Monetary Policy | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
MONETARY POLICY
It is a macroeconomic policy tool in which the central bank (RBI) regulates the money supply and interest rates to control inflation, boost growth and stabilise currency.
Monetary policy is the process of managing a nations’ money supply to achieve specific goals - such as controlling inflation, achieving full employment etc.
TYPES OF MONETARY POLICY
(a) Expansionary: Increases the total supply of money in the economy by relaxing interest rates (cheap money).
(b) Contractionary: Reduces the money supply by increasing interest rates (dear money).

MONETARY POLICY TOOLS
To achieve the goals of monetary policy the following 2 types of tools are available to the RBI
1. Quantitative:It includes repo, reverse repo,open market operations , CRR and SLR.
(i) CRR: It is the portion of bank deposits that a bank should keep with the RBI in the form of cash.
(ii) SLR:It is the portion of time(fixed deposits) and demand(saving and current account)deposits of the banks that it should keep in the form of RBI approved liquid assets like cash, gold and government securities.
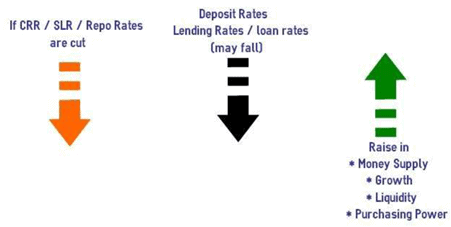 (iii) Repo rate: It is the rate at which RBI lends to the banks or injects money . It is used as the policy rate.
(iii) Repo rate: It is the rate at which RBI lends to the banks or injects money . It is used as the policy rate.
(iv) Reverse repo: It is the rate at which RBI borrows from the banks or sucks out excess money.
2. Qualitative Tools: These include Moral suasion, credit control and direct action.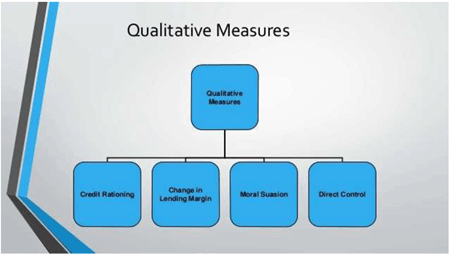
(i) Credit rationing: A maximum limit to loans and advances to a particular sector is set by RBI.
(ii) Moral suasion: Is an informal tool to persuade banks to adopt a certain behavior, to lower interest rates or to lend to small businesses . It is moral encouragement.
(iii) Direct control: The RBI here takes control of the functioning of the bank and sets parameters of business itself.
DEVELOPMENT OF INDIAN BANKING
(i)In order to make the Reserve Bank of India more powerful, the Indian Government nationalised it on January 1,1949.
(ii)With a view to have the co-ordinated regulation of Indian banking, the Indian Banking Act was passed in March 1949.
(iii)According to this Act, the Reserve Bank of India was granted extended powers for the inspection of non-scheduled banks.
(iv)For the development of the banking facilities in the rural areas the Imperial Bank of India was partially nationalised on July 1, 1955 and it was named as the State Bank of India.
(v)Other 8 banks were converted as its associate banks which form what is named as the State Bank Group.
(vi)After one decade, on April 15, 1980, those 6 private sector banks whose reserves were more than Rs. 200 crore each were nationalised.
RESERVE BANK OF INDIA
- It is the Central Bank of the country.
- The Reserve Bank of India was established in 1935 with a capital of Rs. 5 crore.
- This capital of Rs. 5 crore was divided into 5 lakh equity shares of Rs. 100 each.
- In the beginning the ownership of almost all the share capital was with the non-government shareholders.
- In order to prevent the centralisation of the equity shares in the hands of a few people, the Reserve Bank of India was nationalised on January 1,1949.
- The general administration and direction of RBI is managed by a Central Board of Directors consisting of 20 members which includes one Governor, four Deputy Governors, 1 Government official appointed by the Union Government of India to give representation to important stratas in economic life of the country.
- Besides, four directors are nominated by the Union Government to represent local boards.
- Apart from the central board there are four local boards also an d their head offices are situated in Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata and New Delhi.
- Five members of local boards are appointed by the Union Government for a period of four years.
- The local boards work according to the instructions and orders given by the Central Board of Directors, and from time to time they also tender useful advice on important matter.
- The head office of Reserve Bank of India is in Mumbai.
FUNCTIONS OF THE RBI
- Banker to Government: It acts as an agent and adviser of central and state governments
- Banker’s Bank: By providing the facility of opening accounts for banks, it acts as a common banker
- Lender of Last Resort: It rescues banks that face liquidity problems to protect the interests of the depositors
- Controller of Credit
- Debt Manager of The Government
- Custodian of Foreign Reserves.
MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE It was set up in 2016 after the Monetary Policy Framework Agreement which made inflation targeting a legal responsibility of RBI.
It was set up in 2016 after the Monetary Policy Framework Agreement which made inflation targeting a legal responsibility of RBI.
It amended the RBI act,1934.
It was recommended by the Urijit Patel committee in 2014.
Composition:3 members from RBI (Governor -who acts as the ex-officio chairman, RBI deputy governor, one official nominated by the RBI board) and 3 independent members to be selected by the government.
Functions of the MPC
- To control the inflation targets at 4 percent(give or take 2 percent)in the medium term( inflation target set by central government).
- Decide the changes to the policy rate(repo rate) to contain the inflation within the target level
- The RBI has to publish a Monetary policy report every six months.
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS
- Quantitative easing - It involves printing fresh currency to overcome debt . Lending is made easier . May lead to Inflation.
- Liquidity trap - It is a situation when lowering interest rates does not revive demand and growth.It happens during recession.
- Money supply - It indicates the total value of monetary assets available in an economy at a given point of time.
RBI Monetary Policy
Introduction:
Reserve Bank of India has once again raised the repo rate. Monetary Policy Committee on took a unanimous decision to raise benchmark lending rate by 50 basis points to 5.40%. This is the third hike of policy repo rate by RBI this year after 40 basis points hike in May followed by another hike of 50 basis points in June. Pointing out that consumer price inflation or CPI remains uncomfortably high and is expected to remain above 6% RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das said MPC decided to focus on withdrawal of accommodative policy stance to check inflation. He also said domestic economic activity is showing signs of broadening and Bank credit growth has accelerated 14 pc as against 5.5 pc year ago. RBI has also retained its economic growth projection at 7.2 per cent for current fiscal.
Monetary Policy committee:
- It is a statutory and institutionalized framework under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, for maintaining price stability, while keeping in mind the objective of growth.
- The 6-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) constituted by the Central Government as per the Section 45ZB of the amended RBI Act, 1934. The first meeting of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) was held on in Mumbai on October 3, 2016.
- The Governor of RBI is ex-officio Chairman of the committee. The MPC determines the policy interest rate (repo rate) required to achieve the inflation target (4%).
Monetary Policy objectives:
- It is the macroeconomic policy laid down by the central bank. It involves management of money supply and interest rate and is the demand side economic policy used by the government of a country to achieve macroeconomic objectives like inflation, consumption, growth and liquidity.
- In India, monetary policy of the Reserve Bank of India is aimed at managing the quantity of money in order to meet the requirements of different sectors of the economy and to increase the pace of economic growth.
- The RBI implements the monetary policy through open market operations, bank rate policy, reserve system, credit control policy, moral persuasion and through many other instruments.
Challenges before the RBI:
- When it comes to monetary policy, the RBI’s most important mandate is to maintain price stability.
- To this end, the RBI is required by law to maintain retail inflation which is based on Consumer Price Index (CPI) at the 4% level (with a band of variation of 2 percentage point).
- But, another key concern for the RBI is the overall economic growth in the economy.
- So the challenge before the RBI was to balance the concerns of boosting growth while making sure that inflation does not spiral out of control.
Monetary Policy Instruments and how they are managed?
- Monetary policy instruments are of two types namely qualitative instruments and quantitative instruments.
- The list of quantitative instruments includes Open Market Operations, Bank Rate, Repo Rate, Reverse Repo Rate, Cash Reserve Ratio, Statutory Liquidity Ratio, Marginal standing facility and Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF).
- Qualitative Instruments refer to direct action, change in the margin money and moral suasion.
Quantitative Easing for India:
- According to some economists, the only medicine that can work is quantitative easing, a remedy authority isn’t even discussing.
- QE, quantitative easing, may not cure the patient, but it may well succeed in bringing India’s economy out of a coma.
- This kind of QE does have a couple of advantages. One, it lowers the long-term government bond yield.
- That reduces loan costs for risky borrowers, since government bond yields act as a benchmark.
- Two, a more liquid banking system with more low-yielding cash than higher-yielding bonds will be impatient to lend at least in theory.
- Yet this type of QE relies on loans being made. If the demand side of the economy is struggling, the impact may be limited because of the one thing it doesn’t do: lift money supply in the broader economy.
Rising Inflation over a period of time:
Inflation encourages current consumption (buy goods and services now before prices rise) and discourages savings.
- People with savings suffer in times of inflation as the purchasing power of their savings decreases as price levels rise.
- The real rate of interest (nominal rate less the inflation rate) is reduced in times of inflation.
- Real interest rates may be negative if inflation rate is greater than the interest rate. If so the purchasing power of savings declines. This discourages savings.
- People who have borrowed money benefit as the real value of loans decreases as price levels rise (loans are easier to repay in the future as prices and income rise over time).
Conclusion:
- The latest Consumer Price Index data show retail inflation accelerated by almost 100 basis points to a three-month high of 5.03% in February, with food and fuel costs continuing to remain volatile.
- Domestic economic activity is starting to recover with the ebbing of the second wave.
- Looking ahead, agricultural production and rural demand are expected to remain resilient.
- Although investment demand is still anaemic, improving capacity utilisation and congenial monetary and financial conditions are preparing the ground for a long-awaited revival.
|
108 videos|430 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Monetary Policy - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is monetary policy? |  |
| 2. How does the Reserve Bank of India implement monetary policy? |  |
| 3. What are the objectives of monetary policy? |  |
| 4. How does monetary policy impact the economy? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced by the Reserve Bank of India in implementing monetary policy? |  |

















