Shankar IAS Summary: Environmental Pollution | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Introduction
- Defined as 'an addition or excessive addition of certain materials to the physical environment (water, air and lands), making it less fit or unfit for life'.
- Pollutants are the materials or factors, which cause adverse effect on the natural quality of any component of the environment.
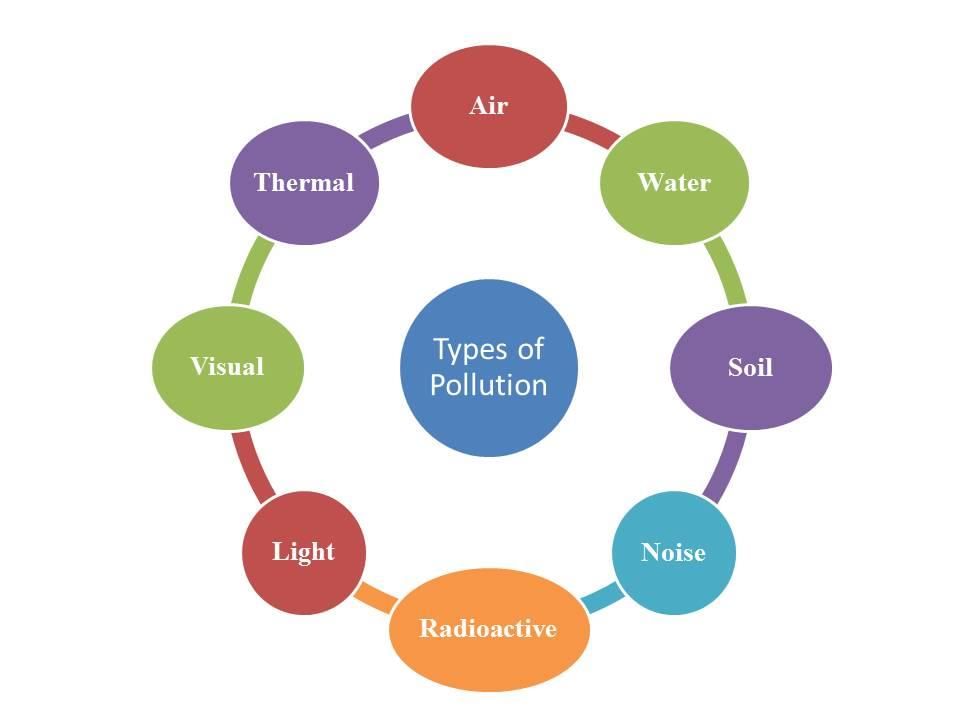
Classifications
- According to the form in which they persist after release into the environment.
(i) Primary pollutants: These persist in the form in which they are added to the environment. Example: DDT, plastic.
(ii) Secondary Pollutants: These are formed by interaction among the primary pollutants. For example, peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) is formed by the interaction of nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons. - According to their existence in nature.
(i) Quantitative Pollutants: These occur in nature and become pollutant when their concentration reaches beyond a threshold level. Example: carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide.
(ii) Qualitative Pollutants: These do not occur in nature and are man-made. Example: fungicides, herbicides, DDT etc. - According to their nature of disposal.
(i) Biodegradable Pollutants: Waste products, which are degraded by microbial action. Example: sewage.
(ii) Non-biodegradable Pollutants: Pollutants, which are not decomposed by microbial action. Example: plastics, glass, DDT, salts of heavy metals, radioactive substances etc. - According to origin
(i) Natural
(ii) Anthropogenic
Air Pollution
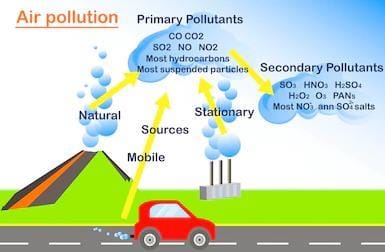
Aggravated because of four developments: Increasing traffic, growing cities, rapid economic development, and industrialization contamination of air by the discharge of harmful substances.
Major air pollutants and their sources
1. Carbon monoxide (CO)
- It is a colourless, odourless gas that is produced by the incomplete burning of carbon - based fuels including petrol, diesel, and wood.
- It is also produced from the combustion of natural and synthetic products such as cigarettes.
- It lowers the amount of oxygen that enters our blood. It can slow our reflexes and make us confused and sleepy.
2. Carbon dioxide CO2
- Principe greenhouse gas
3. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC)
- Gases that are released mainly from air-conditioning systems and refrigeration.
- When released into the air, CFCs rise to the stratosphere, where they come in contact with few other gases, which lead to a reduction of the ozone layer that protects the earth from the harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun.
4. Lead
- Present in petrol, diesel, lead batteries, paints, hair dye products, etc.
- Affects children in particular.
- Cause nervous system damage and digestive problems and, in some cases, cause cancer.
- Occurs naturally in the upper layers of the atmosphere.
- At-the ground level, it is a pollutant with highly toxic effects.
- Vehicles and industries are the major source of ground-level ozone emissions.
- Ozone makes our eyes itch, burn, and water. It lowers our resistance to cold and pneumonia.
6. Nitrogen oxide (Nox)
- Causes smog and acid rain. It is produced from burning fuels including petrol, diesel, and Coal.
- Nitrogen oxide can make children susceptible to respiratory diseases in winters.
7. Suspended particulate matter (SPM)
- Consists of solids in the air in the form of smoke, dust, and vapour that can remain suspended for extended periods
- The finer of these particles when breathed in can lodge in our lungs and cause lung damage and respiratory problems.
8. Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
- A gas produced from burning coal, mainly in thermal power plants.
- Some industrial processes, such as production of paper and smelting of metals, produce sulphur dioxide.
- A major contributor to smog and acid rain.
- Sulphur dioxide can lead to lung diseases
9. Smog
- A combination of the words fog and smoke. Smog is a condition of fog that had soot or smoke in it.
- Interaction of sunlight with certain chemicals in the atmosphere.
- Primary components of photochemical smog is ozone.
- Oxides, and sunlight. It is formed when pollutants released from gasoline.
- Ozone is formed through a complex reaction involving hydrocarbons, nitrogen diesel- powered vehicles and oil-based solvents react with heat and sunlight from biofuels, the four most serious pollutants are particulates, carbon monoxide, polycyclic organic matter, and formaldehyde.
Pollutants
1. Volatile organic compounds
- The main indoor sources are perfumes, hair sprays, furniture polish, glues, air fresheners, moth repellents, wood preservatives, and other products.
- Biological pollutants - It includes pollen from plants, mite, and hair from pets, fungi, parasites, and some bacteria.
2. Formaldehyde
It is a gas that is emitted naturally by the soil. Due to modern houses having poor ventilation, it is confined inside the house and causes lung cancers.
Fly Ash
Ash is produced whenever combustion of solid material takes place.
- Aluminium silicate (in large amounts)
- Silicon dioxide (SiO2) and
- Calcium oxide (CaO)
Fly ash particles are oxide rich and consist of silica, alumina, oxides of iron, calcium, and magnesium and toxic heavy metals like lead, arsenic, cobalt, and coppers.
Policy measures of MoEF
- The Ministry of Environment and Forests vide its notification in 2009, has made it mandatory to use Fly Ash based products in all construction projects, road embankment works and low lying land filling works within 100 kms radius of Thermal Power Station.
- To use Fly Ash in mine filling activities within 50 kms radius of Thermal Power Stations.
- Arresters: These are used to separate particulate matters from contaminated air.
- Scrubbers: These are used to clean air for both dusts and gases by passing it through a dry or wet packing material.
Government Initiatives
- In India, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has been executing a nationwide programme of ambient air quality monitoring known as National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP).
- The National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP) is undertaken in India:
(i) To determine status and trends of ambient air quality.
(ii) to ascertain the compliance of NAAQS.
(iii) to identify non-attainment cities.
(iv) to understand the natural process of cleaning in the atmosphere; and
(v) to undertake preventive and corrective measures. - Annual average concentration of SOx levels are within the prescribed National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS).
- National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAas) were notified in the year 1982, duly revised in 1994 based on health criteria and land uses.
- The NAAQS have been revisited and revised in November 2009 for 12 pollutants, which include, Sulphur dioxide (S02), nitrogen dioxide (N02), particulate matter having size less than 10 micron.
- (PM 10),particulate matter having size less than 2.5micron (PM2.5), ozone, lead, carbon monoxide (CO), arsenic, nickel, benzene, ammonia, and. Benzopyrene.
Water Pollution
- Addition of certain substances to the water such as organic, inorganic, biological, radiological, heat, which degrades the quality of water so that it becomes unfit for use.
- Putrescibility is the process of decomposition of organic matter present in water by microorganisms using oxygen.
- Water having DO (dissolved oxygen) content below 8.0 mg/L may be considered as contaminated. Water having DO content below. 4.0 mg/L is considered to be highly polluted.
- Water pollution by organic wastes is measured in terms of Biochemical Oxygen Demand-(BOD). BOD is the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by bacteria in decomposing the organic wastes present in water.
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is a slightly better mode used to measure pollution load in water. It is the measure of oxygen equivalent to the requirement of oxidation of total organic matter (i.e. biodegradable and non- biodegradable) present in water.
- A crippling deformity called Minamata disease due to consumption of fish captured from mercury contaminated Minamata Bay.
- Water contaminated with cadmium can cause itai-itai disease also called ouch-ouch disease (a painful disease of bones and joints) and cancer of lungs and liver.
- The compounds of lead cause anaemia, headache, loss of muscle power and bluish line around the gum.
- Excess nitrate in drinking water reacts with hemoglobin to form non -functional methaemoglobin, and impairs oxygen transport. This condition is called methemoglobinemia or blue baby syndrome.
- Over exploitation of ground water may lead to leaching of arsenic from soil and rock sources and contaminate ground water. Chronic exposure to arsenic causes black foot disease. It also causes diarrhoea, -peripheral neuritis, hyperkeratosis and also lung and skin cancer.

Soil Pollution
- Industrial waste includes chemicals such as mercury, lead, copper, zinc, cadmium, cyanides, thiocynates, chromates, acids, alkalies, organic substances etc.
- Four R’s: Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle.
Noise Pollution
- Sound is measured in decibels (dB). An increase of about 10 dB is approximately double the increase in loudness.
- A person's hearing can be damaged if exposed to noise levels over 75 dB over a prolonged period of time.
- The World Health Organization recommends that the sound level indoors should be less than 30 dB .
- Noise Level Monitoring - Noise Pollution (Control and Regulation) Rules, 2000 define ambient noise levels for various areas as follows-
(i) Industrial Area- 75DB to 70Db (Day time-6 am to 10 pm and night time 10pm to 6am..75 is day time and 70 is night time)
(ii) Commercial Area- 65 to 55
(iii) Residential Area- 55 to 45
(iv) Silence Zone- 50 to 40 - The Government of India on Mar 2011 launched a Real time Ambient Noise Monitoring Network.
- Under this network, in phase- 1, five Remote Noise Monitoring Terminals each have been installed in different noise zones in seven metros (Delhi, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai and Lucknow).
- In Phase II another 35 monitoring stations will be installed in the same seven cities.
- Phase III will cover installing 90 stations in 18 other cities.
- Phase-II cities are Kanpur, Pune, Surat, Ahmedabad, Nagpur, Jaipur, Indore, Bhopal, Ludhiana, Guwahati, Dehradun, Thiruvananthapuram, Bhubaneswar, Patna, Gandhinagar, Ranchi, Amritsar and Raipur.
- Silence Zone is an area comprising not less than 100 metres around hospitals, educational institutions, courts, religious places or any other t area declared as such by a competent authority.
Radio Active Pollution
- Non-ionising radiations affect only those components which absorb them and have low penetrability. They include short-wave radiations such as ultraviolet rays, which forms a part of solar radiation. Sunburns is due to these radiation
- Ionising radiations have high penetration power & cause breakage of macro molecules They include X-rays, cosmic rays and atomic radiations -(radiations emitted by radioactive elements
- Alpha particles, can be blocked by a piece of paper and human skin. Beta particles can penetrate through skin, while can be blocked by some pieces of glass
- Gamma rays can penetrate easily to human skin and damage cells on its way through, and metal.
- Reaching far, and can only be blocked by a very thick, strong, massive piece of concrete radium-224, uranium-238, thorium-232, potassium-40, carbon-14, etc.
- The nuclear arms use uranium-235 and plutonium-239 for fission and hydrogen or lithium as fusion material
- The radio nuclides with long half-time are the chief source of environmental radioactive pollution.
E-Waste
- E-waste is not hazardous if it is stocked in safe storage or recycled by scientific methods or transported from one place to the other in parts or in totality in the formal sector. The e-waste can be considered hazardous if recycled by primitive methods
- Survey was carried out by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) during 2005
- In India, among top ten cities; Mumbai ranks first in generating e-waste followed by Delhi, Bangalore, Chennai, Kolkata, Ahmadabad, Hyderabad, Pune, Surat and Nagpur.
Solid Waste
- The discarded (abandoned or considered waste-like) materials in irrigation return flows or industrial discharges, Conventional plastics have been associated with reproductive problems in both.
- Does not include solid or dissolved materials in domestic sewage, or solid or dissolved humans and wildlife.
 Solid Waste Management
Solid Waste Management - Dioxin (highly carcinogenic and toxic) by-product of the manufacturing process is one of the chemicals believed to be passed on through breast milk to the nursing infant.
- Burning of plastics, especially PVC releases this dioxin and also furan into the atmosphere.
- Pyrolysis-It is a process of combustion in absence of oxygen or the material burnt under controlled atmosphere of oxygen. It is an alternative to incineration. The gas and liquid thus obtained can be used as fuels.
- Helps Small and Medium Industrial Clusters in waste minimization in their industrial plants, assisted by the World Bank with the Ministry of Environment and Forests acting as the nodal ministry.
- Being implemented with the assistance of National Productivity Council (NPC), New Delhi.
- Aims to realise the objectives of the Policy Statement for Abatement of Pollution (1992), which states that the government should educate citizens about environmental risks, the economic and health dangers of resource degradation and the real economic cost of natural resources.
Bioremediation
The use of microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) to degrade the environmental contaminants into less toxic forms. Phytoremediation is use of plants to remove contaminants from soil and water.
A water remediation technique that involves the uptake of contaminants by plant roots. Used to reduce contamination in natural wetlands and estuary areas.
Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 is a robust measure for environmental protection.
- Rooted in Article 48A and Article 51A of the Indian Constitution.
- The Central Government is empowered to prevent and control pollution, establishing effective mechanisms.
- Authorization for collecting samples as evidence of environmental offenses.
- Special procedure for handling hazardous substances.
- Relaxation of "Locus Standi," allowing common citizens to approach the court with a 60-day notice.

- Central Government can issue directives for industry operation, prohibition, closure, or regulation.
- Authority to stop or regulate the supply of electricity, water, or services without a court order.
- Stringent penal provisions, include imprisonment up to five years, fines, and daily penalties for persistent violations.
- The immunity granted to government officers for actions under the Act.
- Civil Courts are barred from entertaining suits related to actions by the Central Government or statutory authorities.
- Supremacy of the Act's provisions over anything inconsistent in other enactments, excluding the Act itself.
Environment Protection Act Amendment 2022
- The provision for imprisonment is set to be replaced with a requirement for fines as an alternative.
- The proposed fines, serving as an alternative to imprisonment, are substantially increased, ranging from 3 lakh to 5 crore rupees for contraventions of the Act.
- However, severe violations resulting in grievous injury or loss of life will subject offenders to the provisions of the Indian Penal Code, 1860, along with Section 24 of the EP Act.
- This shift away from prison terms also extends to the Air Act, primarily addressing air pollution, and the Water Act, addressing violations related to water bodies.
- An "adjudication officer" will be appointed to determine penalties in cases of environmental violations, such as failing to submit reports or provide requested information.
- The funds collected as penalties will be directed to an "Environmental Protection Fund."
 Globalization
Globalization
Thermal Pollution
Thermal pollution refers to the alteration in the temperature of a natural aquatic environment, either an increase or decrease, induced by human activities. This has emerged as a growing and contemporary environmental concern, driven by the pervasive influence of globalization.
Thermal pollution occurs through practices such as discharging hot water from factories and power plants or clearing trees and vegetation that provide shade to streams, allowing sunlight to elevate water temperatures. Additionally, the release of cold water can have a cooling effect.
Similar to other types of water pollution, thermal pollution spreads, impacting numerous lakes, rivers, and water bodies across different regions of the world.
Major sources
Power plants generating electricity from fossil fuels utilize water as a cooling agent in industrial facilities, contributing to shoreline deforestation and soil erosion.
Ecological Effects — Warm Water
- Temperature changes impact organisms by decreasing oxygen supply and affecting ecosystem composition.
- Warm water, with reduced oxygen levels, alters the decomposition of organic matter and may lead to the dominance of less desirable blue-green algae.
- Increased metabolic rates in aquatic animals result in higher food consumption, potentially causing food source shortages and population decreases.
 Blue-green Algae
Blue-green Algae
- Environmental changes may prompt organism migration and competition for resources, compromising food chains and reducing biodiversity.
- Even slight temperature changes can adversely affect organism metabolism and cellular biology.
- Warm water can affect plant growth, leading to species overpopulation, algae blooms, reduced oxygen levels, and nutrient enrichment similar to eutrophication.
- Higher temperatures can denature enzymes, impacting aquatic organisms' ability to break down lipids and causing malnutrition.
Ecological Effects — Cold Water
- Thermal pollution can occur when very cold water is released from reservoirs into warmer rivers, affecting fish, macroinvertebrates, and river productivity.
 Reservoir
Reservoir
Control Measures
- Instead of discharging heated water directly into lakes and streams, power plants and factories can pass it through cooling towers or ponds for evaporation cooling.
- Power plants can be designed or retrofitted for efficiency to minimize waste heat production.
- Cogeneration involves using excess heat energy from electricity generation in other manufacturing processes or for heating in nearby buildings.
- To prevent thermal pollution due to devegetation, it is advised to maintain vegetation along streams and shorelines.
- Efforts to control erosion also contribute to water clarity, helping to mitigate thermal pollution.
Light Pollution
Causes
- Most sources of visiblelight, except lasers, emit light in various directions, potentially causing scattering into the atmosphere.
 Light Pollution
Light Pollution
- In urban environments, almost all surfaces can reflect light, causing downward-directed light to bounce back upwards, exacerbating nighttime light pollution.
- Recent research indicates that artificiallight not of natural origin has been annually increasing the overall brightness of the night sky (skyglow) by approximately 9.2-10%.
Light pollution in India
- India, according to recent studies, has the lowest percentage among G20 nations, with approximately 19.5% of its population residing in areas where skyglow obscures the view of the Milky Way and prevents human eyes from adapting to darkness.
Effects
- Stimulates cone cells in human eyes that activate in well-lit environments or during the day.
- Light pollution can disrupt circadianrhythms and melatonin production, potentially leading to sleep disorders and health issues, including an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Poses a serious threat to nocturnal animals, migrating creatures, and cross-light hatchery animals and their physiology.
- Skyglow disrupts insect behavior, extending hunting time for insect predators. Artificial nighttime light exposure results in the failure of clownfisheggs to hatch, leading to offspring death. Guidelines adopted by the Convention on Migratory Species parties in 2020 aim to address this issue.
 Clownfish
Clownfish
Control measures
- Use light only when and where necessary.
- Use only the necessary amount of light.
- Use energy-efficient bulbs.
- Use bulbs with the right spectral power distributions.
- The "Outdoor Lighting Code" in the United Kingdom aims to reduce light pollution by encouraging the use of lighting that is only as bright and as long as necessary for the task.
Plastic Pollution
- The marine environment covers 70% of Earth's surface, a vital asset in the biosphere.
- Nearly 1.5 million known species, with a quarter of a million residing in oceans.
- Almost 50% of global primary production occurs in the upper layers of seawater.
- Seafood constitutes 20% of the world's protein in global diets.
- The health of the marine food web and fisheries relies on the long-term viability of autotrophic algae (phytoplankton) and zooplankton.
- Plastic pollution is a significant contemporary threat to the marine environment.
- Increased plastic use leads to negativeenvironmental impacts.
- Plastic pollution can interfere with plankton species, affecting the foundation of the food web.
- Adverse effects on other organisms disrupt the delicate balance in the marineecosystem.
 Marine Ecosystem
Marine Ecosystem
Plastics as a Waste Material in the Marine Environment
- Annual estimation of plastic waste introduced into the marine environment is unavailable.
- Plastic waste primarily results from fishing-related activities and non-point source influx from beaches.
- Differences in the fate of plastics in the ocean environment compared to on land: a) UV-induced photo-oxidative degradation is slower at sea. b) Lack of easy retrieval, sorting, and recycling mechanisms for plastic waste in the ocean.
- Extended lifetimes for plastics at sea due to these factors.
- Accumulation of plastic waste in the world's oceans, with potential disintegration into microparticulate debris.
- Impact of microparticles on Antarctic krill and zooplankton, with ingestion rates dependent on particle concentration.
Impact of Plastics in the Marine Environment
- Plastics are bio-inert, not conventionally toxic, but can concentrate toxic and non-toxic organic compounds from seawater.
- Plastic-related distress is documented in over 250 species worldwide, particularly focused on larger surface water and beach species.
- Negligible research by government agencies or the plastics industry on plastic issues in the marine environment.
 Beach Species
Beach Species
Plastics as a Waste Material in Land Environment
- Problems with uncollected plastic waste, include choking of drains, illness in animals, and non-biodegradable nature.
- The presence of additives and chemicals in plastics poses health and groundwater pollution risks.
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016: 15,000 tonnes of plastic waste generated daily, with 6,000 tonnes uncollected.
- Lack of an eco-friendly alternative to plastic; the challenge is to improve plastic waste management systems.
Salient Features of Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016
- Increase the minimum thickness of plastic carry bags for easier collection and recycling.
- Promote the use of plastic waste for road construction or energy recovery.
- Extension of rules to rural areas with responsibility given to Gram Panchayat.
- Waste generators, including individuals and industries, must segregate and manage plastic waste.
- Organizers of public events are responsible for waste management from their events.
- Regulation of plastic sheets for packaging, ensuring proper collection and channelization.
- Introduction of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for producers and brand owners.
- State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) to regulate plastic bags and packaging.
- Retailers and street vendors are assigned the responsibility not to provide non-compliant plastic bags.
- Restriction on the availability of plastic carry bags to registered vendors.

Amendment Rules, 2018
- Phasing out of Multilayered Plastic (MLP) for non-recyclable, non-energy recoverable, or with no alternative use.
- The central registration system for producer/importer/brand owner.
- National registry for producers with a presence in more than two states, state-level registration for smaller producers/brand owners.
- Omission of explicit pricing of carry bags.
Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021
- Prohibition of manufacture, import, stocking, distribution, sale, and use of certain single-use plastics from 1st July, 20.
- Increase in thickness of plastic carry bags from fifty microns to seventy-five microns in September 2021 and to one hundred and twenty microns in December 2022.
- Collection and management of plastic packaging waste through Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR).
- The legal force is given to guidelines for EPR through Plastic Waste Management AmendmentRules, 2021.
Environmental Pollution and Health
First: Pollution Inventory and Health Impact
- Assess the relative contribution of sources in a coherent health protection framework.
- Prioritize sources leading to greater exposure to health-damaging pollutants, not just based on emission quantities.
- Vehicles globally contribute significantly to particulates in cities.
Second: Exposure Levels and Health Risks
- People are exposed to higher health-damaging pollutants than ambient conditions.
- Each breath contains three to four times more pollutants than ambient air concentration.
- Highest exposure to vehicular fumes occurs on roads and within 500 meters.
 Environmental Pollution
Environmental Pollution
Third: Multi-Pollutant Approach for Health Benefits
- People are exposed to a mixture of pollutants with serious health impacts.
- Benefits increase when pollution sources are regulated for multi-pollutants.
- Delhi's air contains particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, ozone, and toxins.
- Focus on diesel emissions, a class one carcinogen linked to lung cancer.
Fourth: Disconnect Between Policies and Health Realities
- Air quality policies are disconnected from reported health realities.
- India is undergoing a rapid health transition with a rising burden of chronic diseases.
- Chronic diseases like cancer, stroke, and lung diseases are strongly influenced by air pollution.
- Policies must align with the health sector's reported reality for effective solutions.
Acid Rain
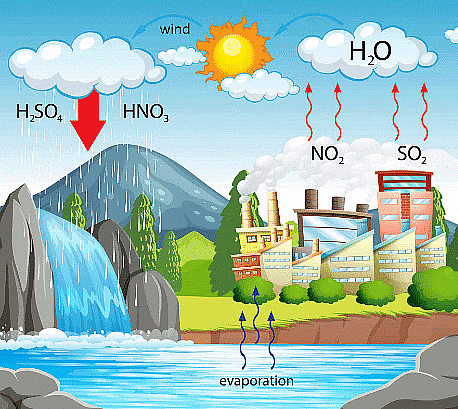
Acid rain refers to precipitation that has undergone acidification, resulting from the interaction of sulfur and nitrogen oxides with atmospheric moisture. With a pH below 5.6, acid rain harms ecosystems, particularly lakes, streams, and forests, impacting the flora and fauna residing in these environments.
 Acid Rain
Acid Rain
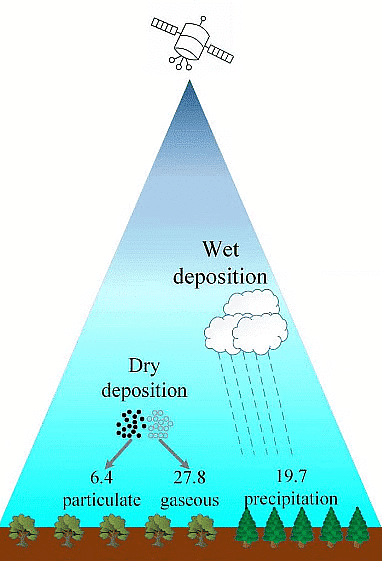
Types of Acid Deposition
"Acid rain" is a comprehensive term encompassing a blend of wet and dry deposition from the atmosphere.
A. Wet Deposition
- Acidic chemicals in the air, when carried to wet weather regions, can precipitate as rain, snow, fog, or mist.
- As this acidic water moves over and through the ground, it impacts a variety of plants and animals.
- The effects' intensity depends on factors such as water acidity, soil chemistry, buffering capacity, and the reliance of living organisms on the water.
- Precipitation removes atmosphericgases and particles through rain-out (particles incorporated into cloud drops) and washout (materials swept down by rain or snow).
B. Dry Deposition
- In dry-weather areas, acid chemicals may mix with dust or smoke and fall to the ground via dry deposition, adhering to surfaces like the ground, buildings, vegetation, and vehicles.
- Rainstorms can wash dry-deposited gases and particles from surfaces through runoff, making the mixture more acidic.
- Approximately half of atmospheric acidity returns to Earth through dry deposition.
The pH Scale
- The pH scale gauges a solution's acidity or basicity (alkalinity), ranging from 0 to 14.
- A pH of 7 is neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is basic.
- Devised in 1909, it's a logarithmicindex for hydrogen ion concentration.
- pH values decrease as hydrogenion levels increase.
- A solution with pH 4 is ten times more acidic than pH 5, and a hundred times more acidic than pH 6.
- Although the pH range is typically stated as 0 to 14, theoretically, lower and higher values are possible.
Sources of Compounds Causing Acid Rain
A. Sulphur
(i) Natural Sources:
- Seas and oceans.
- Volcanic eruptions.
- Biological processes in the soil, such as the decomposition of organic matter.
(ii) Man-made Sources:
- Burning of coal (contributing to 60% of SO) and petroleum products (30% of SO).
- Smelting of metal sulfideores for obtaining pure metals.
- Industrial production of sulfuric acid in metallurgical, chemical, and fertilizer industries.

B. Nitrogen Natural Sources:
- Lightning.
- Volcanic eruptions.
- Biological activity.
Anthropogenic Sources:
- Forest fires.
- Combustion of oil, coal, and gas.
C. Formic Acid
- Biomass burning during forestfires releases formic acid (HCOOH) and formaldehyde (HCHO) into the atmosphere.
- A significant portion of formaldehyde undergoes photo-oxidation, forming formic acid.
Other Acids
- Chlorine.
- Phosphoric acid.
- Hydrochloric acid (from smokestacks).
- Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide from automobiles can become carbonic acid.
Common Characteristics of Areas Prone to Acid Rain
- Concentrated in the industrialized belt of the northern hemisphere.
- Often upland and/or mountainous, well-watered by rain and snow.
- Abundance of water, with numerous lakes, streams, and extensive vegetation-covered land.
- Upland areas often have thin soils and glaciated bedrock.
 Great Smoky MountainsWorld Scenario
Great Smoky MountainsWorld Scenario
- Regions in Scandinavia, Canada, the North and Northeast United States, and Northern Europe, including parts of West Germany and upland Britain, share these characteristics.
- Acid rain hot spots across the Atlantic include Nova Scotia, Southern Ontario, Quebec in Canada, the AdirondackMountains in New York, the Great Smoky Mountains, parts of Wisconsin, Minnesota, and the ColoradoRockies in the US.
In India
- Bombay reported the first instances of acid rain in 1974.
- Acid rain cases are now reported in metropolitan cities.
- Annual SO2emissions in India have nearly doubled in the last decade due to increased fossil fuel consumption.
- Lowering of soilpH is noted in northeastern India, coastal Karnataka and Kerala, parts of Orissa, West Bengal, and Bihar.
Chemistry of Acid Rain
Six fundamental steps contribute to the formation of acid rain:
- The atmosphere receives sulfur and nitrogen oxides from both natural and man-made sources.
- Some of these oxides precipitate directly to the ground as dry deposition, either near the source or at a distance.
- Sunlight induces the formation of photooxidants, including ozone, in the atmosphere.
- These photo-oxidants react with sulfur and nitrogen oxides, resulting in the production of H2SO4 and HNO3 through oxidation.
- The sulfur and nitrogen oxides, photo-oxidants, and other gases (such as NH3) are involved in the process.
- Acid rain, containing ions of sulfate, nitrate, ammonium, and hydrogen, falls as wet deposition.
 Infertile Soil
Infertile Soil
Impact of Acid Rain
A. Soil
- Exchange between hydrogen ions and nutrient cations like potassium and magnesium causes the leaching of nutrients, leading to soil infertility.
- Decreased respiration of soil organisms is observed.
- An increase in ammonia due to decreased nutrients reduces the rate of decomposition.
- The nitrate level in the soil is found to decrease.
- Acid rain impact on soil is less in India due to predominantly alkaline soils with good buffering capacity.
B. Vegetation
- Acid rain affects trees and undergrowth, causing reduced or abnormal growth.
- Symptoms include discoloration and loss of foliar biomass, loss of feeder-root biomass (especially in conifers), premature aging of older needles in conifers, increased susceptibility to damage, death of herbaceous vegetation under affected trees, and prolific lichen production on affected trees.
C. Microorganisms
- pH influences the proliferation of microbial species, leading to a shift from bacteria-bound to fungi-bound microflora.
- This shift causes a delay in the decomposition of soil organic material and an increase in fungal diseases in aquatic life and forests.
D. Wildlife
- Effects on wildlife are not always evident but can impact productivity and survival.
- Direct effects include damage to eggs and tadpoles of breeding frogs and salamanders.
- Indirect effects involve the release of metals from soils into the aquatic environment, where they may be ingested by animals, leading to potential toxic effects.
- Other indirect effects include loss or alteration of food and habitat resources.
 WildlifeE. Humans
WildlifeE. Humans
- Acid rain affects human health in various ways.
- Obvious effects include bad smells, reduced visibility, and irritation of the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract.
- Direct effects encompass chronic bronchitis, pulmonary emphysema, and cancer.
- Indirect effects involve food poisoning through contaminated drinking water and food.
- Increased levels of toxic heavy metals like manganese, copper, cadmium, and aluminum contribute to adverse effects on human health.
F. Acid rain damage on Materials
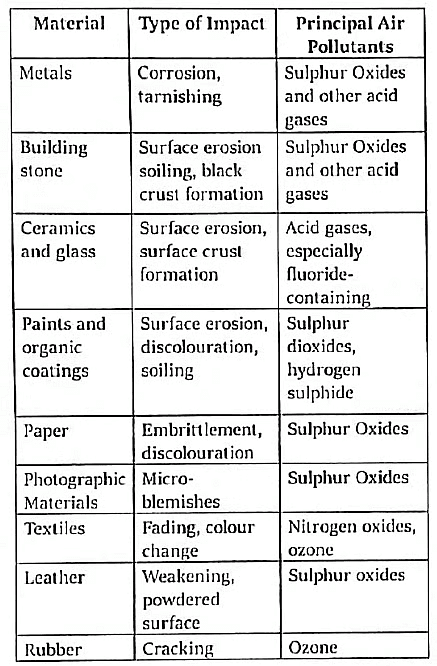
G. Socio-economic Impacts of Acid Rain: The detrimental effects of acid rain on agriculture and fishing contribute to the degradation of key life quality indicators, including Gross National Product (GNP) and per capita income. This impact is particularly pronounced in predominantly agricultural and developing nations such as India.
Trigger Effect of Acid Rain on Pollutants
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has devised criteria for categorizing industrial sectors into Red, Orange, Green, and White categories.
- The categorization is based on the Pollution Index, a numerical value (0 to 100) derived from factors such as emissions (air pollutants), effluents (water pollutants), hazardous waste generation, and resource consumption.
- The Pollution Index (PI) signifies the degree of pollution load, with a higher PI indicating increased pollution from the industrial sector.
- The re-categorization process is a scientific exercise aimed at addressing challenges in the old categorization system, which did not accurately reflect industries' pollution levels.
- The newly introduced White category, representing practically non-polluting industries, does not require Environmental Clearance (EC) and Consent. This facilitates obtaining financing from lending institutions.
- No industries in the Red category, indicating higher pollution levels, will typically be permitted in ecologically fragile or protected areas.
Recent Developments
Air Pollution & National Programs
- City-level updates: As per 2024–25 NCAP monitoring, Derabassi ranked 9th worst in India for PM10 levels, while Faridabad recorded only a 17% reduction in PM2.5 despite NCAP targets.
- Thermal Power Emissions: Punjab's coal-based power plants emit over 9 times more SO2 than seasonal stubble burning. Many units continue to be exempt from Flue Gas Desulphurization (FGD) requirements.
- Delhi Post-Monsoon Smog: Studies in 2024 highlighted that crop stubble burning in Punjab is a major contributor to Delhi’s severe post-monsoon smog episodes, leading to hundreds of pollution-linked deaths annually.
- Kolkata AQI Trends: July 2025 was the city’s wettest and one of its cleanest months in over a decade, with 80% days classified as ‘Good’ AQI — seasonal rains reduced dust suspension but raised concerns for post-monsoon spikes.
Waste & Pollution Control Initiatives
- Municipal Performance: The Pimpri Chinchwad Municipal Corporation (PCMC) 2024–25 Environment Status Report revealed continued high air and river pollution levels despite green bond investments and national awards.
- Regulatory Change: Haryana introduced a new ‘Blue Category’ for essential environmental services such as waste-to-energy and landfill management projects, easing compliance norms to boost sustainable infrastructure.
National Reports & Data
- State of India’s Environment 2025: Released by CSE and Down To Earth in February 2025, the report detailed climate change adaptation, pollution trends, waste management performance, and biodiversity threats.
- Landfill Fires: The Bandhwari landfill in Gurugram experienced over 70 fire incidents between March 2024 and June 2025, with April 2025 seeing multiple flare-ups. NGT mandated stricter fire safety protocols and biomining acceleration.
Plastic Waste Management
- EPR Implementation Status: By mid-2025, MoEFCC reported that over 85% of registered producers had submitted Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) action plans. Enforcement against non-compliant brand owners has intensified.
- Alternative Materials: Several state governments have initiated pilot projects using biodegradable polymers from agricultural waste for packaging to reduce dependence on single-use plastics.
Noise Pollution Monitoring
- Real-time Ambient Noise Monitoring Network Phase III is now complete, with 125 stations operational across 25 cities, integrating AI-based anomaly detection for festivals, construction, and traffic surges.
Thermal & Light Pollution Research
- 2024–25 studies linked thermal pollution in Himalayan rivers to glacier meltwater inflow shifts, affecting endemic fish species.
- Light pollution mapping in 2025 shows urban skyglow increasing by 9% annually in Indian metros, impacting nocturnal pollinators and migratory birds.
Legislative & Policy Developments
- The Environment Protection Act fine-based amendment (2022) is now in effect nationwide. As of 2025, adjudication officers have resolved over 2,500 violation cases, collecting ₹140+ crore in penalties for the Environmental Protection Fund.
- MoEFCC is piloting a ‘Polluter Pays Performance Index’ to rank industrial clusters based on compliance, emissions, and environmental restoration contributions.
|
1209 videos|2197 docs|849 tests
|
FAQs on Shankar IAS Summary: Environmental Pollution - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What are the different types of pollution mentioned in the article? |  |
| 2. What is the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 and why is it important? |  |
| 3. How does bioremediation help in addressing pollution issues? |  |
| 4. What are the consequences of radio active pollution on the environment and human health? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to reducing pollution in their daily lives? |  |

















