Ramesh Singh Summary: Public Finance in India- 1 | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Budgeting |

|
| Union Budget |

|
| Deficit Financing |

|
| Recent Developments |

|
| 8. Fiscal Federalism and 15th Finance Commission |

|
Introduction
- Public finance encompasses all matters related to the management of public money, including government receipts, expenditures, borrowing, lending, and financial management.
- It addresses how much of a country's resources the government should acquire for its own use and the efficiency with which these resources are utilized.
- Referenced in ancient texts like the Arthashastra, public finance covers treasury management, revenue sources, accounts, and audits in detail.
 Public Finances
Public Finances - Post-World War II, the role of governments in the economy expanded significantly due to factors like the rise of the public sector and the provision of essential services such as law enforcement, defense, and public goods.
- Experts and policymakers recognized that leaving all economic activities to the market (private sector) wouldn't suffice, especially in critical areas like national defense and security.
Budgeting
- Budgeting entails the preparation of an annual financial statement outlining a government's income (revenue) and expenditure.
- Originating from a British parliamentary practice dating back to the mid-18th century, the word "budget" is derived from the French word "bouger," meaning a leather bag from which financial documents were presented.

- In modern times, budgeting is a standard practice for governments worldwide, akin to companies and organizations preparing financial statements.
- In India, Article 112 of the Constitution mandates the presentation of an Annual Financial Statement, known as the Union Budget, before Parliament at the start of each fiscal year. This provision extends to the states as well.
Data in the Budget
The Union Budget presents three sets of data for each sector or sub-sectorof the economy:
- Actual data of the preceding year (e.g., for the budget presented for 2022-23, actual data for 2021-22 is provided). Denoted by 'A' or left blank in Indian context.
- Provisional data of the current year (e.g., 2021-22), since the budget for the previous year (2020-21) is presented a year in advance. Shown as 'PE' in brackets.
- Budgetary estimates for the following year (e.g., 2022-23). Indicated with 'BE' in brackets.
- Additional types of data found in government economic literature:
- Revised Estimate (RE): Offers a current estimation of either budgetary estimates (BEs) or provisional estimates (PEs), reflecting the contemporary situation.
- Quick Estimate (QE): A type of RE providing the latest situation, useful for future projections for sectors or sub-sectors. It's interim data.
- Advance Estimate (AE): Similar to QE but conducted in advance of the final stage, serving as interim data.
 Sectors of Economy
Sectors of Economy
Developmental and Non-developmental Expenditure
- Government expenditure is divided into two categories: developmental and non-developmental.
- Developmental expenditures include investments in productive endeavors like new factories, infrastructure projects, and transportation networks.
- Non-developmental expenditures are consumptive and non-productive, covering items like salaries, pensions, interest payments, subsidies, and defense expenses.
- This classification is no longer used in Indian public finance, replaced by the distinction between Plan and Non-Plan Expenditure.
Plan and Non-Plan Expenditure
- Expenditures are categorized as either plan or non-plan.
- Plan expenditures are asset-creating and productive, while non-plan expenditures are consumptive and non-productive.
- In 1987-88, India transitioned from using developmental and non-developmental expenditure terms to plan and non-plan expenditures, following recommendations by the Sukhamoy Chakraborty Committee.
- The Rangarajan Committee suggested further redefining plan and non-plan expenditures as capital and revenue expenditures to better align with outcomes and public expenditure management.
 Sukhamoy Chakraborty
Sukhamoy Chakraborty
Analysis of the Situation
- Many factors cast doubts on the efficacy and relevance of the fiscal instrument.
- The division of Plan and Non-Plan expenditure poses problems such as:
1. Plan Expenditure:
Allocation between official and non-official expenditure creates prioritization challenges, especially during austerity measures for fiscal consolidation. - Non-Plan expenditure often receives less attention even when crucial for economic development. For instance, budget provisions for the maintenance of essential facilities like hospitals and schools might suffer.
- Review and implementation of schemes lack direct responsibility, with roles spread between the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- Programs and schemes are not allowed to continue indefinitely across plan periods without independent evaluations, diluting the Ministry's role.
- The introduction of Output and Outcome Budgeting by the central government in the 2005-06 Budget aimed to bring more scrutiny to Non-Plan expenditure. However, outcomes like expenditure on running schools and hospitals may not be adequately evaluated, revealing flaws in Plan and Non-Plan classifications.
- Revenue, Non-revenue, and Receipts:
- Revenue: Any income or earnings for a firm or government.
- Non-revenue: Money raised via borrowings, increasing financial liabilities.
- Receipts: Every receiving or accrual of money to a government, including both revenue and non-revenue sources. Total receipts encompass all incomes and non-income accruals of a government.
- The classification shift from the traditional "Plan and Non-Plan" to "Revenue and Capital" since the fiscal year 2017-18 announced in the Union Budget reflects ongoing changes in expenditure management.
Union Budget
- The annual financial statement of the Government of India (GoI) is termed the Union Budget, following the practice outlined in Article 112.
- Originating from the British tradition, the budgeting process in India has evolved to be technically similar to most budgets worldwide.
- Broadly classified into two parts: A. Revenue Budget and B. Capital Budget, encompassing Revenue and Capital Receipts and Expenditures, respectively.
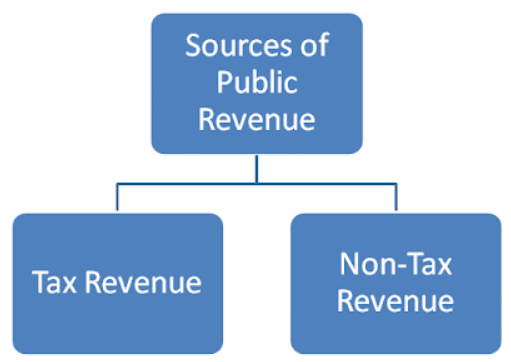
Revenue Budget
- Tax Revenue Receipts: Collections from direct and indirect taxes like income tax, corporate tax, GST, etc.
- Non-Tax Revenue Receipts: Income from sources other than taxes, such as profits from public sector undertakings (PSUs), interests on loans, fiscal services, general services, fees, penalties, fines, and grants.
- Consist of all expenditures incurred by the government, which are consumptive and do not involve the creation of productive assets.
- Items include interest payments, salaries, subsidies, defense expenses, postal deficits, law and order expenditures, and expenditures on social services like education, health, and poverty alleviation.
- Represents the balance of total revenue expenditures and total revenue receipts. If negative, it indicates a revenuesurplus.
- The effective management of revenue deficit ensures prudent fiscal policy and allows government spending in productive areas.
D. Effective Revenue Deficit
- Introduced to capture the RD "excluding" revenue expenditures of the GoI used for asset creation, termed Government of India's Contributions to States and Union Territories (GoCAs).
- GoCAs represent grants forwarded to States and UTs for centrally sponsored programs involving asset creation.
- The concept of effective revenuedeficit justifies higher RDs by highlighting that certain expenditures contribute to asset creation, aiming for a zero percent effective RD by 2017-18.
- The government has set targets for effective revenue deficit, signaling fiscal prudence and efficient utilization of resources.
 Union Territories of India
Union Territories of India
Capital Budget
- Concerns about the management of capitalreceipts and expenditures by the government.
- Indicates how capital is handled and where it is allocated.
A. Capital Receipts
- Non-revenue receipts are directed towards investments and planned development.
- Can be diverted to meet other financial needs due to rising revenue expenditure.
- It includes:
- Loan Recovery: Money repaid to the government from past loans, both internal and external.
- Borrowings by the Government: Long-term loans acquired domestically and internationally.
- Other Receipts by the Government: Long-term accruals through schemes like PF, Postal Deposits, and government bonds.
B. Capital Expenditure
- Allocations of capital by the government, covering various areas such as:
- Loan Disbursals by the Government: Loans provided internally and externally.
- Loan Repayments by the Government: Repayment of loans, comprising the capital portion.
- Plan Expenditure of the Government: Financing planned development and supporting state plans.
- Capital Expenditures on Defence: Funding for defense maintenance, equipment purchase, and modernization.
- General Services: Capital expenditure on services like railways, postal department, water supply, education, and rural extension.
- Other Liabilities of the Government: Repayment liabilities arising from other receipts.
C. Capital Deficit
- Conceptually indicates a scarcity of capital required for government expenditure.
- Represents the challenge of managing funds necessary for both revenue and capital expenditures.
D. Fiscal Deficit (FD)
- Arises when total government expenditures exceed total receipts.
- Indicates that the government is spending more than its income, considering all forms of government receipts.
- Can be expressed quantitatively or as a percentage of GDP.
- Rising FDs have been a concern, prompting fiscal consolidation efforts.
Primary Deficit: - FD excluding interest liabilities for a year.
- Indicates FD without considering interest payments, offering insights into expenditure patterns.
- Helps in evaluating dependence on loans and potentialexpenditure cuts.
 Primary Surplus:
Primary Surplus: - Occurs when tax receipts exceed total expenditures excluding interest payments.
- Indicates fiscal health and the government's capacity for revenue and capital expenditures.
- Reflects the availability of fiscal space for government expenditure decisions.
Monetised Deficit: - The deficit provided by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to the government in a specific year.
- Reflects the government's reliance on short and long-term borrowings for expenditure needs.
- Despite changes in monetary policy, RBI continues to manage governmentsecurities.
Deficit and Surplus Budget: - Deficit Budget: Proposed when expenditures exceed receipts, indicating spending beyond means.
- Surplus Budget: Proposed when expenditures are less than receipts, symbolizing a lower concern towards development.
- Governments usually avoid presenting surplusbudgets due to ongoing development needs.
Deficit Financing
- The act/process of financing a deficit budget by a government.
- Involves financialpolicies enacted by the government to sustain deficits.
- Initially used in public finance in the early 1930s in the United States.
- Adopted by governments worldwide and also seen in corporate financial management strategies.
Need of Deficit Financing
- Emerged in the late 1920s when governments needed to spend more money than expected earnings.
- Necessary to achieve desired levels of growth and development.
- Aims to realize socio-political goals by allowing more expenditure with less income and receipts.
- Extra money spent above income is expected to be reimbursed once growth occurs.

Means of Deficit Financing
- External Aids:
- The best option, even with soft interest or interest-free.
- Provides sustainable budget support, as seen in India's borrowing from the IMF.
- External Grants:
- Preferable but often comes with conditions.
- Not extensively utilized due to attached conditions.
- External Borrowings:
- Favorable if loans are cheap and long-term.
- Brings foreign currency, beneficial for developmental requirements.
- Internal Borrowings:
- Third, preferred route but impacts investment prospects and expenditure patterns.
- Can lead to economic stagnation or slowdown if extensively utilized.
 Economic Stagnation
Economic Stagnation
- Printing Currency:
- Last resort for governments.
- Increases inflation and governmentexpenditures.
- Creates a vicious cycle of currency printing and inflation.
Composition of Fiscal Deficit
- Focuses on the expenditure composition of governments.
- Optimal composition:
- Fiscal deficit with surplus revenue budget or zero-revenue expenditure.
- Higher capitalexpenditures and lower revenue expenditures ideal for deficit financing.
- Less favorable compositions:
- Majority of deficitfinancing is directed towards revenue expenditures.
- Lack of judicious mix between plan and non-plan expenditures.
- Third World economies often overlook favorable composition, leading to higher deficits and non-revenue expenditures.
Recent Developments
1. Modern Budget Classifications
India’s budget classifications have shifted to enhance fiscal efficiency and transparency.
- Revenue and Capital Expenditure: Plan and Non-Plan classifications were abolished in 2017–18, replaced by revenue and capital expenditure per NITI Aayog and C. Rangarajan Committee (2011).
- Outcome-Based Budgeting: Budget 2024–25 allocates ₹1 lakh crore for performance-linked grants, with ministries submitting outcome budgets (e.g., 95% PM-KISAN coverage).
- Capital Focus: ₹10 lakh crore (60% of budget) allocated to capital expenditure in 2024, driving infrastructure like PM GatiShakti.
Example: Capital expenditure funded 5,000 km of highways in 2024, creating 1 crore jobs.
2. Updated Fiscal Targets
Fiscal policy aligns with revised FRBM targets for consolidation.
- Fiscal Deficit: Reduced to 4.9% of GDP in 2024, targeting 4.5% by FY26 (Union Budget 2024–25).
- Revenue Deficit: At 1.8% of GDP (2024), targeting 1.5% by 2025 (Economic Survey 2023–24).
- Primary Deficit: Lowered to 1.2% of GDP (2024), reflecting reduced interest burdens.
Example: Fiscal consolidation saved ₹50,000 crore in interest payments (2024), boosting capex.
3. Revenue Budget Updates
Revenue receipts and expenditures reflect tax reforms and efficiency gains.
- Revenue Receipts: GST collections at ₹2.1 lakh crore/month (2024), with non-tax revenue (e.g., PSU dividends) at ₹5 lakh crore.
- Revenue Expenditures: Subsidies rationalized to ₹3.8 lakh crore (2024), with DBT saving ₹2.7 lakh crore (2020–24) via Aadhaar.
- Tax Reforms: New tax regime (default since 2024) offers 30% rate above ₹15 lakh; corporate tax at 22%, 15% for new units.
Example: AI-based GST audits saved ₹50,000 crore in evasion (2024), boosting fiscal health.
4. Capital Budget Trends
Capital budget prioritizes asset creation and infrastructure.
- Capital Expenditure: ₹10 lakh crore (2024) funds railways, highways, and PM GatiShakti.
- Capital Receipts: Sovereign green bonds (₹20,000 crore, 2024) and internal borrowings dominate, with external borrowings at 20% of GDP.
- Defense Capex: ₹1.5 lakh crore (2024) for modernization, up 10% from 2023.
Example: ₹2 lakh crore railway capex (2024) electrified 90% of tracks, cutting emissions.
5. Deficit Financing Strategies
Modern financing avoids inflationary methods, focusing on sustainable borrowing.
- Green Bonds: ₹20,000 crore issued (2024) for renewable energy projects.
- External Borrowings: Supported by $700 billion forex reserves, external debt is 20% of GDP (2024).
- RBI Operations: ₹1 lakh crore OMO sales (2024) stabilize liquidity, avoiding currency printing.
Example: Green bonds funded 10 GW solar capacity (2024), reducing coal dependency by 5%.
6. Digital Public Finance
Digital tools enhance fiscal transparency and efficiency.
- e-Bill/e-Sanchit: Streamlined customs, collecting ₹50,000 crore (2024).
- UPI for Taxes: ₹2 lakh crore collected (2024) via 150 billion transactions.
- PFMS: Tracks ₹34 lakh crore DBT payments (2024), ensuring 100% delivery.
Example: UPI’s tax integration reduced compliance costs by 30% (2024).
7. Climate-Responsive Budgeting
Fiscal policy supports net-zero by 2070 through green initiatives.
- Green Budgeting: ₹10,000 crore for renewables (2024), supporting PM Suryaghar Yojana.
- Climate Cess: ₹5,000 crore collected (2024) for afforestation and disaster management.
- G20 Leadership: India’s 2023 G20 pushed $500 billion global climate finance by 2030.
Example: ₹5,000 crore climate cess funded 1 million hectares of afforestation (2024).
8. Fiscal Federalism and 15th Finance Commission
Fiscal federalism strengthens through devolution and state reforms.
- 15th Finance Commission: 41% tax devolution (2021–26), transferring ₹10.7 lakh crore (2024).
- Performance Grants: ₹1 lakh crore for urban local bodies (2024).
- State Finances: States’ fiscal deficit at 3% of GSDP (2024); Tamil Nadu’s 2.5% deficit sets a benchmark.
Example: Kerala’s debt restructuring saved ₹10,000 crore (2024), enhancing fiscal health.
9. Post-COVID Fiscal Recovery
Fiscal measures post-2020 drove economic recovery.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat: ₹27 lakh crore package (2020–23) boosted 7% GDP growth (2024).
- Capex Push: ₹10 lakh crore (2024) revived infrastructure, creating 2 crore jobs.
- Global Comparison: India’s 4.9% fiscal deficit (2024) is below advanced economies’ 5% (IMF, 2024).
Example: ₹2 lakh crore PM-KISAN disbursals (2024) supported 10 crore farmers, aiding rural recovery.
|
108 videos|431 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Ramesh Singh Summary: Public Finance in India- 1 - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the concept of budgeting? |  |
| 2. What is the Union Budget in India? |  |
| 3. What is deficit financing? |  |
| 4. Who is Ramesh Singh and what is his contribution to the field of public finance in India? |  |
| 5. How does deficit financing impact the economy? |  |





















