NEET Previous Year Questions(2016-25): Morphology of Flowering Plants | Biology Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Which of the following is an example of a zygomorphic flower? (NEET 2025)
(a) Pea
(b) Chilli
(c) Petunia
(d) Datura
Ans: (a)
- Flowers can be classified based on their symmetry into two main types: actinomorphic and zygomorphic flowers.
- Actinomorphic flowers: These flowers are radially symmetrical, meaning they can be divided into equal halves along multiple planes. Examples include mustard, chilli, and datura.
- Zygomorphic flowers: These flowers are bilaterally symmetrical, meaning they can only be divided into equal halves along one particular plane. Examples include pea, gulmohar, cassia and bean.
- A flower is asymmetric (irregular) if it cannot be divided into two similar halves by any vertical plane passing through the centre, as in canna.

Q2: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2025)
- Statement I: In a floral formula ⊕ stands for zygomorphic nature of the flower, and G stands for inferior ovary.
- Statement II: In a floral formula ⊕ stands for actinomorphic nature of the flower and G stands for superior ovary.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Ans: (b)
- A floral formula is a symbolic representation of the structure of a flower using specific symbols and abbreviations to denote its various characteristics.
- It provides information about the symmetry of the flower, the number and arrangement of floral organs, and the position of the ovary.
Key symbols used in a floral formula include:
- ⊕: Represents actinomorphic (radially symmetrical) flowers.
- %: Represents zygomorphic (bilaterally symmetrical) flowers.
- G : Represents an inferior ovary (the ovary is below other floral parts).
- G: Represents a superior ovary (the ovary is above other floral parts).
Therefore, Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
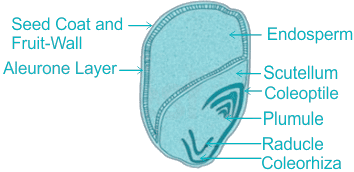
Q3: In the seeds of cereals, the outer covering of endosperm separates the embryo by a protein-rich layer called: (NEET 2025)
(a) Integument
(b) Aleurone layer
(c) Coleoptile
(d) Coleorhiza
Ans: (b)
Aleurone layer:
- The aleurone layer is a single layer of specialized cells found at the interface of the endosperm and the seed coat.
- The outer covering of the endosperm separates the embryo by a proteinous layer called the aleurone layer.
- It is rich in proteins and plays a crucial role during seed germination by secreting enzymes such as amylase and protease.
- These enzymes break down starch and proteins stored in the endosperm into simpler compounds, which are then utilized by the growing embryo.
- The aleurone layer also contributes to the seed's nutritional value in cereal grains.
 Incorrect Options:
Incorrect Options:
- Coleoptile: This is a protective sheath that covers the emerging shoot or plumule of monocot seeds during germination.
- Coleorhiza: The coleorhiza is a protective covering that encloses the emerging radicle (root) in monocot seeds.
- Integument: The integument is the protective outer layer of the ovule that eventually develops into the seed coat.
Q4: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2025)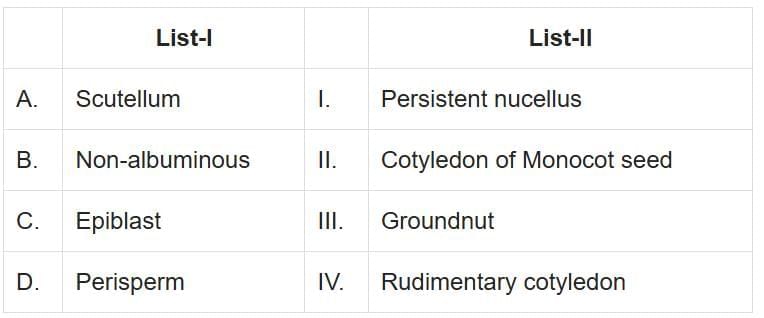 Choose the option with all correct matches.
Choose the option with all correct matches.
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(b) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
(c) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(d) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
Ans: (c)
- (A) Scutellum: The scutellum is a specialized cotyledon found in monocot seeds, such as those of grasses. It is part of the monocotyledonous embryo and assists in the absorption of nutrients from the endosperm during seed germination.
- (B) Non-albuminous seeds: Non-endospermous seeds (also known as non-albuminous seeds) do not contain endosperm at maturity because it is absorbed by the developing embryo. Non- albuminous seeds have no residual endosperm as it is completely consumed during embryo development. Examples include groundnut,bean, gram, and pea seeds.
- (C) Epiblast: Epiblast refers to a structure in some monocot seeds, such as grasses. It is a rudimentary or vestigial structure. The epiblast in seeds is typically a small, scale-like outgrowth that does not develop into a significant part of the plant but may assist in some way during germination or early seedling development
- (D) Persiperm: In some seeds such as black pepper and beet, remnants of nucellus are also persistent. This residual, persistent nucellus is the perisperm.
2024
Q1: Identify the type of flowers based on the position of calyx, corolla and androecium with respect to the ovary from the given figures (a) and (b) (NEET 2024)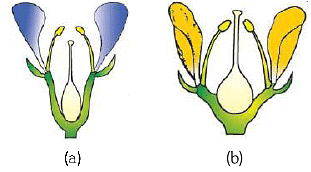 (a) (a) Epigynous; (b) Hypogynous
(a) (a) Epigynous; (b) Hypogynous
(b) (a) Hypogynous; (b) Epigynous
(c) (a) Perigynous; (b) Epigynous
(d) (a) Perigynous; (b) Perigynous
Ans: (d)
If gynoecium is situated in the centre and other parts of the flower are located on the rim of the thalamus almost at the same level, it is called perigynous.
Both diagram shows perigynous condition.
Q2: Which of the following is an example of actinomorphic flower? (NEET 2024)
(a) Datura
(b) Cassia
(c) Pisum
(d) Sesbania
Ans: (a)
When a flower can be divided into two equal radial halves in any radial plane passing through the centre, it is said to be actinomorphic, e.g., mustard, datura, chilli.
The other options are incorrect:
- Cassia: Zygomorphic (bilateral symmetry)
- Pisum: Zygomorphic (bilateral symmetry)
- Sesbania: Zygomorphic (bilateral symmetry)
Q3: Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)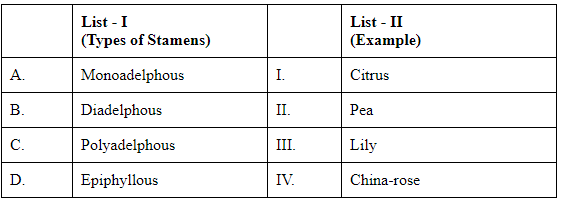 (a) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
(a) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
(b) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
(c) A-I, B-II, C-IV, D-III
(d) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Ans: (a)
The correct answer is: Option A: A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
Monoadelphous: Stamens united into a single bundle by their filaments. Example: China rose
Diadelphous: Stamens united into two bundles by their filaments. Example: Pea
Polyadelphous: Stamens united into more than two bundles by their filaments. Example: Citrus
Epiphyllous: Stamens arise from the perianth (sepals and petals) rather than from the receptacle. Example: Lily
Q4: Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)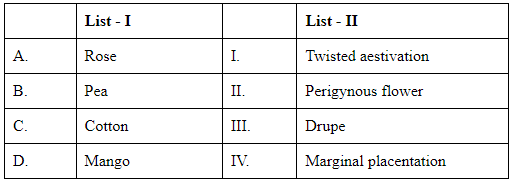 Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(b) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(d) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
Ans: (a)
Rose have half-inferior ovary, thus it is known as Perigynous flower.
In Pea, the placenta form a ridge along the ventral suture of the ovary and ovules are borne on this ridge forming two rows.
In Cotton, twisted aestivation is present.
In Mango, fruit is drupe.
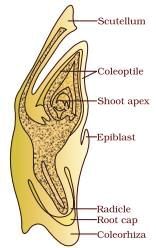
Q5: Identify the part of the seed from the given figure which is destined to form root when the seed germinates. (NEET 2024)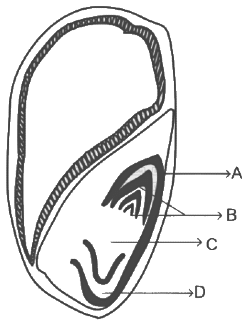 (a) A
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Ans: (c)
The radicle is the part of the seed that will develop into the root when the seed germinates.
In the provided diagram, 'C' represents the radicle.
Q6: Read the following statements and choose the set of correct statements : (NEET 2024)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C only
(b) B, D, E only
(c) A, C, D only
(d) C, D, E only
Ans: (d)
- A is incorrect because in cymose inflorescence, the flowers are borne in a basipetal (from the bottom upwards) rather than acropetal (from the top down) succession.
- B is incorrect because the flowers of gulmohar are zygomorphic (bilaterally symmetrical) and not actinomorphic (radially symmetrical).
- C is correct as described in the cucumber flowers, where the thalamus grows upward and fuses with the ovary.
- D is correct as bracts are modified or reduced leaves found at the base of the pedicel (flower stalk).
- E is correct as mustard flowers are hypogynous, meaning the ovary is at the base, and other parts (sepals, petals, stamens) are above it.
Thus, the correct answer is (D). C, D, E only.
Q7: Match List-I with List-II. (NEET 2024)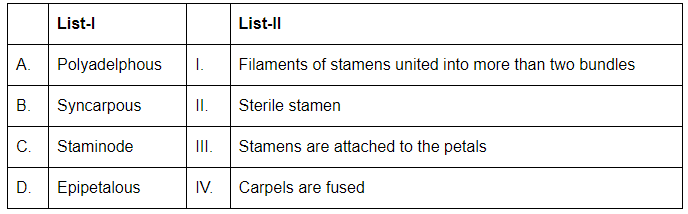
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
(b) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(c) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-I, B-II, C-IV, D-III
Ans: (a)
- A. Polyadelphous refers to the condition where the filaments of stamens are united into more than two bundles. This corresponds to I.
- B. Syncarpous refers to the condition where the carpels are fused. This corresponds to IV.
- C. Staminode refers to a sterile stamen, which is a stamen that does not produce pollen. This corresponds to II.
- D. Epipetalous refers to the condition where the stamens are attached to the petals. This corresponds to III.
Therefore, the correct answer is (A). A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III.
Q8: Match List I with List II: (NEET 2024)
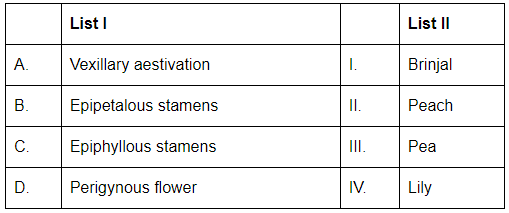
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A- III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(b) A- III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(c) A- III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(d) A- II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
Ans: (a)
- A. Vexillary aestivation refers to the arrangement of petals in a flower, where the largest petal (standard) overlaps the two lateral petals (wings), which in turn overlap the smallest petal (keel). This arrangement is found in Pea (III).
- B. Epipetalous stamens means that the stamens are attached to the petals. This is characteristic of Brinjal (I).
- C. Epiphyllous stamens refers to stamens attached to the leaves. This arrangement is found in Lily (IV).
- D. Perigynous flower refers to a flower where the ovary is placed at the centre, and the other floral parts (petals, sepals, and stamens) are attached to the rim of the ovary. This is seen in Peach (II).
Thus, the correct answer is (A). A- III, B-I, C-IV, D-II.
Q9: Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)
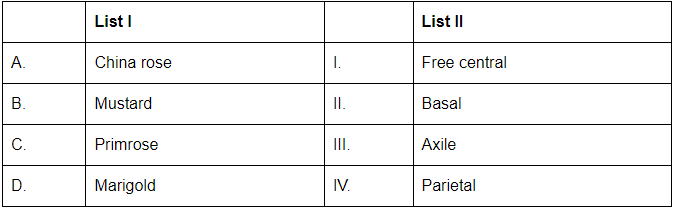
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A- IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(b) A- II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(c) A- III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A- III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
Ans: (c)
- A. China rose: The ovary in China rose is axile (I), meaning the ovules are attached to the central column (axis) of the ovary, with chambers formed by the partition.
- B. Mustard: The ovary in mustard is parietal (IV), meaning the ovules are attached to the walls of the ovary.
- C. Primrose: The ovary in primrose is free central (I), meaning the ovules are attached to a central column without partition.
- D. Marigold: The ovary in marigold is basal (II), meaning the ovary is positioned at the base of the flower, and the ovules are attached to the base.
Thus, the correct answer is (C). A- III, B-IV, C-I, D-II.
2023
Q1: Family Fabaceae differs from Solanaceae and Liliaceae. With respect to the stamens, pick out the characteristics specific to family Fabaceae but not found in Solanaceae or Liliaceae. (NEET 2023)
(a) Diadelphous and Dithecous anthers
(b) Polyadelphous and epipetalous stamens
(c) Monoadelphous and Monothecous anthers
(d) Epiphyllous and Dithecous anthers
Ans: (a)
- Fabaceae → Diadelphous and dithecous anther.
- Solanaceae → Polyandrous, epipetalous and dithecous anther.
- Liliaceae → Polyandrous, epiphyllous and dithecous anther.
Q2: Given below are two statements : One is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R :
Assertion A : A flower is defined as modified shoot wherein the shoot apical meristem changes to floral meristem.
Reason R : Internode of the shoot gets condensed to produce different floral appendages laterally at successive node instead of leaves.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below : (NEET 2023)
(a) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(b) A is true but R is false
(c) A is false but R is true
(d) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Ans: (d)
- Statement A is true. A flower is indeed a modified shoot wherein the shoot apical meristem changes to a floral meristem.
- Statement R is also true. In the process of flower formation, the internodes of the shoot get condensed, and instead of leaves, different floral appendages (such as sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels) are produced laterally at successive nodes.
- Moreover, Statement R is indeed the correct explanation for Statement A. The transition from the shoot apical meristem to the floral meristem involves the condensation of internodes and the lateral production of floral appendages at nodes, which leads to the formation of a flower.
Q3: Axile placentation is observed in: (NEET 2023)
(a) China rose, Petunia and Lemon
(b) Mustard, Cucumber and Primrose
(c) China rose, Beans and Lupin
(d) Tomato, Dianthus and Pea
Ans: (a)
- Axile placentation refers to the arrangement of ovules in an ovary where the ovules are attached to the central axis, forming several chambers. This type of placentation is typically seen in bi- or multi-carpellary ovaries (ovaries with two or more carpels).
- China rose, Petunia, and Lemon all exhibit axile placentation. In these plants, the ovules are arranged along the central axis of the ovary, with different locules (chambers) for each carpel.
The other options:
(b) Mustard, Cucumber, and Primrose: These exhibit parietal placentation, not axile.
(c) China rose, Beans, and Lupin: Beans and Lupin exhibit axile placentation, but China rose is correctly matched in option (a).
(d) Tomato, Dianthus, and Pea: These have axile or other placentation types, but they do not match the typical axile placentation as seen in China rose, Petunia, and Lemon.
Hence, the correct answer is (a) China rose, Petunia and Lemon.
Q4: In Calotropis, aestivation is: (NEET 2023)
(a) Valvate
(b) Vexillary
(c) Imbricate
(d) Twisted
Ans: (a)
- Aestivation refers to the arrangement of sepals or petals in a flower bud before it opens. In different plants, this arrangement can vary.
- In Calotropis, the aestivation is valvate, meaning that the petals (or sepals) are arranged in such a way that they just touch each other at the edges without overlapping.
Let’s go over the other options:
Vexillary: This type of aestivation is seen in the pea family (Fabaceae), where the largest petal (the standard) overlaps the two lateral petals (the wings), and the smallest petal (the keel) overlaps the wings.
Imbricate: In this type, the petals overlap each other, but they are arranged in a specific way where each petal overlaps two others. This is seen in plants like cassia.
Twisted: In twisted aestivation, each petal overlaps the next one in a spiral fashion, which is common in plants like china rose.
Thus, the correct answer for Calotropis is (a) Valvate.
Q5: In a pea flower, five petals are arranged in a specialized manner with one posterior, two lateral and two anterior. These are named as___________, ____________ and ________ respectively. (NEET 2023)
(a) Keel, Wings and standard
(b) Vexillum, Keel and standard
(c) Keel, Standard and Carina
(d) Standard, Wings and Keel
Ans: (d)
In a pea flower (a member of the Fabaceae family), the five petals are arranged in a specific pattern, which is referred to as vexillary aestivation. This arrangement consists of:
- Standard (or Vexillum): The largest petal, located at the top, is called the standard. It is often broad and serves as a shield for the other petals.
- Wings: The two lateral petals are called the wings, and they are situated on either side of the standard.
- Keel: The two smaller, fused petals at the bottom form the keel, which is shaped like the keel of a boat and encloses the reproductive parts of the flower (stamens and pistil).
Thus, the correct arrangement is: Standard, Wings, and Keel.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) Standard, Wings and Keel.
Q6: Match List - I with List - II (NEET 2023)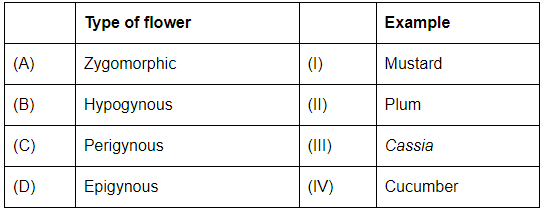 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A)-I (B)-III (C)-IV (D)-III
(b) (A)-II (B)-II (C)-III (D)-IV
(c) (A)-IIV (B)-I (C)-III (D)-II
(d) (A)-III (B)-I (C)-II (D)-IV
Ans: (d)
- Zygomorphic (A): This refers to flowers that are bilaterally symmetrical, meaning they can be divided into two equal halves in only one plane. The example for this is Cassia (III), as it has bilaterally symmetrical flowers.
- Hypogynous (B): In hypogynous flowers, the ovary is positioned below the other floral parts (sepals, petals, and stamens). The example for this is Mustard (I).
- Perigynous (C): In perigynous flowers, the ovary is placed at the center, with other floral parts (petals, sepals, and stamens) attached around the ovary at the same level. The example for this is Plum (II).
- Epigynous (D): In epigynous flowers, the ovary is situated above the other floral parts. The example for this is Cucumber (IV).
Correct Match:
(A) Zygomorphic → (III) Cassia
(B) Hypogynous → (I) Mustard
(C) Perigynous → (II) Plum
(D) Epigynous → (IV) Cucumber
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) (A-III) (B-I) (C-II) (D-IV).
2022
Q1: Match List - I with List - II : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
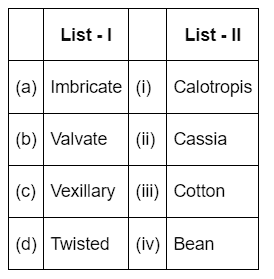
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) - (a) - (i), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (ii)
(b)- (a) - (ii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iii), (d) - (iv)
(c) - (a) - (ii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (iii)
(d) - (a) - (ii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (iii), (d) - (i)
Ans: (d)
- Imbricate aestivation is found in Cassia
- Valvate aestivation is found in Calotropis
- Vexillary aestivation is found in Bean
- Twisted aestivation is found in cotton
Q2: The Floral Diagram represents which one of the following families? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
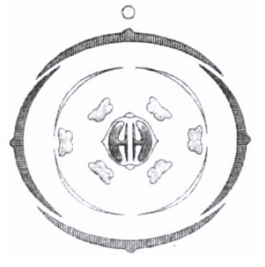 (a) Liliaceae
(a) Liliaceae
(b) Fabaceae
(c) Brassicaceae
(d) Solanaceae
Ans: (c)
The floral diagram given in the question represents Brassicaceae family. It can be easily identified by looking on its parietal placentation.
Q3: Which one of the following plants shows vexillary aestivation and diadelphous stamens? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) Pisum sativum
(b) Allium cepa
(c) Solanum nigrum
(d) Colchicum autumnale
Ans: (a)
- Vexillary aestivation and diadelphous stamens are the characteristic features of family Fabaceae.
- Pisum sativum (garden pea) belongs to family Fabaceae.
- Allium cepa (onion) and Colchicum autumnale (colchicine) belong to family Liliaceae.
- Solanum nigrum belongs to Solanaceae.
Q4: The flowers are Zygomorphic in: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(A) Mustard
(B) Gulmohar
(C) Cassia
(D) Datura
(E) Chilly
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (C) Only
(b) (D), (E) Only
(c) (C), (D), (E) Only
(d) (A), (B), (C) Only
Ans: (a)
When a flower can be divided into two similar halves only in one particular vertical plane, it is zygomorphic for e.g. pea, gulmohar, bean, Cassia. Mustard, Datura and Chilly show actinomorphic flowers.
2021
Q1: Match Column-I with Column-II (NEET 2021)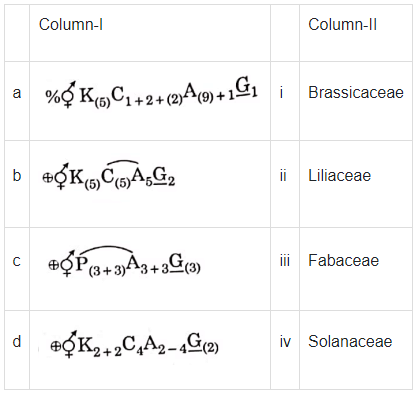
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) a-(ii), b-(iii), c-(iv), d-(i)
(b) a-(iv), b-(ii), c-(i), d-(iii)
(c) a-(iii), b-(iv), c-(ii), d-(i)
(d) a-(i), b-(ii), c-(iii), d-(iv)
Ans: (c)
The floral formula of
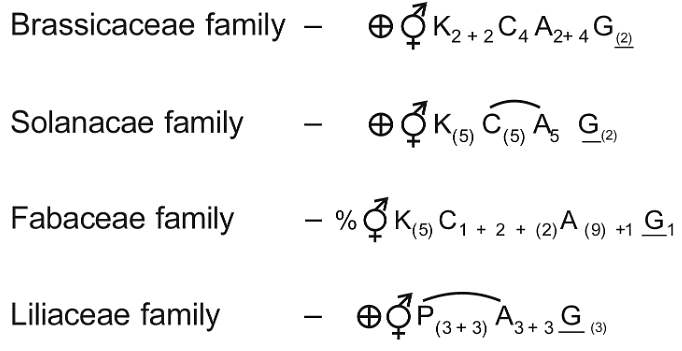
So, a(iii), b(iv), c(ii), d(i) is correct matching.
2020
Q1: Ray florets have (NEET 2020)
(a) Superior ovary
(b) Hypogynous ovary
(c) Half inferior ovary
(d) Inferior ovary
Ans: (d)
Ray floret have inferior ovary. Ray floret is condition in flower where any of a number of strap-shaped and typically sterile florets that form the ray e.g., Sunflower Epigynous flower are formed in family Asteraceae.
Q2: The ovary is half inferior in: (NEET 2020)
(a) Mustard
(b) Sunflower
(c) Plum
(d) Brinjal
Ans: (c)
The ovary is half inferior in Plum. A half inferior ovary is embedded or surrounded by the receptacle. Such flowers are termed perigynous or half-epigynous. In some classifications, half-inferior ovaries are not recognized and are instead grouped with either the superior or inferior ovaries.
2017
Q1: Coconut fruit is a (NEET 2017)
(a) Berry
(b) Nut
(c) Capsule
(d) Drupe
Ans: (d)
Coconut fruit is a drupe. A drupe is a fleshy fruit with thin skin and central stone containing the seed.
Q2: The morphological nature of the edible part of coconut is (NEET 2017)
(a) Cotyledon
(b) Endosperm
(c) Pericarp
(d) Perisperm
Ans: (b)
The edible part of coconut is its endosperm. Coconut has double endosperm, liquid endosperm and cellular.
2016
Q1: The term ‘polyadelphous’ is related to (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Gynoecium
(b) Androecium
(c) Corolla
(d) Calyx
Ans: (b)
Polyadelphous condition represents cohesion of stamens. In this condition stamens of a flower are fused by their filaments only to form many groups, e.g., Citrus.
Q2: Free central placentation is found in (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Dianthus
(b) Argemone
(c) Brassica
(d) Citrus
Ans: (a)
Free central placentation is found in Dianthus. Parietal placentation is present in Argemone and Brassica whereas Citrus has axile placentation in ovary.
Q3: Radial symmetry is found in the flowers of (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Brassica
(b) Trifolium
(c) Pisum
(d) Cassia
Ans: (a)
The flowers of Brassica are radially symmetrical whereas flowers of Trifolium, Pisum and Cassia are zygomorphic.
Q4: Cotyledon of maize grain is called (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Coleoptile
(b) Scutellum
(c) Plumule
(d) Coleorhiza
Ans: (b)
The cotyledons are known as seed leaves, they are attached to the embryonic axis. Dicotyledons typically have two cotyledons and monocotyledons have only one cotyledon. The single shield-shaped cotyledon in grains known as scutellum.
Q5: Tricarpellary, syncarpous gynoecium is found in flowers of (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Fabaceae
(b) Poaceae
(c) Liliaceae
(d) Solanaceae
Ans: (c)
The Liliaceae are a huge variety, comprising about 280 genera and 4000 species of perennial herbs mostly. It includes starchy rhizomes, corms or bulbs, characterized by alternate leaves which are whorled. The flowers are often showy, mostly bisexual and actinomorphic. Also, they exhibit tricarpellary syncarpous gynoecium. Example of such a class is the Erythronium montanum, the alpine fawn lily.
|
169 videos|531 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions(2016-25): Morphology of Flowering Plants - Biology Class 11
| 1. What is the importance of studying the morphology of flowering plants for NEET exam preparation? |  |
| 2. How can a student effectively study the morphology of flowering plants for the NEET exam? |  |
| 3. What are some common types of questions related to the morphology of flowering plants in the NEET exam? |  |
| 4. How can understanding the morphology of flowering plants help in solving complex NEET exam questions? |  |
| 5. Are there any specific topics within the morphology of flowering plants that are frequently tested in the NEET exam? |  |

















