PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR MEASUREMENT - Class 11 PDF Download
PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR MEASUREMENT
Physical Property : The property which can be measured without changing the chemical composition of the substance is known as physical property.
Example : mass, volume, density, refractive index, boiling point, melting point etc.
Chemical Property : The property which can be evaluated at the cost of matter itself is known as chemical property.
For example oxygen gas can be verified by burning of flame in presence of oxygen gas.
Units for Measurement
All physical quantities have to be measured. The value of a physical quantity is expressed as the product of the numerical value and the unit in which it is expressed.
Fundamental Units
Fundamental units are those units which can neither be derived from one another nor they can be further resolved into any other units.
- Metric System was based on the decimal system.
- The International System of Units (SI).
The International System of Units (in French Le Systeme International d’Unites– abbreviated as SI) was established by the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM from ConferenceGenerale des Poids at Measures).
The SI system has seven base units.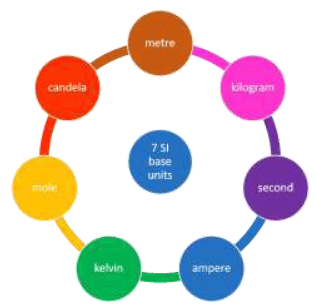
SEVEN BASIC SI UNITS
The SEVEN FUNDAMENTAL UNITS of measurement in S.I. system.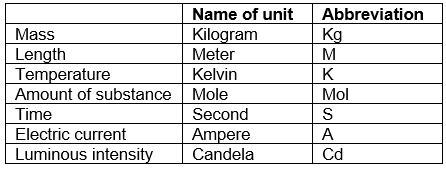
DEFINITIONS OF SI BASE UNITS
- Unit of length Metre : The metre is the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/299 792 458 of a second. Unit of mass kilogram
- The kilogram is the unit of mass; it is equal to the mass of the international prototype of the kilogram.
- Unit of time second : The second is the duration of 9 192 631 770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium-133 atom.
- Unit of electric current ampere : The ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross-section, and placed 1 metre apart in vacuum, would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2 × 10–7 newton per metre of length.
- Unit of thermodynamic kelvin : Is the fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water.
- Unit of amount of substance mole : The mole is the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram of carbon-12; its symbol is “mol.” 2. When the mole is used, the elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such particles.
- Unit of luminous intensity candela : The candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 × 1012 hertz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian.
Derived units
Some quantities are expressed as a function of more than one fundamental units known as derived units. For example velocity, acceleration, work, energy, area, density etc.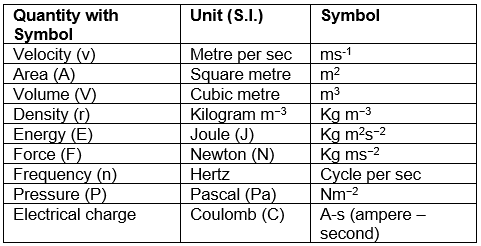
Try Yourself!
Q.1. The temperature at which both the Celsius and Fathrenheit scales will have the same reading is
(a) −10°
(b) − 20°
(c) −30°
(d) − 40°
Ans. (d)
Solution. Suppose both read the same value as “x”
Then as 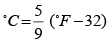
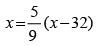 or 9x = 5x - 160
or 9x = 5x - 160
or 4x = −160 or x = − 40°
Q.2. Pressure is determined as force per unit area of surface. The SI unit of pressure, pascal is as shown below:
1Pa = 1Nm−2 If the mass of air at sea level is 1034 g cm-2, the pressure in pascal is
(a) 1.01 x 106
(b) 1.01 x 107
(c) 1.01 x 105
(d) 1.01 x 105
Ans. (c)
Solution. Pressure is the force (i.e., weight) acting per unit area But weight = mg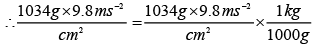
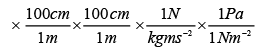
= 1.01332 x 105 Pa ≅ 1.01 x 105 Pa
Q.3. The prefix femto stands for
(a) 109
(b) 10-12
(c) 10-15
(d) 105
Ans. (c)
Solution. 1 femto = 10-15
Q.4. N kg-1 is the unit of
(a) Momentum
(b) Velocity
(c) Pressure
(d) Acceleration
Ans. (d)
Solution. Force = mass x acceleration.
Hence, a = F / m = N / kg = N kg-1.
Q.5. Which of the following is correct?
(a) 1 L = 1 dm3
(b) 1 L = 10 dm3
(c) 10 L = 1 dm3
(d) 1 L = 1 m3
Ans. (c)
Solution. I L = 1000 cm3 = 1000 (0.1dm)3 =1dm3.
Q.6. The units, nanometer, Fermi, Angstrom and attometre, Arrangement in decreasing order are expressed as
(a) Angstrom, nanometer, Fermi, attometre
(b) Fermi, attometre, angstrom, nanometer
(c) Nanometer, angstrom, Fermi, attometre
(d) Attometre, angstrom, Fermi, nanometer
Ans. (c)
Solution. 1 nm = 10-9 m, 1 fermi =10-15 m,
1 A° = 10-10 m, 1 attometre = 10-18 m.
Q.7. Dimensions of pressure are same as that of
(a) Energy
(b) Force
(c) Energy per unit volume
(d) Force per unit volume
Ans. (c)
Solution. 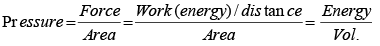
FAQs on PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR MEASUREMENT - Class 11
| 1. What are the properties of matter? |  |
| 2. How are physical properties of matter measured? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of chemical properties of matter? |  |
| 4. How can we determine the melting point of a substance? |  |
| 5. What is density and how is it measured? |  |














