SSC JE Civil Past Year Paper Technical - 2016 | Civil Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
CIVIL & STRUCTURAL
Q.101. Mean sea level (MSI,) adopted by Survey of' lndia for reference, is located at
(a) Kolkata
(b) Mumbai
(c) Karachi
(d) Delhi
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Before independence is Karachi, but after independence Mumbai is M.S.L. of India.
Mean sea level is a reference datum as established by permanent service for mean sea level. Used for Buildings and Railway Platforms.
Q.102. Black cotton soil is not suitable for foundation because of its
(а) Low bearing capacity
(b) Cohesive particles
(c) Swelling and shrinkage
(d) Black colour
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Because black soil has high plasticity index.
Q.103. Optimum moisture content is obtained from
(a) Triaxial test
(b) Standard proctor test
(c) Consolidation test
(d) Hydrometer test
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Optimum moisture content is obtained from standrd proctor test because it contains the density of maximum dryness.
Q.104. The effective size of particles of soil is denoted by
(a)D10
(b) D20
(c) D30
(d) D60
Ans. (a)
Solution.
D10 → 10% of sample finer in weight on. Grain Size Distribution Curve.
Q.105. When the plasticity index of a soil is zero, the soil is
(a) Clay
(b) Silt
(c) Sand
(d) Silty sand
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Because clay contains high plasticity index and sand contains zero plasticity index.
Q.106. Francis turbine is
(a) A reaction turbine
(b) An impulse turbine
(c) A tangential flow impulse turbine
(d) An axial flow turbine
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Francis Turbine is a inward reaction turbine.
Q.107. Most economical circular channel gives maximum discharge while
(a) Flow depth = 0.95 diameter
(b) Flow velocity high
(c) Area of flow is full
(d) Wetted perimeter is least
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Most economical circular gives flow depth with 95% of its diameter.
Q.108. Two pipe systems are said to be equivalent when
(a) They carry same discharge
(b) They are satisfying Bernoulli’s theorem
(c) Both have same head loss and discharge values
(d) They are of same length and having same head loss
Ans. (c)
Solution.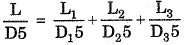
Discharge is same
Q.109. The specific speed of a pump is defined as the speed of a unit of such a size that it discharges
(a) Unit discharge at unit power
(b) Unit work at unit head loss
(c) Unit discharge at unit head
(d) Unit volume at unit time
Ans. (c)
Solution.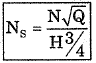
Q = Discharge, H = Head
Ns = Specific Speed
Q.110. The dimensions of Chezy’s C is
(a) Non-dimensional
(b) L/T
(c) LT
(d) [L/T2]1/2
Ans. (d)
Solution.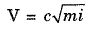
V → Velocity = L/T
=> C =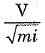
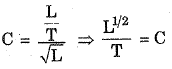
m → meter
Q.111. The velocity distribution for turbulent flow through circular pipes is
(a) uniform
(b) linear
(c) parabolic
(d) logarithmic
Ans. (d)
Solution.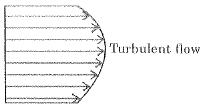
Velocity Profile
Q.112. With increase in temperature the viscosity of air and water varies as
(a) viscosity of air increases and viscosity of water decreases
(b) viscosity of air increases and viscosity of water increases
(c ) viscosity of air decreases and viscosity of water decreases
(d) viscosity of air decreases and viscosity of water increase
Ans. (a)
Solution.
In Air, viscosity increases with temperature and water V↓T↑. In Air molecules have high spaced.
Q.113. The construction joints in cement concrete
(a) should not be provided at the corners
(b) should be spaced at a distance of 3 m apart in case of huge structures
(c) should be located where shear force is large
(d) should be located where bending moment is large
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Constructor joint should be provided whenever the construction works stop temporarily. The joint could be either along transverse or longitudinal direction.
Q.114. The fineness modulus of an aggregate is roughly proportional to
(a) average size of particles in the aggregate
(b) grading of the aggregate
(c) specific gravity of the aggregate
(d) shape of the aggregate
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Fineness Modulus of an aggregate is an index number which is roughly proportional to average size of the particles in the aggregate. The coarser the aggregates the higher the fineness modules.
Q.115. The aggregate is said to be flaky when
(a) its length is equal to 1.8 times its mean dimension
(b) its length is equal to its mean dimension
(c) its least dimension is equal to its mean dimension
(d) its least dimension is three fifth of its mean dimension
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Flank index = 0.6 mean dimension.
Q.116. The soundness of cement is tested by
(a) Vicat’s apparatus
(b) Le Chatelier’s apparatus
(c) Compression testing machine
(d) Standard briquette test
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Soundness of cement is tested by Le’chatelier apparatus. Soundness mean change of volume or expansion in volume.
Q.117. In lime concrete, lime is used as
(a) admixture
(b) binding aggregate
(c) fine aggregte
(d) coarse aggregate
Ans. (b)
Solution.
When lime is mixed with water, lime slowly turns into the mineral portlandlite in reaction before Portland cement lime is widely used.
Q.118. The minimum quantity of cement content needed in one m3 of a reinforced concrete which is exposed to sea weather conditions is (in kg)
(a) 350
(b) 200
(c) 250
(d) 300
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Concrete in sea water as per IS : 456 along the sea cost be atleast M20 grade in plain concrete and M30 in case of reinforced concrete. For M30 grade minimum cement tightly 320 kg/m3 is used.
Q.119. Shrinkage in concrete increases its
(a) bond strength
(b) compressive strength
(c) flexural strength
(d) tensile
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Shrinkage concrete cause the concrete to grip reinforcing bars more. This increases friction between concrete and steel and so, improves bond strength, especially for plain bars.
Q.120. The strength of concrete mainly depends on
(а) quality of fine aggregates
(b) water cement ratio
(c) fineness of cement
(d) quality of course aggregates
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Water cement ratio decreases with increase in strength.
Q.121. Green concrete may be made by adding
(a) iron hydroxide
(b) barium manganate
(c) iron oxide
(d) chromium oxide
Ans. (c)
Solution.
For making green concrete with blast furnace slay with low heat. Green concrete made with SiO2 + Al2O3 + Fe2O3 of flyash.
Q.122. Gypsum is added to cement in small quantity to
(a) control initial setting time
(b) control final setting time
(c) give colour to the cement
(d) make cement hydrophobic
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Gypsum retard the initial setting of concrete.
Q.123. The Indian standard mix design for fly ash and cement concrete recommends water content
(a) to increase by 3% to 5%
(b) to reduce by 15%
(c) to increase by 15%
(d) to reduce by 3% to 5%
Ans. (d)
Solution.
The fly ash is replacement of cement with about 20-30% and also reduce the water demand of 10-15% with low heat of hydration.
Q.124. The thickness of the flange of a tee beam of a ribbed slab is assumed as
(a) half the thickness of the rib
(b) thickness of the concrete topping
(c) depth of the rib
(d) width of the rib
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Thickness of flange (df). This is equal to the overall depth of the slab forming the flange of the T-Beam.
Q.125. Co-efficient of wind resistance of a circular surface is
(a) 2/3
(b) 3/2
(c) 1/3
(d) 1/2
Ans. (a)
Q.126. Total number of elastic constants of an isotropic material are
(a) 2
(b)3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Two elastic constant E and μ.
Q.127. The stiffness of a spring is
(a) load per coil of the spring
(b) load required to produce unit deflection
(c) load required to compress the spring up to shearing proportional limit
(d) the load required for breaking the spring
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Q.128. Creep of a material is
(a) not being ductile
(b) to become brittle
(c) disappearance of deformation of removal of load
(d) continued deformation with time under sustained loading
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Creep is a permanent deformation which is recorded with passage of time at constant loading. Plastic deformation in nature ⇒ d∞/dT
Q.129. A propped cantilever is indeterminate externally of
(a) second degree
(b) fourth degree
(c) first degree
(d) third degree
Ans. (c)
Solution.
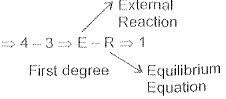
Q.130. Which of the following is a relatively ductile material?
(a) High carbon steel
(b) Bronze
(c) Mild steel
(d) Cast iron
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Carbon content is 0.2 - 0.35% in mild steels.
Q.131. A beam is supported over three rollers lying in the same plane. The beam is stable for
(a) loading with no component perpendicular to the direction of beam
(b) only when no load except self weight acts
(c) loading with no component in the direction of the beam
(d) any general loading
Ans. (c)
Solution. —> Movement in x-direction.
—> Movement in x-direction.
Q.132. The resistance of an aggregate to the effect of hydration of cement and weather is called
(a) impact value
(b) soundness
(c) crushing strength
(d) abrasion resistance
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Soundness of cement is determined either by ’Autoclave Test’ soundness of aggregate loss in mass for C. Aggregate with mg. S increases as fraction size is reduced and extent of wearthering on aggregate.
Q.133. Under which conditions highest water cement ratio is used?
(a) Heavy sections such as piers, foundations etc. exposed to alternate wetting and drying
(b) Heavy sections such as piers foundations etc. protected against rain and frost
(c) Hydraulic structure exposed to rain and snow
(d) Light structural members exposed to alternate wetting and drying
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Because of congested reinforcement is used in piers and high slum is required.
Q.134. Snowcem is
(а) coloured cement
(b) powdered lime
(c) chalk powder
(d) mixture of chalk powder and lime
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Snowcem paints leaders in exterior waterproof cement paints.
Q.135. In a singly reinforced beam, if the concrete is stressed to its allowable limit earlier than steel, the section is said to be
(a) economical section
(b) over reinforced section
(c) balanced section
(d) under reinforced section
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Actual Neutral Axis > Critical Neutral Axis.
Q.136. One cubic meter of mild steel weighs about
(a) 1000 kg
(b) 3625 kg
(c) 7850 kg
(d) 12560 kg
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Unit weight of steel = 7850N.
Q.137. The total length of a cranked bar through a distance (d) at 45° in case of a beam of effective length L, and depth (d) is
(a) L + 0.42 d
(b) L + 2 x 0.42 d
(c) L - 0.42 d
(d) L - 2 x 0.42 d
Ans. (b)
Solution.
L + 2 x 0.42d
L ⇒ effective length = clear distance.
Q.138. For building project estimate which method is generally used in PWD?
(а) Long wall and short wall method
(b) Centre line method
(c) Crossing method
(d) Short wall method
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Centre line method estimates prepared or most accurate and quick.
Q.139. An estimate is
(a) Cost of the structure using thumb rules
(b) Random guess of cost of structure
(c) Probable cost arrived at before construction
(d) Actual cost of construction
Ans. (c)
Q.140. The depth of foundation is usually calculated from
(a) Rankine’s formula
(b) Newton’s formula
(c) De Almbert’s formula
(d) Gutter’s formula
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Depth of foundation is calculated from Ramekin formula.
Q.141. When two points of surveying are mutually invisible the following method of ranging is adopted
(a) Direct ranging
(b) Indirect ranging
(c) Horizontal ranging
(d) Vertical ranging
Ans. (b)
Solution.
When ends of a line are not visible as in case of hill ground or distance between the stations are so large then use 2-Point resection method.
Q.142. The distance between two brass rings in a surveyor’s chain is
(a) 20 cm
(b) 40 cm
(c) 75 cm
(d) 1 m
Ans. (a)
Solution.
It is the standard distance.
Q.143. The sum of the interior angles of a closed traverse is equal to
(a) (2n - 4) 90°
(b) (3n - 4) 90°
(c) (2n - 4) 180°
(d) (3n - 4) 180°
Ans. (a)
Solution.
(2n - 4 ) x 90° → For correct bearing
n → Number of angles.
Q.144. Survey line provided to verify the accuracy of the framework is known as
(a) Tie line
(b) Base line
(c) Subsidiary line
(d) Check line
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Check line → It is a proof line is a line joining apex of a triangle to some fixed points on any 2 sides of a triangle. It measured the accuracy of frame work.
Tie/Subsiding lines → A tie line joints 2 fixed points on main survey lines helps checking accuracy of surveying and locate interior details.
Base line → Main longest line, which posses through the centre of fields shown the details of work w.r.t. line.
Q.145. The total number of links provided in a Gunter’s chain is
(a) 132
(b) 100
(c) 66
(d) 50
Ans. (b)
Solution.
It is a standard chain.
Q.146. If the fore bearing of a line is observed to be AB 12°24', the back bearing of line AB should be
(a) 102°24'
(b) 77° 36'
(c) 167°36'
(d) 192°24'
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Back Bearing = 12°24' + 180° = 192° 24'
Q.147. The direction of a line relative to a given meridian is known as
(a) Angle of line
(b) Direction of line
(c) Bearing of line
(d) Relative meridian
Ans. (c)
Solution.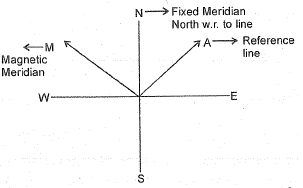
Q.148. When compared with chain surveying plane table is
(a) more accurate
(b) less accurate
(c) not accurate
(d) accurate
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Chain surveying is practically work find out with standard chain
Q.149. Number of satellites involved in the orbit for the GPS survey technique
(a) 14
(b) 24
(c) 34
(d) 44
Ans. (b)
Q.150. Slump test for concrete is carried out to determine
(a) Strength
(b) Durability
(c) Workability
(d) Water content
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Slump test is used to find the fluidity of concrete
Q.151. The leaching action in concrete is the example of
(a) Decomposition
(b) Creeping
(c) Crystallization
(d) Chemical reaction
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Concrete degradation may have various causes by sea water effects, corossion, callicum leaching, it is a chemical R ∝ N
Q.152. Poission’s ratio of cement concrete is about
(a) 0.28
(b) 0.50
(c) 0.40
(d) 0.15
Ans. (a)
Q.153. The span to depth ratio limit is specified in IS : 456-2000 for the reinforced concreted beams, in order to ensure that the
(a) Shear failure is avoided
(b) Tensile crack width is below a limit
(c) Deflection of the beam is below a limiting value
(d) Stress in the tension reinforcement is less than the allowable value
Ans. (c)
Solution.
It is depend on ℓ/d Ratio with support condition ℓ→span, d → depth of beam.
Q.154. A 300 x 300 mm R.C. column in reinforced with 8 bars, four bars are of 12 mm diameter. The diameter of lateral ties is 6 mm. The pitch of lateral ties shall be kept as
(a) 288 mm
(b) 160 mm
(c) 192 mm
(d) 300 mm
Ans. (c)
Q.155. The width of lacing bars in mm is kept
(a) Twice the nominal rivet diameter
(b) Thrice the nomial rivet diameter
(c) Maximum of the all rounded to nearest 5 mm
(d) Equal to normal rivet diameter
Ans. (b)
Solution.
As per IS : 800 B = 3d
Q.156. The bearing stress at bends for limit state method compared to working stress method of design is
(a) 1.5 times more
(b) 2.5 times more
(c) 2.5 times less
(d) 1.5 times less
Ans. (a)
Solution.
The bearing stress at bends for limit state method compared to working stress method of design is 1.5 times more
Q.157. The base width of retaining wall of height h is generally taken as, b =
(a) 0.8 h
(b) 0.95 h
(c) 0. 6 h
(d) 0.3 h
Ans. (a)
Q.158. The steel beam of light section placed in plain cement concrete are called
(a) Filler joists
(b) Concrete joists
(c) Simple joists
(d) Joists
Ans. (b)
Solution.
The joist to attached an outside wall. Then, span to an inside wall. The concrete and joist combined.
Q.159. Partial safety factor on steel stresses is
(a) 1.67
(b) 1.15
(c) 1.77
(d) 1.5
Ans. (b)
Solution.
As per IS: 456
⇒ 0.8 fy or fy/1.15 ⇒ for steel
Q.160. When a load is exerted or transferred from one surface to another in contact, the stress is known as
(a) Bearing stress
(b) Shear stress
(c) Binding stress
(d) Direct stress
Ans. (b)
Solution.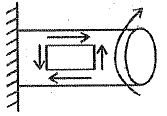 When Torque is applied then shear stress is develop at surface.
When Torque is applied then shear stress is develop at surface.
Q.161. When R.C.C. footing is not to extend in the plot of the neighbouring house, the type of footing preferred is
(a) Cellular flat not footing
(b) Inverted flat not footing
(c) Strap footing
(d) Both (a) and (b) above
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Q.162. Harbour model are based on the following law
(a) Froude law
(b) Reynold’s law
(c) Stoke’s law
(d) Euler’s law
Ans. (a)
Solution.
It is based on continum M/C (Mechanism) shipmodes one to other catchment area.
Q.163. For stability of floating bodies, the metacentre should be
(a) Above the centre of gravity
(b) Below the centre of gravity
(c) Above the centre of buoyancy
(d) Below the centre of buoyance
Ans. (a)
Solution.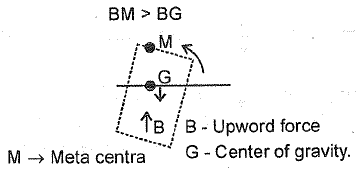
Q.164. A vessel containing water of depth h is accelerated upward with an acceleration of g/2. The pressure at the bottom of the vessel is
(a) γh
(b) γh/2
(c) 2γh
(d) 3/2γh
Ans. (d)
Solution.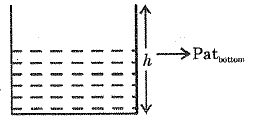
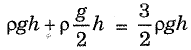
Q.165. The most desirable alignment of an irrigation canal is along
(a) The contour line
(b) The ridge line
(c) Normal to contour line
(d) The valley line
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Ridge line is cut to collect water in that area
Q.166. Clay is an example of
(a) Aquifer
(b) Aquitard
(c) Aquifuge
(d) Aquiclude
Ans. (d)
Solution.
These are porous but non-permeable which can hold water but don’t permit flow of water (Aquiclude).
Q.167. Aggregate impact value indicates which of the following properties of aggregates?
(a) Durability
(b) Toughness
(c) Hardness
(d) Strength
Ans. (b)
Q.168. The shape of the STOP sign according to IRC : 67-2001 is
(a) Circular
(b) Triangular
(c) Rectangular
(d) Octogonal
Ans. (d)
Q.169. Pollution potential of domestic sewage generated in a town and its industrial sewage can be compared with reference to
(a) Their BOD value
(b) Population equivalent
(c) Their volume
(d) The relative density
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Population equivalent
Q.170. The valve which protects the water meter from the damages of water hammer
(a) Pressure relief valve
(b) Stop cock
(c) Reflux valve
(d) Water hammer valve
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Brinnell Hardness No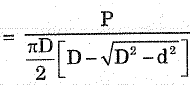
P → Load
D → Diameter of hard steel ball
Ability of material to Resist indentation.
Q.171. In Brinell Hardness test, the type ofindentor used is
(a) Hard steel ball
(b) Diamond cone
(c) Mild steel ball
(d) Hard steel cone
Ans. (a)
Q.172. The intensity of direct longitudinal stress in the cross-section at any point distant r from the neutral axis, is proportional to
(a) 1/r2
(b) 1/r
(c) r
(d) r2
Ans. (c)
Solution.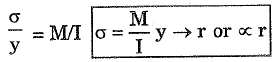
Q.173. A column is known as medium size if its slenderness ratio is between
(a) 160 and 180
(b) 20 and 32
(c) 32 and 120
(d) 120 and 160
Ans. (c)
Q.174. An arch may be subjected to
(a) Shear force and thrust
(b) Bending moment and shear force
(c) Shear and axial force
(d) Bending moment and axial force
Ans. (b)
Solution.
A simply Arch resist SF, BM and thrust also, 3 hinge arch with UDL SF & BM are zero but thrust is obtained.
Q.175. In order to determine the allowable stress in axial compression, Indian Standard Institution has adopted
(а) Rankine’s formula
(b) Secant formula
(c) Euler’s formula
(d) Perry-Robertson formula
Ans. (d)
Q.176. The sag tie in a truss is mainly used to reduce
(a) Moment and deflection
(b) Tension
(c) Weight of the truss
(d) Compression
Ans. (c)
Solution.
A Sag Tie is a vertical member joining the Apex of truss to mid point of bottom chord.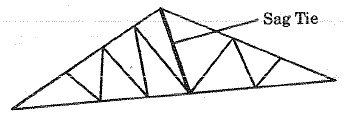
Q.177. A simply supported beam carrying uniformly distributed load will be safe in deflection if the ratio of its span and depth is
(a) <24
(b) >19
(c) < 19
(d) > 24
Ans. (c)
Q.178. The actual thickness of a butt weld when compared with the thickness of the plate is
(a) Less
(b) More or less
(c) More
(d) Equal
Ans. (d)
Solution.
The size of butt weld is specified by throat thickness which is normally the thickness of thinner plate jointed by weld.
Q.179. The fillet weld whose axis is parallel to the direction of the applied load is known as
(a) Side fillet weld
(b) End fillet weld
(c) Flat fillet weld
(d) Diagonal fillet weld
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Q.180. Tacking rivets in compression plates exposed to weather have a pitch not exceeding 200 mm or
(a) 8 times the thickness of outside plate
(b) 16 times the thickness of outside plate
(c) 24 times the thickness of outside plate
(d) 32 times the thickness of outside plate
Ans. (b)
Solution.
In tension = 32t or In compression = I6t
Q.181. If the depth of the section of an upper column is much smaller than the lower column
(а) Bearing plates are provided with column splice
(b) Filler and bearing plates are provided with column splice
(c) Filler plates are provided with column
(d) Neither filler nor bearing plates are provided with column splice
Ans. (c)
Q.182. Web crippling in beams generally occurs at the points where
(а) Concentrated loads act
(b) Bending moment is maximum
(c) Shear force is maximum
(d) Deflection is maximum
Ans. (a)
Solution.
When web is crippling use bearing stiffness these are used on support and where point paint.
Q.183. The minimum thickness of the plates used in pressed steel tanks is
(a) 4 mm
(b) 5 mm
(c) 6 mm
(d) 3 mm
Ans. (c)
Q.184. A column splice is used to increase
(a) The strength of the column
(b) The rigidity of the column
(c) The cross-sectional area of the column
(d) The length of the column
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Column splice is used to increase the length of the column.
Q.185. Percentage increase of carbon in steel, decreases its
(a) Hardness
(b) Ductility
(c) Strength
(d) Brittleness
Ans. (d)
Q.186. The process of providing smooth face and regular face to stones is known as
(a) Quarrying
(b) Seasoning
(c) Pitching
(d) Dressing
Ans. (d)
Q.187. The bulking of sand occurs due to
(a) Air in voids
(b) Moisture in voids
(c) Surface tension,
(d) Capillary action
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Bulking of sand occurs due to moisture in voids.
Q.188. The compressive strength of common building bricks should not be less than
(a) 3.5 N/mm2
(b) 5.5 N/mm2
(c) 7.5 N/mm2
(d) 10.5 N/mm2
Ans. (a)
Q.189. The natural bedding plane of stones and the direction of pressure in stone masonry is
(a) normal
(b) parallel
(c) at 30°
(d) at 45°
Ans. (a)
Q.190. Following stone is suitable for damp-proofing
(a) Slate
(b) Marble
(c) Laterite
(d) Granite
Ans. (a)
Q.191. The number of standard bricks in one cubic meter of brick masonry is
(a) 300
(b) 500
(c) 700
(d) 1000
Ans. (b)
Q.192. The resistance of a material to penetration is
(a) Toughness
(b) Hardness
(c) Fatigue
(d) Roughness
Ans. (b)
Q.193. The standard size of a masonry brick is
(a) 18 cm x 8 cm x 8 cm
(b) 18 cm x 9 cm x 9 cm
(c) 19 cm x 9 cm x 9 cm
(d) 19 cm x 8 cm x 8 cm
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Short column →<32
Medium → 32-120
Long column → > 120
Q.194. White cement should have least percentage of
(a) Aluminium oxide
(b) Iron oxide
(c) Silica
(d) Magnesium oxide
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Magnesium oxide: MgO is used for expansion and plasticity in cement or remoulding in cement.
Q.195. Turpentine oil is used in paint as a
(a) Base
(b) Carrier
(c) Drier
(d) Thinner
Ans. (d)
Q.196. Connecting pipe in mm for septic tank should not be less than
(a) 150
(b) 100
(c) 50
(d) 25
Ans. (b)
Q.197. Total depreciation during first five years of a cement concrete structure is
(a) zero per cent
(b) 0.5 per cent
(c) 1 per cent
(d) 2 per cent
Ans. (c)
Q.198. Estimate for electrical wiring is prepared on the basis of
(а) Voltage
(b) Power
(c) Number of appliances
(d) Number of points
Ans. (d)
Q.199. Which of the following tax generally not applicable to residential building is
(a) Municipal tax
(b) Property tax
(c) Sales tax
(d) Wealth tax
Ans. (c)
Q.200. The value of demolished material is known as
(а) Scrap value
(b) Salvage value
(c) Resultant value
(d) Material value
Ans. (a)
|
2 videos|122 docs|55 tests
|
FAQs on SSC JE Civil Past Year Paper Technical - 2016 - Civil Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is the syllabus for the SSC JE Civil exam? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for the SSC JE Civil exam? |  |
| 3. Are there any recommended books for the SSC JE Civil exam? |  |
| 4. What is the eligibility criteria for the SSC JE Civil exam? |  |
| 5. Can I apply for the SSC JE Civil exam while in the final year of my engineering degree? |  |























