Shankar IAS Summary: Ocean Acidification | Environment for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Ocean Acidification
Oceans serve as significant reservoirs for carbon dioxide (CO2), absorbing a substantial portion (approximately one-third) of anthropogenically generated emissions, thus acting as a buffering mechanism against climate change. However, this absorption process contributes to a phenomenon known as ocean acidification, which denotes alterations in oceanic chemistry.
Ocean acidification is characterized by a reduction in ocean pH, attributable to an augmented concentration of hydrogen ions resulting from the absorption of carbon compounds from the atmosphere.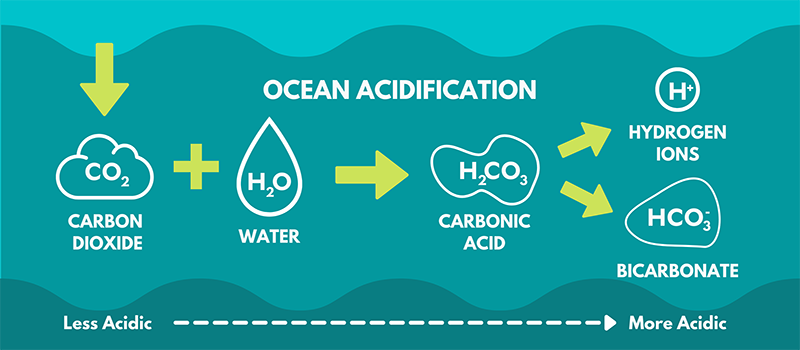 Chemical Reaction involved in ocean acidification
Chemical Reaction involved in ocean acidification
With the increasing uptake of atmospheric carbon dioxide by the ocean, the concentration of hydrogen ions rises. Concurrently, the concentration of carbonate ions decreases, leading to a decline in the pH of the oceans. Consequently, the oceans undergo a shift toward reduced alkalinity. This process, recognized as ocean acidification, raises concerns due to its potential adverse impacts on marine ecosystems and organisms.
CO2 effect on ocean acidification
- The ocean absorbs CO2, but the rate is too much for it to handle naturally.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air is causing ocean acidification.
- Over time, the surface waters of the ocean have become slightly more acidic.
 CO2 effect on ocean acidification
CO2 effect on ocean acidification - The pH of the ocean has decreased by about 0.1 unit since the start of the industrial revolution.
- Currently, the ocean is around pH 8.0, which is still basic.
- Even though it's not turning into a strong acid, the term "ocean acidification" is used because the overall trend is moving towards increased acidity.
- The 0.1 pH unit decrease represents a 26% increase in the concentration of hydrogen ions in the ocean.
- "Ocean acidification" is used to highlight the direction of the trend, emphasizing that the waters are becoming less basic over time.
Local Influences on Ocean Acidification
Acid Rain
 Effect of acid rain on ocean acidification
Effect of acid rain on ocean acidification- Effect: Acid rain, with a pH between 1 and 6, impacts the chemistry of surface ocean waters.
- Extent: Major effects on ocean acidification are seen locally and regionally but have a relatively small global impact.
Eutrophication
 Effect of ocean acidification on Eutrophication
Effect of ocean acidification on Eutrophication- Cause: Coastal waters are influenced by excess nutrients, mainly nitrogen, from sources like agriculture, fertilizers, and sewage.
- Result: This leads to eutrophication, causing significant plankton blooms. When these blooms collapse and sink, bacteria decompose them, reducing seawater oxygen and increasing CO2 (lowering pH).
Reactions in Ocean Acidification
- Processes: The term 'ocean acidification' summarizes reactions between CO2 and seawater.
 Ocean Acidification
Ocean Acidification - Key Reactions:
- Formation of Carbonic Acid:
- Reaction: CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3-
- Effect: This releases hydrogen ions, increasing acidity and lowering pH.
 Chemical Reaction involved in ocean acidification
Chemical Reaction involved in ocean acidification
- Interaction between Carbonate Ions, CO2, and Water:
- Reaction: CO3^2- + CO2 + H2O → 2HCO3-
- Combined Effect: Increases acidity and reduces the availability of carbonate ions.
- Formation of Carbonic Acid:
- Processes: The term 'ocean acidification' summarizes reactions between CO2 and seawater.
Effect of Ocean Acidification
Seawater and CO2: Seawater naturally absorbs CO2 from the air, creating compounds like carbonic acid and carbonate ions.
Importance of Carbonate Ions: Carbonate ions are essential for the building process of marine organisms such as corals, sea urchins, and lobsters, forming their shells and skeletons.
Problem with More CO2: Elevated levels of atmospheric CO2 lead to increased acidity in the ocean, affecting the balance of carbonic acid and carbonate ions.
Consequences of Less Carbonate Ions: The reduced availability of carbonate ions makes it challenging for marine creatures to perform calcification, impacting their ability to build structures like shells.
Resulting Challenge: This difficulty in building structures due to decreased carbonate ions may have significant consequences for ocean life, particularly for economically important marine species.
Mitigation
- Reducing CO2: We can help by reducing the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) released into the air.
- Government Policies: Supporting government rules that limit CO2 emissions helps control the problem.
- Eliminating Offshore Drilling: Stopping offshore drilling can be a way to reduce the impact on ocean acidification.
- Advocating for Energy Efficiency: Encouraging the use of energy-efficient practices can also make a positive difference.
 Wind and Solar Power
Wind and Solar Power - Alternative Energy Sources: Embracing alternative energy sources like wind and solar power provides cleaner options.
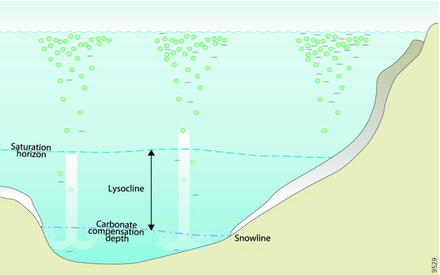
Saturation Horizons
The saturation horizon is a level where calcium carbonate minerals start dissolving
 Saturation horizon.
Saturation horizon.- Deep, Cold Ocean Waters: These waters naturally lack enough carbonate ions, causing the shells of many organisms to dissolve.
- Surface Waters: Surface waters have more carbonate ions, which protect the shells of organisms from dissolving.
- Survival Mechanisms: Some organisms below this horizon have special ways to protect their shells from dissolving.
- Impact of Ocean Acidification: As ocean acidification occurs, the saturation horizon rises vertically. This exposes more organisms to under-saturated water, making their shells and skeletons vulnerable to dissolution.
- Changes Over Time: The saturation horizon for calcite and aragonite, minerals in shells, has moved closer to the surface compared to the 1800s. This means more organisms are now at risk.
Ocean acidification and the short and long-term fate of carbon in the system
Long-Term Fate of Carbon:
- Natural Balance: Over a super long time (more than 100,000 years), Earth naturally handles CO2. Volcanoes release it, and plants and rocks soak it up.
Upwelling: Coastal Upwelling
Coastal Upwelling
Definition: Sometimes, ocean areas get a visit from deep water that's full of nutrients and CO2.
Effect of Ocean Acidification: Because the upper ocean is becoming less saturated with CO2 each year due to ocean acidification, these visits might bring up water that could affect sea life, especially creatures that make shells.
 Rock Weathering
Rock WeatheringRock Weathering: However, the process of rocks soaking up CO2 is slow and can't quickly get rid of the CO2 we're putting into the air.
Short-Term Carbon Cycling: Carbon Cycling
Carbon Cycling
Internal Feedback: Over shorter times (more than 1,000 years), the ocean has a way of managing carbon. It's like a self-regulating system that involves carbonate-rich sediment.
Ocean Layers: The upper ocean is good at keeping carbonate (like a shell material) without it dissolving. Deeper ocean layers dissolve carbonate.
Lysocline: Think of the lysocline as the point where deep ocean dissolving really starts to kick in.
Sinking Shells: Shells from sea creatures sink to the ocean floor. In shallow water, they get buried and stick around for a long time. But in deep water, most of them dissolve, not trapping carbon for millions of years.
 Carbonate Compensation Depth (CCD)
Carbonate Compensation Depth (CCD)Impact of Ocean Acidification: More CO2 going into the ocean messes up this balance. As the ocean becomes more acidic, it makes the lysocline and another depth (called carbonate compensation depth or CCD) shallower. This exposes more trapped shells to conditions that might dissolve them, which helps a bit with ocean acidification, but it takes a long time—like a thousand years.
Effects on Marine Plants
 Effect of ocean acidification on marine life
Effect of ocean acidification on marine life
Some Benefit: Certain marine plants and phytoplankton might grow more and do better with higher CO2 levels.
Not a General Rule: But this doesn't happen for all plants. It's not a rule that applies to everyone.
Varied Responses: For some, more CO2 and increased acidity might be bad or not really affect them much.
Important Action: To stop ocean acidification from getting worse, it's crucial to lower the levels of CO2 in the air. This needs to happen before it's too late.
So, some marine plants will do well, some might struggle, and others may not show any clear changes, but change is bound to happen.
|
97 videos|203 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Shankar IAS Summary: Ocean Acidification - Environment for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is ocean acidification and how is it caused by CO2? |  |
| 2. What are some local influences on ocean acidification? |  |
| 3. How does ocean acidification affect marine life? |  |
| 4. What are some mitigation strategies for ocean acidification? |  |
| 5. How does ocean acidification impact the fate of carbon in the system? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|





























