The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 7th Sept, 2020 | Additional Study Material for UPSC PDF Download

1. TOO CLOSE FOR COMFORT: ON INDIA-CHINA BORDER ROW-
GS 3- Security challenges and their management in border areas
Context
Following Friday’s talks in Moscow between the Defence Ministers of India and China, the prospects of an imminent(likely to happen) diplomatic solution to the continuing stand-off along the LAC do not appear bright.
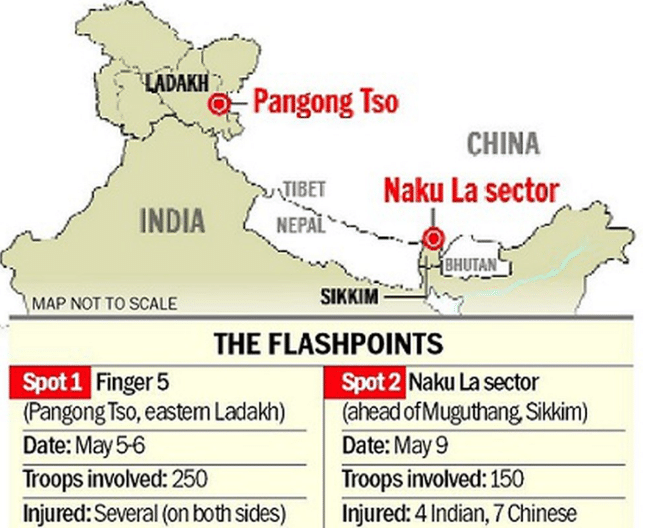
Unprecedented Developments
(i) The statements issued by the two sides have underlined(highlight) the sharp differences in how New Delhi and Beijing have continued to view the unprecedented(not happened before) developments along the border since May.
(ii) Defence Minister Rajnath Singh “categorically conveyed” India’s stand, emphasising that China’s actions “were in violation of the bilateral agreements”.
(iii) He also expressed hope that both sides would be able to resolve the ongoing situation “peacefully through dialogue”.
(iv) His Chinese counterpart, General Wei Fenghe, appeared to only reiterate(repeat) the stand conveyed by China in recent statements that it had no blame to bear for this summer’s developments.
(v) He said “the responsibility lies entirely with the Indian side”, while China “kept maximum restraint to prevent potential escalation”. He called on India to “immediately withdraw its troops”.
(vi) He did, also, add that both sides should “stay committed to resolving the issue through dialogue and consultation” and “make joint efforts to meet each other halfway”.
Diplomacy
(i) As External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar said last week, diplomacy is the only way out of the crisis, and that can only happen “if both sides understand that it is in each of their best interests if the events of this summer are not repeated”.
(ii) The problem, so far, has been a stark mismatch between China’s statements and the actions of its troops.
(iii) Its consistent labelling of India as the aggressor this summer contradicts the reality that India has, since May, ceded(given) about 1,000 square kilometres in Ladakh to Chinese control.
(iv) If China’s diplomats have spoken repeatedly of the need to keep in mind “the big picture” of bilateral ties, the actions of its military on the ground have suggested an intent that is precisely the opposite.
(v) China have emphasized achieving tactical gains at the border over the broader strategic relationship.
(vi) Until that calculus changes, India will have to be prepared to be tested along the border and to stand its ground over the long haul(pull).
(vii) India has signalled its intent to do so with the latest developments on August 29 in Chushul.
(viii) If the statements following the Moscow meet did not exactly inspire confidence, both sides will have the chance to reassess the situation when Mr. Jaishankar will likely meet his counterpart, Wang Yi, at a meeting of SCO Foreign Ministers on September 10.
(ix) Military talks can occasionally help to avert(prevent) a flare-up, but the two neighbours need to work toward a diplomatic solution to ensure undisturbed peace and quiet along the border.
2. MIXED MESSAGING: ON INDIA AS AN INVESTMENT DESTINATION-
GS 2- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Context
Prime Minister last week elaborately(detail) pitched India as an investment destination that could serve as a manufacturing hub at the heart of global supply chains.
Exploring Supply-Chain Synergies
(i) The pitch made at the U.S.-India Strategic Partnership Forum comes in the backdrop of the government’s keenness to lure(attract) potential investors, especially those looking to relocate from China, to India.
(ii) This tack is consistent with recent initiatives to explore supply-chain synergies with other economies, including Japan, as an escalating border feud(fight) casts a shadow over India’s economic and trade ties with China.
(iii) The reasoning appears to be that if even a few multinational enterprises can be drawn to set up manufacturing bases, either by shifting facilities or as new additional plants, then not only does the Indian economy stand to gain FDI, new jobs and tax revenue but it also makes a statement.
(iv) Clearly, officials must have advised Mr. Modi that U.S. businesses were the ideal target given the worsening relationship between Washington and Beijing and the ongoing trade stand-off between the world’s two largest economies.
(v) On the face of it, the approach seems inarguably sound. The rub(problem), however, lies in the government’s recent ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative, of making India more self-reliant.
Import Substitution
(i) Over the decades, it has been established that global FDI investors prioritise and are even willing to pay a premium for policy stability and largely barrier-free access to local and international markets.
(ii) The drive for self-reliance has spurred several Ministries to urge companies and industry sectors to replace imports with ‘Made in India’ substitutes.
(iii) From the Shipping Ministry’s call for the design and manufacture of indigenous tugboats to auto component makers being told to abjure(reject) foreign parts, the thrust of the initiative is evidently ‘import substitution’.
(iv) It is hard to imagine any potential foreign investor in manufacturing being ready to source capital goods locally — assuming they are available — even at the cost of possibly compromising on quality or price or both.
(v) Betraying the government’s anxiety, Mr. Modi took pains to stress that the push for self-reliance should not be interpreted as India turning its back on the world.
(vi) Separately, from the market access perspective, India’s decision to not join the RCEP multilateral trade pact would put investor companies seeking to tap consumers in RCEP member countries at a tariff disadvantage.
(vii) Interestingly, most of the recent FDI announcements have been by way of stake acquisitions in existing businesses, and predominantly in the services sector.
(viii) Attracting FDI into manufacturing will require the government to convince investors that it is committed not merely in words but in deeds as well to an open, barrier-free global trade and investment order.
Conclusion
India’s efforts to attract capital will not result in a flood of FDI till investors see policy stability.
3. FINANCING ECONOMIC RECOVERY-
GS 3- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment
Context
(i) As the socioeconomic impacts of the pandemic spread across Asia and the Pacific, finance ministries are continuing their efforts to inject trillions of dollars for emergency health responses and fiscal packages.
(ii) With continued lockdown measures and restricted borders, economic rebound seems uncertain.
(iii) Compared to 2019’s economic situation, over the past six months, countries in Asia and the Pacific have been experiencing sharp drops in foreign exchange inflows due to declines in export earnings, remittances, tourism and FDI.
(iv) This is worrying as policymakers are tackling difficult choices over how to prioritise development spending, while continuing to expand their squeezed fiscal space.
Financing In Three Key Areas
(i) The United Nations is contributing through a global initiative, Financing for Development in the Era of COVID-19 and Beyond to articulate a comprehensive financing strategy to safeguard the Sustainable Development Goals.
(ii) Governments are united to ensure that adequate financial resources are available to steer an inclusive, sustainable and resilient post-COVID-19 recovery.
(iii) In the Asia-Pacific region, several countries have already adopted financing plans in three key areas.
(iv) They aim to address the challenge of diminished fiscal space and debt vulnerability; to ensure sustainable recovery, consistent with the ambitions of the Paris Agreement and the 2030 Agenda; and to harness the potential of regional cooperation in support of financing for development.
(v) The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) has recently launched its first-ever Regional Conversation Series on Building Back Better.
(vi) We are joining forces with ministers, decision-makers, private sectors and heads of international agencies to share collective insights on sharing pathways to resilient recovery from health pandemic and economic collapse.
(vii) To improve the fiscal space and manage high levels of debt distress, a growing call for extending the debt moratorium under global initiatives like the Debt Service Suspension initiative is timely.
(viii) Central banks can continue to keep the balance of supporting the economy and maintaining financial stability.
(ix) This further involves enhancing tax reforms and improving debt management capacities, while using limited fiscal space to invest in priority sectors.
(x) Exploring sustainability-oriented bonds and innovative financing instruments options such as debt swaps for SDG investment should be explored further.
(xi) In addition to economic considerations, the policy paradigm must mainstream affordable, accessible and green infrastructure standards, while promoting social equality and environmental sustainability principles as enshrined in the Paris Agreement.
(xii) As we scale up the use of digital technology and innovative applications, the financing support of micro, small and medium-sized enterprises must go hand in hand with these national job-rich recovery strategies.
Regional Cooperation
(i) No country can take this agenda forward alone. Regionally coordinated financing policies can restart trade, reorganise supply chains and revitalise sustainable tourism in a safe manner.
(ii) Across Asia and the Pacific, governments must pool financial resources to create regional investment funds.
(iii) Strengthening regional cooperation platforms to ensure that all countries receive an equitable number of doses of the vaccine on short notice to everyone everywhere is particularly essential.
(iv) Through ESCAP, we can scale these efforts across the region, working closely with our member states, the private sector and innovators to build a collective financing response to mobilise the necessary additional resources.
(v) Together, we can chart financing strategies of Asia and the Pacific which can enhance societal well being and economic resilience of future pandemics and crises.
|
21 videos|562 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 7th Sept, 2020 - Additional Study Material for UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of the Hindu Editorial Analysis for UPSC exam preparation? |  |
| 2. How can the Hindu Editorial Analysis be utilized effectively for UPSC exam preparation? |  |
| 3. What are the key benefits of reading the Hindu Editorial Analysis for UPSC exam aspirants? |  |
| 4. How can the Hindu Editorial Analysis help in improving answer writing skills for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. Are there any alternative sources for editorial analysis that can be used for UPSC exam preparation? |  |





















