Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Overview of Asexual reproduction with amazing codes and tricks to remember the concept.
Overview of Asexual reproduction with amazing codes and tricks to remember the concept. - Class 10 PDF Download
I'm explaining about the concept of Asexual reproduction which is belongs to the chapter "How do organism reproduce".
SO WHY LATE, LET US START THE CONCEPT...
Asexual reproduction:- It is a type of reproduction where only single parent is involved to produce offspring exactly similar to the parent. (OR) You can define it as "Reproduction which does not involve in fusion of gametes".
In Asexual reproduction, there are mainly six types. They are:-
(1) Fission.
(2) Fragmentation.
(3) Regeneration.
(4) Budding.
(5) Vegetative propagation.
(6) Spore formation.

Tricks to remember the types of Asexual reproduction..
Now, let us discuss all the types of Asexual reproduction one by one..
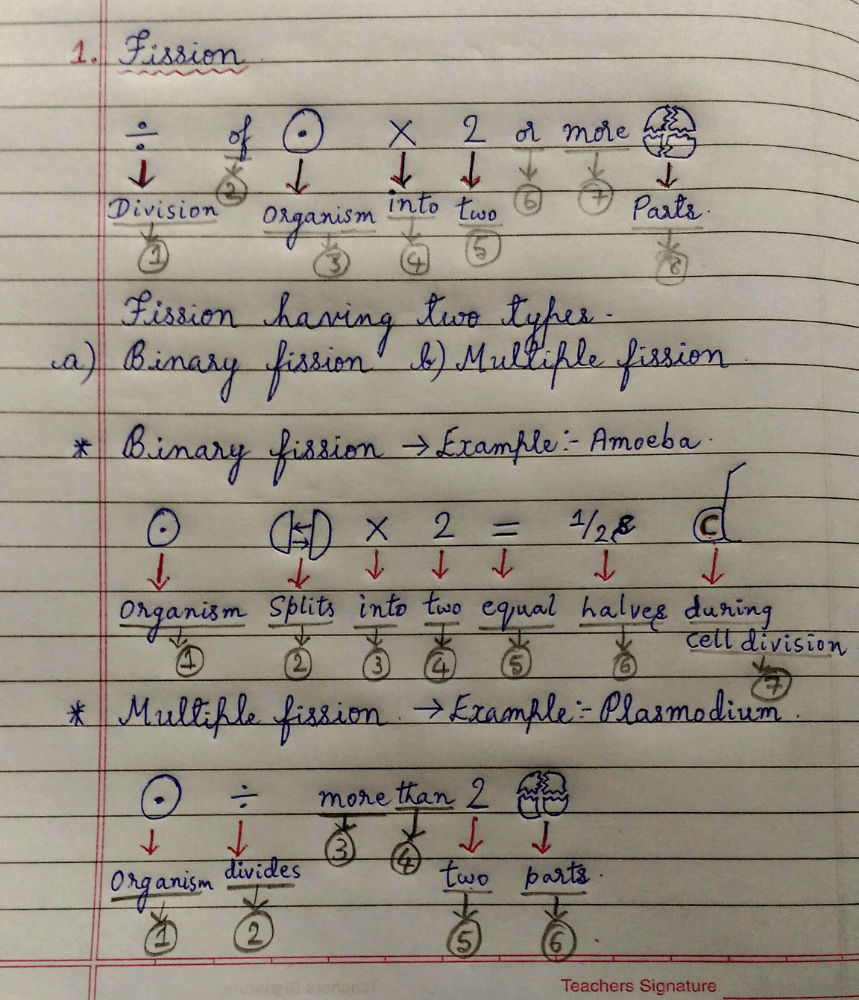
(1) Fission:- Division of organisms into two or more parts, each of which grows into a complete organism.
In Fission, there are mainly two types. They are:-
(a) Binary fission.
(b) Multiple fission.
(a) Binary fission:- Organism splits into two equal halves during cell division which can takes place in any plane.
Examples:- Amoeba, Bacteria.
In Leishmania (causes Kala - Azar) there is a whip like structure, binary fission takes place in definite orientation related to these structures.
Note:- Binary fission takes place when environmental condition is favourable.
(b) Multiple fission:- Nucleus will divide number of times inside the cell and each nuclei gets enclosed by Cytoplasm to form separate individual units. Thanks come out of parent cell after breaking wall of cell. (OR) In simple words, "Organism divides more than two pieces".
Examples:- Plasmodium (causes Malaria) , Paramecium.
Note:- Multiple fission takes place when environmental condition is not favourable.
Tricks to remember the definition of Fission and their types..
(2) Fragmentation:- An individual (organism) breaks into pieces on maturation and each pieces grows into new individual (organism).
Simple multicellular organism like Spirogyra having just connection of cells and cells are not specialized into tissue organs, organ system.
Note:- Advanced organisms are multicellular, but formed from single cell Zygote, which is result of fusion of male and female gamete. This Zygote is capable of growing proliferately and helps to make other cell types under right circumstances.

Tricks to learn the definition of Fragmentation..
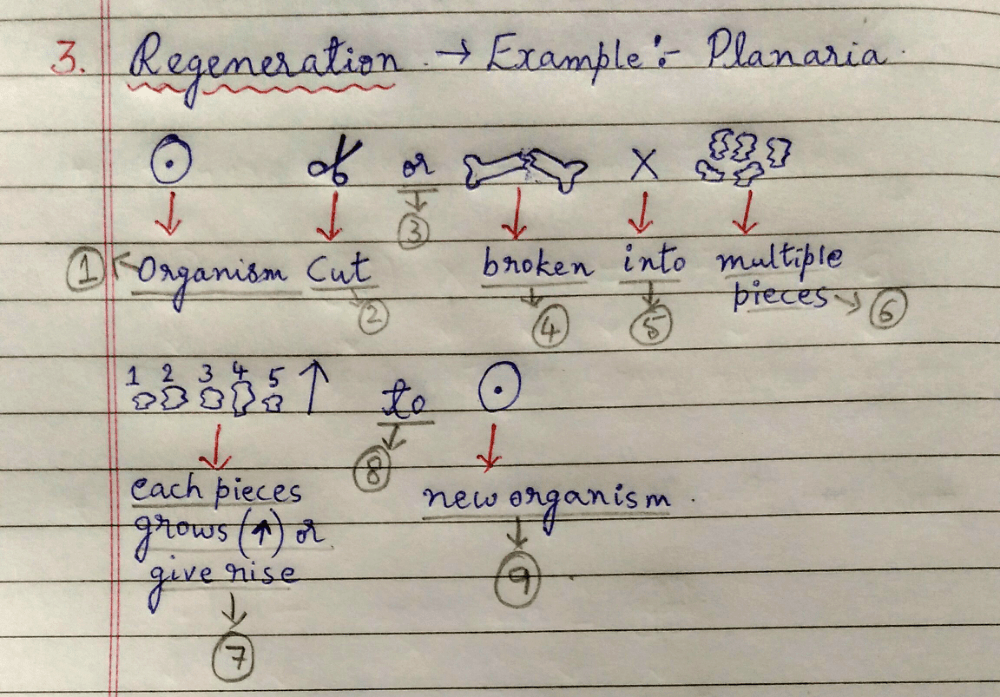
(3) Regeneration:- Organism is cut or broken into multiple pieces, each give rise to new individual (organism).
Examples:- Hydra, Flatworms (Planaria), Tapeworm.
Note:- These organisms consist specialized cell all over the body, which proliferate into large number of cells, among these different cell undergo changes to become various cell type and tissue. This takes place in an organized sequence called "Development".
Development:- Growth of each part of body into entire organism takes place in an organized sequence.
Note:- Regeneration is not same as reproduction. Because, generally, organism would not depend on this method of cutoff to reproduce.
Tricks to learn the definition of Regeneration..
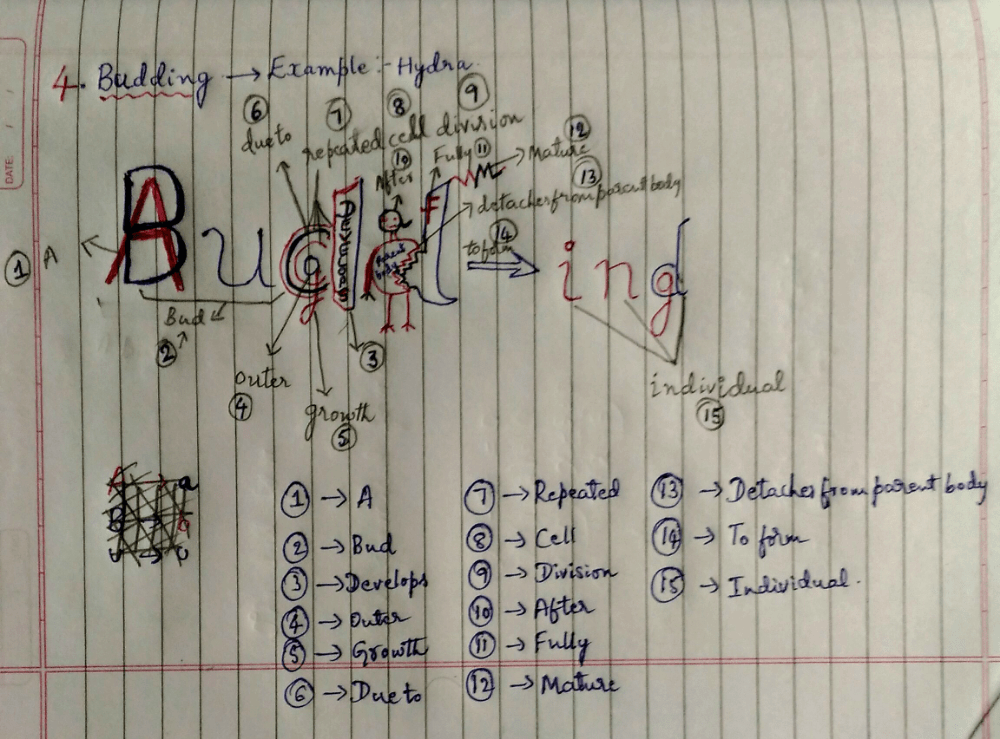
(4) Budding:- A bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site of parent body. These buds are tiny individual and when fully mature, detaches from parent body to form (become) a new individual.
Example:- Hydra.
Tricks to learn the definition of Budding..
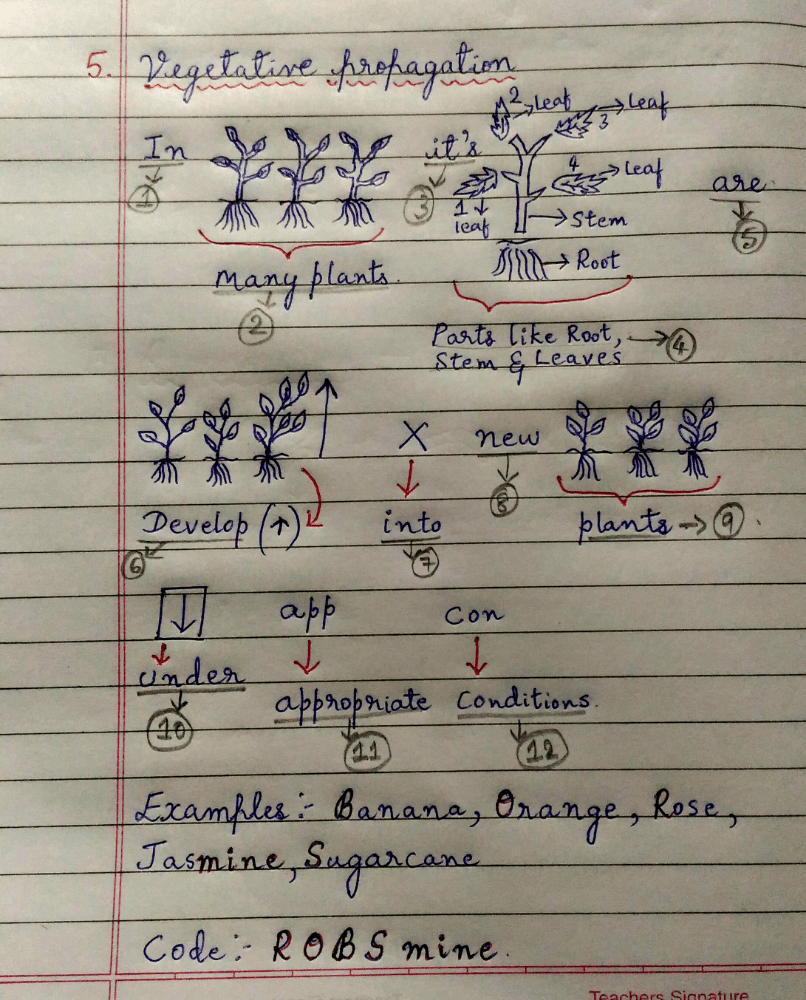
(5) Vegetative propagation:- In many plants, it's parts like root, stem and leaves develop into new plants under appropriate conditions.
Examples:- Banana, Orange, Jasmine, Sugarcane.
Tricks to learn the definition of Vegetative propagation..
Vegetative propagation having two types. They are:-
(1) Natural vegetative propagation.
(2) Artificial vegetative propagation.
(1) Natural vegetative propagation:- Which takes place on their own.
Example:- Root → Sweet Potato.
Stem:- Stem having two types. They are:-
(a) Runners (Outside stem).
Examples:- Strawberry, Grass.
(b) Tubers (Inside stem).
Example:- Onion, Potato.
Leaves:- In Bryophyllum leaves, consist buds in the notches which falls off on the soil to developed to new plant.
(2) Artificial vegetative propagation:- Man made vegetative propagation.
Examples:- Cutting, Layering, Grafting.
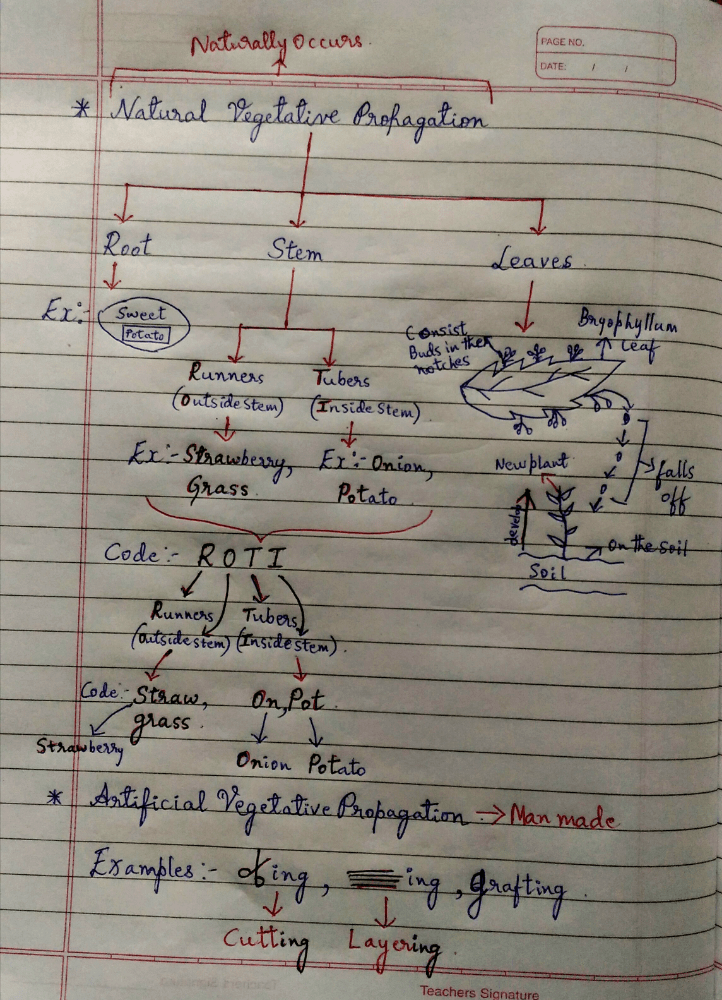
Tricks to learn the concept of Natural vegetative propagation and Artificial vegetative propagation..
Tissue Culture:- The practice of growing plants, plant cells and tissue in a suitable synthetic cultural medium under controlled laboratory condition.
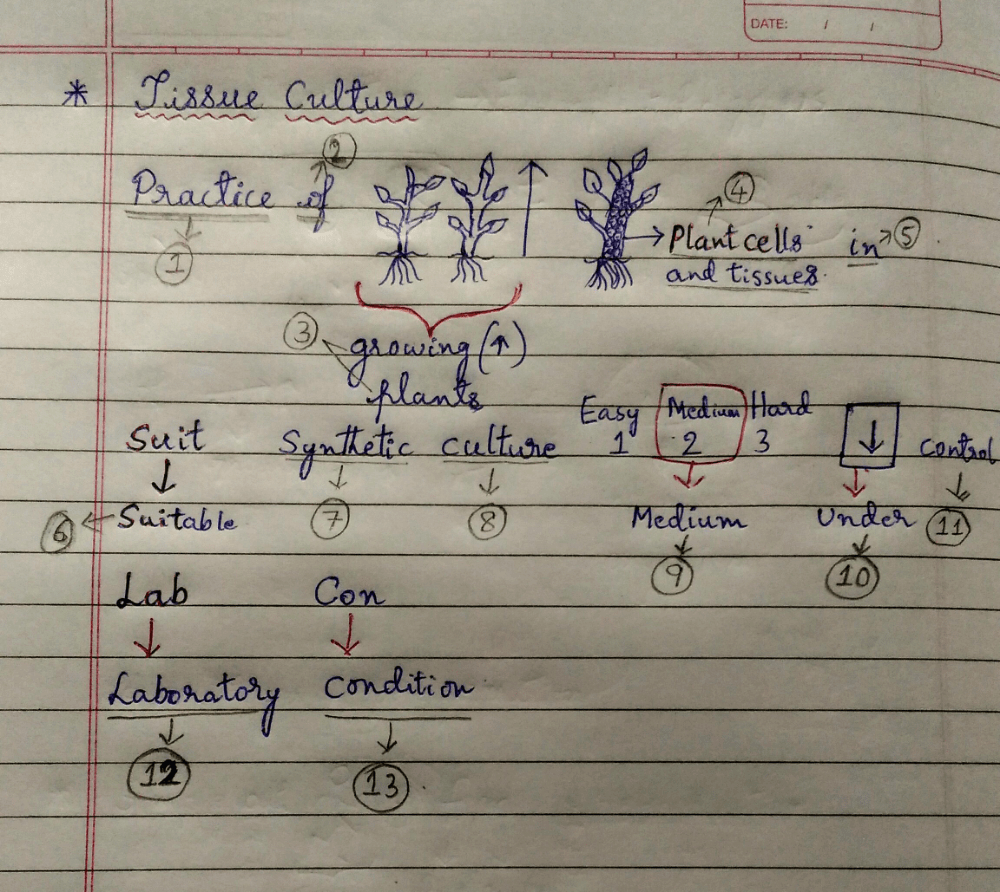
Tricks to remember the definition of Tissue Culture..
Advantages of Vegetative propagation:-
[•] It is only the method of reproduction of seedless plant.
[•] We get fully mature plant in very short time.
[•] Shortcut method for rapid multiplication.
[•] Helps to preserve pure character of parent.
[•] Easy and economial method for multiplication of ornamental plant.
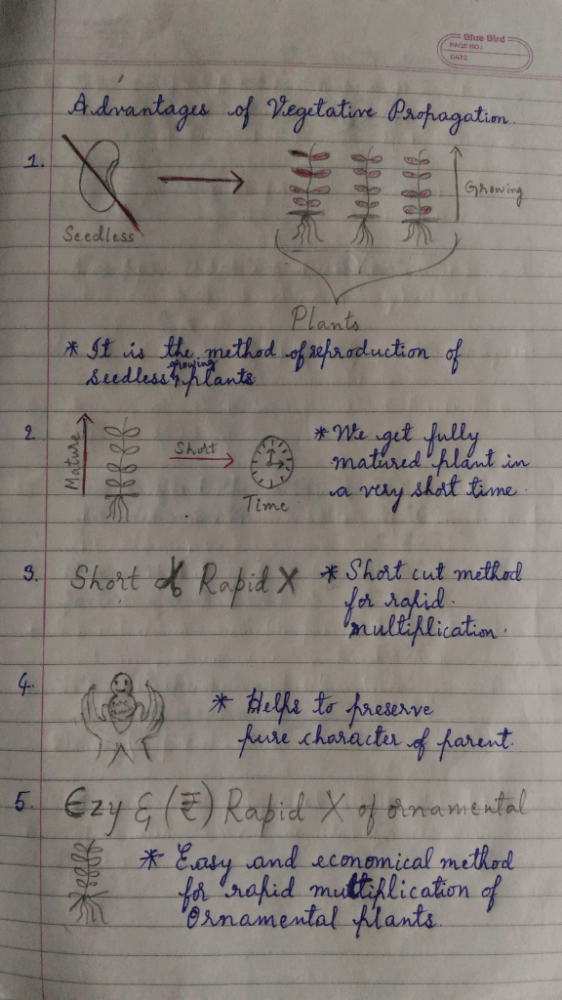
Tricks to remember the Advantages of Vegetative propagation..
(6) Spore formation:- Spores are unicellular bodies in the parent, they are capable of growing into a new individual.
Example:- Rhizopus.

Tricks to learn the definition of Spore formation..
Advantages of Spore formation:-
[•] Simple but fast mode of reproduction.
[•] Being light weight, Spores disperse easily.
[•] Covered by thick wall to survive under unfavorable condition.
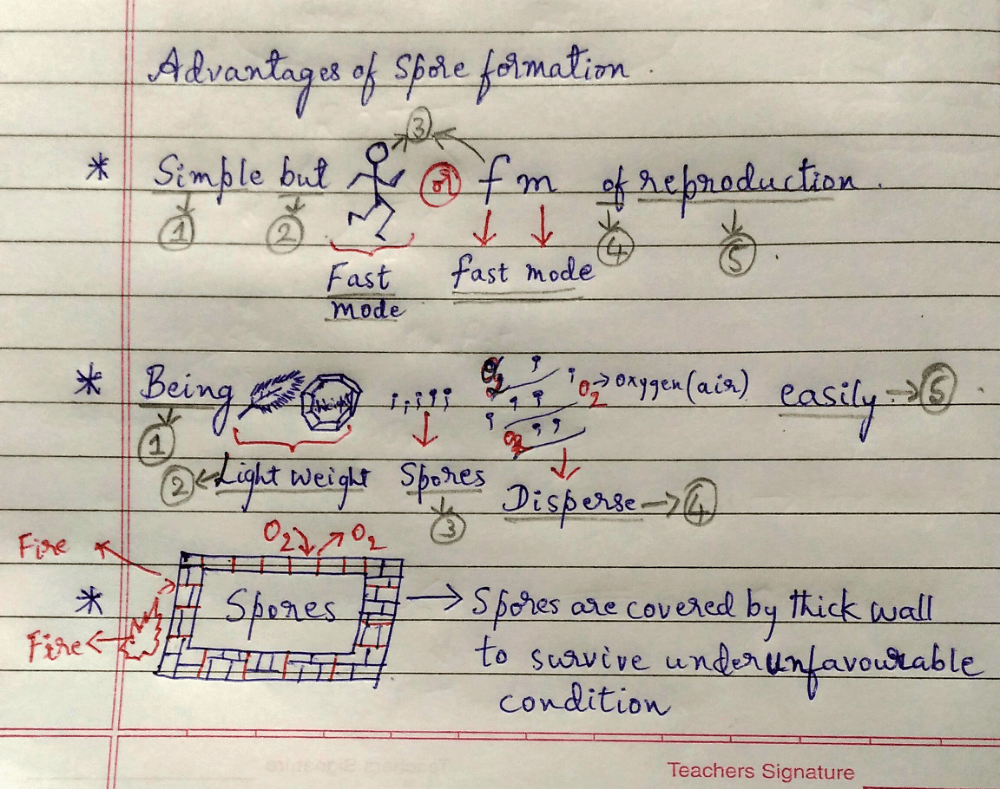
Tricks to learn the Advantages of Spore formation..
Hope this document may helps a lot... Please if you like this document, please... please share this document so that, it may help others and also helps you to understand very well...:-):-).
SO WHY LATE, LET US START THE CONCEPT...
Asexual reproduction:- It is a type of reproduction where only single parent is involved to produce offspring exactly similar to the parent. (OR) You can define it as "Reproduction which does not involve in fusion of gametes".
In Asexual reproduction, there are mainly six types. They are:-
(1) Fission.
(2) Fragmentation.
(3) Regeneration.
(4) Budding.
(5) Vegetative propagation.
(6) Spore formation.

Tricks to remember the types of Asexual reproduction..
Now, let us discuss all the types of Asexual reproduction one by one..
(1) Fission:- Division of organisms into two or more parts, each of which grows into a complete organism.
In Fission, there are mainly two types. They are:-
(a) Binary fission.
(b) Multiple fission.
(a) Binary fission:- Organism splits into two equal halves during cell division which can takes place in any plane.
Examples:- Amoeba, Bacteria.
In Leishmania (causes Kala - Azar) there is a whip like structure, binary fission takes place in definite orientation related to these structures.
Note:- Binary fission takes place when environmental condition is favourable.
(b) Multiple fission:- Nucleus will divide number of times inside the cell and each nuclei gets enclosed by Cytoplasm to form separate individual units. Thanks come out of parent cell after breaking wall of cell. (OR) In simple words, "Organism divides more than two pieces".
Examples:- Plasmodium (causes Malaria) , Paramecium.
Note:- Multiple fission takes place when environmental condition is not favourable.

Tricks to remember the definition of Fission and their types..
(2) Fragmentation:- An individual (organism) breaks into pieces on maturation and each pieces grows into new individual (organism).
Simple multicellular organism like Spirogyra having just connection of cells and cells are not specialized into tissue organs, organ system.
Note:- Advanced organisms are multicellular, but formed from single cell Zygote, which is result of fusion of male and female gamete. This Zygote is capable of growing proliferately and helps to make other cell types under right circumstances.

Tricks to learn the definition of Fragmentation..
(3) Regeneration:- Organism is cut or broken into multiple pieces, each give rise to new individual (organism).
Examples:- Hydra, Flatworms (Planaria), Tapeworm.
Note:- These organisms consist specialized cell all over the body, which proliferate into large number of cells, among these different cell undergo changes to become various cell type and tissue. This takes place in an organized sequence called "Development".
Development:- Growth of each part of body into entire organism takes place in an organized sequence.
Note:- Regeneration is not same as reproduction. Because, generally, organism would not depend on this method of cutoff to reproduce.

Tricks to learn the definition of Regeneration..
(4) Budding:- A bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site of parent body. These buds are tiny individual and when fully mature, detaches from parent body to form (become) a new individual.
Example:- Hydra.

Tricks to learn the definition of Budding..
(5) Vegetative propagation:- In many plants, it's parts like root, stem and leaves develop into new plants under appropriate conditions.
Examples:- Banana, Orange, Jasmine, Sugarcane.

Tricks to learn the definition of Vegetative propagation..
Vegetative propagation having two types. They are:-
(1) Natural vegetative propagation.
(2) Artificial vegetative propagation.
(1) Natural vegetative propagation:- Which takes place on their own.
Example:- Root → Sweet Potato.
Stem:- Stem having two types. They are:-
(a) Runners (Outside stem).
Examples:- Strawberry, Grass.
(b) Tubers (Inside stem).
Example:- Onion, Potato.
Leaves:- In Bryophyllum leaves, consist buds in the notches which falls off on the soil to developed to new plant.
(2) Artificial vegetative propagation:- Man made vegetative propagation.
Examples:- Cutting, Layering, Grafting.

Tricks to learn the concept of Natural vegetative propagation and Artificial vegetative propagation..
Tissue Culture:- The practice of growing plants, plant cells and tissue in a suitable synthetic cultural medium under controlled laboratory condition.

Tricks to remember the definition of Tissue Culture..
Advantages of Vegetative propagation:-
[•] It is only the method of reproduction of seedless plant.
[•] We get fully mature plant in very short time.
[•] Shortcut method for rapid multiplication.
[•] Helps to preserve pure character of parent.
[•] Easy and economial method for multiplication of ornamental plant.
Tricks to remember the Advantages of Vegetative propagation..
(6) Spore formation:- Spores are unicellular bodies in the parent, they are capable of growing into a new individual.
Example:- Rhizopus.

Tricks to learn the definition of Spore formation..
Advantages of Spore formation:-
[•] Simple but fast mode of reproduction.
[•] Being light weight, Spores disperse easily.
[•] Covered by thick wall to survive under unfavorable condition.

Tricks to learn the Advantages of Spore formation..
Hope this document may helps a lot... Please if you like this document, please... please share this document so that, it may help others and also helps you to understand very well...:-):-).
FAQs on Overview of Asexual reproduction with amazing codes and tricks to remember the concept. - Class 10
| 1. What is asexual reproduction and how does it work? |  |
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction where offspring are produced without the involvement of gametes or fertilization. It occurs in many organisms such as bacteria, fungi, plants, and some animals. In this process, a single parent cell or organism divides into two or more identical offspring through various methods like binary fission, budding, regeneration, or spore formation.
| 2. What are the advantages of asexual reproduction? |  |
Asexual reproduction offers certain advantages to organisms. Firstly, it allows for rapid reproduction and population growth since there is no need to find a mate. Secondly, it ensures that favorable traits are passed down to the offspring without the risk of genetic variation. Lastly, asexual reproduction is more energy-efficient compared to sexual reproduction as it does not require the production of gametes or the process of mating.
| 3. What are some examples of asexual reproduction in plants? |  |
Plants have various methods of asexual reproduction. One example is vegetative propagation, where new plants are produced from vegetative parts like stems, roots, or leaves. This can occur through processes such as runners (e.g., strawberry plants), rhizomes (e.g., ginger), or tubers (e.g., potatoes). Another example is apomixis, where seeds are formed without fertilization, seen in some plants like dandelions and dandelion-like flowers.
| 4. How does binary fission work in bacteria? |  |
Binary fission is a common method of asexual reproduction in bacteria. It involves the division of a single parent bacterium into two identical daughter cells. The process begins with DNA replication, where the genetic material is duplicated. The cell then elongates, and the copies of DNA move to opposite ends of the cell. Finally, the cell membrane pinches inward, dividing the cytoplasm and creating two separate daughter cells.
| 5. Can asexual reproduction lead to genetic diversity? |  |
No, asexual reproduction does not directly lead to genetic diversity. Since offspring produced through asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent, there is no introduction of new genetic material. However, mutations can occur over time, leading to some genetic variation within a population. Additionally, genetic diversity can still arise through other mechanisms such as horizontal gene transfer or genetic recombination in organisms that can undergo both asexual and sexual reproduction.
Related Searches



















