Laxmikanth Summary: Fundamental Duties | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
The original constitution included only fundamental rights and not fundamental duties. The framers felt it unnecessary to incorporate citizens' duties initially but included the State's duties as Directive Principles of State Policy. In 1976, fundamental duties for citizens were added, and in 2002, another was included. Fundamental Duties India
Fundamental Duties India
The concept of Fundamental Duties in the Indian Constitution was influenced by the former USSR's constitution. Unlike major democratic countries like the USA, Canada, France, Germany, and Australia, which don't specify citizens' duties, the Japanese Constitution is an exception, having a list of duties.
Socialist countries, like the former USSR, valued both citizens' rights and duties, stating that exercising rights was inseparable from fulfilling duties and obligations.
 Evolution of Fundamental Duties
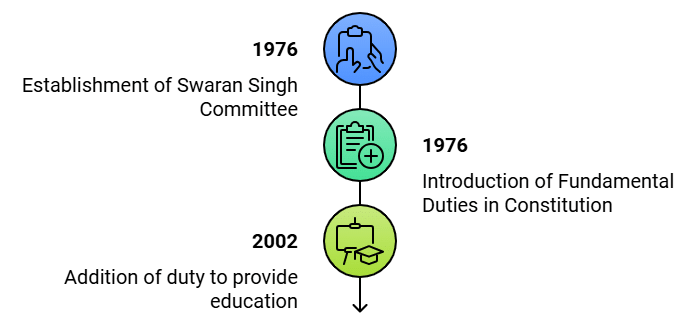
Evolution of Fundamental Duties1. Swaran Singh Committee Recommendations
In 1976, the Congress Party established the Sardar Swaran Singh Committee to discuss fundamental duties, prompted by the internal emergency (1975-1977).
The committee recommended adding a separate chapter on fundamental duties in the Constitution, emphasizing that citizens should be aware of both their rights and responsibilities.
The Congress Government accepted these suggestions and introduced the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act in 1976. This amendment created a new part, Part IVA, in the Constitution, featuring only one Article, namely Article 51A. For the first time, this article specified a code of ten fundamental duties for citizens.
The ruling Congress party acknowledged the historical oversight of not including fundamental duties in the Constitution and asserted that they were rectifying this.
While the Swaran Singh Committee proposed incorporating eight fundamental duties, the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act (1976) eventually included ten Fundamental Duties. Notably, some recommendations of the Committee were not adopted by the Congress Party and, therefore, not included in the Constitution. These recommendations included:
- Allowing the Parliament to determine penalties or punishments for non-compliance with or refusal to observe any of the duties.
- Stating that no law imposing such penalties or punishments could be challenged in any court on the grounds of violating Fundamental Rights or conflicting with any other provision of the Constitution.
- Specifying the duty to pay taxes as a Fundamental Duty of citizens.
2. List of Fundamental Duties (Article 51A)
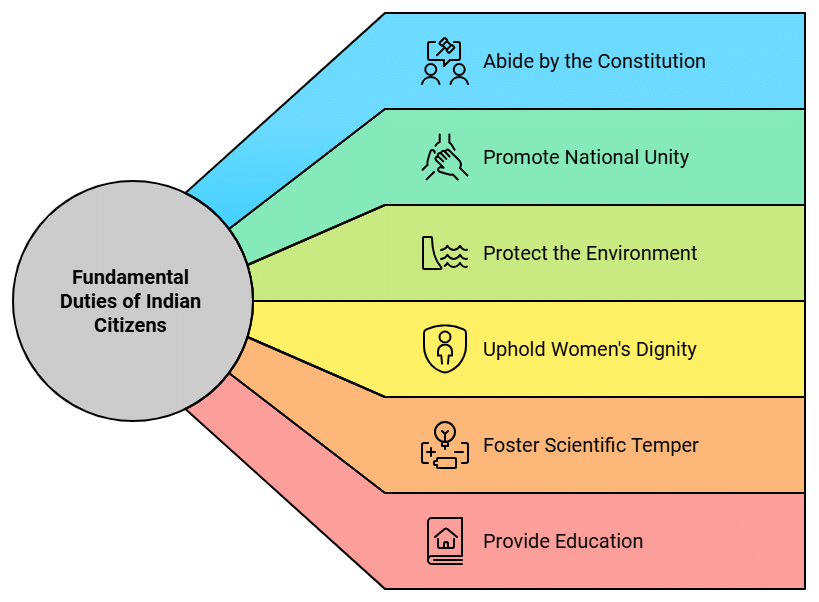
According to Article 51 A, it shall be the duty of every citizen of India:
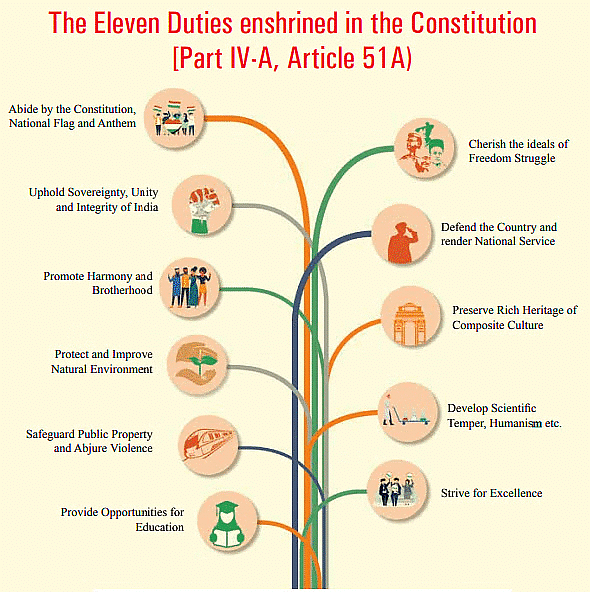
- Abide by the Constitution, respect its ideals and institutions, the National Flag, and the National Anthem.
- Cherish and follow the noble ideals that inspired the national struggle for freedom.
- Uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity, and integrity of India.
- Defend the country and render national service when called upon to do so.
- Promote harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood amongst all people, transcending religious, linguistic, and regional diversities. Renounce practices derogatory to the dignity of women.
- Value and preserve the rich heritage of the country's composite culture.
- Protect and improve the natural environment, including forests, lakes, rivers, and wildlife. Have compassion for living creatures.
- Develop scientific temper, humanism, and the spirit of inquiry and reform.
- Safeguard public property and abjure violence.
- Strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity, so that the nation constantly rises to higher levels of endeavor and achievement.
- Provide opportunities for education to children aged six to fourteen, as mandated by the 86th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2002.
3. Features of Fundamental Duties
The characteristics of Fundamental Duties can be summarized as follows:
They encompass both moral and civic duties. For instance, holding noble ideals from the freedom struggle is a moral obligation, while respecting the Constitution, National Flag, and National Anthemis a civic duty.
Fundamental Duties reflect values ingrained in Indian tradition, mythology, religions, and practices. Essentially, they codify tasks integral to the Indian way of life.
Unlike some Fundamental Rights applicable to all, whether citizens or foreigners, Fundamental Duties are specific to citizens and do not extend to foreigners.
Similar to Directive Principles, Fundamental Duties are non-justiciable. Courts cannot directly enforce them, and there's no legal sanction for violations. However, Parliament has the freedom to enforce them through appropriate legislation.
4. Criticism of Fundamental Duties
Critics have raised several concerns about the Fundamental Duties outlined in Part IVA of the Constitution:
The list of duties is incomplete, omitting important responsibilities such as voting, tax payment, and family planning. The Swaran Singh Committee even recommended including the duty to pay taxes.
Some duties are unclear and challenging for the common man to understand. Phrases like 'noble ideals,' 'composite culture,' and 'scientific temper' can be interpreted differently.
Critics view these duties as a set of moral principles since they are non-justiciable. Interestingly, the Swaran Singh Committee suggested penalties for not fulfilling Fundamental Duties.
Critics argue that incorporating these duties into the Constitution was unnecessary, as people would naturally perform them without constitutional inclusion.
Critics believe that placing Fundamental Duties in Part IVA diminishes their importance. They suggest adding them after Part III to align them with Fundamental Rights.
5. Significance of Fundamental Duties
Despite criticisms, fundamental duties are vital for the following reasons:
Reminder of Responsibilities: They remind citizens to be conscious of duties alongside their rights.
Warning Against Anti-national Activities: Act as a warning against activities like flag burning.
Inspiration and Discipline: Inspire discipline and commitment, making citizens active participants in national goals.
Legal Significance: Aid courts in determining the constitutionality of laws, as seen in cases like Mohan Kumar Singhania (1991) and Ramlila Maidan Incident (2012).
Enforceability by Law: Parliament can impose penalties for non-compliance.
 Fundamental Duty Chart
Fundamental Duty Chart
Leaders like R. Gokhale and Indira Gandhi justified their inclusion, with Gandhi emphasizing the democratic balance between rights and duties. Despite initial opposition, the Janata Government did not annul them, indicating a consensus on their necessity.
One more duty was added in 2002 through the 86th Amendment Act.
6. Verma Committee Observations
The Verma Committee on Fundamental Duties of Citizens in1999highlightedlegal provisions for implementing some Fundamental Duties. These include:
- The Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act (1971) prevents disrespect to the Constitution, National FlagandNational Anthem.
- Criminal laws penalize actions promoting enmity based on factors like language, race, place of birth, and religion.
- The Protection of Civil Rights Act (1955) addresses offences related to caste and religion.
- The Indian Penal Code (IPC) treats assertions prejudicial to national integration as punishable offences.
- The Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (1967) allows the declaration of a communal organization as an unlawful association.
- The Representation of People Act (1951) disqualifies Parliament or state legislature members for corrupt practices, including soliciting votes based on religion or promoting enmity.
- The Wildlife (Protection) Act (1972) prohibits trade in rare and endangered species.
- The Forest (Conservation) Act (1980)prevents indiscriminate deforestation and diversion of forest land for non-forest purposes.
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikanth Summary: Fundamental Duties - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key recommendations of the Swaran Singh Committee regarding Fundamental Duties? |  |
| 2. What are the Fundamental Duties listed under Article 51A of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 3. What are the features of the Fundamental Duties in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. What are some criticisms of the Fundamental Duties? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of Fundamental Duties in the context of Indian democracy? |  |

















