Q.1. At 35°C, the vapor pressure of CS2 is 512 mm Hg and that of acetone is 344 mm Hg. A solution of CS2 in acetone has a total vapor pressure of 600 mm Hg. The false statement amongst the following is (2020)
(a) Raoult’s law is not obeyed by this system.
(b) A mixture of 100 mL CS2 and 100 mL acetone has a volume < 200 mL.
(c) CS2 and acetone are less attracted to each other than to themselves.
(d) Heat must be absorbed in order to produce the solution at 35°C.
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Since, in the given mixture, the solvent – solvent and solute – solute interaction is more than that of solvent – solute interaction, thus, the above mixture shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
Hence, statement (b) is incorrect.
Q.2. Two open beakers one containing a solvent and the other containing a mixture of that solvent with a nonvolatile solute are together sealed in a container. Over the time, (2020)
(a) The volume of the solution increases and the volume of the solvent decreases.
(b) The volume of the solution decreases and the volume of the solvent increases.
(c) The volume of the solution and the solvent does not change.
(d) The volume of the solution does not change and the volume of the solvent decreases.
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Due to the non-volatile solute in the mixture, there is a lowering of vapor pressure, thus, the volume of solution increases. Since, volume of container is constant, so on increasing the volume of solution, the volume of solvent alone decreases.
Q.3. A graph of vapor pressure and temperature for three different liquids X, Y, and Z is shown below: (2020)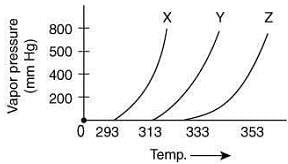 The following inferences are made
The following inferences are made
(I) X has higher intermolecular interactions compared to Y.
(II) X has lower intermolecular interactions compared to Y.
(III) Z has lower intermolecular interactions compared to Y.
The correct inference(s) is/are
(a) (I) and (III)
(b) (I)
(c) (II)
(d) (III)
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Since, the boiling point of X is lower than Y, thus, the intermolecular interaction between molecules of X is less than that of Y.
Q.4. How much amount of NaCl should be added to 600 g of water (ρ = 1.00 g mL–1) to decrease the freezing point of water to −0.2°C ? (The freezing point depression constant for water = 2 K kg mol−1) (2020)
Ans. (1.74)
Solution.
Given, ΔTf = 0.2°C
We know
ΔTf = T iKf m (1)
Substituting the values in Eq. (1), we get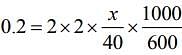
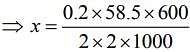
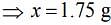
Thus, 1.75 g of NaCl should be added to 600 g of water to decrease the freezing point of water to –0.2°C
Q.5. A cylinder containing an ideal gas (0.1 mol of 1.0 dm3) is in thermal equilibrium with a large volume of 0.5 molal aqueous solution of ethylene glycol at its freezing point. If the stoppers S1 and S2 (as shown in the figure) are suddenly withdrawn, the volume of the gas in litres after equilibrium is achieved will be ______. (2020)
(Given, Kf (water) = 2.0 K kg mol−1, R = 0.08 dm3 atm K−1 mol−1)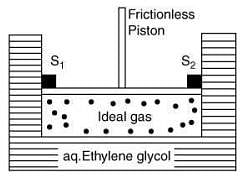
Ans. (2.18)
Solution.
We know
ΔTf = Kfm
⇒ 273 - Tf = 2 x 0.5
⇒ Tf = 272 K
Using Ideal gas equation,
pV = nRT (1)
Substituting the values in Eq. (1), we get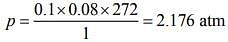
Since, ideal gas is in thermal equilibrium with aqueous solution of ethylene glycol
⇒ P1V1 = P2V2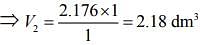
Q.6. Which one of the following statements regarding Henry's law is not correct? (2019)
(a) Higher the value of KH at a given pressure, higher is the solubility of the gas in liquids.
(b) Different gases have different KH (Henry's law constant) values at the same temperature.
(c) The partial pressure of the gas in vapour phase is proportional to the mole fraction of the gas in the solution.
(d) The value of KH increases with increase of temperature and KH is function of the nature of the gas.
Ans. (a)
Solution.
The solubility of the gas in liquids decreases with the increase in value of KH at a given pressure.
Q.7. A solution containing 62 g ethylene glycol in 250 g water is cooled to - 10°C. If Kf for water is 1.86 K kg mol-1, the amount of water (in g) separated as ice is: (2019)
(a) 48
(b) 32
(c) 64
(d) 16
Ans. (c)
Solution.
As we know,
ΔTf = Kf x m
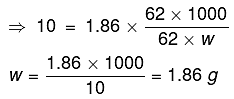
Total amount of water = 250 g
∴ The amount of water separated as ice = 250 - 186 = 64 g
Q.8. Liquids A and B form an ideal solution in the entire composition range. At 350 K, the vapour pressures of pure A and pure B are 7 x 103 Pa and 12 x 103 Pa, respectively. The composition of the vapour is in equilibrium with a solution containing 40 mole percent of A at this temperature is: (2019)
(a) xA = 0.37 ; xB = 0.63
(b) xA = 0.28 ; xB = 0.72
(c) xA = 0.4 ; xB = 0.6
(d) xA = 0.76 ; xB = 0.24
Ans. (b)
Solution.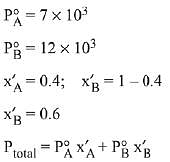
= 7 x 103 x 0.4 + 12 x 103 x 0.6
= (7 x 0.4 + 12 x 0.6) x 103 = 104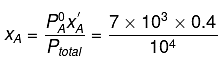
∴ xA = 0.28, xB = 1-0.28 = 0.72
Q.9. The amount of sugar (C12H22O11) required to prepare 2 L of its 0.1 M aqueous solution is: (2019)
(a) 136.8 g
(b) 17.1 g
(c) 68.4 g
(d) 34.2 g
Ans. (c)
Solution.
As we know,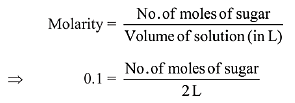
So, no. of moles of sugar = 0.2 mole
Mass of sugar = No. of moles of sugar × Molar mass of sugar
= 0.2 × 342 = 68.4 g
Q.10. Elevation in the boiling point for 1 molal solution of glucose is 2 K. The depression in the freezing point for 2 molal solution of glucose in the same solvent is 2 K. The relation between Kb and Kf is: (2019)
(a) Kb= 1.5Kf
(b) Kb = Kf
(c) Kb = 0.5Kf
(d) Kb = 2Kf
Ans. (d)
Solution.
According to the question we can write
ΔTb = Kbm ⇒ Kb (1) = 2 ⇒ Kb = 2Km-1
ΔTf = Kfm ⇒ Kf (2) = 2 ⇒ Kf = 1 Km-1
∴ Kf = 0.5 Kb
∴ Kb = 2 Kf
Q.11. The freezing point of a diluted milk sample is found to be - 0.2°C, while it should have been - 0.5°C for pure milk. How much water has been added to pure milk to make the diluted sample? (2019)
(a) 1 cup of water to 2 cups of pure milk
(b) 3 cups of water to 2 cups of pure milk
(c) 1 cup of water to 3 cups of pure milk
(d) 2 cups of water to 3 cups of pure milk
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Freezing point of diluted milk = -0.2°C
ΔT'f = 0.2ºC
Freezing point of pure milk = -0.5°C
ΔTf = 0.5ºC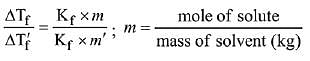
∵ Moles of solute are same in both samples
2 cups of pure milk is mixed with 3 cups of water to make 5 cups of diluted milk.
Q.12. K2HgI4 is 40% ionised in aqueous solution. The value of its van’t Hoff factor (i) is: (2019)
(a) 1.6
(b) 1.8
(c) 2.0
(d) 2.2
Ans. (b)
Solution.
K2Hgl4 ⇋ 2K+ + [Hgl4]2- ; n=3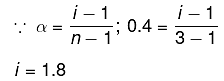
Q.13. Freezing point of a 4% aqueous solution of X is equal to freezing point of 12% aqueous solution of Y. If molecular weight of X is A, then molecular weight of Y is: (2019)
(a) 3A
(b) 2A
(c) A
(d) 4A
Ans. (a)
Solution.
(ΔTf)x = (ΔTf)y
Kf.mx = Kf.my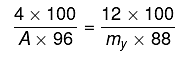
my= 3.27 A; y ≈ 3 A
Q.14. 8 g of NaOH is dissolved in 18 g of H2O. Mole fraction of NaOH in solution and molality (in mol kg-1) of the solution respectively are: (2019)
(a) 0.2,22.20
(b) 0.2,11.11
(c) 0.167,11.11
(d) 0.167,22.20
Ans. (c)
Solution.
No. of moles of H2O (n1) = 18/18 = 1
No. of moles of NaOH (n2) = 8/40 = 1/5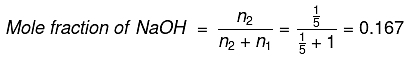

Q.15. Molecules of benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) dimerise in benzene, ‘w’ g of the acid dissolved in 30 g of benzene shows a depression in freezing point equal to 2 K. If the percentage association of the acid to form dimer in the solution is 80, then w is:
(Given that Kf = 5 K kg mol-1, Molar mass of benzoic acid = 122 g mol-1) (2019)
(a) 2.4 g
(b) 1.0 g
(c) 1.5 g
(d) 1.8 g
Ans. (a)
Solution.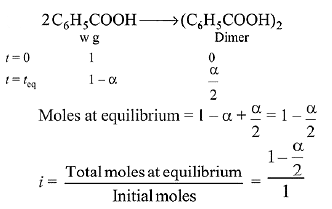
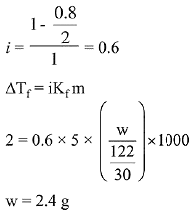
Q.16. The vapour pressures of pure liquids A and B are 400 and 600 mm Hg, respectively at 298K. On mixing the two liquids, the sum of their initial volumes is equal to the volume of the final mixture. The mole fraction of liquid B is 0.5 in the mixture. The vapour pressure of the final solution, the mole fractions of components A and B in vapour phase, respectively are: (2019)
(a) 450 mm Hg, 0.4, 0.6
(b) 500 mm Hg, 0.5, 0.5
(c) 450 mm Hg, 0.5, 0.5
(d) 500 mm Hg, 0.4, 06
Ans. (d)
Solution.

= 0.5 × 600 + 0.5 × 400 = 300 + 200 = 500
Using the relation pi = yi PTotal, we can calculate the mole fractions of the components in vapour phase.
PB = yB Ptotal
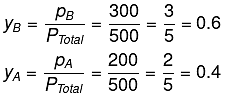
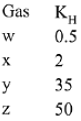
Q.17. For the solution of the gases w, x,y and z in water at 298K, the Henry's law constants (KH) are 0.5, 2, 35 and 40 kbar, respectively. The correct plot for the given data is: (2019)
(a) 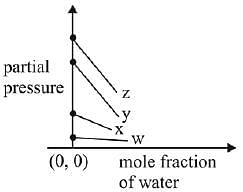
(b) 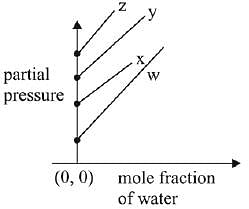
(c) 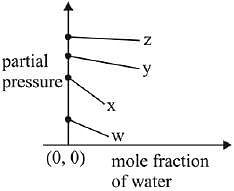
(d) 
Ans. (a)
Solution.
According to Henry’s law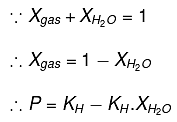
y = c + mx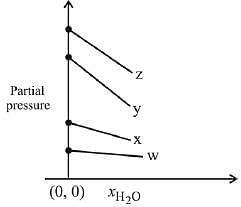
Q.18. Liquid 'M' and liquid 'N' form an ideal solution. The vapour pressures of pure liquids 'M' and 'N' are 450 and 700 mm Hg, respectively, at the same temperature. Then correct statement is:
(xM = Mole fraction of 'M' in solution;
xN = Mole fraction of'N' in solution;
yM = Mole fraction of 'M' in vapour phase;
yN = Mole fraction of 'N’ in vapour phase) (2019)
(a) 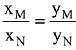
(b) 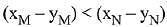
(c) 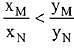
(d) 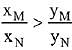
Ans. (d)
Solution.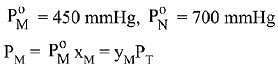
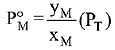
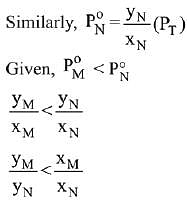
Q.19. The osmotic pressure of a dilute solution of an ionic compound XY in water is four times that of a solution of 0.01 M BaCl2 in water. Assuming complete dissociation of the given ionic compounds in water, the concentration of XY (in mol L-1) in solution is: (2019)
(a) 4 x 10-2
(b) 6 x 10-2
(c) 4 x 10-4
(d) 16 x 10-4
Ans. (b)
Solution.
we know,
∴ 2[XY] = 4(0.01)3
[XY] = 0.06
= 6 × 10-2 mol/L
Q.20. Molal depression constant for a solvent is 4.0 K kg mol-1. The depression in the freezing point of the solvent for 0.03 mol kg-1 solution K2SO4 is:
(Assume complete dissociation of the electrolyte) (2019)
(a) 0.18 K
(b) 0.24 K
(c) 0.12 K
(d) 0.36 K
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Dissociation of Potassium Sulphate (K2SO4),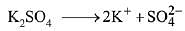
i (Van’t Hoff factor) = 3
We know that, ΔTf= iKfm
where, Kf is molal depression constant and m is molality.
= 3 × 4 × 0.03 = 0.36 K
Q.21. What would be the molality of 20% (mass/mass) aqueous solution of Kl? (molar mass of KI = 166 g mol-1) (2019)
(a) 1.08
(b) 1.35
(c) 1.48
(d) 1.51
Ans. (d)
Solution.
20% W/W KI solution (Given)
i.e. 100 g solution contains 20 g KI
∴ Mass of solvent = 100 - 20 = 80 g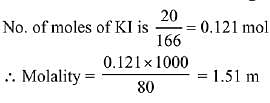
Q.22. At room temperature, a dilute solution of urea is prepared by dissolving 0.60 g of urea in 360 g of water. If the vapour pressure of pure water at this temperature is 35 mm Hg, lowering of vapour pressure will be:
(molar mass of urea = 60 g mol-1) (2019)
(a) 0.027 mm Hg
(b) 0.028 mm Hg
(c) 0.017 mm Hg
(d) 0.031 mm Hg
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Relative lowering of vapour pressure, is given by,
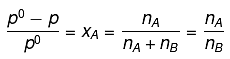
Given,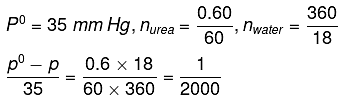
Δp = pº - p = 0.017
Q.23. 1 g of a non-volatile non-electrolyte solute is dissolved in 100 g of two different solvents A and B whose ebullioscopic constants are in the ratio of 1 : 5. The ratio of the elevation in their boiling points, ΔTb(A)/ΔTb(B) is: (2019)
(a) 5 : 1
(b) 10 : 1
(c) 1 : 5
(d) 1 : 0.2
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Ebullioscopic constant (molal elevation const.) is given by,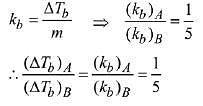
Q.24. For 1 molal aqueous solution of the following compounds, which one will show the highest freezing point? (2018)
(a) [CO(H2O)6]Cl3
(b)[CO(H2O)5CI]CI2.H2O
(c) [CO(H2O)4CI2]CI.2H2O
(d) [CO(H2O)3CI3].3H2O
Ans. (d)
Solution.
The complex giving least number of ions will have lowest depression in freezing point and therefore highest freezing point. Hence, option 1 is correct. (Van’t Hoff factor = 1)
Q.25. Which of the following statements about colloids is False? (2018)
(a) Freezing point of colloidal solution is lower than true solution at same concentration of a solute
(b) When silver nitrate solution is added to potassium iodide solution, a negatively charged colloidal solution is formed
(c) Colloidal particles can pass through ordinary filter paper
(d) When excess of electrolyte is added to colloidal solution, colloidal particle will be precipitated
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Freezing point of colloidal solution is higher than true solution at same concentration of a solute.
Q.26. The mass of a non-volatile, non-electrolyte solute (molar mass = 50 g mol-1) needed to be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce its vapour pressure to 75 %, is: (2018)
(a) 37.5 g
(b) 75 g
(c) 150 g
(d) 50 g
Ans. (d)
Solution.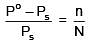
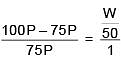
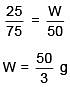
Q.27. The freezing point of benzene decreases by 0.45ºC when 0.2 g of acetic acid is added to 20 g of benzene. If acetic acid associates to form a dimer in benzene, percentage association of acetic acid in benzene will be
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol–1) (2017)
(a) 64.6%
(b) 80.4%
(c) 74.6%
(d) 94.6%
Ans. (d)
Solution.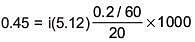
⇒ i = 0.527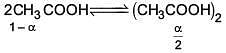

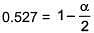
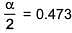
α = 0.946
∴ % association = 94.6%
Q.28. 5 g of Na2SO4 was dissolved in x g of H2O. The change in freezing point was found to be 3.82°C. If Na2SO4 is 81.5% ionised, the value of x
(Kf for water = 1.86°C kg mol-1) is approximately:
(molar mass of S = 32 g mol-1 and that of Na = 23 g mol-1) (2017)
(a) 25 g
(b) 65 g
(c) 15 g
(d) 45 g
Ans. (4)
Solution.
Q.29. A solution is prepared by mixing 8.5 g of CH2Cl2 and 11.95 g of CHCl3. If vapour pressure of CH2Cl2 and CHCl3 at 298 K are 415 and 200 mm Hg respectively, the mole fraction of CHCl3 in vapour form is : (Molar mass of Cl = 35.5 g mol-1) (2017)
(a) 0.162
(b) 0.675
(c) 0.325
(d) 0.486
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Molar mass of CHCl3 = 119.5 g/mol.
Molar mass CH2Cl2 = 85 g/mol.
Moles of CHCl3 = 11.95/119.5 = 0.1 mol.
Moles of CH2Cl2 = 8.5/85 = 0.1 mol.
Mole of CHCl3 = 0.1/0.2 = 0.5 mol.
Mole fraction of CH2Cl2 = 0.1/0.2 = 0.5 mol.
(Given - Vapour pressure of CHCl3 = 200 mm Hg = 0.263 atm.
Vapour pressure of CH2Cl2 = 415 mm Hg = 0.546 atm.)(1 atm = 760 mm Hg)
∴ P(above solution)
= mole fraction of CHCl3 × (Vapour pressure of CHCl3) + Mole fraction of CH2Cl2 × (Vapour pressure of CH2Cl2)
= 0.5 × 0.263 + 0.5 × 0.546 = 0.4045
Mole fraction of CHCl3 in vapour form = 0.1315/0.4045 = 0.325.
Q.30. 18 g glucose (C6H12O6) is added to 178.2 g water. The vapour pressure of water (in torr) for this aqueous solution is: (2016)
(a) 7.6
(b) 76.0
(c) 752.4
(d) 759.0
Ans. (c)
Solution.
According to Raoult's Law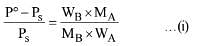
Here P° = Vapour pressure of pure solvent,
Ps = Vapour pressure of solution
WB = Mass of solute, WA = Mass of solvent
MB= Molar mass of solute, MA = Molar mass of solvent
Vapour pressure of pure water at 100° C (by assumption = 760 torr)
By substituting values in equation (i) we get,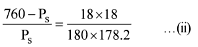
On solving (ii) we get
Ps = 752.4 torr
Q.31. The solubility of N2 in water at 300 K and 500 torr partial pressure is 0.01 g L-1. The solubility (in g L-1) at 750 torr partial pressure is: (2016)
(a) 0.02
(b) 0.015
(c) 0.0075
(d) 0.005
Ans. (c)
Solution.
According to Henry's law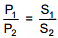
S1 & S2 are solubility of gas (g/L)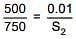
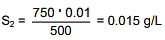
Q.32. An aqueous solution of a salt MX2 at certain temperature has a van't Hoff factor of 2. The degree of dissociation for this solution of the salt is: (2016)
(a) 0.67
(b) 0.33
(c) 0.80
(d) 0.50
Ans. (d)
Solution.
For MX2 type salt
van 't Hoff factor (i) = 1 + 2α = 2
⇒ α = 0.5

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|


















