
- It is not found in animal cells.
8. Plasma Membrane
- Definition: Every living cell is externally covered by a thin transparent electron microscopic, elastic regenerative and selectively permeable membrane called the plasma membrane.
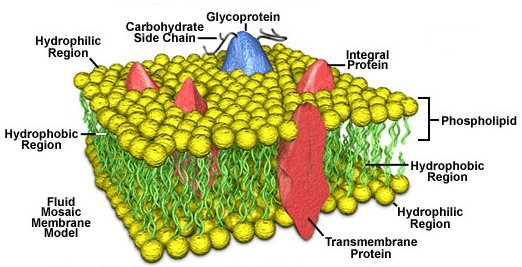
- It is quasi fluid in nature.
- According to Singer and Nicolson, it is a “protein iceberg in a sea of lipid”.
- A cell wall lies external to plasmalemma in plant cells, many monerans, some protists and fungal cells.
- Membranes also occur inside the cells.
- They are collectively called biomembranes.
- The term cell membrane was given by C. Nageli and C. Cramer (1855) for the outer membrane covering of the protoplast.
- It was replaced by the term plasmalemma or plasma membrane by Plowe (1931).
9. Protoplasm
- Definition: Protoplasm is a complex, granular, elastic, viscous and colourless substance. It is selectively or differentially permeable.
- It is considered as a “Polyphasic colloidal system”.
- Discoveries
(i) J. Huxley defined it as the “physical basis of life”.
(ii) Dujardin (1835) discovered it and called them “sarcode”.
(iii) Purkinje (1837) renamed it “Protoplasm”.
(iv) Hugo Von Mohl (1844) gave the significance of it.
(v) Max Schultz (1861) gave the protoplasmic theory for plants.
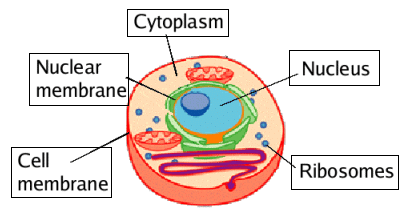
10. Cytoplasm
- The substance that occurs around the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane containing various organelles and inclusions is called cytoplasm.
11. Mitochondria
- Definition: (Gk – Mito = thread; chondroitin = granule) Mitochondria are semi-autonomous having hollow sac-like structures present in all eukaryotes except mature RBCs of mammals and sieve tubes of phloem.
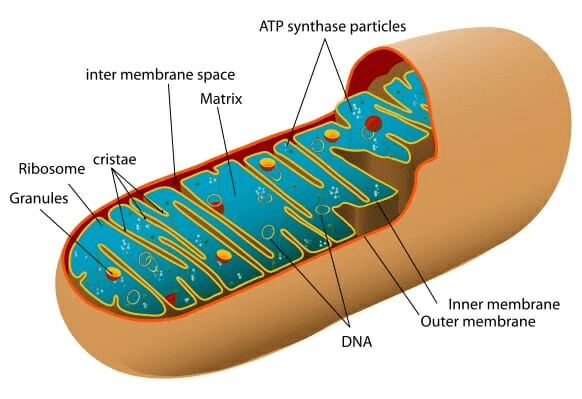
- These are absent in all prokaryotes like bacteria and cyanobacteria.
- Mitochondria are also called chondriosome, chondrioplast, plasmosomes, plastosomes and plastochondriane.
12. Plastids
- Definition: Plastids are semiautonomous organelles having DNA, RNA, Ribosomes and double-membrane envelope that store or synthesize various types of organic compounds such as ATP and NADPH + H+ etc.
- These are the largest cell organelles in a plant cell.
- History: Haeckel (1865) discovered plastid, but the term was first time used by Schimper (1883).
Table: Difference between chlorophyll a and b
13. Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Definition: It is a well-developed electron microscopic network of interconnected cisternae, tubules and vesicles present throughout the cytoplasm, especially in the endoplasm.
- Discovery: Garnier (1897) was the first to observe the ergastoplasm in a cell. The ER was first noted by Porter, Claude, and Fullman in 1945 as a network. It was named by Porter in 1953.
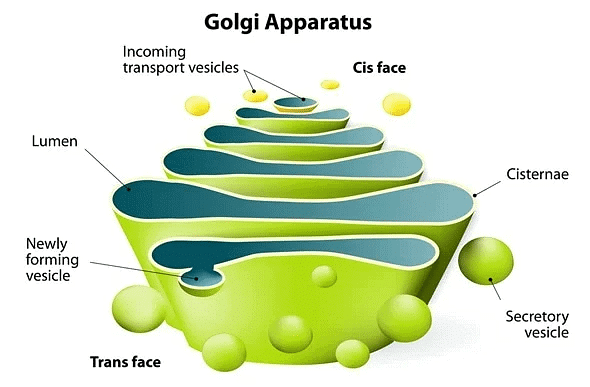
14. Golgi Complex
- Definition: Golgi complex is made up of various membranous systems e.g. cisternae, vesicles and vacuoles.
- These are also called Golgi bodies, golgisomes, lipochondrion, dictyosomes, Dalton complex, idiosomes or Baker’s body.
- These are also called “traffic police” of the cell.
- Discovery: First observed by George (1867) but it’s morphological details were given by Camillo Golgi (1898), in nerve cells of barn fowl and cat.
FAQs on Cell - The Unit of Life Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 8
| 1. What is a cell? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of cells? |  |
| 3. What is the function of a cell? |  |
| 4. How are cells structured? |  |
| 5. How do cells communicate with each other? |  |

















