Adiabatic Expansion: Reversible & Irreversible | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
ADIABATIC EXPANSION
In adiabatic expansion, no heat is allowed to enter or leave the system, hence, q = 0. When this value is substituted in first law of thermodynamics, ∆U= q + w, we get ∆U = w.
In expansion,
- Work is done by the system on the surroundings, hence, w is negative.
- Accordingly ∆U is also negative, i.e., internal energy decreases and therefore, the temperature of the system falls.
In case of compression,
- ∆U is positive, i.e., internal energy increases and therefore,
- The temperature of the system rises.
The molar specific heat capacity at constant volume of an ideal gas is given by.
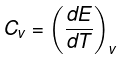
dU=Cv ·dT
∆U=Cv∆T
So, w=∆U=Cv∆T
The value of ∆T depends upon the process whether it is reversible or irreversible.
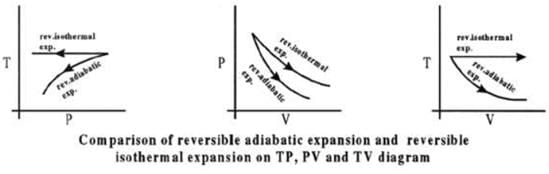
REVERSIBLE ADIABATIC EXPANSION
Let P be the external pressure and ∆V the increase in volume. Thus, the work done by the system is
w = ∆U = – PdV
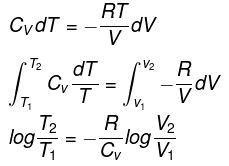
We know CP – CV = R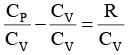
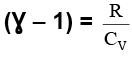
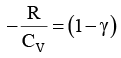
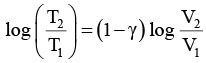
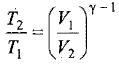

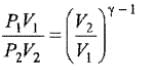
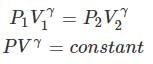
Thus, knowing Ɣ, V1 , V2 and initial temperature, T1 , the final temperature, T2, can be readily evaluated.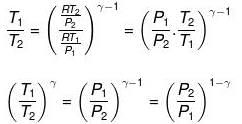
Thus, knowing Ɣ, P1, P2 and initial temperature, T1, the final temperature, T2, can be readily evaluated.
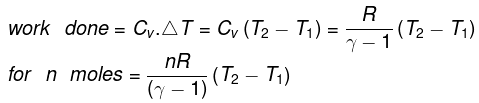
IRREVERSIBLE ADIABATIC EXPANSION
In free expansion, the external pressure is zero, i.e. , work done is zero. Accordingly, ∆U which is equal to w is also zero. If ∆U is zero, ∆T should be zero. Thus, in free expansion (adiabatically),
∆T = 0, ∆U= 0, w = 0 and ∆H = O.
In intermediate expansion, the volume changes from V1 to V2 against external pressure, Pext
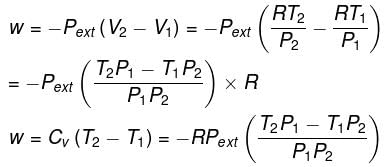
or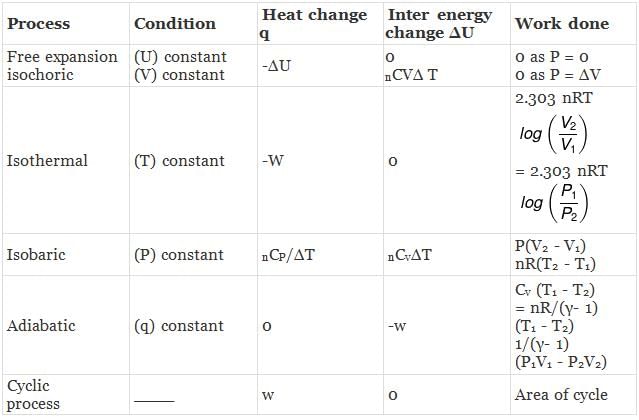
Example 1. Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas at NTP are compressed adiabatically and reversibly to occupy a volume of 4.48 dm3. Calculate the amount of work done, ∆U, final temperature and pressure of the gas. Cv for ideal gas 12.45J K -1 mol-1.
Solution. For an ideal gas,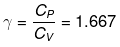
Initial volume, V1 = 2 × 22.4 = 44.8 dm3
Initial pressure, P1 = 1 atm
Initial temperature, T1 = 273 K
Final volume, V2 = 4.48 dm3
Let the final pressure be P2 and temperature be T2
Applying
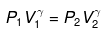
or
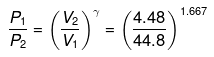
or
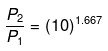
P2 = (10)1.667(P1 = 1 given)
log P2 = 1.667 log 10= 1.667
P2 = antilog 1.667= 46.45 atm
Final temperature
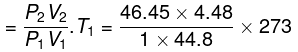
= 1268 K
Work done on the system = n.Cv.ΔT
= 2 × 12.45 × (1268 - 273)
= 2 × 12.45 × 995 = 24775.5 J
From the first law of thermodynamics,
ΔE = q + w = 0 + 24775.5 = 24775.5 J
Example 2. A certain volume of dry air at NTP is expanded reversibiy to four times its volume (a) isothermally (b) adiabatically. Calculate thefinal pressure and temperature in each case, assuming ideal behaviour.
(CP \ CV for air = 1.4)
Solution.
Let V1 be the initial volume of dry air at NTP.
(a) Isothermal expansion: During isothermal expansion, the temperature remains the same throughout. Hence, final temperature will be 273 K.
Since P1V1 = P2V2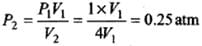
(b) Adiabatic expansion: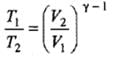
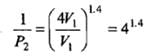
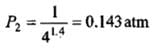
CALCULATION OF ∆H, ∆U. WORK, HEAT ETC.
Case - 1 For an ideal gas undergoing a process. the formula to be used are:
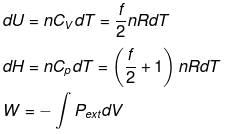
dH = dU + d(PV)
ΔH = ΔU + nRΔT
du = dQ + dw
Calculation of q, w , ∆H, ∆U for a reversible isothermal process involving an ideal gas :
ΔU = q + w = 0 ⇒ -w
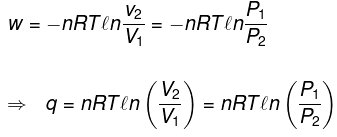
Calculation of q, w, ∆H, ∆U for an Irreversible isothermal process involving an ideal gas:
For isothermal process involving
ΔH = ΔU = 0 ∵ ΔT = 0
Also,
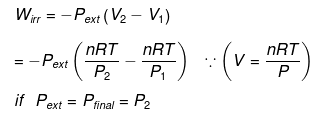
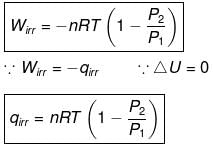
For isobaric process
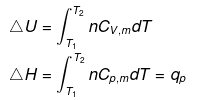
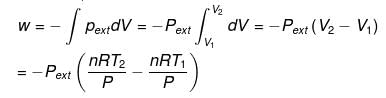
= -nR(T2 - T1) (∵ Pext = P)
= -nRΔT
Calculation of q, w, ∆H, ∆U for an IRREVERSIBLE ISOCHORIC process involving an ideal gas:
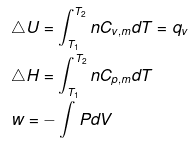
w= 0 ∵ dV = 0
Calculation of q, w, ∆H, ∆U for reversible adiabatic process
For an adiabatic process,
dq = 0 ⇒ dU = dw
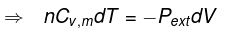
for a reversible change
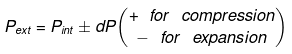
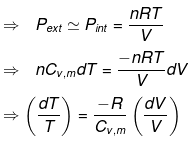
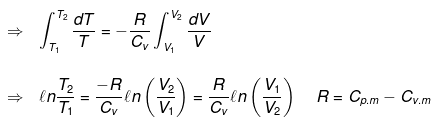
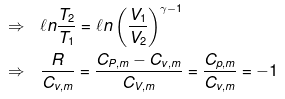
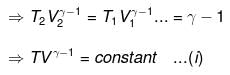
Now substituting V = nRT/P in equation
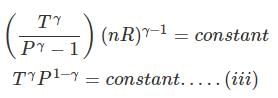
substituting T = PV/nR in eq...
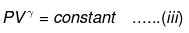
⇒ Equation (i), (ii) and (iii) is valid only for reversible adiabatic process, for irreversible adiabatic process these equations are not applicable.
- Expression for work:
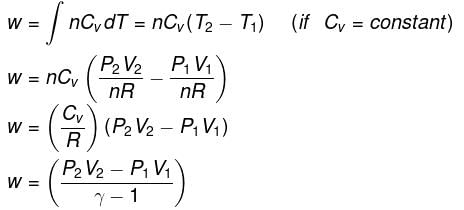
- Expression for ΔH and ΔU
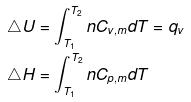
CALCULATION OF Q, W, ∆H, ∆U FOR IRREVERSIBLE ADIABATIC
PROCESS INVOLVING AN IDEAL GAS:
Operation wise adiabatic process and isothermal process are similar hence all the criteria that is used for judging an isothermal irreversible process are applicable to adiabatic process.
If large amount of dust particles are removed abruptly an irreversible adiabatic expansion take place.
In an irreversible adiabatic process, an ideal gas is subjected to compression or expansion in a thermally insulated vessel.
The heat absorbed in the process =0
⇒ dU = wirr ....(i)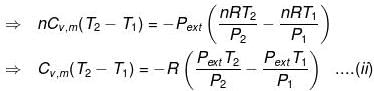
If Pext, = P2 = Pfinal
Then
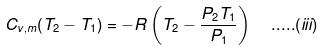
eq. (ii) or (iii) can be solved for T2
Expression for w
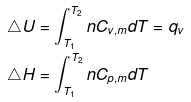
Note: If two states A and B are connected by a reversible path then they can never be connected by an irreversible path.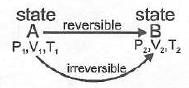 If the two states are linked by an adiabatic reversible and irreversible path then wrev = ∆Urev
If the two states are linked by an adiabatic reversible and irreversible path then wrev = ∆Urev
But as U is a state function
Therefore, ∆U irrev = ∆Urev
wirrev = wrev
as work is a path function.
If we assume that
wirrev = wrev
It implies that which again is a contradiction as U is a state function.
∆U irrev ≠ ∆Urev
Two states A and B can never lie both on a reversible as well as irreversible adiabatic path.
There lies only one unique adiabatic path linkage between two states A and B.
|
117 videos|226 docs|237 tests
|
FAQs on Adiabatic Expansion: Reversible & Irreversible - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What is adiabatic expansion? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between reversible and irreversible adiabatic expansion? |  |
| 3. How is adiabatic expansion related to work done by a gas? |  |
| 4. Can adiabatic expansion be both reversible and irreversible? |  |
| 5. What are some real-life examples of adiabatic expansion? |  |






















